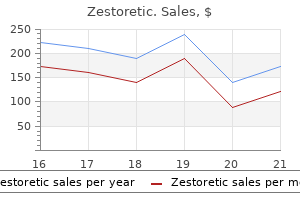
Zestoretic
Zestoretic dosages: 17.5 mg
Zestoretic packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Discount zestoretic 17.5 mg without prescription
Vulnerability of the bulbopon tine respiratory facilities within the mind stem to inhibitory mechanisms could explain why apneic episodes are precipitated in preterm infants by such a large variety of particular clinico pathologic events arrhythmia tachycardia zestoretic 17.5 mg cheap with amex. In different words arrhythmia list 17.5 mg zestoretic discount free shipping, apnea might represent the final common response of incompletely organized and intercon nected respiratory neurons to a large number of afferent stimuli. Unfortunately, the maturation of central respiratory integrative mechanisms and of their bio chemical neurotransmitters is inaccessible to study in human infants, and no perfect animal mannequin of spontaneous apnea has been recognized for examine in the nonanesthetized state. Brain stem conduction times of auditory evoked responses are longer in infants with apnea than in matched untimely infants without apnea. This observation supplies indirect proof that infants with apnea exhibit greaterthanexpected immaturity of mind stem function on the basis of postmenstrual age and sup ports the idea that stability of central respiratory drive improves as dendritic and different synaptic interconnections mul tiply in the maturing mind. The absence of respiratory muscle activity during central apnea unequivocally factors to the melancholy of respiratory heart output. Thus both central and blended apneic episodes share a component of decreased respiratory middle output to the respiratory muscle tissue. It is possible that antenatal or postnatal expo positive of the lung to a proinflammatory stimulus may activate mind circuits by way of vagally mediated processes. An curiosity ing related line of investigation is the position of intermittent hypoxia and resultant oxidant stress on inflammatory pathways. In distinction, "highdose," or continual intermittent hypoxia, might activate microglia to a poisonous, proinflammatory phenotype that triggers neuronal apoptosis and undermines synaptic plasticity. The higher incidence of apnea throughout energetic sleep probably is the result of the variability of the respiratory rhythmicity char acterizing that state. Chest wall movements are predominantly asynchronous (or paradoxic) during energetic sleep, in distinction with quiet sleep. Specifically, stomach growth throughout inspiration is almost at all times accom panied by inward motion of the rib cage throughout lively sleep; whereas throughout quiet sleep, rib cage and abdomen broaden collectively. These paradoxic chest wall movements during energetic sleep appear to be the end result of decreased intercostal muscle exercise, secondary to spinal motor neuron inhibition. In very preterm infants, nevertheless, the paucity of quiet sleep, along with an especially compliant rib cage, makes paradoxic chest wall movements an almost constant characteristic. Asynchronous chest wall movements might predispose the toddler to apnea by decreas ing practical residual capacity and impairing oxygenation. The compensatory improve in diaphragm activity that results could enhance diaphragmatic work, doubtlessly resulting in diaphrag matic fatigue and collapse of the pharyngeal airway. Apnea was observed to occur extra commonly during active (or rapid eye movement) and indeterminate (or transitional) sleep, when respiratory patterns are irregular in both timing and amplitude. Apnea is less com monly observed during quiet sleep, when respiration is charac teristically common with little breathbybreath change in tidal volume or respiratory frequency, although periodic respiration may actually occur predominantly in quiet sleep. In time period neo nates, respiratory variability alone can be utilized to stage sleep with a high degree of accuracy. In these infants, hypercapnia may be accompanied by prolongation of expiratory duration. Interestingly, the hypercapneic response of infants born to smoking and substanceabusing mothers is decreased, which can contribute to susceptible respiratory control on this inhabitants. Obvious limitations come up in extrapolating data from anesthetized newborn piglets to apneic human infants. It has been known for a couple of years that preterm infants respond to a fall in impressed oxygen focus with a transient increase in air flow over approximately 1 minute, followed by a return to baseline or even depression of air flow. The attribute response to low oxygen in infants seems to outcome from preliminary peripheral chemoreceptor stimulation, followed by overriding despair of the respiratory heart as a result of hypoxemia. Such hypoxic respiratory depression may be helpful in the hypoxic intrauterine environment the place respiratory activ ity is simply intermittent and never contributing to gasoline exchange. This unstable response to low impressed oxygen concentration could play an essential position in the origin of neonatal apnea. It presents a physiologic rationale for the decreased incidence of apnea observed when a barely elevated focus of inspired oxygen is administered to apneic infants. The mixture of sustained and intermittent hypoxia to which preterm infants could additionally be uncovered has barely been addressed. Afferent neural input from pulmonary stretch receptors is capable of substantially modulating respiratory timing in human neonates. This vagally mediated response, called the HeringBreuer reflex, acts to inhibit inspiration, extend expiration, or both, with growing lung volume, thereby limiting lung overin flation. Active shortening of expiratory period with decrease in lung volume might similarly provide a neonatal respiration strat egy to protect useful residual capability within the presence of a highly compliant chest wall. Another manifestation of this reflex response to lung inflation is that inspiratory length is often extended after endexpiratory airway obstruction when lung inflation is prevented. This capability of neonates to enhance the length of an obstructed inspiratory effort appears to be an acceptable compensatory mechanism throughout airway occlusion. More necessary, higher airway obstruction contrib utes considerably to the initiation of apneic episodes in preterm infants, and higher airway muscles show preferential reflex acti vation in response to airway obstruction in infants. According to this model, negative luminal pressures generated in the higher airway during inspiration predispose a compliant pharynx to collapse. Patency can be maintained by activation of higher airway muscles, which can improve tone inside the extratho racic airway via tonic or phasic contraction in synchrony with the chest wall muscle tissue. The relative roles performed by energetic higher airway muscle contraction and passive rigidity of the anatomic framework of the higher airway in maintaining pharyn geal patency in preterm infants are unclear. Whereas many higher airway muscular tissues, together with the alae nasi, laryngeal abductor, and adductor muscular tissues, modulate patency of the extrathoracic airway, failure of genioglossus activation has been most generally implicated in combined and obstructive apnea in both adults and infants. Carlo and coworkers22 in contrast activ ity of the genioglossus muscle with that of the diaphragm in response to hypercapnic stimulation. This instability may predispose affected infants to obstruction of inspiratory efforts after a interval of central apnea. Consistent with this speculation is the observa tion that quick apneic episodes usually tend to be central, and longer episodes (lasting longer than 15 seconds) usually have a tendency to be accompanied by obstructed breaths. Furthermore, airway obstruction often occurs toward the end of the longer episodes of blended apnea, when diaphragmatic exercise may be enhanced before that of the higher airway muscles. Gauda and coworkers23 used sublingual floor electrodes (placed over the insertion of the genioglossus within the man dible) to examine the genioglossus responses with finish expiratory airway occlusion in preterm infants with blended and obstructive apnea and in nonapneic control infants. In infants with apnea, nevertheless, activation of the genioglossus in response to occlusion was sig nificantly delayed. Subsequently, Gauda and coworkers10 evaluated the exercise of the genioglossus and diaphragm during spontaneously occur ring combined and obstructive apneic episodes. Thus decreased diaphragmatic exercise is a significant component of spon taneous apnea associated with airway obstruction, and neither diaphragm nor genioglossus exercise is increased till resolu tion of apnea. These findings suggest that central, blended, and obstructive apneas are caused by a common mechanism-a discount in central drive affecting the diaphragm and dilating muscles of the higher airway.
Shark Cartilage. Zestoretic.
- How does Shark Cartilage work?
- Dosing considerations for Shark Cartilage.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Arthritis, eye complications, kidney cancer, wound healing, psoriasis, osteoarthritis, and other conditions.
- What is Shark Cartilage?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96875
Zestoretic 17.5 mg generic on line
With pubertal onset heart attack high come over to the darkside feat jimi bench 17.5 mg zestoretic cheap with visa, germ cell proliferation equalizes the variety of germ cells and Sertoli cells within the pubertal testis blood pressure chart based on age zestoretic 17.5 mg buy discount. The Sertoli cells divide quickly during childhood till the onset of puberty, after they differentiate, form tight junctions, and no longer undergo cell division. As they mature to prespermatogonia, they shift to the periphery of the tubules close to the basal lamina. The prespermatogonia are linked by residual cytoplasmic bridges that stay after incomplete cytokinesis throughout mitosis. These interconnections between differentiating spermatogonia enable synchronized maturation of adjoining germ cells. Each germ cell division replenishes the spermatogonial pool and generates germ cells that endure spermatogenetic maturation. Spermatogonia are categorised by their morphology, maturational stage, position within the germinal epithelium, and variations in nuclear chromatin precipitation. Type A spermatogonia, divided into darkish sort A (Ad) and pale kind A (Ap) teams are thought of a part of the spermatogonial stem pool. Progressive differentiation to kind B spermatogonia represents the first step of spermatid formation. Sequential stages of spermatogenesis may be recognized within a testis, including, from the least mature to the maturest varieties: Ad spermatogonia; Ap spermatogonia; sort B spermatogonia; primary spermatocytes (leptotene, zygotene, and pachytene); secondary spermatocytes, Sa, Sb1, Sb2, Sc, Sd1, and Sd2 spermatids; and mature spermatozoa. In men who had orchidopexy earlier than the age of 2 years, the chance for infertility correlated with the presence of Ad spermatogonia at the time of orchidopexy; it was proposed that elevated testosterone ranges in the course of the minipuberty of infancy may be important for transformation of germ cells to Ad spermatogonia. They have little clean endoplasmic reticulum however comprise abundant ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum. The presence of tight junctions between adjoining cell membranes creates the blood-testis barrier. This unique characteristic allows the Sertoli cells to create a microenvironment for controlling the biochemical milieu within the cords in addition to to facilitate the migration of germ cells within the seminiferous tubules. Inhibin indirectly regulates spermatogenesis through its modulation of follicle-stimulating hormone and is also believed to have direct paracrine effects on spermatogenesis. From the apical side of the tubules, the spermatogonia full maturation and are launched from the seminiferous epithelium. In humans the lamina propria accommodates five to seven layers separating the seminiferous tubules from the interstitium. The middle layers include myoid cells which have fibroblastic traits and help create the blood-testis barrier. These myofibroblasts have contractile ability and may subsequently have a major position in movement of spermatozoa by way of the tubules to the rete testis. The collagen-rich innermost layer is immediately adjoining to the basal membrane of the tubules. Complex cell-to-cell interactions and numerous signaling pathways are used to establish the organizational construction of the testes and to full the maturational processes that are needed for virilization of the genitalia and reproductive competence. The descent of the testes from an intraabdominal to a scrotal place is a key early developmental step to attain reproductive competence. The blood-testis barrier helps maintain the microenvironment of the apical adluminal compartment of the seminiferous tubules. Experimental knowledge show that the tight junctions prevent passage of large tracers from the basal compartment. This bodily barrier enables the Sertoli cell to maintain the microenvironment of the tubular lumen to facilitate spermatogenesis. The blood-testis barrier can be thought to provide immunoprotection to stop autoimmune destruction of differentiating germ cells. Some of the mechanisms by which Sertoli cells maintain the barrier have been elucidated: a variety of extracellular matrix proteins and ectoplasmic specialization proteins are critical for its structural and useful integrity. In the rat testis, inhibitors of protein phosphatase disrupt the barrier, whereas pretreatment with protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors can stop this impact. Similarly, both protein kinase A activator and protein kinase C inhibitors perturb the Sertoli cell tight junctions, indicating a regulatory position for protein kinases. Formation of the barrier may be disrupted by sure toxins, hormonally energetic compounds such as diethylstilbestrol, and heavy metals such as cadmium. Immature spermatogonia (spermatogonia and preleptotene spermatocytes) are located close to the basement membrane, whereas maturer, differentiating spermatocytes and spermatids are discovered in the adluminal compartment. The regulation of testicular descent from an stomach to a scrotal place has been well studied in rodents, with complementary insights gained from detailed hormonal, radiologic, surgical, and pathologic assessments to assist clarify this course of during human improvement. Differences amongst species in timing, anatomy and ultimate testicular position, and hormonal milieu limit the ability to absolutely extrapolate observations in animal fashions to human testicular descent. For instance, in humans, testes transfer into the scrotum during late gestation, whereas testicular descent happens at puberty in rodents, when the pouchlike processus vaginalis is formed. During the transabdominal part of descent from week 10 to week 15 of gestation, the cranial suspensory ligament regresses underneath the influence of androgens, whereas the caudal end of the gubernaculum enlarges in a "swelling reaction" to form an outgrowth. The testes are anchored by the gubernaculum to the abdominal wall close to the site of the future inner ring of the inguinal canal. The gubernacular outgrowth ("swelling") is characterised by hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the mesenchymal cells because of an increase in the levels of glycosaminoglycans and hyaluronic acid that promotes water retention and makes the gubernaculum gelatinous. Male mice with a null mutation of Insl3 have a poorly developed gubernacular bulb, intact cranial suspensory ligament, and undescended testes,fifty four,fifty five whereas overexpression of Insl3 in females results in descent of the ovaries to the inguinal region. In rodent models, prenatal antiandrogen remedy prevents full regression of the cranial suspensory ligaments and prenatal androgen remedy induces regression of the ligaments and partial descent of ovaries. The predominant role of androgens is to mediate the movement of the testes from the inguinal area by way of the inguinal canal into the scrotum in the course of the inguinoscrotal phase of testicular descent. From week 25 to week 35 of gestation, the testes shift from their intraabdominal position at the level of the anterior iliac backbone through the interior and exterior rings of the inguinal canal into the scrotal sacs. Subsequent shortening of the proximal part of the gubernaculum and involution of the caudal bulb facilitates movement of the testes from the external inguinal ring to the bottom of the scrotal sacs. In addition to hormonal regulators, intraabdominal pressure is also believed to play a role on this ultimate stage of testicular descent. Cryptorchidism is a cardinal function of numerous animal models and human problems associated with either inadequate androgen motion or perturbation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Patients with hypothalamic hypogonadism or different types of secondary testosterone deficiency have an increased price of inguinal testes. Undescended testes are also a common finding in undervirilized infants with androgen insensitivity syndrome or defects in testosterone biosynthesis. Animal studies have also explored the adjunct position of other hormones on this advanced process. For instance, in postnatal rats, removing of the salivary glands, the most important source of epidermal development issue, compromises testicular descent and epidermal development issue reverses cryptorchidism induced by flutamide (an antiandrogen), but whether epidermal development issue modulates testicular descent in humans is unknown. Clinical research have examined variations in gonadal and pituitary hormones between kids with cryptorchidism and those with regular testicular descent.
17.5 mg zestoretic purchase amex
Three markers that can be determined in the early second trimester are potentially helpful arrhythmia what to do purchase zestoretic 17.5 mg with amex. Additional facial markers have been investigated that could enhance detection even additional blood pressure chart over 60 zestoretic 17.5 mg free shipping. This can be improved by the routine simultaneous determination of ultrasound markers. In addition, numerous gentle sonographic markers which may be detected through the sonographic study have been recognized; the presence of a number of such markers suggests an increased threat for aneuploidy. Sequential Screening the model predicted performance of the four protocols utilizing both first and second trimester markers is shown in Table 18. The serum integrated check has a performance worse than the first trimester mixed check but higher than the second trimester quad take a look at. Given the human and practical benefits and decrease prices, the contingent test should be the sequential strategy of selection. Anomaly Scan Results It is frequent for a woman who had a borderline positive combined take a look at to delay a choice over invasive prenatal analysis till the second trimester ultrasound examination has been carried out. Similarly, most ladies with adverse mixed test results finally have a routine anatomy scan. The detection of an anomaly or a gentle marker generates appreciable nervousness, regardless of the normal result of the combined check. Contingent: as stepwise but second stage only if danger above 1 in 1500 (1 in 1200 at midtrimester). Final danger cutoffs for the Integrated test, the second stage of the stepwise sequential and contingent checks based on all first and second trimester markers included. Although there may be clinical utility in these advert hoc makes use of of the anatomy scan to modify combined take a look at results, it will not be an effective protocol if adopted routinely. For triplets, no matter chorionicity, screening must solely be based on ultrasound markers. Furthermore, the deceased twin could nicely have had a chromosome abnormality, given the very excessive aneuploidy price in early singleton miscarriages. The question that subsequently arises is whether serum screening markers can reliably be used to assess danger. In one study, first trimester serum markers had been measured in cases in which the demise was thought to have occurred within 4 weeks of testing. In theory, bearing in mind the results from a earlier pregnancy may therefore enhance screening efficacy. Incidental Diagnoses A big selection of abnormalities are detected incidentally with extraordinarily excessive or low marker levels; most fall into 5 teams. If a donor egg was used, threat is calculated using the age of the donor at the time of assortment. The most constant finding for first trimester serum Other Adverse Outcomes Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome this could be a rare autosomal recessive disorder with an incidence of about 1 per 20,000 to forty,000 births. Clinical options embrace mental retardation and skeletal, genital, cardiac, pulmonary and renal malformations. Maternal-Fetal Conditions Nicolaides has proposed that when ladies undergo the mixed check they can be assessed for their danger for frequent maternal-fetal conditions that normally seem during the third trimester, such as preeclampsia, development restriction, preterm delivery and fetal macrosomia. This idea has been most absolutely developed for preeclampsia, a complex dysfunction with variable presentation and end result that starts when the uterine spiral arteries fail to rework in early being pregnant. In normal pregnancies, trophoblasts invade the spiral arteries, replacing the graceful muscle and endothelium. The remodelled arteries have lowered resistance and due to this fact increased blood move into the placenta. When this course of fails, there are inadequate perfusion, placental injury and imbalance of thromboxane� prostacyclin with consequent platelet aggregation. However, a meta-analysis of 9 published trials, by which therapy started before sixteen weeks, has led to a shift in the consensus. However, not like aneuploidy, there are distinct forms of preeclampsia: one related to maternal mortality and morbidity, prematurity, growth restriction and fetal dying and one other creating across the time of delivery, more usually having a benign course, and never related to prematurity. Classifications based mostly on gestation at delivery are extra goal than gestation of onset or severity. The greatest estimate of screening performance could be derived from the large population-based study at Kings College Hospital, London. It is attributable to deficiency of steroid sulfatase, with consequent abnormal estriol biosynthesis, resulting in extraordinarily low maternal serum uE3 ranges. In one sequence of nine pregnancies with low or absent second trimester serum uE3 ranges, six had been discovered to have a whole and one a partial deletion of the steroid sulfatase deficiency gene. This could be mixed with the lifetime price of an affected individual, restricted to the direct medical, educational and social service costs or including indirect societal prices similar to lack of income. In addition to the marginal cost, public health planners need to contemplate the whole cost of fixing to the new technique or the typical cost per girl screened. Among the previous are major cardiac defects, and this aspect alone could also be sufficient to justify retaining the scan. A case can also be made for retaining some first trimester biochemical markers, specifically for use in screening for opposed pregnancy outcomes similar to preeclampsia and development restriction. These outcomes are much more common than all aneuploidies mixed, and a big proportion could be prevented through first trimester screening followed by every day low-dose soluble aspirin in screen-positive women. Prenatal screening and diagnostic applications therefore need to have entry to counsellors skilled in the clinical and social features. Retrospective quality assurance measures include periodic evaluation of control information, continuous monitoring of MoM values, screen-positive charges and, when potential, assortment of being pregnant end result information. Optimal design of a model new screening program due to this fact focuses on early testing every time possible. Until recently, the design of a model new prenatal screening program was largely focused on the constraints of invasive testing, specifically, minimising the variety of invasive procedure-related fetal losses and making certain the prices of the invasive testing have been manageable. There were a extensive range of serum and ultrasound markers available, and the design of the screening was therefore determined largely by the supply of sonographers who were proficient in biometry, gestational age of women referred for screening, and other sensible considerations corresponding to costs and individual affected person preferences. Components of variance which differ regionally will embody analytic precision (assay performance varies) and gestational error which is largely depending on the extent to which ultrasound dating is carried out earlier than testing. In practice, the cutoff is usually decided by the recommendation of nationwide or international bodies. There is a growing recognition that conventional prenatal screening tests have an essential position within the identification of nonchromosomal fetal disorders and being pregnant issues. Women would require extra prenatal counselling as these advances are introduced into routine prenatal care. Maternal serum alpha fetoprotein measurement in antenatal screening for anencephaly and spina bifida in early being pregnant. An association between low maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein and fetal chromosome abnormalities.
17.5 mg zestoretic purchase otc
The presence of a standard vermis in association with unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia is often affiliate with a traditional neurologic consequence pulse pressure physiology cheap zestoretic 17.5 mg fast delivery. Prenatal ultrasound analysis is extraordinarily difficult and has solely been reported in a very limited number of circumstances arterial network generic zestoretic 17.5 mg online. The vermis has an hypoplastic look: the superior half is current, however the inferior part is absent, producing a midline cleft connecting the fourth ventricle to the cisterna magna. The poor prognosis is characterised by periodic seizures, abnormal eye actions, hypotonia, ataxia, developmental delay and psychological retardation. In most patients, the superior part stays normal, and solely the inferior vermis becomes attenuated. Current theories suggest that this malformation outcomes from a global developmental defect affecting the realm membranacea of the roof of the rhombencephalon, which explains the affiliation with a variable diploma of cerebellar dysplasia. This condition was originally outlined as Dandy-Walker variant, a term not in use. The analysis of inferior vermian agenesis stays questionable till 24 weeks of gestation. The presence and measurement of the vermis can simply be assessed by a 3D sweep of the posterior fossa alongside the axial airplane with subsequent multiplanar analysis. The vermis seems as an oval echogenic structure, interposed between the fourth ventricle and the cisterna magna. A communication between the ventricle and cisterna magna at any degree is suspicious of a partial vermian agenesis or a hypoplastic vermis. A sagittal view of the posterior fossa allows the differentiation between these entities. The recent update of the classification displays the advances in embryology and of molecular biology of normal and irregular cortical improvement. Ultrasound features embody premature irregular sulci, irregular and thin cortical mantle, extensive abnormal overdeveloped gyri and nodular projections within the lateral ventricle. In truth, most prenatal instances are part of a syndrome or chromosomal abnormality or are associated with primary cerebral organisation problems or with damaging occasions. The increased growth of cerebral buildings relates to benign familial incidence, metabolic situations. A familial historical past of similar problems with a recessive hereditary pattern either autosomal or sex-linked is suggestive. The clinical course is progressive and other organ constructions are involved, including the heart, eye, liver and spleen. The group of anatomic megalencephaly manifest with developmental megalencephaly linked to a single gene mutation involving early mind mobile progress, migration or replication. However, neurons that fail to stop at their meant cortical destination and continue to migrate onto the cortical floor lead to cobblestone malformation. Lissencephaly is outlined as a clean brain and characterised by abnormalities within the width of the gyri and the thickness of the cortex. The neocortex of lissencephalic sufferers lacks normal cortical lamination and accommodates two to 4 layers as a substitute of six. Furthermore, dysgenesis of the Sylvian fissure, delayed sulcal appearance, callosal abnormality and cortical thickening could also be current. Cobblestone malformation, formerly referred to as kind 2 lissencephaly, is characterised by a nodular cortical surface accompanied by ocular anomalies and congenital muscular issues. Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy is the mildest type and muscle-eye mind illness being the moderate type. The structural abnormalities result from lack of connection of the radial glia to the pial limiting membrane and neuronal overmigration through pial gaps. Other suggestive findings are early enlargement of the lateral ventricles, abnormal vermis, retinal detachment, cataract, irregular sulcation, kinked brainstem and bifid pons. Heterotopia occurs when neurons originating within the periventricular region fail to migrate, leaving tracks or nodules of regular neurons in abnormal places adjoining to the ependymal lining or in subcortical topography. The sonographic diagnosis is difficult, mainly when the lateral ventricle width is normal. These are clefts which transverse the total thickness of the hemisphere, connecting the ventricle to the subarachnoid space. In sort I or closed-lip schizencephaly, most frequently a unilateral finding, the partitions of the cleft are opposed. Depending on the degree of severity and related anomalies, extreme mental and motor retardation have been observed. Irregular hypointense lining of the lateral ventricle (circles) with irregular cortical folding consistent with migrational abnormalities consisting of subependymal heterotopia and polymicrogyria. The findings had been confirmed at post-mortem after the dad and mom decided for termination of pregnancy. Polymicrogyria is brought on by an interruption in regular cerebral cortical growth in the late neuronal migration or early postmigrational development durations. It is a spectrum of cortical malformations with the frequent characteristic being excessive gyration. All have in widespread a derangement of the traditional six-layered lamination of the cortex, an associated derangement of sulcation and fusion of the molecular layer across sulci. Nevertheless, the sensitivity and predictive worth of those markers on routine ultrasound scanning is poor. These information point out that brain and visceral markers suggestive for congenital infections have a low sensitivity. Cytomegalovirus infection is by far the commonest prenatal and perinatal an infection, inflicting more perinatal mortality and long-term morbidity than all other congenital infections put together. The seroprevalence, which is about 50% in industrialised international locations, rises to 90% in developing regions around the world. In the periventricular areas, the excessive viral density and the presumed lower performance of the cellular immunity contribute to the cytotoxic and lytic lesions and calcifications. Adverse neonatal consequence has been associated with cerebral ultrasound anomalies,167 particularly, microcephaly, polymicrogyria and periventricular intraparenchymal cystic lesions. After ingestion of uncooked meat containing bradyzoites, Toxoplasma gondii starts a sexual copy cycle within the intestinal tract of the cat. Cat faeces contain oocytes crammed with infective sporozoites and are unfold on vegetables, soil, water and grass. These tachyzoites are liable for the haematogenous spread and for the vertical transmission to the fetus. After growth of an immune response, Toxoplasma stays current in the body as tissue cysts containing slowly dividing parasites: bradyzoites. Ingestion of raw meat by people can activate these bradyzoites and start the sexual replication. The precise seroconversion rate for toxoplasmosis in pregnancy dropped significantly due to the rigorous introduction of hygienic measures and is taken into account to be around zero.
Zestoretic 17.5 mg otc
Postnatal administration is dependent on the remaining function of the diseased kidney arteria radialis order zestoretic 17.5 mg fast delivery. In bilateral uropathies blood pressure chart for geriatrics buy zestoretic 17.5 mg on line, the prognosis and management depend upon the anticipated damage to renal function, which is usually predicted based on detailed renal imaging supplemented by sampling of fetal urine, serum or renal tissue, when imaging alone is uncertain. Ultrasonography is an effective predictor of renal perform and includes evaluation of amniotic fluid quantity and renal parenchyma. The presence of hyperechogenic renal parenchyma, thinning of the cortex, loss of corticomedullary differentiation and cortical cysts are indicators of severe renal injury. A above the ninety fifth percentile for gestational age and sodium above the 95th percentile for gestational age seem most predictive of poor renal end result. The benefit of serial urinalysis as opposed to evaluation at a single time point also remains a matter of debate. Several authors have instructed that serial sampling increased the predictive potential of urinary analytes, but this remark has not been confirmed by others. In case of enchancment, the renal prognosis is healthier, and prenatal therapy could be considered. The drawback is the necessity for fetal blood sampling, carrying a barely greater risk than vesicocentesis, particularly at early gestational ages. Bunduki and associates assessed the feasibility of renal biopsy in detecting renal dysplasia. They performed ultrasound-guided renal biopsy, as nicely as urine sampling, on 10 fetuses with severe urinary tract obstruction. The sampling was profitable in solely 50% of the cases and was clinically helpful in just one third. Dilated uterus with uterine septum (large arrow), urinary ascites (stars) and hydronephrosis (arrow) in a fetus with a persistent cloaca. In a fetus, urine manufacturing is exclusively reflective of renal function as a result of the mother supplies balanced nutrients and ensures fetal homeostasis without a contribution from the fetal kidneys. Accordingly, because the composition of fetal urine depends only on fetal renal operate (filtration, excretion, reabsorption), fetal urinalysis can assess the ability of the renal tubules to reabsorb a selection of parts (sodium, calcium, phosphorus, B2 microglobulin, glucose). Clinically, the usage of fetal urinalysis to predict renal operate is a topic of controversy in fetal medicine. A systematic evaluation concluded that research are extraordinarily heterogenous and globally of poor quality. A, Anatomical landmarks: a, veru montanum; b, plicae colliculi; c, urethral opening; and d, urethral valves. The options embrace termination of pregnancy, conservative administration with postnatal evaluation and treatment, or prenatal therapy. Termination of Pregnancy In essentially the most extreme circumstances (multiple congenital anomalies, terminal renal failure), the prognosis is unequivocally poor, and heaps of couples elect to terminate the pregnancy if legally attainable. Postmortem testing (additional genetic testing together with whole-exome sequencing for identification of single-gene issues, necropsy or digital necropsy) ought to be organized and medical and psychosocial follow-up provided to the parents. Conservative Management Conservative management is commonly possible and requires followup scans by way of the third trimester to reassess the situation and determine postnatal care necessities. In instances potentially requiring postnatal comply with up and surgical procedure, the paediatric subspecialists (nephrologist, urologist) are finest involved within the prenatal counselling of the couples. In many uropathies, no specific therapy is needed in the neonatal period, permitting the mother to deliver within the maternity hospital of her selection. In situations requiring urgent surgical intervention through the immediate neonatal period, the mother and father are inspired to give delivery in a centre providing specialised paediatric care. Some dad and mom additionally go for conservative management in cases with a deadly postnatal prognosis. In these cases, the dad and mom must ship in specialised items as the neonate would require tailored palliative assistance. Fetal Therapy in Obstructive Uropathy the rationale for in utero remedy is that restoration of the amniotic fluid quantity prevents lung hypoplasia, and decompression of the obstruction could relieve the stress on the fetal kidneys before irreversible renal damage happens. From a technical point of view, restoring normal urinary outflow can be achieved by totally different approaches: Fetal Cystoscopy for Lower Urinary Tract Obstruction. Direct destruction of the urethral valves by laser or electrocoagulation presents the benefit of restoring the urine circulate through the urethra and therefore the cycle of filling and emptying the bladder in a single procedure. In a recent multicentre collection, Martinez and coworkers reported on the results of the centres in Barcelona and Leuven. No infants developed pulmonary hypoplasia, and all were alive at 15 to one hundred ten months. Additionally, the direct fulguration of the valves entails the chance for creating essential collateral injury on the stage of the bladder neck and adjacent fetal anatomical constructions. The first reviews on the usage of a shunt from the fetal bladder into the amniotic cavity to bypass the obstruction are greater than 30 years old. Chronic renal illness was identified in 62% of the survivors, 25% of whom underwent renal transplantation. In addition, a standardised classification of sufferers primarily based on severity would facilitate comparison of treatments both retrospectively and prospectively. This classification is hampered by the shortage of uniform criteria for renal dysplasia and regular or irregular urinary biochemistry and due to this fact needs further refinement and potential validation. Also, it is necessary to recuperate the shunts at supply because they might stay in the uterine cavity and act as a contraceptive system. Fetal decrease urinary tract obstruction: proposal for standardised multidisciplinary prenatal administration based on illness severity. The bowels protrude via the stomach insertion site of the shunt (large arrow). Renal Abnormalities Anomalies of Number Renal agenesis Renal agenesis is the results of either failure of the ureteric bud to arise or failure of the bud to have interaction with the renal mesenchyme. Bilateral renal agenesis ends in the oligohydramnios sequence (pulmonary hypoplasia, dysmorphic face and limb deformities). It is a common renal anomaly occurring with an incidence of 1 in a hundred twenty five within the basic inhabitants. If uncomplicated, this situation remains asymptomatic and is considered a standard variant. However, duplex kidneys are regularly sophisticated by hydronephrosis, recurrent urinary tract infections and wish for surgical treatment. The ureter of the higher pole ends ectopically (more caudally and medially) within the bladder or really ectopic (in the vagina, urethra, seminal vesicle or rectum), which outcomes in obstructive hydronephrosis and renal dysplasia. Duplex kidneys are incessantly related to a ureterocele, which is the dilated intravesical a part of the (upper pole) ureter. A ureterocele presents as a cystic construction in the bladder on prenatal ultrasound, and its detection is strongly related to a confirmed duplex kidney postnatally. Horseshoe kidney Horseshoe kidney is the most common sort of fusion anomaly with an incidence of zero.
17.5 mg zestoretic cheap overnight delivery
Human evolution as hunter-gatherers has led to the coordination of sleep with metabolic homeostatic mechanisms; hunger blood pressure medication quiz buy zestoretic 17.5 mg low price, vigilance pulse pressure 67 17.5 mg zestoretic order free shipping, and food-seeking behaviors happen primarily during daylight hours, whereas satiety and somnolence happen together for periodic rest. Parasympathetic exercise ends in slowing of the guts fee, peripheral vasodilation, and increased gastrointestinal motility. Alternatively, sympathetic stimulation ends in pupillary dilation, elevated coronary heart price and blood pressure, and different responses related to elevated emotional stress. This finding probably reflects a later maturation of the neuroregulatory system that controls heart price variability. For occasion, in normal fetuses, the fetal autonomic activity that controls heart fee follows a 12-hour cycle, as opposed to the maternal 24-hour rhythm. For example, several hypothalamic nuclei project to the medulla oblongata to keep homeostatic features via the serotonergic system. In the suprachiasmatic nucleus, these signals have an result on gene expression for no less than four transcription elements that act in a transcription-transduction feedback loop to determine the oscillations. Fever results from an elevation of the temperature setpoint by inflammatory cytokines, corresponding to interleukin-1, that elevate prostaglandin E levels in the hypothalamus; regular physiologic mechanisms then preserve physique temperature at this elevated setpoint. Heat loss happens through the placenta, fetal pores and skin, amniotic fluid, and uterine wall. After birth, the neonate has large heat losses via the pores and skin that require functioning thermoregulatory mechanisms to forestall hypothermia. Premature and low-birthweight infants are often unable to preserve applicable physique temperature and behave like poikilotherms quite than homeotherms. How the hypothalamus matures to the environmental circumstances after birth remains to be unknown. Although the hypothalamus is essential for integrating and expressing emotion, different areas of the mind, including the cortex, limbic system, and thalamus, work together with the hypothalamus to bring about the varied types of responses. The sympatheticadrenal-medullary system causes the well-known stress-induced launch of epinephrine. Sympathetic-adrenal-medullary activation, which depends on characteristics of each the situation and the person, happens in response to challenges, with a sooner onset than activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Stress induction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is lively in newborns, al although it might be transiently blunted in extraordinarily preterm infants. Once the noxious stimulus has been removed, in healthy neonates cortisol levels quickly return to basal levels. Hypothalamic endocrine exercise may be divided into two distinct categories as established by the anatomy of the hypothalamopituitary unit. Because the posterior pituitary gland, or neurohypophysis, is composed of axonal projections from the hypothalamus, the hormones launched into the circulation by the posterior pituitary are actually made in cell our bodies of the hypothalamus. In contrast, the anterior pituitary gland, or adenohypophysis, is a definite gland. The hypothalamus secretes various releasing and inhibiting elements that regulate anterior pituitary hormone synthesis and launch. These components are made in hypothalamic neurons and are carried down axons to the median eminence. They then reach the anterior pituitary by the particular hypothalamohypophysial portal circulation, whereas the anterior pituitary hormones attain their goal organs by the peripheral circulation. Hypothalamic hormones stimulate or inhibit anterior pituitary launch of a hormone, and the circulating levels of the pituitary hormone feed back to regulate hypothalamic hormone release. For example, will increase in circulating prolactin concentrations stimulate hypothalamic secretion of dopamine (prolactin-inhibiting factor) into the hypothalamohypophysial portal circulation to forestall extreme prolactin launch by the pituitary; high prolactin levels also inhibit hypothalamic launch of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, a hormone that stimulates prolactin launch. Within a third-order feedback pathway, a number of forms of feedback loops exist: lengthy, quick, and ultrashort suggestions. Long-loop suggestions happens when hormones from peripheral endocrine target cells or substances from tissue metabolism affect the manufacturing of hypothalamic hormones. Short-loop feedback is second-order feedback inside a third-order feedback system. When hypothalamic hormone release affects its own synthesis, ultrashort suggestions has occurred. The mechanism of this ultrashort feedback is either via neurotransmission between two cells in the hypothalamus or through pituitary tanycyte launch of the hormone into cerebrospinal fluid, which can regulate hypothalamic activity as a end result of the hypothalamus is located at the base of the third ventricle. Two neurosecretory methods produce hypothalamic hormones (summarized in Table 142-4): magnocellular and parvocellular. Stimulatory feedback is depicted as a solid arrow, and inhibitory feedback is depicted as a dashed arrow. Ultrashort suggestions is coloured in pink, quick suggestions in blue, and lengthy suggestions in black. In distinction, the parvocellular secretory cells are small neurons, mostly in the region of the tuber cinereum below the third ventricle, that produce the hypophysiotropic hormones. Because the hormonal techniques of the anterior pituitary are reviewed in detail in Chapters 144 to 146 and 148, we concentrate on the magnocellular system. Vasopressinergic neurons appear 1 week earlier in the supraoptic nucleus than within the paraventricular nucleus. Although an grownup group of vasopressinergic neurons could be identified early within the second trimester, the variety of those neurons appears to improve until the twentysixth week of gestation. The vasopressinergic system of neurons is also highly energetic in the perinatal period. Both genes are composed of three exons; the whole mature hormone is encoded within the first exon. Cholinergic and -adrenergic fibers carry the stimulatory inputs, whereas -adrenergic fibers present inhibition of oxytocin launch. Oxytocin serves two physiologic functions: it aids in parturition by stimulating uterine contractions, and it facilitates nursing by stimulating contraction of myoepithelial cells within the lactating mammary gland (milk "let-down" reflex). Oxytocin release, which happens in brief secretory bursts, increases in both the fetus and the mom during labor. Most of the magnocellular neurons are situated within the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei but further small nuclei additionally contain these neurons. V1 receptors stimulate vasoconstriction, glycogenolysis, platelet aggregation, and vascular clean muscle hypertrophy. A subclass of V1 receptors (V1b) is positioned in the anterior pituitary and stimulates corticotropin launch. V2 receptors improve water permeability of the renal accumulating ducts by inducing aquaporins; this ends in higher water retention and decreased urine volume. The regulation is so precise that, under moderately steady-state situations, deflections within the physique weight and fats mass of mammals remain within zero. The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus has been recognized as a satiety middle, whereas the lateral hypothalamic space stimulates feeding. Many of these receptors are located in the hypothalamus and control pathways involved within the regulation of appetite and thermogenesis. When the hypothalamic melanocortin 3 receptors and melanocortin four receptors are stimulated by -melanocyte-stimulating hormone, meals intake is decreased and power expenditure is elevated. Those additionally beneath leptin regulation embody orexins,75 cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript, glucagon-like peptide 1, melanin-concentrating hormone, and cholecystokinin. Obesity extra frequently outcomes from leptin resistance than from leptin deficiency.
Syndromes
- To prevent or reverse fat loss
- Exposure to children in a day care setting
- Vomiting
- Time it was swallowed
- Faintness
- How quickly did the clammy skin develop?
17.5 mg zestoretic purchase free shipping
For example arteria princeps pollicis zestoretic 17.5 mg amex, extended hypoglycemia at a susceptible time would possibly signal a trajectory for development in a nutritionally challenged environment prehypertension systolic pressure order zestoretic 17.5 mg with mastercard, with the consequence of completely altering mechanisms for the uptake of glucose. Among crucial animal fashions developed for this research are those by which metabolic substrates, corresponding to oxygen or protein, are restricted throughout gestation. These models include those of global substrate discount, accomplished by placental embolism,37,38 placental restriction via the surgical excision of attachment sites,39-41 uterine artery ligation,42,43 umbilical twine occlusion,forty four and a quantity of being pregnant (in monovulatory species). These embrace decreased maternal meals or protein intake,48-51 insulin-induced hypoglycemia,fifty two decreased oxygen availability via gestation at altitude,53 and decreased fraction of maternal inspired oxygen. Among the more interesting fetal variations are people who occur in response to prolonged hypoxemia. This has been sometimes studied in sheep and completed in a number of experimental methods. Of specific significance are studies that involve early or periconceptional undernutrition. These information recommend that one or two doses of antenatal corticosteroid therapy are able to attenuating the adrenal response to stimulation within the newborn. In a small examine, salivary cortisol production after heel stick blood sampling was monitored in nine newborns whose moms had antenatal betamethasone remedy and in nine infants from untreated moms. All the infants were born at 33 to 34 weeks of gestation and studied inside three to 6 days of supply. The cortisol response to a heel stick was blocked within the infants exposed to betamethasone prenatally. At that point, the cortisol response to the stress of a heel stick remained blocked. As famous, this peptide is thought to play a task in feeding conduct and diet. Ongoing analysis, similar to that of Wattez and colleagues,sixty eight is according to programming of energy steadiness and is more probably to be an intensive area of analysis sooner or later. Clearly, extra research is needed on the normal growth of this system to better perceive its impression on prenatal and postnatal health. Fadalti M, Pezzani I, Cobellis L, et al: Placental corticotropin-releasing issue: an update. Schwartz J, Kleftogiannis F, Jacobs R, et al: Biological activity of adrenocorticotropic hormone precursers on ovine adrenal cells. Karpac J, Ostwald D, Bui S, et al: Development, maintenance, and performance of the adrenal gland in early postnatal proopiomelanocortin-null mutant mice. Lesage J, Blondeau B, Grino M, et al: Maternal undernutrition during late gestation induces fetal overexposure to glucocorticoids and intrauterine progress retardation, and disturbs the hypothalamo-pituitary adrenal axis in the new child rat. Glover V, Miles R, Matta S, et al: Glucocorticoid exposure in preterm babies predicts saliva cortisol response to immunization at 4 months. Gagnon R, Challis J, Johnston L, et al: Fetal endocrine responses to chronic placental embolization within the late-gestation ovine fetus. Murotsuki J, Gagnon R, Pu X, et al: Chronic hypoxemia selectively downregulates 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase sort 2 gene expression in the fetal sheep kidney. Carmichael L, Sadowsky D, Olson D, et al: Activation of the fetal hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis with prolonged and graded hypoxemia. Takahashi A, Mizusawa K: Posttranslational modifications of proopiomelanocortin in vertebrates and their organic significance. Mastorakos G, Ilias I: Maternal and fetal hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axes during being pregnant and postpartum. Muglia L, Jacobson L, Dikkes P, et al: Corticotropin-releasing hormone deficiency reveals major fetal however not adult glucocorticoid want. Venihaki M, Carrigan A, Dikkes P, et al: Circadian rise in maternal glucocorticoid prevents pulmonary dysplasia in fetal mice with adrenal insufficiency. Burlet G, Fernette B, Blanchard S, et al: Antenatal glucocorticoids blunt the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis of neonates and disturb some behaviors in juveniles. Muglia the adrenal cortex undergoes remarkable growth and distinctive metamorphosis during the fetal and neonatal interval. Its morphology, features, and secretory product profiles are distinctly completely different throughout fetal and postnatal life. The features of the adrenal cortex during fetal life-participation within the maintenance of pregnancy and initiation of parturition, as well as secretion of cortisol to promote organ maturation earlier than birth-also change postnatally to upkeep of homeostasis, notably within the presence of stress, and modulation of inflammatory challenges. Wherever potential, this chapter will focus on research of people and different primates. This outstanding development during fetal life occurs via a mixture of hyperplasia, hypertrophy, and reduced apoptosis. During the embryonic period, mitotic activity has been observed all through the fetal adrenal cortex. Using newer strategies, nonetheless, investigators have identified mitotic figures throughout the fetal zone, suggesting that it grows by hyperplasia as well as hypertrophy. After start, maximal apoptosis is observed within the fetal zone, which subsequently disappears. These factors mix to shield the fetus from untimely exposure to excess cortisol early in gestation and then to stimulate the elevated cortisol production important for preparation for extrauterine survival. Stereologic studies of adrenal cortex structure in anencephalic fetuses have shown a hanging decrease in both cell quantity and whole volume of the fetal zone and transitional zone (zona fasciculata), with less effect on the zona glomerulosa. That is, if the cells primarily originate from the definitive zone and then migrate inward, why do they express different enzyme profiles in different zones, resulting in the useful zonation noticed in the gland In addition, the interrelationship of the placenta and adrenal cortex serves to protect the fetus from untimely exposure to excess cortisol. Because fetal androgens are the first substrate for placental estrogen manufacturing, the fetal adrenal cortex is central to these capabilities. In the baboon model, estrogen receptors- and - are expressed all through the fetal adrenal cortex. Estrogen also might play an element in sustaining being pregnant by rising progesterone synthesis in the placenta. Estrogen promotes low density lipoprotein uptake and P450scc exercise by the placenta, rate-limiting steps for progesterone manufacturing. Notably, maternal malnutrition and stress during being pregnant have each been convincingly linked to decreased fetal growth and adverse outcomes later in life. In the rhesus monkey, infusion of androstenedione increases placental estradiol synthesis and induces premature labor. However, two circumstances could also be exceptions to that statement: the primary a quantity of days of transition to extrauterine life and preterm delivery. Hydrocortisone treatment of infants with vasopressor-resistant hypotension results in amelioration of hypotension and weaning of vasopressor help.
Buy zestoretic 17.5 mg visa
Braun T blood pressure normal or high zestoretic 17.5 mg buy, Bober E blood pressure value ranges generic 17.5 mg zestoretic mastercard, Buschhausen-Denker G, et al: Differential expression of myogenic willpower genes in muscle cells: potential autoactivation by the Myf gene products. Rochard P, Rodier A, Casas F, et al: Mitochondrial activity is involved in the regulation of myoblast differentiation by way of myogenin expression and exercise of myogenic elements. Petersen W, Pufe T, Kurz B, et al: Angiogenesis in fetal tendon growth: spatial and temporal expression of the angiogenic peptide vascular endothelial cell growth factor. Fidziaska-Dolot A, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I: Morphology of the decrease motor neuron and muscle. Jurkat-Rott K, Holzherr B, Fauler M, Lehmann-Horn F: Sodium channelopathies of skeletal muscle result from gain or loss of function. Wang Y, Jaenisch R: Myogenin can substitute for Myf5 in promoting myogenesis but much less efficiently. Andres V, Walsh K: Myogenin expression, cell cycle withdrawal and phenotypic differentiation are temporally separable occasions that precede cell fusion upon myogenesis. Kitzmann M, Carnac G, Vandromme M, et al: the muscle regulatory components MyoD and Myf5 bear distinct cell cycle�specific expression in muscle cells. Jin Y, Murakami N, Saito Y, et al: Expression of MyoD and myogenin in dystrophic mice, mdx and dy, during regeneration. Astolfi A, De Giovanni C, Landuzzi L, et al: Identification of recent genes related to the myogenic differentiation arrest of human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Mennerich D, Braun T: Activation of myogenesis by the homeobox gene Lbx1 requires cell proliferation. Ohto H, Kamada S, Tago K, et al: Cooperation of Six and Eya in activation of their target genes by way of nuclear translocation of Eya. Daston G, Lamar E, Olivier M, Goulding M: Pax-3 is important for migration however not differentiation of limb muscle precursors in the mouse. Katagiri T, Akiyama S, Namiki M, et al: Bone morphogenetic protein-2 inhibits terminal differentiation of myogenic cells by suppressing the transcriptional activity of MyoD and myogenin. Wood A, Thorogood P: Patterns of cell behavior underlying somitogenesis and notochord formation in intact vertebrate embryos. Wagner M, Thaller C, Jessell T, Eichele G: Polarizing exercise and retinoid synthesis in the flooring plate of the neural tube. Fan C-M, Tessier-Lavigne M: Patterning of mammalian somites by surface ectoderm and notochord: evidence for sclerotome induction by a hedgehog homolog. Brand-Saberi B, Ebensperger C, Wilting J, et al: the ventralizing effect of the notochord on somite differentiation in chick embryos. Lucarelli M, Fuso A, Strom R, Scarpa S: the dynamics of myogenin site-specific demethylation is strongly correlated with its expression and with muscle differentiation. Braun T, Buschhausen-Denker G, Bober E, et al: A novel human muscle issue related to however distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. Ott M-O, Bober E, Lyons G, et al: Early expression of the myogenic regulatory gene Myf-5, in precursor cells of skeletal muscle within the mouse embryo. Weintraub H, Davis R, Tapscott S, et al: the myoD gene household: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Funakoshi Y, Matsuda S, Uryu K, et al: An immunohistochemical research of fundamental fibroblast growth factor in the developing chick. Takano H, Komuro I, Oka T, et al: the Rho family G proteins play a crucial role in muscle differentiation. Tajbakhsh S, Vivarelli E, Cusella-De Angelis G, et al: A inhabitants of myogenic cells derived from the mouse neural tube. Ishikawa H: Electron microscopic observations of satellite tv for pc cells with particular reference to the development of mammalian skeletal muscular tissues. Prelle A, Chianese L, Moggio M, et al: Appearance and localization of dystrophin in normal human fetal muscle. Muntoni F, Brockington M, Godfrey C, et al: Muscular dystrophies as a end result of defective glycosylation of dystroglycan. Donalies M, Cramer M, Ringwald M, Starzinski-Powitz A: Expression of M-cadherin, a member of the cadherin multigene household, correlates with differentiation of skeletal muscle cells. Bornemann A, Schmalbruch H: Immunocytochemistry of M-cadherin in mature and regenerating rat muscle. Hillaire D, Leclerc A, Faur� S, et al: Localization of merosin-negative congenital muscular dystrophy to chromosome 6q2 by homozygosity mapping. Vuolteenaho R, Nissinen M, Sainio K, et al: Human laminin M chain (merosin): complete main construction, chromosomal task and expression of the M and A chain in human fetal tissues. Ferns G, Shams S, Shafi S: Heat shock protein 27: its potential function in vascular disease. Sakurai T, Fujita T, Ohto E, et al: the decrease of the cytoskeletal tubulin follows the decrease of the associated molecular chaperone -B-crystallin in unloaded soleus muscle atrophy with out stretch. Wohlfart G: �ber das Vorkommen verschiedener Arten von Muskelfasern in der Skelettmuskulatur des Menschen und einiger Saugetiere. Kumagai T, Hakamada S, Hara K, et al: Development of human fetal muscles: a comparative histochemical evaluation of the psoas and the quadriceps muscular tissues. Zelen� J: the morphological influence of innervation of the ontogenetic growth of muscle-spindles. Zelen� J, Soukup T: the differentiation of intrafusal fiber varieties in rat muscle spindles after motor denervation. Zelen� J, Soukup T: Increase within the number of intrafusal muscle fibres in rat muscle tissue after neonatal motor denervation. Novotov� M, Soukup T: Neomyogenesis in neonatally de-efferented and postnatally denervated rat muscle spindles. Jurkat-Rott K, R�del R, Lehmann-Horn F: Muscle channelopathies: myotonias and periodic paralyses. Brehm P, Henderson L: Regulation of acetylcholine receptor channel function during development of skeletal muscle. Evidence that a useful neuromuscular interplay is involved within the regulation of naturally occurring cell demise and the stabilization of synapses. Kugelberg E: Adaptive transformation of rat soleus motor models throughout growth: histochemistry and contraction velocity. It is on the identical time a part of the mind, an intrinsic element of neural pathways, and an endocrine gland, specially related to the pituitary gland to form the "grasp gland" unit of the physique. It has been long understood that, to refine this regulation, the hypothalamus responds both to information from the mind and to the degrees of the peripheral hormones and body fluids it regulates. Appreciation has grown that the hypothalamus also receives input from the intestine and fat shops, in essence closing the loop of metabolic regulation. All these incoming components are compared with intrinsic setpoints, and outgoing messages are then launched to enact modifications that will match the physique to the suitable setpoint. We have reviewed pediatric problems of the neuroendocrine system, each congenital and purchased, elsewhere;1 this chapter focuses on regular anatomy, embryology, and physiology of the hypothalamus. It is composed of four major buildings: the tuber cinereum, the median eminence, the infundibulum, and the mammillary our bodies. The median eminence, a central swelling positioned on the tuber cinereum, types the floor of the third ventricle. The infundibulum is a stalk that connects the median eminence to the posterior lobe of the pituitary, and the mammillary bodies are two spherical protuberances at the posterior finish of the inferior floor of the hypothalamus.
Zestoretic 17.5 mg buy cheap
The proximal a part of the left vitelline vein disappears Umbilical Veins Paired veins join the sinus lateral to the vitelline veins and medial to the cardinal veins heart attack treatment zestoretic 17.5 mg cheap without prescription. The proximal parts of both proper and left veins disappear arteria d8 zestoretic 17.5 mg with amex, and the distal left umbilical vein persists and drains to the hepatic sinusoids. A direct anastomosis develops between the left umbilical vein and the proximal right vitelline vein � the venous duct (ductus venosus). The Venous System There are three pairs of main veins in the embryo in the fifth week. Section of the creating aortic root of a mouse embryo exhibiting the connection of the coronary artery with the aortic lumen. Cardinal Veins the paired common cardinal veins be part of the sinus most laterally and are fashioned by the confluence of anterior cardinal veins (draining the head) and posterior cardinal veins. From the fifth to the seventh week, additional veins type: the subcardinal veins draining mostly the kidneys, the supracradinal veins draining the physique wall by the intercostal veins following regression of the posterior cardinal veins, and the sacrocardinal veins draining the lower limbs. The brachiocephalic vein is fashioned of the anastomosis between the 2 anterior cardinal veins. The superior caval vein is shaped from the proximal proper anterior cardinal vein and the proper widespread cardinal vein. The anastomosis between the 2 subcardinal veins becomes the left renal vein and the left subcardinal vein and then regresses with its distal half, turning into the left gonadal vein. The anastomosis between the sacrocardinal veins turns into the left frequent iliac vein. The right supracardinal vein turns into the supracardinal phase of the inferior caval vein. The azygos vein derives from the proper supracardinal vein and part of the posterior cardinal vein. Initially, the veins draining to the center are embedded within the mesenchyme at the venous pole of the center with growth of the pericardial cavity excavating the connecting veins from this mesenchyme. By this process, the common cardinal veins, which are the confluence of the left and right superior and inferior cardinal veins, turn into included throughout the pericardial cavity. They then purchase a sleeve of myocardium, and the confluence of the systemic veins is then known as the sinus venosus, or left and right sinus horns, which each ultimately connect to the best atrium. The iliac veins and inferior vena cava bifurcation derive from the publish cardinal veins (orange). The segment between the renal veins and the bifurcation derives from the supra cardinal vein (yellow). The segment between the liver and the renal veins derives from the subcardinal vein (green). The brief phase between the liver and the best atrium derives from the best vitelline vein (red). The Arterial System Folding of the embryo during the fourth week (days 22�24) causes the paired dorsal aortae connected to the cranial end of the guts to type a pair of dorsoventral loops � the primary aortic arches. The paired dorsal aortae fuse under the level of the fourth thoracic section and turn into linked with the umbilical arteries. The first two pairs of arch arteries regress while the later arch arteries are forming. It is subsequently the aortic arch arteries 3, 4 and 6 that give rise to the arteries of the head, neck and thorax (Table 10. The aorta and caval vein ascend together by way of the diaphragm, the vein because the azygos vein that enters the superior caval vein. In addition to left atrial isomerism, there were complete atrioventricular septal defect, bilateral superior caval veins and situs inversus with polysplenia. B, Schematic representation of the aortic arches following remodelling displaying the persistence of some and involution of others. As in A, the specimen is seen from the left facet with the head to the left of the sphere. The third arch derivatives are symmetrical, but the derivatives of the fourth and sixth arches are asymmetrical. The truncus arteriosus offers rise to the most proximal segments of the aorta and pulmonary trunk (orange). The aortic sac provides rise to the ascending aorta and brachiocephalic artery (green). The fourth aortic arch gives rise on the proper facet to the primary part of the subclavian artery and on the left to the phase of aortic arch between the left common carotid and left subclavian arteries (purple). The distal right subclavian artery and all of the left subclavian artery derive from the seventh intersegmental arteries (yellow). The pulmonary arteries and arterial duct derive from the sixth aortic arch arteries (blue). The the rest of the descending aorta (uncoloured) derives from the left dorsal aorta. The normal right subclavian artery develops from the connection of the seventh intersegmental artery with the proper fourth arch artery. Instead the seventh proper intersegmental artery takes origin from the right dorsal aorta. In this photograph, the thoracic contents are seen from behind, and the best subclavian artery is seen to take origin from the descending aorta on the left side and to run behind the oesophagus to reach its regular location. A collection of ventral branches that offer the gut derivatives derived from a community of vitelline arteries 2. Lateral branches that supply retroperitoneal buildings similar to adrenals, kidneys and gonads three. The segments of dorsal aorta connecting arches 3 and 4 regress, leaving the third aortic arch to provide blood to the top. The fourth and sixth arches bear asymmetrical remodelling to provide the upper extremities, dorsal aorta and lungs. The left fourth arch becomes the aortic arch between the left common carotid and left subclavian arteries and the most cranial a half of the descending aorta. The proper and left subclavian arteries derive from the seventh intersegmental arteries. The sixth arch arteries present the pulmonary arteries, and the left arch offers the arterial duct. The ascending aorta provides rise to left and proper common carotid arteries and the best subclavian artery. It then arches over the hilum of the proper lung, and the descending aorta lies on the right facet. The pulmonary trunk offers rise to the right and left pulmonary arteries, with a left-sided arterial duct connecting the left subclavian artery to the left pulmonary artery. The left subclavian artery arises from the descending aorta by way of a socalled retro-oesophageal diverticulum (diverticulum of Kommerell). There is thus a whole vascular ring which surrounds the trachea and oesophagus; viewed posteriorly, the vessels display a Y-configuration fashioned by the aortic arch on the proper and the left subclavian artery or diverticulum of Kommerell on the left.
17.5 mg zestoretic buy with amex
Multiple-marker screening in pregnancies with hydropic and nonhydropic Turner syndrome blood pressure medication morning or evening generic zestoretic 17.5 mg line. Second-trimester maternal serum inhibin a ranges in fetal trisomy 18 and Turner syndrome with and without hydrops hypertension level 2 discount 17.5 mg zestoretic fast delivery. Preliminary estimate for the second-trimester maternal serum screening detection rate for the forty five,X karyotype using -fetoprotein, unconjugated estriol and human chorionic gonadotropin. Identifying Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome in conjunction with prenatal screening for down syndrome. Low or absent unconjugated estriol in being pregnant, an indicator for steroid sulfatase deficiency detectable by fluorescence in situ hybridization and biochemical evaluation. Second-trimester maternal serum markers in twin pregnancies with complete mole, report of two instances. Nuchal translucency and major congenital heart defects in fetuses with normal karyotype: a meta-analysis. Prevention of perinatal demise and adverse perinatal consequence using: a meta-analysis. Competing risks mannequin in early screening for preeclampsia by biophysical and biochemical markers. Prediction of small-for-gestation neonates from biophysical and biochemical markers at 11-13 weeks. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American College of Medical Genetics. The influence of bias in MoM values on affected person danger and screening performance for Down syndrome. Impact of bias in serum free beta-human chorionic gonadotropin and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-a multiples of the median levels on first-trimester screening for trisomy 21. A combination mannequin of nuchal translucency thickness in screening for chromosomal defects. About half of the congenital anomalies may be identified in the late first trimester. Severe and infrequently deadly anomalies can be diagnosed, permitting dad and mom the choices of constant with the pregnancy or, if acceptable, termination of pregnancy. Women recognize the opportunity of early reassurance or early analysis, making this scan an essential first step in screening for congenital anomalies. The focus was initially on high-risk pregnancies6 however gradually prolonged in the direction of more unselected populations. What is still lacking is a consensus on when this investigation should be carried out (12�14 weeks), on the preferred strategy (transabdominal or transvaginal) and how extended it ought to be. The fetal backbone, although not yet utterly ossified, may additionally be noticed alongside its entire extension from the cervical origin to the sacrum. By tilting the probe on each side of the fetal physique, the extremities are visualised along with the long bones. A first trimester fetus has commonly open palms, easily enabling counting of fingers. The legs are often flexed and the feet close to one another in order that in a single sweep, their positions could be assessed. Cross-sectional planes from cranial to caudal show within the head the image of the falx (midline) and of the choroid plexuses, filling at this stage virtually completely the comparatively giant lateral ventricles. More caudally, the fetal stomach is seen beneath the heart just above the extent of the umbilical cord insertion. Finally, lower within the pelvis, the bladder is seen, flanked by the 2 umbilical arteries. The kidneys can sometimes be observed as two more echogenic oval buildings on both sides of the spine. This quick and gross anatomical survey allows exclusions of major and mostly deadly structural anomalies such as acrania, exencephaly, holoprosencephaly, gross spinal anomalies, stomach wall defects, megacystis and gross skeletal or limb deformities. Appreciation of the heart axis and of the fourchamber view and outflow tracts by color Doppler excludes gross cardiac anomalies. In lean ladies, this probe can present wonderful photographs, especially of the fetal coronary heart. The largest study to date, on forty four,850 euploid fetuses examined at the time of the nuchal scan, showed that structural anomalies were observed in 1. The authors state that about one-third of the structural anomalies are amenable to early prognosis, and about 40% can doubtlessly be detected within the first trimester. Arrays reveal in these fetuses an extra 5% of pathological copy quantity variants. Early detection offers parents the option to terminate the being pregnant at a stage when termination may be much less traumatic. Neurodevelopment begins from the neurulation section, from around 19 days of embryonic life to round day 26. The neural plate becomes the neural tube, and this further develops into prosencephalon (forebrain), mesencephalon (midbrain), rhombencephalon (hindbrain) and the spinal twine. First Trimester Fetal Brain and Spine Investigation Cranial bone ossification ought to be accomplished by 11 weeks. It is helpful to look particularly for bone ossification within the axial and coronal planes. Neurosonography can already be performed at 12 to 13 weeks, transabdominally with use of high-frequency transducers (in lean women), or transvaginally. Later in being pregnant, acrania evolves into exencephaly and within the second trimester into anencephaly, by which hardly no more brain tissue is visible. Acrania can be in 12% of instances a half of chromosomal or genetic situation (Meckel-Gruber syndrome) or amniotic band syndrome and is associated with aneuploidy in as a lot as 5% of cases. To not miss this situation, an early scan ought to be carried out after eleven weeks by trained sonographers. The prognosis is variable and depends of associated conditions, localisation, size and anatomical structures concerned. Open spina bifida (in Europe, 1 in 2000 pregnancies) is attributable to failure of closure of the neural tube 24 to 27 days after conception. The creating spinal wire and exposed nerves are broken by direct trauma and by the neurotoxicity of the amniotic fluid. Recently, a new promising marker for the early detection of spina bifida, the maxillo-occipital line, has been proposed. The anomaly is reported in and is often related to extreme skull and facial defects and with greater than two thirds of circumstances associated with chromosomal abnormalities, primarily trisomies thirteen and 18. Lateral ventricles measuring greater than 10 mm are mainly a second and third trimester prognosis. Although normal ranges for the fetal ventricular system within the first trimester can be found, gentle ventriculomegaly should still be a traditional variant. Four strains: (1) superior mind stem border, (2) inferior mind stem border, (3) choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle, and (4) internal border occipital bone. Facial Anomalies Recently, a quantity of studies have advised that facial anomalies, similar to micrognathia and labiopalatum cleft, can already be diagnosed in the first trimester.