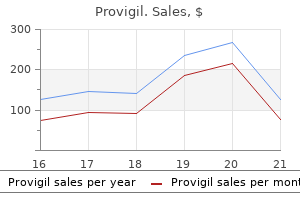
Provigil
Provigil dosages: 200 mg, 100 mg
Provigil packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Purchase provigil 200 mg on line
Epinephrine is used to advertise inotropy during weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass insomnia pictures provigil 100 mg generic with amex. It can be used as a vasoconstrictor to extend oxygen supply and increase cardiac output in sepsis sleep aid high blood pressure provigil 200 mg order on line. Chapter 18 � Sympathomimetic Drugs 451 a decrease of plasma volume due to a loss of proteinfree fluid into the extracellular house. Arterial wall injury and local areas of myocardial necrosis may also accompany continual circulating excesses of epinephrine. The hemodynamic effects of epinephrine are attenuated and can be blocked by prior administration of a- or b-adrenergic receptor antagonists. Airway Smooth Muscle Smooth muscular tissues of the bronchi are relaxed by epinephrine-induced activation of b2 receptors. In the presence of b-adrenergic blockade, epinephrine as a substitute induces bronchoconstriction from stimulation of bronchial a receptors. Metabolic Effects Epinephrine has essentially the most vital impact on metabolism of all of the catecholamines. Liver glycogenolysis outcomes from epinephrine-induced activation of hepatic phosphorylase enzyme. Lipolysis is as a result of of epinephrine-induced activation of triglyceride lipase, which accelerates the breakdown of triglycerides to type free fatty acids and glycerol. Infusions of epinephrine usually improve plasma concentrations of glucose, cholesterol, phospholipids, and low-density lipoproteins. In addition, epinephrine can inhibit peripheral glucose uptake, which is also due in part to inhibition of insulin secretion. Increased plasma concentrations of lactate presumably mirror epinephrine-induced glycogenolysis in skeletal muscles. The naturally occurring catecholamines are epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine. Epinephrine will increase coronary heart rate by accelerating the rate of spontaneous section four d epolarization, which also increases the likelihood of cardiac dysrhythmias. Epinephrine will increase conduction velocity and reduces the refractory interval within the atrioventricular node, bundle of His, Purkinje fibers, and ventricular muscle. Tachycardia, untimely ventricular contraction, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation all could happen. Increased cardiac output reflects epinephrine-induced will increase in heart rate, myocardial contractility, and venous return. Repeated doses of epinephrine produce similar cardiovascular results in contrast to the tachyphylaxis that accompanies administration of artificial noncatecholamines that cause the release of norepinephrine, similar to ephedrine. Myocardial oxygen consumption is increased with enhanced left ventricular preload, elevated contractility, increased afterload, and tachycardia. Diastolic operate is improved by growing the speed of myocardial relaxation, and early left entricular filling is enhanced. Epinephrine stimulates renal b receptors, leading to elevated secretion of renin. In traditional therapeutic doses, epinephrine has no significant vasoconstrictive effect on cerebral arterioles. Epinephrine-induced hypokalemia could contribute to cardiac dysrhythmias, which occasionally accompany stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. Conversely, epinephrine could stimulate the release of potassium from the liver, tending to offset the lower in extracellular focus of this ion produced by entrance into skeletal muscles. Ocular Effects Epinephrine causes contraction of the radial muscular tissues of the iris, producing mydriasis. Adrenergic receptors liable for these ocular effects are likely a receptors as norepinephrine is less potent than epinephrine and isoproterenol has practically no ocular effects. Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary Effects Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and isoproterenol produce rest of gastrointestinal clean muscle. Activation of b-adrenergic receptors relaxes the detrusor muscle of the bladder, whereas activation of a-adrenergic receptors contracts the trigone and sphincter muscles. Hypokalemia before induction of anesthesia and prevention by beta 2 adrenoceptor antagonism. The impairment of splanchnic circulation that happens is larger than that associated with norepinephrine or dopamine. A hypercoagulable state current in the course of the intraoperative and postoperative interval might mirror stress-associated release of epinephrine. Chronic infusion of norepinephrine or increased circulating concentrations of this catecholamine, as may be associated with pheochromocytoma, could cause precapillary vasoconstriction and loss of protein-free fluid into the extracellular area. Placement of norepinephrine in a 5% glucose answer supplies sufficient acidity to stop oxidation of the catecholamine. Extravasation during infusion can produce extreme native vasoconstriction and attainable necrosis; hence, administration should be by way of central venous access. Norepinephrine administration must be accompanied by invasive hemodynamic monitoring. Clinical Uses the primary use of norepinephrine is as a potent vasoconstrictor to increase complete peripheral vascular resistance and imply arterial pressure. Norepinephrine can be used for patients with low systemic vascular resistance after cardiopulmonary bypass. In patients with coronary artery disease, norepinephrine can be used to keep up perfusion strain, although it should be balanced with the resultant increased afterload associated with high doses. Side Effects Norepinephrine should be used cautiously in patients with right ventricular failure. Norepinephrine increases venous return to the center and also raises pulmonary artery pressures through stimulation of pulmonary vascular a1-adrenergic receptors. The use of norepinephrine as an inotropic agent is restricted by its action as a potent vasoconstrictor. The increased peripheral resistance and afterload could decrease cardiac output and enhance the work of the left ventricle. Its use can be limited by the potential for tachycardia, although its arrhythmogenic potential is lower than that of epinephrine. However, when giant doses of norepinephrine accompanied by enough fluid volume resuscitation are used with caution to treat profound Norepinephrine Norepinephrine is the endogenous neurotransmitter synthesized and stored in postganglionic sympathetic nerve endings and released with sympathetic nerve stimulation. It is roughly equal in potency to epinephrine for stimulation of b1 receptors but, in contrast to epinephrine, has minimal impact at b2 receptors (see Table 18-1). Through its action on b1 receptors, norepinephrine will increase coronary heart rate, conduction, and contractility. Norepinephrine is a potent a1 agonist producing intense arterial and venous vasoconstriction in all vascular beds aside from the coronary arteries. Venous vasoconstriction decreases venous capacitance, thereby growing venous return to reinforce stroke volume and cardiac output. Heart fee adjustments could also be minimal as baroreceptor reflexes triggered by arterial vasoconstriction are counteracted by b1-mediated will increase in coronary heart price.
Diseases
- Metatarsus adductus
- Polyneuropathy hand defect
- 3 methylcrotonic aciduria
- Leukodystrophy, Sudanophilic
- Catel Manzke syndrome
- Dibasic aminoaciduria type 1
Discount 100 mg provigil
Suppression of gastric acid secretion in sufferers with gastroesophageal reflux disease leads to gastric bacterial overgrowth and deconjugation of bile acids insomnia stephen king movie provigil 100 mg generic with mastercard. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a fourth histamine receptor (H(4)) expressed in bone marrow insomnia norwegian movie provigil 100 mg safe. The first potent and selective non-imidazole human histamine H4 r eceptor antagonists. Bispyrimidines as potent histamine H(4) r eceptor ligands: delineation of structure-activity relationships and detailed H(4) r eceptor binding mode. Effects of the selective H1 and H2 histamine receptor antagonists loratadine and ranitidine on autonomic control of the heart. Best proof in anesthetic apply: prevention: dimenhydrinate prevents postoperative nausea and vomiting. The effect of three completely different ranitidine dosage regimens on reducing gastric acidity and quantity in ambulatory surgical patients. A comparative evaluation of the transport of H2-receptor antagonists by the human and baboon placenta. The effect of intravenous pantoprazole and ranitidine for enhancing preoperative gastric fluid properties in adults undergoing elective surgical procedure. The impact of metoclopramide on the decrease oesophageal sphincter in late pregnancy. Drug insight: from disturbed motility to disordered movement-a evaluation of the medical advantages and medicolegal risks of metoclopramide. Current points on security of prokinetics in critically unwell sufferers with feed intolerance. Effects of metoclopramide and ranitidine on preoperative gastric contents in day-case surgery. Metoclopramide within the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a q uantitative systematic evaluate of randomized, placebo-controlled studies. Interventions for preventing nausea and vomiting in girls present process regional anaesthesia for caesarean part. Comparison of intermittent versus continuous infusion metoclopramide in control of acute nausea induced by cisplatin chemotherapy. Comparison of intermittent ondansetron versus steady infusion metoclopramide used with commonplace combination antiemetics in charge of acute nausea induced by cisplatin chemotherapy. Postoperative neurologic dysfunction associated with preoperative administration of metoclopramide. Akathisia and anesthesia: refusal of surgery after the administration of metoclopramide. Extrapyramidal unwanted effects after metoclopramide administration in a post-anesthesia care unit- a case report. Dose-dependent impact of metoclopramide on cholinesterases and suxamethonium metabolism. The use of H1 and H2 histamine antagonists with morphine anesthesia: a double-blind examine. The affiliation between cognition and histamine-2 receptor antagonists in African Americans. The hemodynamic effects of intravenous cimetidine in intensive care unit sufferers: a d oubleblind, prospective examine. Intragastric acidity, micro organism, nitrite, and N-nitroso compounds before, during, and after cimetidine remedy. Does pretreatment with cimetidine and ranitidine have an result on the disposition of bupivacaine Effect of famotidine and lansoprazole on serum phosphorus ranges in hemodialysis patients on calcium carbonate therapy. Short-term treatment with proton pump inhibitors, H2-receptor antagonists and prokinetics for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease-like signs and endoscopy unfavorable reflux disease. A comparability of lansoprazole, omeprazole, and ranitidine for decreasing preoperative gastric secretion in adult patients undergoing elective surgery. Influence of metoclopramide on plasma cholinesterase and period of action of mivacurium. The antibiotic azithromycin is a motilin receptor agonist in human abdomen: comparison with erythromycin. Intravenous erythromycin dramatically accelerates gastric emptying in gastroparesis diabeticorum and normals and abolishes the emptying discrimination between solids and liquids. Motilin agonist erythromycin increases human lower esophageal sphincter pressure by stimulation of cholinergic nerves. The use of erythromycin as a gastrointestinal prokinetic agent in grownup crucial care: benefits versus risks. Parenteral diet is defi ed as supply of vitamins immediately into the venous circulation (peripheral vein or central vein). Although the advantages of parenteral nutrition in the perioperative period are controversial, postoperative enteral feeding has been proven to decrease complication charges in malnourished patients although mortality rates are unchanged. For example, vitality requirements could double and protein necessities may triple in severely burned sufferers. Minimally careworn patients require about 25 to 30 cal/ kg and 1 g/kg of protein every day to remain in nitrogen and vitality equilibrium. Moderately to severely careworn sufferers ought to be resuscitated first after which began on a hypocaloric regimen (20 cal/kg) till the stress response abates. Lipid calories from infusions of propofol could also be vital and ought to be included when calculating caloric consumption. Th ee many years in the past, it was thought that the primary aim of vitamin support in the hospitalized affected person was to satisfy vitality necessities and to make the affected person anabolic. Current goals include meeting and attenuating the metabolic response to stress and, as nicely as, attenuating mobile injury and modulating the immune response to damage. A number of enteral options containing numerous quantities of protein (amino acids), carbohydrates (glucose), fat (medium- and long-chain triglycerides), micronutrients, macronutrients, and electrolytes can be found. Carbohydrates may be the source of as much as 90% of the energy, which will increase the osmolarity of those solutions. Unless the affected person has maldigestion or malabsorption of fats (and even then a formulation containing medium-chain triglycerides could be tried), formulation with a traditional range of fats content material (30%) are most well-liked. Selection of a formulation that provides enough total nitrogen as protein (1 to 1. It was once thought that low-protein formulations were indicated for sufferers with severe renal dysfunction; nevertheless, we now recognize that these patients require the same quantity of protein as do different sufferers, even when one has to resort to dialysis to maintain homeostasis. The solely exception is the patient with hepatic encephalopathy for whom an enteral or parenteral formula containing branched-chain amino acids might improve the encephalopathy, but when not, one ought to change again to a standardized formulation. Commercial formulations of natural foods could be so finely suspended that they pass through small-bore tubes. Defined-formula diets are needed when luminal hydrolysis or absorption is impaired, as in malabsorption syndromes. An essential consideration when utilizing enteral nutrition is placement and positioning of the smallbore (8 t o 12 F rench) silastic supply tube.
Provigil 200 mg line
Unfortunately, this refle genioglossus exercise is easily abolished by low doses of most anesthetics, with the exception of ketamine sleep aid overdose provigil 200 mg buy on line. The inlet of the larynx is bordered by the epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds, and the arytenoids insomnia during pregnancy 200 mg provigil purchase with mastercard. The larynx itself bulges into the pharynx posteriorly making a deep pharyngeal recess anterolaterally on both aspect, the pyriform fossae. The pyriform fossae, which lie to every aspect of midline, are clinically related due to their tendency to entice meals or international objects within the pharynx and as potential websites for the application of topical anesthesia to dam the inner department of the superior laryngeal nerve. The larynx serves because the organ of phonation, plays an essential position in coughing, and in protection of the airway from entrainment of solids and liquids throughout swallowing. Other essential buildings embody the hyoid bone and its attachments, the epiglottis, the cricoid cartilage, and the corniculate cartilages. Beneath the hyoid bone is the rest of the larynx suspended by its attachment, the thyrohyoid membrane and muscle. The epiglottis is the midline elastic cartilage discovered inferior to the bottom of the tongue. It is anchored anteriorly to the hyoid bone and inferiorly to the within of the anterior portion of the thyroid cartilage instantly above the vocal cords. Bilateral folds of the epiglottis curve posteriorly to kind a mucosal ridge attached to the arytenoid cartilages sitting on prime of the posterior lamina of the cricoid, the aryepiglottic folds. The epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds, and the corniculate tubercles kind the inlet into the glottis below. The thyroid cartilage incorporates the larynx with its paired lamina fused anteriorly on the laryngeal prominence and extending posteriorly to terminate in superior and inferior horns or cornu. The thyroid cartilage serves as a secure level of attachment for quite a few small muscles and Chapter 24 � Gas Exchange 551 ligaments which manipulate the vocal cords. The mean length of the relaxed open glottis is approximately 23 mm in males and 17 mm in females. The glottis at its widest (posterior) level is 6 t o 9 m m but can be "stretched" to 12 mm. However, the folds of mucosa and fibrous tissue lying parallel to the true vocal cords simply superiorly within the glottis, the vestibular folds or "false vocal cords," can turn out to be edematous. The intrinsic laryngeal musculature functions to open the glottis throughout inspiration; close the glottis and constrict the superior structures throughout swallowing; and finely management abduction, adduction, and tension of the true vocal cords throughout phonation. The internal department of the superior laryngeal nerve pierces the lateral side of the thyrohyoid membrane together with the superior laryngeal artery and vein to provide sensation for the bottom of the tongue, vallecula, epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds, pyriform recesses, and the superior side of the true vocal cords. The external department of the superior laryngeal nerve supplies motor to the cricothyroid muscle, a tensor of the true vocal cords. The recurrent laryngeal nerves provide sensation to the vocal cords and tracheobronchial tree as properly as motor to all of the remaining intrinsic musculature of the larynx. The proper recurrent laryngeal nerve passes inferior to the best subclavian artery however the left originates on the stage of the aortic arch and loops across the ligamentum arteriosum then both nerves ascend cephalad along the tracheoesophageal groove. This anatomy have to be appreciated throughout esophageal and thyroid surgery and through both cervical and anterior mediastinoscopy, as these structures could be in danger. The larynx receives its blood supply from the superior and inferior laryngeal arterial branches of the superior and inferior thyroid arteries, respectively. The main perform of the upper airway is to supply a conduit for the preliminary inhalation then exhalation of gases to and from the lungs while contributing to multiple other functions. With respect to inhalation, the nasopharynx and posterior pharynx heat and humidify the impressed gas. This aids in maintaining core temperature and protects the extra delicate epithelia lining the decrease airways from desiccation. The airway epithelium secrets and techniques mucus, which coats the airway surface and maintains tissue hydration and in addition serves to trap particulate matter, bacteria, and viruses. Mucus also contains a selection of enzymes with antioxidant, antiprotease, and antibacterial properties. Passage of bronchoscopes, endotracheal tubes, and particularly, double-lumen tubes must be directed posteriorly the place the vocal cords will unfold the widest. Note that the vocal means of the arytenoid cartilage pivots on a small point and could be traumatized and displaced with rough handling. There are three mechanisms at work to supply mechanical filtering of impressed gases. Gas flow slows inside the bifurcating and branching tracheobronchial tree until it becomes more laminar. Normally, the particles, including micro organism and similar-sized particles, are trapped within the mucus at this degree of more proximal airways and are transported cephalad by the fixed motion of the cilia, an apical function of the respiratory epithelium, at a ra the of approximately 2. Lower airway mucus is normally cleared in about 24 hours although this can be drastically retarded in illness states such as cystic fibrosis or continual bronchitis or situations altering ciliary perform or progress, similar to tobacco smoking. When a gas (or liquid) flows by way of a straight unbranched tube, flow will normally be laminar and resistance is instantly proportional to the viscosity of the gasoline and inversely proportional to the 4th power of the radius. Resistance 5 8 three size 3 (viscosity/p) three (radius)4 However, at very excessive circulate rates or when fuel flows via an irregular tube or orifice, circulate tends to turn out to be turbulent and resistance becomes proportional to the density of the gas and inversely proportional to the 5th power of the radius. Reynolds number is a dimensionless quantity that allows estimation of whether a move is turbulent or laminar. Helium is a gas with a low density compared to air or oxygen; nevertheless, the viscosity of the three is kind of equal. Tracheal and Bronchial Structure the trachea originates at the cricoid cartilage (at the level of vertebra C6) and extends approximately 10 to 12 cm (females) and 12 to 14 cm (males) to terminate in a bifurcation (carina) on the T4/5 vertebral level (2nd intercostal space, the angle of Louis). True cords Cricoid Epiglottis Teeth Uvula Chapter 24 � Gas Exchange 553 segmental bronchi that can be readily visualized during versatile bronchoscopy. The proper upper lobe bronchus gives off three segmental bronchi (apical, anterior, posterior). The left upper lobar bronchus splits into the superior division with "3" segments (a "fused" apicalposterior and an anterior) and the inferior division or lingual with 2 s egments (superior and inferior). The left lower lobe bronchus branches into 4 l ower segmental branches (superior, a "fused" anteromedial basal, lateral basal, and posterior basal) for a total of "10" segments on the left. An online interactive bronchoscopy simulator is out there to demonstrate this anatomy. Respiratory Airways and Alveoli the airways proceed to divide into smaller diameter conduits until one arrives on the bronchioles with diameters less than 0. At this stage, the airways lose all remnants of cartilage and begin the transformation from purely conducting airways to those described as respiratory bronchioles. Respiratory bronchioles eventually divide into the final four generations of alveolar ducts, which then consist primarily of openings into the terminal alveolar sacs. The first 15 generations serve as conducting airways and the next eight generations turn out to be sufficiently thin-walled to allow some extent of gasoline trade and are referred to as acinar airways. One medical side of this geometric development of increasingly narrower airways (and blood vessels) by divergence and multiplication is that the general cross-sectional space and therefore resistance to fuel circulate (or blood flow) becomes markedly less compared to the resistance of the proximal airway (or blood vessel). This has an important influence on distribution of fuel and blood flow, move velocity, and, hence, transit time through key areas of gasoline exchange.
Generic provigil 100 mg line
Dobutamine stress echocardiograph for orthotopic liver transplantation analysis sleep aid on morning joe 200 mg provigil discount with amex. The effect of bisoprolol on perioperative mortality and myocardial infarction in high-risk sufferers undergoing vascular surgery insomnia 4 weeks post hysterectomy provigil 100 mg trusted. Dutch Echocardiographic Cardiac Risk Evaluation Applying Stress Echocardiography Study Group. The pathogenesis of accelerated fibrinolysis in liver cirrhosis: a critical role for tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor. Intravascular thrombosis and thromboembolism throughout liver transplantation: antifibrinolytic therapy implicated? Aprotinin administration and pulmonary thromboembolism throughout orthotopic liver transplantation: report of two cases. Intraoperative adjustments in blood coagulation and thromboelastographic monitoring in liver transplantation. Continuous insulin infusion reduces mortality in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. Arterial ketone physique ratio as a attainable indicator for liver transplantations in fulminant hepatic failure. Circulatory, respiratory, cerebral, and renal derangements in acute liver failure: pathophysiology and management. A completely failing liver may be extra harmful than no liver in any respect: three circumstances of whole hepatic devascularization in preparation for emergency liver transplantation. Worsening of cerebral hyperemia by the administration of terlipressin in acute liver failure with extreme encephalopathy. Use of marginal donors for liver transplantation: A retrospective research of 365 liver donors. Drug metabolism in liver disease: exercise of hepatic microsomal metabolizing enzymes. Duration of vecuronium induced neuromuscular blockade as a predictor of liver allograft dysfunction. Duration of rocuronium induced neuromuscular block throughout liver transplantation: a predictor of primary allograft perform. Coronary artery vasospasm following placement of a cold liver graft during orthotopic liver transplantation. Effects of end-stage liver failure on the incidence and backbone of the grownup respiratory distress syndrome. Adult respiratory distress syndrome secondary to end stage liver disease-successful consequence following liver transplantation. Ascites, renal failure, and electrolyte issues in cirrhosis: Pathogenesis, analysis, and treatment. Working Party proposal for a revised classification system of renal dysfunction in sufferers with cirrhosis. Perioperative renal perform in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Effect of intraoperative low-dose dopamine on renal function in liver transplant recipients. Postreperfusion syndrome throughout liver transplantation for cirrhosis: end result and predictors. Effect of imply arterial stress, haemoglobin and blood transfusion during cardiopulmonary bypass on postoperative acute kidney injury. The response to methylene blue in patients with extreme hypotension throughout liver transplantation. Risk of severe serotonin toxicity following co-administration of methylene blue and serotonin reuptake inhibitors: an update on a case report of postoperative delirium. Reduced use of intensive care after liver transplantation: influence of early extubation. Impact of graft sort on consequence in pediatric liver transplantation: a report from Studies of Pediatric Liver Transplantation. The main objectives of imaging are to understand donor vascular and biliary anatomy, determine variant anatomy, assess hepatic segmental volumes, and exclude underlying hepatobiliary pathological situations. Donors with inadequate liver quantity, detectable pathology, or anatomical variations that will require extensive vascular or biliary reconstruction will not be chosen for residing associated liver transplantation. The optimal protocol includes a noncontrast sequence and postcontrast sequences within the arterial, portal venous, and venous phases. The noncontrast sequence may be acquired with 5-mm collimation thickness, arterial part with zero. Three-dimensional (3-D) hepatic arteriograms, portal venograms, and hepatic venograms can then be rendered with any certainly one of a number of forms of commercially available software program. Breath-hold axial T1-weighted in-phase and opposed-phase gradient-echo and T2-weighted images are acquired to assess for diffuse liver disease, particularly steatosis, and to rule out focal lesions that would render the allograft unacceptable for transplantation. Donor Liver Volume Analysis Volume evaluation of the donor proper and left lobes is critical to guarantee adequate proper lobe perform in the recipient and adequate left lobe reserve in the donor. The residual liver quantity in the donor ought to exceed 35% of the total liver volume. The results are correct with maximal deviation from true quantity estimated to be lower than 10%. Intravenous gadolinium distinction is run, and a 3-D gradient-echo sequence is often acquired with generation of subtraction arteriograms and venograms. The vertical axis of the widespread hepatic duct is used as the middle of rotation in coronal/off-coronal thick slabs. This additionally results in higher picture quality because of shorter acquisition occasions and higher patient cooperation. Although the exact fats fraction cutoff for irregular liver fat has not been definitively established, a fat fraction of 5. T2* correction decreases the likelihood that the fats fraction will be underestimated due to the presence of iron. Other confounding elements embrace the scanner platform used and the particular imaging parameters. These variations require twin anastomoses to the right and left portal vein in the recipient, whereas standard bifurcation anatomy requires solely a single anastomosis. Hepatic Venous Anatomy It is necessary to establish the branching sample of the center hepatic vein and hepatic venous variants to ensure that the graft could be adequately drained. The branching pattern of the middle hepatic vein impacts the location of the hepatectomy airplane. This aberrant vein requires special consideration if it is bigger than 5 mm and must be preserved during surgical procedure to stop the risk for graft malfunction. Biliary Anatomy Evaluation Anatomic variants of the biliary system ought to be recognized preoperatively to decrease the risk for biliary leak. Huang et al26 classified the variants of proper lobe ductal drainage into 5 sorts: 1. In donor livers with biliary trifurcation or aberrant proper lobe duct drainage, two separate biliary anastomoses are necessary to stop postoperative biliary leakage and long-term segmental atrophy of the graft.
Lipoic Acid (Alpha-Lipoic Acid). Provigil.
- Treating HIV-related brain problems.
- Treating alcoholic liver disease.
- Treating type 2 diabetes.Improving symptoms such as burning, pain, and numbness in the legs and arms of people with diabetes.
- How does Alpha-lipoic Acid work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What other names is Alpha-lipoic Acid known by?
- What is Alpha-lipoic Acid?
- Dosing considerations for Alpha-lipoic Acid.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Treating a heart-related nerve problem called cardiac autonomic neuropathy.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96749
Buy 100 mg provigil mastercard
Transmission of bacterial pathogens from the donor to the recipient has lengthy been a priority after transplantation insomnia icd code 9 discount 200 mg provigil visa. Cultures of blood insomnia 720p yify order 200 mg provigil with visa, urine, and peritoneal fluid or perfusate are routinely obtained at most institutions. Two large studies retrospectively evaluated the discovering of bacteremia in donors of strong organs, including livers. However, recipients in all circumstances had been receiving antibiotic protection, and caretakers have been knowledgeable of the bacteremia in order that appropriate modifications in antibiotic regimens to cover these pathogens might be made. These studies recommend that prophylactic antibiotics can allow the successful use of organs even from bacteremic donors. Another examine evaluating the use of organs from donors with bacterial meningitis (Escherichia coli, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis) also discovered an absence of antagonistic occasions in recipients; donors had been handled earlier than organ harvest, and recipients obtained 5 to 10 days of antibiotic therapy. In the past, a confirmed optimistic take a look at end result for syphilis was thought-about a contraindication to use of the organ. However, profitable transplantation has been carried out by giving penicillin to the deceased donor before harvest and by then treating the recipients. Examples of those infections embody toxoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, coccidioidomycosis, and histoplasmosis. Screening of candidates ought to include a cautious historical past of prior sickness with fungal or parasitic infections. Stool should be screened for ova and parasites in patients coming from areas the place parasitic diseases are regularly encountered. Antifungal prophylaxis must be considered in candidates with a optimistic historical past of prior fungal infection with pathogens recognized to recur after decision of the primary infection. Experience with coccidioidomycosis in transplant recipients means that antifungal remedy, corresponding to an azole agent, should be given in transplant recipients with this history to forestall reactivation. Donor transmission of histoplasmosis has also been documented in a recipient of a kidney transplant whose donor was from an endemic area. Amphotericin B or a liposomal formulation is the most reliable therapy in the immunocompromised host, although azoles (itraconazole, fluconazole, and voriconazole) which have good in vitro activity towards Blastomyces dermatitidis may be efficient. Accordingly, individuals recognized to have energetic disease with Aspergillus ought to receive aggressive remedy aimed at eradication. If yeast is found, low-dose amphotericin, azoles, or echinocandins must be used to deal with disease or eradicate colonization. Because of the danger for hepatotoxicity with azoles in patients awaiting liver transplantation, many choose the utilization of echinocandins or lowdose amphotericin or liposomal formulations over fluconazole. Screening for past fungal illness for liver transplantation recipients has not been routine, nevertheless it ought to be considered in patients from endemic areas or those who have high-risk elements. Candidate Immunizations It is crucial to doc the immunization history of the transplant candidate. Likewise, proof of safety against measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella should be documented because these require stay virus vaccines which are contraindicated after transplantation. Seasonal influenza vaccination is recommended for all candidates over 6 months of age, household contacts, and health care employees. Pearls and Pitfalls Pretransplant screening ought to do the next: · Identify potential pathogens present in: · Candidate · Donor · Allow staff to devise appropriate prophylaxis strategies Screening assays can have false-negative results for the following reasons: · Recent an infection · New an infection in candidate since time of initial evaluation · Level below the limit of detection To lower false-negative results, on the time of transplantation repeat serological checks that beforehand had adverse outcomes. Screening assays can have false-positive outcomes because of the following: · Passive antibody from blood merchandise · Maternal antibody in children youthful than 12 to 18 months · Cross-reacting assay Evaluating Fever at Time of Transplant Fevers in candidates might characterize acute episodes of an infection that require remedy and dedication of potential want for removal of the affected person from the candidate ready list and/or delaying the time of transplantation. The input of the infectious disease specialist could additionally be critical in optimizing the care of these episodes and figuring out when the patient may safely tolerate both liver transplantation and subsequent immunosuppression. In children, specific viral infections, even limited to the higher respiratory tract, can be associated with important morbidity and mortality once they persist or develop within the early postoperative interval. These viruses embody adenovirus,fifty two respiratory syncytial virus,sixty one parainfluenza, and influenza virus. Evaluation of fever and/or respiratory symptoms in children and adult candidates should embody these speedy assays during epidemiologically applicable occasions. If no focus is discovered and transplantation proceeds, antibiotic prophylaxis ought to be continued for at least 48 hours while awaiting culture results. Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and other viral infections in kids after liver transplantation. Role of the laboratory in analysis and management of cytomegalovirus infection in hematopoietic stem cell and solid-organ transplant recipients. Quantitative oropharyngeal Epstein-Barr virus shedding in renal and cardiac transplant recipients: relationship to immunosuppressive remedy, serologic responses, and the danger of posttransplant lymphoproliferative dysfunction. In stopping rejection of the brand new organ, these antirejection drugs disturb various features of the immune system and put the recipient in danger for opportunistic infections. Careful screening of the candidate and donor will assist determine potential infectious brokers earlier than they turn into a complicating issue. The impact of human herpesvirus-6 and -7 infection on the outcome of liver transplantation. Improved end result of orthotopic liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B cirrhosis with aggressive passive immunization. Tenofovir remedy in hepatitis B virus-positive solid-organ transplant recipients. Prevention of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B recurrence after liver transplantation with entecavir plus tenofovir combination remedy and perioperative hepatitis B immunoglobulin only. Clinical and histologic patterns of early graft failure because of recurrent hepatitis C in 4 patients after liver transplantation. Mortality predictors in liver transplant recipients with recurrent hepatitis C cirrhosis. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in sufferers with solidorgan transplants: report of 5 circumstances and evaluation. Impact of human immunodeficiency virus on survival after liver transplantation: evaluation of United Network for Organ Sharing database. Transmission of human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus from an organ donor to 4 transplant recipients. Update: Investigations of West Nile virus infections in recipients of organ transplantation and blood transfusion. Early end result of liver transplantation in sufferers with a history of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Liver transplantation after an acute episode of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Mycobacterial infection after liver transplantation: a report of three instances and review of the literature. Mycobacterium tuberculosis after liver transplantation: Management and guidelines for prevention. Is there a place for prophylaxis in opposition to tuberculosis following renal transplantation? Clinical significance of donor-unrecognized bacteremia in the consequence of solid-organ transplant recipients. Successful transplantation of organs retrieved from donors with bacterial meningitis.
Generic 200 mg provigil with visa
Bariatric surgical procedure versus nonsurgical therapy for obesity: a s ystematic evaluate and metaanalysis of randomised managed trials sleep aid with melatonin order 100 mg provigil mastercard. The pharmacokinetics and tolerability of an intravenous infusion of the new hydroxyethyl starch 130/0 insomnia weight loss provigil 200 mg cheap otc. Assessment of quantity responsiveness throughout mechanical ventilation: current advances. Predicting quantity responsiveness through the use of the end-expiratory occlusion in mechanically ventilated intensive care unit patients. Shanewise Naturally Occurring Catecholamines Naturally occurring catecholamines are epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine (see Table 18-1 and. Epinephrine is used in native and fi ld blocks to advertise a cold surgical fi ld. Cardiovascular Effects the cardiovascular results of epinephrine end result from stimulation of a- and b-adrenergic receptors (see Table 18-1). The web effect of those changes in peripheral vascular tone is preferential distribution of cardiac output to skeletal muscles and elevated systemic vascular resistance. Renal blood fl w is considerably decreased by epinephrine, even in the absence of changes in systemic blood stress. Epinephrine is estimated to be 2 to 10 times more potent than norepinephrine as a renal vasoconstrictor. In common, b2 receptors are extra sensitive to decrease epinephrine doses whereas effects on a1 receptors predominate at higher doses. At excessive doses, the predominant a activity and resultant vasoconstriction leads to elevated afterload, which may impede will increase in cardiac output. Initial tachycardia may be adopted by coronary heart fee decreases because of baroreceptor reflexes. Venous return is also enhanced by venoconstriction from the excessive density of a receptors within the venous vasculature system. Blood pressure is increased by a rise in cardiac index as well as a rise in systemic vascular resistance. Epinephrine stimulates b1 receptors causing a rise in heart fee, myocardial contractility, and cardiac output. The net effect of these systemic blood strain modifications is a rise in pulse strain and a mild change in imply arterial pressure. It is a circulating hormone synthesized, stored, and launched from the adrenal medulla. It is a potent activator of a-adrenergic receptors and likewise prompts b1 and b2 receptors. Therefore, epinephrine is administered subcutaneously, intravenously, or intramuscularly. Absorption after subcutaneous injection is gradual because of native epinephrine�induced vasoconstriction. This is in distinction to epinephrine, which has a extra signifi ant chronotropic effect. Norepinephrine will increase mean arterial pressure primarily by vasoconstriction and to lesser diploma by increasing stroke volume and cardiac output. Norepinephrine and epinephrine increase total peripheral vascular resistance more than dobutamine (described within the following texts). Intravenous administration of norepinephrine ends in intense vasoconstriction in skeletal muscle, liver, kidneys, and pores and skin vascular beds. Dopamine regulates cardiac, vascular, and endocrine function and is a vital neurotransmitter in the central and peripheral nervous methods. The pharmacology of dopamine is complex as this catecholamine differentially stimulates a wide selection of dopaminergic in addition to adrenergic receptors. D2 receptors are principally presynaptic and inhibit adenylate cyclase exercise and launch of norepinephrine in autonomic nervous system ganglia and adrenergic nerves (in renal and mesenteric vessels) resulting in vasodilation. Nausea and vomiting produced by dopamine in all probability mirror stimulation of D2 receptors. Traditionally, the pharmacokinetics of dopamine has been attributed to dose-dependent results on varying receptors. The lower in diastolic blood stress might result in a reflex increase in heart fee. At greater infusion rates (3 to 10 g/kg/minute), dopamine primarily stimulates b1-adrenergic receptors in the coronary heart in addition to a receptors in the peripheral vasculature. The activation of b receptors leads to elevated cardiac output by growing chronotropy and contractility together with vasodilation and afterload discount. The predominant stimulation of vascular clean muscle a1 receptors at these greater doses result in arterial and venous vasoconstriction, increased systemic vascular resistance, and increased blood pressure attenuating further will increase in cardiac output. There are a extensive range of scientific responses relying on individual variability in pharmacokinetics in addition to other variables. Dopamine will increase cardiac output by stimulation of b1 receptors, growing stroke quantity. This increase in cardiac output is usually accompanied by only modest will increase in coronary heart price, systemic blood stress, and systemic vascular resistance. A portion of the effect of dopamine can also be due to stimulation of endogenous norepinephrine launch, which may predispose to the development of cardiac dysrhythmias. The release of norepinephrine caused by dopamine may be an unreliable mechanism for increasing cardiac output when catecholamine stores are depleted, as happens with sufferers in persistent cardiac failure. Dopamine causes both relaxation and contraction of vascular easy muscle with the predominant impact various by vascular mattress, predominant receptor sort, and dose administered. Rapid metabolism of dopamine with an elimination half-life of 1 to 2 minutes mandates its use as a steady infusion (1 to twenty g/kg/minute) to take care of therapeutic plasma concentrations. Extravasation of dopamine, like norepinephrine, produces intense native vasoconstriction, which can be treated with native infiltration of phentolamine. The immediate precursor of dopamine, L-dopa, is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and readily crosses the blood�brain barrier. Clinical Uses Dopamine is used clinically to increase cardiac output in patients with decreased contractility, low systemic blood strain, and low urine output as may be current after Chapter 18 � Sympathomimetic Drugs 455 cardiopulmonary bypass or with continual coronary heart failure. Activation of arterial and venous a1 receptors increases systemic vascular resistance, preload, and left ventricular afterload. The divergent pharmacologic results of dopamine and dobutamine make their use in combination doubtlessly helpful. For example, infusions of dopamine and dobutamine in combination have been noted to supply a higher improvement in cardiac output, at lower doses, than can be achieved by either drug alone. Dopamine might distribute the cardiac output to the renal and mesenteric vascular beds, whereas dobutamine could present further afterload discount by dilating pores and skin and skeletal muscle vascular beds. Renal-Dose Dopamine the time period renal-dose dopamine or low-dose dopamine refers back to the continuous infusion of small doses (1 t o three g/kg/minute) of dopamine to patients to promote renal blood circulate. Small doses of dopamine increase renal blood fl w predominantly by D1 receptors in the renal vasculature and possibly by D2 receptors through inhibition of norepinephrine release. Larger doses predominantly enhance renal blood circulate by b-adrenergic�mediated will increase in cardiac output.
Buy provigil 100 mg free shipping
Hypervitaminosis A Hypervitaminosis A is the poisonous syndrome that results from excessive ingestion of vitamin A, notably in kids sleep aid tylenol 200 mg provigil purchase amex. Typically, high vitamin A intake has resulted from overzealous prophylactic vitamin A remedy insomnia vitamin deficiency provigil 200 mg buy with amex. Plasma concentrations of vitamin A of greater than 300 mg/dL are diagnostic of hypervitaminosis A. Treatment consists of withdrawal of the vitamin source, which is often adopted inside 7 days by disappearance of the manifestations of extra vitamin A activity. Fatigue, myalgia, loss of body hair, diplopia, nystagmus, gingivitis, stomatitis, and lymphadenopathy have been noticed. Hepatosplenomegaly is accompanied by cirrhosis of the liver, portal vein hypertension, and ascites. The prognosis is confirmed by radiologic demonstration of hyperostoses underlying tender swellings on the extremities and the occipital region of the pinnacle. Plasma alkaline phosphatase concentrations are increased, reflecting osteoblastic exercise. Bones continue to grow in size however not in thickness, with increased susceptibility to fractures. Congenital abnormalities could happen in infants whose mothers have consumed excessive amounts of vitamin A throughout pregnancy. Vitamin D Vitamin D (Calciferol) has two types, D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol) with similar chemical structure except that D2 h as an additional methyl group on Carbon 24. D2 a nd D3 a re metabolically inert and require two chemical reactions to accumulate exercise. In monocytes, calcitriol stimulates cathelicidin, a peptide with bactericidal and mycobactericidal properties. Parathyroid hormone acts to restore plasma calcium concentrations at the expense of bone calcium. In infants and youngsters, this ends in failure to mineralize newly fashioned osteoid tissue and cartilage, inflicting formation of soft bone, which, with weight bearing, leads to deformities generally recognized as rickets. Anticonvulsant therapy with phenytoin will increase target organ resistance to vitamin D, resulting in an elevated incidence of rickets and osteomalacia. There is evidence that vitamin D supplementation reduces the chance of falling amongst elderly individuals. In addition to withdrawal of the vitamin, therapy consists of increased fluid intake, diuresis, and administration of corticosteroids. In acting as an antioxidant, vitamin E presumably prevents oxidation of essential mobile constituents or prevents the formation of poisonous oxidation merchandise. There appears to be a relationship between nutritional vitamins A and E during which vitamin E facilitates the absorption, hepatic storage, and use of vitamin A. Vitamin E is stored in adipose tissue and is assumed to stabilize the lipid portions of cell membranes. Other functions attributed to vitamin E are inhibition of prostaglandin manufacturing and stimulation of an important cofactor in corticosteroid metabolism. Vitamin E necessities could additionally be elevated in individuals exposed to excessive oxygen environments or in those receiving therapeutic doses of iron or large doses of thyroid hormone substitute. Vitamin E could additionally be important in hematopoiesis, with occasional types of anemia responding favorably to the administration of a-tocopherol. Despite absence of conclusive supportive proof, vitamin E has been administered to women with a historical past of recurrent spontaneous abortions and for sterility in each sexes. Changes just like those noticed in skeletal muscles have occurred in cardiac muscle of animals. A necrotizing myopathy with proximal skeletal muscle weak spot and elevated plasma concentrations of creatine kinase might occur in sufferers self-medicated with massive doses of vitamin E. There are information that support an association between low plasma levels of vitamin E and the chance of growing lung cancer. It is proposed that oxidation of lipids in low-density lipoproteins (lipid peroxidation) initiates the process of atherogenesis. Phytonadione (vitamin K1) is current in quite so much of foods and is the only natural type of vitamin K obtainable for therapeutic use. Vitamin K2 represents a collection of compounds which might be synthesized by grampositive bacteria within the gastrointestinal tract. Synthesis of vitamin K provides roughly 50% of the estimated day by day requirement of vitamin K; the rest is provided by the food plan. Vitamin K is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract only within the presence of adequate quantities of bile salts. The g-carboxyglutamic acid residues make it possible for these coagulation factors to bind calcium ions and fasten to phospholipid surfaces, resulting in clot formation. Vitamin K deficiency is characterised by ecchymoses, epistaxis, hematuria, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Deficiency of vitamin K may be because of (a) insufficient dietary consumption, (b) decreased bacterial synthesis due to antibiotic therapy, (c) impaired gastrointestinal absorption resulting from obstructive biliary tract disease and absence of bile salts, or (d) hepatocellular illness. Neonates have hypoprothrombinemia as a result of vitamin K deficiency until sufficient dietary consumption of the vitamin occurs and normal intestinal bacterial floras are established. These plasma concentrations decrease even further in the course of the first 2 to 3 days after delivery and then start to increase towards adult values after roughly 6 days. Phytonadione and menadione are the vitamin K preparations most often used to deal with hypoprothrombinemia. Phytonadione orally or administered intravenously at a price of 1 mg per minute, is usually adequate to reverse the consequences of oral anticoagulants. Even giant doses of phytonadione are ineffective against heparininduced anticoagulation. Intramuscular administration might produce local hemorrhage at the injection website in hypoprothrombinemic patients. In neonates, doses of phytonadione of larger than 1 mg may cause hemolytic anemia and increase the plasma concentrations of unbound bilirubin, thus rising the danger of kernicterus. The incidence of hemolytic anemia reflects a deficiency of glycolytic enzymes in some neonates. Menadione hemolyzes erythrocytes in patients genetically deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, as nicely as in neonates, particularly untimely infants. This hemolysis and sometimes hepatic toxicity reflect a combination of menadione with sulfhydryl teams in tissues. Administration of enormous doses of menadione or phytonadione might depress liver function, notably in the presence of preexisting liver illness. Dietary Supplements Dietary dietary supplements (vitamins, minerals, herbs, amino acids, enzymes) are products ingested orally and intended to supplement the food plan with vitamins thought to enhance health.
Discount 100 mg provigil otc
Although small anastomotic leaks could be managed conservatively sleep aid oil order provigil 200 mg on line, large leaks on the anastomosis are related to excessive morbidity and mortality and require quick operation insomnia nursing diagnosis buy cheap provigil 200 mg on-line. Leakage of contrast material from the donor biliary tree at nonanastomotic sites is a critical event, presumably indicative of bile duct necrosis secondary to hepatic artery occlusion. Such leaks usually happen in the hilar and parahilar areas; intrahepatic or extrahepatic locations are much less frequent. Bilomas occurring with hepatic artery occlusion are often associated with a poor end result and require retransplantation. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography exhibits filling of the common bile duct (C) and proper biliary ducts. The left biliary ducts are obscured by communication with and opacification of a big biloma. Two drainage catheters are in place, and contrast materials is seen draining into the superiorly positioned catheter. Radiographic Diagnosis and Management of Biliary Obstruction the signs of biliary obstruction could initially be indistinguishable from a selection of different issues, together with rejection, hepatic artery occlusion, major graft dysfunction, and viral infections. Ultrasonography, however, is less dependable, notably within the detection of mild obstruction. The degree of dilatation depends not only on the diploma and duration of the obstruction but additionally on the pliability of both the extrahepatic bile ducts and the parenchymal supporting skeleton of the intrahepatic ducts. Because prolonged biliary obstruction results in inflammatory changes and fibrosis of the biliary tract, even long-term obstruction could happen without significant proximal dilatation. Patients with cirrhosis, for example, could have high-grade obstruction with little or no intrahepatic dilatation. Magnetic resonance cholangiography can also be helpful to assess biliary duct obstruction100 however tends to overestimate stricture severity. A, T-tube cholangiogram exhibits filling of the widespread bile duct (C) and free leakage of contrast materials from the T tube into the peritoneal area (arrows). B, Passage of a guidewire into the T tube exhibits that the wire passes freely into the peritoneum, confirming dislodgment of the T tube. Biliary obstruction in the transplant patient can be brought on by problems corresponding to stricture, biliary sludge,102 stones, a retained stent, T-tube dysfunction, and, hardly ever, an allograft cystic duct remnant mucocele and common duct redundancy. Posttransplant biliary strictures are the most typical cause of biliary obstruction and may be categorized as anastomotic and nonanastomotic. Untreated, these may result in ascending cholangitis with intrahepatic multifocal stricture formation. They are normally the result of ischemic duct harm from hepatic artery obstruction, and the status of the hepatic artery must be assessed in these patients. In some cases, the indwelling straight stents utilized in patients undergoing a Roux-en-Y choledochojejunostomy might trigger obstruction. These stents usually pass out of the anastomosis a quantity of weeks after transplantation, but in some situations they become encrusted and trigger obstruction. Biliary obstruction additionally happens on account of the presence of lots of inspissated bile or "biliary sludge. Histological examination of the fabric reveals a composition of sheets of necrotic collagen impregnated with bile pigments. This necrosis could also be the outcomes of ischemic harm throughout preservation of the donor liver, ischemia from hepatic artery obstruction following transplantation, superimposed an infection, rejection, or a combination of factors. It has also been attributed to alterations in bile composition similar to that caused by cyclosporine-induced crystal deposition. Typically, nonanastomotic biliary strictures contain both the proper and left hepatic ducts and a Roux-en-Y choledochojejunostomy. Cholangiogram carried out after placement of a transhepatic drainage catheter shows multiple filling defects (arrows) in the common bile duct and outlining of the left hepatic duct, which are in keeping with the presence of biliary sludge. By surgically changing the choledochocholedochostomy to a choledochojejunostomy, and thereby bypassing the sphincter of Oddi, medical and laboratory improvement normally could be achieved. When transhepatic cholangiography is used to decompress the obstructed biliary system, it is important to bear in mind that in instances of full obstruction it will not be possible to cross the obstruction initially. Standard remedy is preliminary decompression and placement of a temporary drainage catheter. A, Transhepatic cholangiogram in a 6-year-old liver transplant recipient shows biliary dilatation, with biliary strictures in the best and left biliary ducts and on the choledochojejunostomy. C, Cholangiogram after angioplasty exhibits residual stricture within the left duct, improved caliber in the proper ducts, and aid of the stricture on the choledochojejunostomy. Following dilation, an external biliary drainage catheter is left in place for roughly 2 weeks, after which cholangiography is carried out again. It is the follow at our establishment to not depart these tubes in place for long-term stenting because of the chance for infection. In a current collection of 48 sufferers Giampalma et al104 reported general 1- and 3-year main patency charges of 94% and 45% for nonischemic versus ischemic strictures, (P =. The overall secondary patency rates were 94% and 83% at 1 and 3 years with no vital distinction between the ischemic and nonischemic or between the anastomotic versus and nonanastomotic strictures. Balloon dilation (bilioplasty) is an efficient methodology of administration for these strictures. Patients with obstruction brought on by the presence of biliary sludge could be managed in a number of ways. In patients with an indwelling T tube, a guidewire may be passed by way of the T tube and the tip passed up into the biliary tree, the place it can be rotated in the occluded ducts to disrupt the material. To date there are only a few stories of the use of indwelling metallic stents within the management of biliary strictures in liver transplant recipients. In patients who fail to respond to bilioplasty, short-term metallic stents may be placed, however recurrence and stent migration are a problem. Biliary problems happen in each pediatric and adult liver transplant recipients. Although children, in contradistinction to adults, manifest early collateral arterial progress into the allograft liver, which can maintain viability of the liver, they proceed to be vulnerable to ischemic bile duct injury when hepatic artery occlusion happens. Pediatric complications are managed with the interventional strategies utilized in adults. These interventional techniques play a significant position within the upkeep of the allograft and avoidance of further surgical procedure. Although the interventional biliary procedures are essential aids to the upkeep of the allograft, problems could occur because of the intervention. Biliary interventions should be carried out under broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage. A critical complication in these immunosuppressed patients is the development of a biliary vascular communication secondary to placement of a transhepatic biliary drainage catheter. The hemobilia associated with tube placement is poorly tolerated by these sufferers, so persistent hemobilia by way of the drainage tube requires immediate correction. Cholangiography must be carried out to decide the location of vascular communication, which may be venous or arterial.
100 mg provigil cheap visa
Hypothermic machine preservation reduces molecular markers of ischemia/reperfusion damage in human liver transplantation insomnia 411 cheap 100 mg provigil fast delivery. Zero danger tolerance prices lives: loss of transplantable organs because of sleep aid doxylamine order provigil 200 mg with visa human immunodeficiency virus nucleic acid testing of potential donors. First report of the United Network for Organ Sharing Transplant Tumor Registry: donors with a historical past of cancer. Predicted lifetimes for grownup and pediatric cut up liver versus grownup whole liver transplant recipients. Domino liver transplantation: a sensible possibility in the face of the organ shortage. Organs from elderly donors now characterize the most important expanding element of the donor organ pool, and their use has had a major impact on the rate of liver transplantation. These research reveal good outcomes with livers from donors older than 60, 70, and even eighty years. Elderly donors have decreased physiological reserve and frequent comorbidities that may have an result on organ procurement. The presence of atherosclerotic disease, aneurysmal disease, and prior cardiothoracic or belly surgery might require modification of the methods usually used to procure the liver safely. Characteristic options of older liver allografts include smaller size, steatosis, capsular fibrosis, and arterial atherosclerosis. In addition, the higher incidence of undiagnosed malignancy in aged donors requires meticulous examination of the entire operative field to safeguard against the transmission of a previously unknown cancer. Allografts from elderly donors are extra susceptible to chilly ischemia time and might have elevated delayed graft function and extended cholestasis consistent with vital ischemia-reperfusion damage. Older liver allografts even have an elevated threat for hepatitis C virus recurrence and must be used with caution in patients with hepatitis Crelated liver illness. Data within the literature consistently reveal earlier hepatitis C recurrence, elevated graft failure, and decreased survival in hepatitis Cpositive recipients of allografts from donors older than 60 years. Use of allografts from aged donors must be limited to those with minimal steatosis. Attention to different donor risk factors, recipient components, and particularly chilly ischemia time is critical to ensure optimal outcomes after transplantation of older liver allografts. Early useful restoration and regenerative capability of liver allografts are significantly impaired when steatosis is current, doubtless due to more extreme ischemia-reperfusion damage. The prevalence of steatosis within developed international locations ranges between 10% and 30% of the population. In microvesicular steatosis, multiple small fats vacuoles occupy the cytoplasm of the hepatocyte. In macrovesicular steatosis, one large fat vacuole replaces many of the cytoplasm and displaces the nucleus of the hepatocyte. Macrovesicular steatosis may be subcategorized as delicate (<30%), reasonable (30% to 60%), and severe (>60%). Substantial data have correlated the extent of macrovesicular steatosis with the incidence of graft dysfunction. The incidence of delayed function approaches 35%, and first nonfunction is reported as excessive as 15% in grafts with reasonable macrosteatosis. Use of serologically optimistic allografts requires a frank dialogue with the recipient and informed consent before transplantation. Although the overall risk could be very low, transmissions of bacterial, fungal, viral, and parasitic infections via liver transplantation have been reported within the literature. Rare instances of aspergillosis, histoplasmosis, strongyloidiasis, and West Nile virus transmission have also been reported. Systemic bacterial or fungal an infection within the donor used to preclude organ use; however, massive collection have documented that, with appropriate antibiotic remedy, graft and affected person survivals are comparable to those of recipients of grafts from donors without infection. An unknown cause of demise in the donor should raise concern and preclude use of the liver without further investigation to exclude occult infection. There are a quantity of reviews in the literature of transmission of malignancy from the donor to the recipient with poor outcomes. Liver allografts from donors with low-grade central nervous system tumors or a distant history (>5 years) of treated low-grade malignancies. There is a potential benefit to using mammalian goal of rapamycin inhibitors in these sufferers due to the mixed antiproliferative and immunosuppressive effects. Infection in the donor could go undetected because multiple blood transfusions confound testing by serum dilution or as a outcome of the testing happened during the window period for the an infection. These dangers can be tough to quantify and should be individualized to the precise donor and recipient. Frank disclosure concerning the risks and voluntary consent from the recipient are obligatory before transplantation. In Maastricht category 2, arrest occurs unexpectedly, and resuscitation is unsuccessful. Maastricht category three is anticipated cardiac arrest after elimination of ventilator support, and Maastricht class four is unanticipated cardiac arrest in a brain-dead donor. After the household independently decides to withdraw life assist, the organ procurement organization can discuss donation and acquire consent. The procurement and cold preservation thus begins after a variable interval of heat ischemia. This warm ischemia time will increase the danger for delayed graft function, primary graft nonfunction, and long-term biliary issues from ischemic cholangiopathy. The incidence of biliary complications will increase significantly with warm ischemia occasions past half-hour. Hematomas and lacerations should be evaluated on a case-by-case foundation to determine the diploma of damage. In all cases of hepatic trauma, there should be adequate uncompromised hepatic parenchyma to get well and performance after reperfusion. The alternative for reuse arises when a former liver transplant recipient experiences brain dying with a functioning graft and thus turns into an organ donor himself or herself. Reuse of liver allografts can be divided temporally into instant reuse (within hours or days) and late reuse (within months or years). Immediate reuse can happen when a liver transplant recipient suffers mind demise during or shortly after liver transplantation. Most often choledochojejunostomy is required for protected biliary reconstruction of the reused liver allograft. Patients with major hyperoxaluria and acute intermittent porphyria have additionally undergone domino liver transplantation, though outcomes are much less encouraging due to early-onset renal failure in the former and neurotoxicity in the latter. Domino liver transplantation is technically difficult due to the difficulty reconstructing the venous outflow of the domino liver graft. Cava-sparing methods have emerged, as well as strategies using venous patches or interposition grafts.