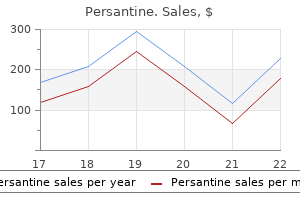
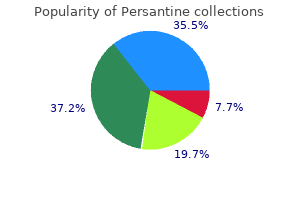
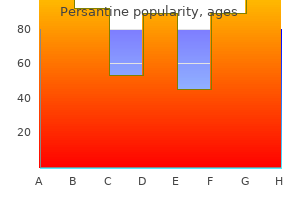
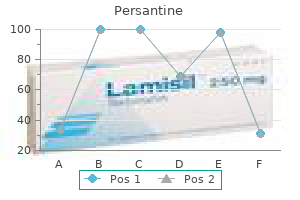
Persantine
Persantine dosages: 100 mg, 25 mg
Persantine packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 120 pills

100 mg persantine discount
This dose should be maintained for at least 2 weeks and subse quently decreased over the following 4�12 weeks symptoms internal bleeding generic 100mg persantine, in accordance with treatment uterine fibroids persantine 25 mg buy without prescription response, to a maintenance dose of 0. This should be guided by weekly, or at minimal fortnightly, labora tory monitoring. Once there was an initial biochemical response, azathioprine should be launched in a dose of 1 mg/kg day by day and if tolerated subse quently increased to 1. Monitoring 6thioguanine Where there has been complete response the options of reduction/discontinuation of therapy should be mentioned with the younger person and their household. This must be con sidered at a time of physiologic stability, spe cifically avoiding the rapid growth part of early adolescence. Many younger people could think about persevering with longterm lowdose monotherapy with azathioprine somewhat than danger relapse with the subsequent necessity for reintroduction of steroids. During relaxation/ withdrawal of therapy, frequent monitoring ought to be undertaken including liver bio chemistry and autoantibody ranges. They should be treated equally to initial presenta tion with adequate steroids to induce remis sion and subsequent gradual rest to upkeep therapy based on response. Secondline Options Firstline therapy fails or is associated with significant side effects in 10�15% of cases. The selection will usually depend on the experience and familiarity with these medicine of the treating doctor and household desire. Tacrolimus is a potent calcineurin inhib itor and is the default immunosuppressive agent following stable organ transplantation in childhood. It is usually commenced twice daily in a decrease dose than used in transplan tation and guided by therapeutic monitoring, aiming for trough ranges of approximately 5 ng/ml. For youngsters resistant or illiberal to sec ondline therapy, there are few confirmed options. There is anecdotal positive experi ence with rituximab, infliximab, and siroli mus. When embarking on such treatment, it should ideally be done as a part of a multidisci plinary group and following appropriate con sultation with regionally obtainable and recognized experience. The survival profit related to immunosuppression using prednisone with or with out azathioprine has been demonstrated in a number of randomized controlled trials with four to sevenfold reduction in mortality in treated sufferers, emphasizing the importance of well timed analysis and immediate institution of remedy [80]. Liverrelated morbidity and transplantation may be avoided with early efficient intervention and upkeep of remission, though in a minority of instances transplantation will be required [80,91]. Treatment failure is extra doubtless in extreme acute shows, particularly in subfulminant disease; prognosis is particu larly poor in this setting, with mortality ranging from 19 to 45% and requirement for liver transplantation in 9�81% [93]. The hepatic indications for transplantation are just like any persistent liver illness. For some younger individuals with Chapter 6 Autoimmune Hepatitis 117 autoimmune liver illness, myalgia and aner gia is a persistent and dominant symptom. The prognosis after liver transplantation is great, with the expectation of in extra of 90% highquality longterm survival. The absolute rate of recurrence following liver transplantation is excessive, with published rates starting from 30 to 80% with rising inci dence over time. Severe recurrent disease requiring retrans plantation is much less common, although a big burden at 15�25% total. Epidemiology and scientific characteristics of autoimmune hepatitis within the Netherlands. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis: present standing and future instructions. Type 1 and kind 2 autoimmune hepatitis in adults share the identical scientific phenotype. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Genomewide affiliation research identifies variants associated with autoimmune hepatitis type 1. Major antigen of liver kidney microsomal autoantibodies in idiopathic autoimmune hepatitis is cytochrome P450db1. Formiminotransferase cyclodeaminase is an organspecific autoantigen recognized by sera of sufferers with autoimmune hepatitis. Interleukin17 contributes to the pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis through inducing hepatic interleukin6 expression. Autoimmune hepatitis in Denmark: incidence, prevalence, prognosis, and causes of demise. Systematic evaluation with meta analysis: scientific manifestations and administration of autoimmune hepatitis in the elderly. Autoimmune hepatitis in African Americans: presenting features and response to therapy. The influence of race/ethnicity on the medical epidemiology of autoimmune hepatitis. Hispanics with major biliary cirrhosis are extra likely to have features of autoimmune hepatitis and reduced response to ursodeoxycholic acid than nonHispanics. Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis: patterns of clinical presentation and differential analysis of the "acute" sort. Clinical features in several age groups of fifty 51 fifty two 53 fifty four 55 56 57 fifty eight 59 patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Autoimmune hepatitis: effect of signs and cirrhosis on natural history and outcome. Clinical traits of fulminanttype autoimmune hepatitis: an evaluation of 11 circumstances. Impact of gender on the longterm consequence and survival of patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Type I autoimmune hepatitis: clinical course and outcome in an Italian multicentre examine. Cytochrome P4502D6(193�212): a new immunodominant epitope and goal of virus/self crossreactivity in liver kidney microsomal autoantibody sort 1positive liver illness. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictability of biopsy interpretations in chronic hepatitis. Fulminant hepatic failure because the preliminary presentation of acute autoimmune hepatitis. Performance parameters of the diagnostic scoring methods for autoimmune hepatitis. Validation of the simplified criteria for 71 seventy two seventy three seventy four seventy five 76 77 78 79 diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis in Chinese sufferers. Sustained remission after corticosteroid therapy for sort 1 autoimmune hepatitis: a retrospective evaluation. Predniso(lo)ne dosage and chance of remission in patients with autoimmune hepatitis.
100mg persantine order fast delivery
They have an extended delay between stimuli and responses than monosynaptic reflexes medicine for yeast infection cheap 25mg persantine mastercard. A motor neuron conducts efferent impulses from the combination heart to an effector organ useless id symptoms purchase persantine 100 mg mastercard, and an effector is outlined as a muscle fiber or gland cell that responds to these impulses by contracting or secreting. The most complex spinal reflexes are referred to as intersegmental reflex arcs, in which many segments work together and produce coordinated motor responses which are extraordinarily variable. A somatic reflex is one that prompts skeletal muscle, permitting for involuntary muscle control. Sensory receptors utilized in stretch reflexes are muscle spindles that each consist of bundled intrafusal muscle fibers. An autonomic reflex is one that activates visceral effectors similar to clean or cardiac muscle or glands. Short reflexes management simple motor responses with localized results corresponding to actions in a specific a half of a target organ. This affects principally heavily myelinated fibers, inflicting buzzing or tingling sensations, motor weakness, and reduced reflexes. Centrally positioned fascicles are most vulnerable to vascular problems corresponding to vasculitis or ischemia, which might trigger sharp pain or burning sensations or motor weak spot proportional to atrophy. Significant axon dysfunction is brought on by harm to the axon transport system, particularly the microtubules and microfilaments. Damage to the myelin sheath similar to by harm or Guillain-Barre syndrome may be repaired by surviving Schwann cells within 6�12 weeks. Regeneration is kind of unimaginable when the cell body dies and is unlikely when axons are totally lost. Spinal Reflexes the spinal twine controls some common somatic reflexes known as spinal reflexes, which often occur with out direct involvement of the higher centers of the mind. These reflexes should happen when the mind is destroyed however the spinal wire remains to be intact and functioning. The mind is conscious of most spinal reflexes and might modify them in most circumstances. For regular spinal reflexes, continuous facilitating signals from the mind should occur. Spinal shock happens when the spinal cord is transected, and consequently, all capabilities controlled by the spinal cord are depressed. These are distributed in segments down the posteromedial aspect of the developing embryo. The spinal nerves branch from the spinal wire in addition to the adjacent neural crest. The spinal nerves provide sensory and motor fibers to the creating muscle tissue, helping to guide their maturing course of. The cutaneous nerves are distributed to the pores and skin in a related sample, with the trigeminal nerves innervating many of the facial skin and scalp. Spinal nerves supply cutaneous branches to sure adjoining dermatomes, which finally turn into dermal segments. Summary 343 Distribution and progress of the spinal nerves is said to the segmented plan of the body. Limb progress and unequal growth of different areas of the physique develop an grownup pattern of dermatomes. Since embryonic muscle cells migrate to a big diploma, much of the early segmented pattern is misplaced. There is slower conduction of impulses, decreased sensation, slower reflexes, and often, clumsiness. The peripheral nerves themselves stay viable and retain regular perform throughout life. However, age-related functional changes are more noticeable when nerves are injured by situations similar to diabetes. Self-repair of axons is slower and incomplete in older people, making them more vulnerable to damage and disease. They embody chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, nociceptors, photoreceptors, and thermoreceptors. The common senses of contact, stress, temperature, and pain are unfold all through the body. Nonencapsulated (free) nerve endings include tactile (Merkel) discs and hair follicle receptors. Complex sense organs include the receptors for the particular senses, which embody hearing, vision, equilibrium, odor, and taste. The primary portions of the spinal nerves largely combine to form complicated networks called plexuses. A reflex arc is shaped by five parts: a receptor, a sensory neuron, an integration heart, a motor neuron, and an effector. Nerve conduction slows, and signs include buzzing or tingling sensations, motor weak point, and reduced reflexes. Conditions such as diabetes trigger age-related practical changes to be more noticeable. The forms of somatic and visceral sensory receptors embody chemoreceptors, which respond to chemicals in answer, including smelled or tasted molecules, adjustments in blood chemistry, and modifications in interstitial fluid chemistry; mechanoreceptors, which respond to mechanical forces corresponding to stress, contact, stretching, and vibrations; nociceptors, which reply to stimuli that could be damaging, leading to pain (stimuli embody extreme heat or cold, excessive stress, and inflammatory chemical substances; various subtypes of chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and thermoreceptors could also be stimulated by these stimuli); photoreceptors, which reply to mild such because the receptors in the retinas of the eyes; and thermoreceptors, which respond to temperature modifications. The somatosensory system is the part of the sensory system that serves the wall of the body and the limbs. It has three major levels of neural integration: the receptor level, which consists of sensory receptors; the circuit degree, in which 4. The five essential parts of a reflex arc are a receptor, a sensory neuron, an integration middle, a motor neuron, and an effector. Somatic reflexes activate skeletal muscle, whereas autonomic reflexes activate visceral effectors, which embrace smooth or cardiac muscle or glands. Spinal reflexes are somatic reflexes controlled by the spinal cord, typically without direct involvement of higher mind centers. Olfactory nerve fibers arise from olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium of the nasal cavity. Trigeminal fibers extend from the pons to the face via the superior orbital fissure, forming ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions. The maxillary division has sensory fibers that transmit impulses from the higher enamel, higher gum, upper lip, lining of the palate, and facial pores and skin. The mandibular division has sensory fibers that transmit impulses from the skin of the jaw, lower teeth, lower gum, and lower lip. This division also has motor fibers that transmit impulses to the chewing muscle tissue and people within the flooring of the mouth. Terminals of somatic motor fibers innervating voluntary muscular tissues kind advanced neuromuscular junctions with their effector cells.
Buy persantine 25 mg overnight delivery
Interconnected cavities often known as ventricles exist within the cerebral hemispheres and brain stem medicine man aurora 100mg persantine cheap with visa. The two massive lateral ventricles are located contained in the frontal symptoms 16 weeks pregnant persantine 100 mg generic otc, occipital, and temporal lobes. The fourth ventricle is within the brain stem and a slim cerebral aqueduct joins it to the third ventricle. All these grooves kind distinct patterns in normal brains, with the gyri and sulci being extra distinguished. The hypothalamus is the first visceral management middle of the physique and vital for homeostasis. Other regulatory functions of the hypothalamus have an result on body temperature, consumption of meals, water steadiness, thirst, and sleep�wake cycles. Afferent impulses reaching the thalamus are principally acknowledged as either pleasant or unpleasant. The thalamic nuclei also interpret instructions aiding in path of motor cortical exercise from the cerebellum and the basal nuclei. In the mind stem, the medulla oblongata incorporates a cardiovascular middle, which incorporates the cardiac middle and vasomotor middle and respiratory facilities that management respiratory rhythm, rate, and depth. Therefore, the cardiovascular and respiratory centers are in control of blood strain and respiration. The three layers of membranes within the meninges are the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. It has two layers of fibrous connective tissue (the periosteal and meningeal layers). The thin pia mater has many blood vessels and nerves that nourish the mind and spinal wire. It is carefully aligned with the surfaces of those organs and consists of many tiny blood vessels and delicate connective tissue. The spinal cord is a thin column of nerves leading from the mind to the vertebral canal. It starts on the level the place nervous tissue exits the cranial cavity near the foramen magnum and eventually tapers off to terminate close to the purpose where the first and second lumbar are situated. An epidural space exists between the dura mater and vertebrae, which is padded by fats and a vein community. The spinal wire terminates inferiorly in a tapered, cone-shaped construction known as the conus medullaris. A fibrous extension of the conus medullaris, called the filum terminale, extends inferiorly to the coccyx to anchor the spinal wire. In the neck, the spinal wire thickens to form the cervical enlargement, which provides nerves to the higher limbs (shoulder girdle and arms). The inside core of the spinal wire is made of grey matter surrounded by white matter. Major nerve pathways called nerve tracts are made up of lengthy bundles of myelinated nerve fibers. The motor neurons send their axons out to the skeletal muscles, which are their effector organs, through ventral rootlets. The dorsal roots are formed by afferent fibers, which carry impulses from peripheral sensory receptors. Associated sensory neuron cell bodies lie in an enlarged region of every dorsal root, which is named the dorsal root ganglion. The spinal wire conducts nerve impulses and spinal reflexes, so known as as a result of their reflex arcs pass through the spinal twine. Tracts carrying information to the brain are called ascending tracts, whereas these carrying info to the muscles and glands are known as descending tracts. The ascending tracts run up to the higher facilities for sensory enter and the descending tracts run down from the brain to the spinal cord or contained in the spinal wire to its lower ranges for motor output. The synaptic group of the brain adjustments because the variety of dendritic branches and other constructions decreases. When deposits and plaques exceed regular amounts brought on by aging, scientific abnormalities could happen. Continued learning throughout the life span happens as a result of remaining neurons can alter their synaptic connections. Aging does cause cognitive declines that will affect notion speed, spatial abilities, making selections, reacting to occurrences, and memory loss. Cognitive declines usually only turn out to be vital when an individual is in his or her 70s. The slender canal that connects the third ventricle with the fourth ventricle is the A. The mind is biochemically isolated from the general circulation by which of the next The respiratory rhythmicity facilities and the cardiovascular centers are located in the A. Which of the following is the middle of feelings, autonomic perform, and hormone manufacturing Midbrain Which of the following waves are produced in a person with a wholesome mind when he or she is awake and resting with the eyes closed Alpha Which of the following is a strand of fibrous tissue that gives longitudinal help as a part of the coccygeal ligament The cell bodies of the related sensory neurons are found in an enlarged area of the dorsal root known as the A. Sensory receptors are various however delicate to sure types of environmental modifications. The mind can then course of awareness of the stimulus (sensation) and interpret the that means of the stimulus (perception). Although not structurally totally different from one another, there are three to 4 extra chilly receptors to every warm receptor. Chemoreceptors: these respond to chemical compounds in answer, including smelled or tasted molecules, modifications in blood chemistry, and changes in interstitial fluid chemistry. Chemoreceptive neurons are also found within the carotid bodies within the neck and the aortic our bodies between the primary branches of the aortic arch. Mechanoreceptors: these reply to mechanical forces similar to stress, touch, stretching, and vibrations. Fine touch and strain receptors allow us to sense sources of stimulation that embody actual location, form, measurement, movement, and texture. Baroreceptors detect stress modifications in blood vessel partitions and in areas of the urinary, reproductive, and digestive tracts.
Persantine 25mg otc
Name the muscular tissues of the stomach wall and explain the motion of the rectus abdominis medicine 2015 song 100mg persantine cheap overnight delivery. Describe the quadriceps femoris group and the function of the muscular tissues it contains medications via g tube buy discount persantine 100 mg online. Overview Skeletal muscular tissues often perform in groups, with the nervous system stimulating the specified muscular tissues to carry out the meant function. A muscle that contracts to present most of a desired motion is known as a main mover or agonist. A good instance is the pectoralis major muscle, which is a prime mover of arm flexion. Other muscle tissue, often recognized as synergists, work with a prime mover to make its action simpler by adding a small quantity of further pressure. For example, if you bend your forearm, the agonist muscular tissues are the biceps and the synergists are the triceps. In muscles that cross a quantity of joints, contraction causes movement at all the spanned joints unless other muscular tissues act as stabilizers of the joints. Other flexors might trigger some undesirable movements in a joint, however synergists prevent this and permit the entire drive of the prime mover to occur in the desired instructions. Some synergists, generally recognized as fixators, may also assist an agonist by preventing another joint from transferring to stabilize the origin of the agonist. Fixator muscular tissues operating from the axial skeleton to the scapula trigger the scapula to be immobilized. Antagonists and their prime movers are situated on the alternative sides of joints throughout which they operate. An instance is the pectoralis main, which acts as an antagonist to the latissimus dorsi, the prime mover that extends the arm. It is essential to perceive that antagonists can actually even be prime movers similar to latissimus dorsi when it acts because the prime mover of arm extension. Origins and Insertions One finish of a skeletal muscle often is fastened to a comparatively immovable half (origin) at a movable joint. The different finish connects to a movable half (insertion) on the other side of the joint. There could also be multiple origin or insertion corresponding to in the biceps brachii muscle of the arm. Arrangement of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscular tissues, according to the arrangement of their fascicles, are divided into four distinct varieties: parallel muscle tissue, convergent muscles, pennate muscular tissues, and round muscles. The pennate muscular tissues are subdivided into unipennate, bipennate, and multipennate muscle tissue. Parallel Muscles Most skeletal muscle tissue are categorized as parallel muscle tissue, during which the fascicles are parallel to the long axes. Some are flat muscular bands with broad 242 Chapter 10 Muscular System Origin Tendon Gaster leg, which has its fascicles inserted into just one facet of the tendon. One example of a bipennate muscle is the rectus femoris in the thigh, which has fascicles inserted into the tendon from reverse sides. One multipennate muscle is the deltoid of the shoulder, which appears as many feather located facet by facet, with each of them inserted into one large tendon. Epimysium Circular Muscles In a circular muscle or sphincter, the fascicles are organized around a gap in a concentric sample. Muscle contractions cause a decrease in the diameter of the opening, such as the orbicularis oris muscle of the mouth or the orbicularis oculi muscle of the eye. Stationary bone Insertion Endostium Articulation Moving bones Arrangement of Fascicles the range of movement and energy of a muscle are based mostly on the arrangement of its fascicles. Skeletal muscle fibers can shorten to approximately 70% of their resting size once they contract. For instance, bipennate and multipennate muscles have more fibers and are very strong while only shortening slightly. An example of a flat parallel muscle is the sartorius muscle, located within the thigh. An example of a parallel muscle is the biceps brachii, which has a spindle form and an expanded body. Convergent Muscles In a convergent muscle, the muscle fascicles lengthen over a broad area, converging on a single attachment site. The muscle could pull on a tendon, aponeurosis, or a slender band of collagen fibers. An instance of a convergent muscle is the pectoralis major, which is triangular or fan-shaped. Classification of the Muscle Fibers There are seven ways by which skeletal muscular tissues are categorised: Pennate Muscles In a pennate muscle, the fascicles create a common angle with the tendon and muscle fibers pull at an angle. The fascicles and muscle fibers are quick and obliquely connected to the central tendon funning the complete length of the muscle. An example of a unipennate muscle is the extensor digitorum of the Location: Muscle names might indicate bones or body regions related to the muscles being categorized. For instance, the intercostal muscular tissues that run between the ribs (costals) and the temporalis muscle that overlies the temporal bone. For example, the best and left trapezius muscular tissues, which kind a trapezoid, and the deltoid muscle, Overview 243 which is mainly triangular (deltoid means "triangle"). Size: Muscle names may use phrases that imply lengthy (longus), brief (brevis), largest (maximus), or smallest (minimus). For example, the gluteus maximus and gluteus minimus, that are the large and small gluteus muscle tissue, respectively. Direction of fibers: Muscle names could additionally be associated to instructions in which their fibers and fascicles run in comparison with an imaginary line. The time period rectus refers to "straight," meaning that the fibers are parallel to an imaginary line (or axis). The term indirect refers to fibers that run obliquely to an axis, which means "neither parallel nor perpendicular. Number of origins: Muscles may have completely different quantities of heads hooked up to completely different origins. Location of attachments: Some muscle names are based mostly on factors of origin and insertion, with the origin all the time being named first. Actions: Muscles that are named for their actions might embody phrases corresponding to adductor, pronator, extensor, or flexor in their names. For example, the sartorius muscle is the longest muscle within the physique and becomes active when the legs are crossed. While not all muscle names are highly descriptive, a few of them are such because the extensor carpi radialis longus. It acts on the carpi or wrist joint and is located close to the radius bone of the forearm (radialis). They are large in diameter, containing giant reserves of glycogen, comparatively few mitochondria, and densely packed myofibrils. Muscles with fast fibers produce powerful contractions as a end result of the produced pressure is proportional to the number of myofibrils, but they fatigue quickly as a outcome of adenosine triphosphate is used in large quantities. Slow fibers are only about half the diameter of quick fibers, taking 3 times as lengthy to reach peak rigidity.
Cheap persantine 100 mg on-line
For instance moroccanoil treatment 25 mg persantine proven, immunotherapy used for the treatment of allergy with repeat antigen stimulation is associated with a decline in IgE ranges and an increase in IgG4 ranges and beekeepers repeatedly uncovered to bee venom develop elevated IgG4 responses medications bad for kidneys 25mg persantine free shipping. An IgG4 response may be generated in response to repeat exposure to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies such as adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. In general, IgG4 antibodies are thought-about to be "regulatory," limiting effector Bcell responses, both within the context of irritation and in addition in most cancers. Uniquely, IgG4 antibodies are able to trade half molecules resulting in bispecific antibodies which might be unable to cross hyperlink and due to this fact end result in the formation of small immune complexes. Because of these properties, IgG4 antibodies are unable to trigger immunologic effector capabilities and have a restricted role within the clearance of antigens and in inflammation and will actively inhibit IgG1 effector capabilities. All are ubiquitous proteins that vary in abundance in organs, and findings must be confirmed in further patient cohorts. IgG4 Antibodies and Pathogenesis There is a few proof to help the notion that IgG4positive B cells or antibodies are driving immune pathology and organ harm. B cells may be linked to pathogenesis since rituximab therapy leads to a decline in circulating IgG4positive plasmablasts in associated with disease decision. Although transfer of both purified IgG1 or IgG4 alone produced the illness phenotype, the transfer of both antibodies together led to decreased IgG1 deposition and reduce in histopathologic severity inside affected organs. No particular self or exogenous antigens have been systematically linked to the IgG4 response, though particular patient subsets could also be associated with immune responses to some self antigens. Hepatobiliary and pancreatic illness generally current with belly ache, weight reduction and jaundice, closely mimicking malignancy, while pancreatic disease may current with endocrine or exocrine insufficiency. Hepatobiliary illness may come up in the absence of any other organ involvement at presentation, though other organs could also be affected subsequently. Disease Outside the Hepatobiliary System IgG4related hepatobiliary illness is commonly present in association with further organ involvement. Renal illness is frequently detected on imaging in patients with other signs, and seems to current relatively occasionally in the absence of different organ involvement. Tubulointerstitial nephritis with plentiful IgG4 constructive plasma cells is the most common finding in biopsy (90%) with a minority having membranous nephropathy [18]. Head and neck disease regularly presents with swelling of mandibular and/or parotid salivary glands, while orbital illness presents with ache within the orbit or proptosis and mostly includes the lacrimal gland and soft tissue, although extraocular muscular tissues and palpebral and optic nerves may also be involved. Recent efforts using giant crosssectional international affected person cohorts (765 cases) have recognized 4 main affected person teams, together with pancreatic�hepatobiliary illness (31%), retroperitoneal fibrosis and/or aortitis (24%), head and necklimited disease (24%), and traditional Mikulicz syndrome with systemic involvement (22%). Interestingly, being Asian or female predisposed individuals to head and neck restricted disease [21]. These pointers each concentrate on a mixture of histopathologic findings, imaging, serum IgG4 levels, and response to remedy. No single criterion can be used to make the diagnosis and the diagnostic criteria have to Table 9. Even with these criteria, diagnosis is often complex and is finest confirmed in a multidisciplinary staff setting, with specialists familiar with the disease. Sjogren syndrome, major sclerosing cholangitis, Castleman illness, secondary retroperitoneal fibrosis, Wegener granulomatosis, sarcoidosis, Churg�Strauss syndrome) by additional histopathologic examination. Histologic Diagnosis of IgG4related Hepatobiliary Disease In general, malignancy is high on the record of differential diagnoses and should be actively excluded. Even then, the quantification of IgG4positive plasma cells will support the prognosis, but additional histologic options might be absent. In sufferers with advanced fibrotic illness, IgG4 optimistic plasma cells may be decreased in numbers although the IgG4/IgG1 ratio might stay elevated. In these cases, the prognosis will need to take into account the scientific options, imaging and ultimately response to remedy. IgG4related liver illness could present portal irritation, giant bile duct obstructive options, portal sclerosis, lobular hepatitis, and evidence of cholestasis. This has led investigators to seek more specific criteria that make the most of serum IgG4 antibody but in a ratio with IgG1, whereby an IgG1/IgG4 ratio above 0. Temporary biliary stenting may be required to relieve biliary obstruction; the stent must be removed once the disease has responded to therapy (typically in roughly 2 months) but might fall out spontaneously. Careful, prospective research of large cohorts will ultimately be wanted to resolve these prospects. Comprehensive crosssectional imaging alongside biopsy and histologic evaluation has a distinct function in both mapping concerned organs and for excluding malignancy and must be carried out each time possible at analysis. Treatment should therefore goal to stop organ damage, enhance organ operate, and relieve affected person symptoms. Optimal regimens for followup imaging will depend on the organs concerned at presentation. The beneficial starting dose is 30�40 mg every day for four weeks, aiming to reduce by 5 mg every 2 weeks, however titrated depending on response. Initial response rates to steroids could be very high (>90%) and typically response occurs within the first 4�6 weeks after beginning therapy [17]. Although as much as 66% obtain complete illness remission 12 months after beginning steroid therapy, illness relapse charges are high and occur in a minimum of 50% of patients, often shortly after steroid discontinuation. Relapse charges are prone to be even higher throughout longterm followup, however at present large prospective cohorts adopted over a long time submit remedy are missing. We have observational expertise of sufferers relapsing up to 8 years after discontinuation of remedy. There is currently significant regional variation about how and when to introduce steroidsparing brokers; the explanation for this is that the evidence base around optimal second line therapies assessed head to head and the longterm relapse charges and medical consequence related to these therapies is at present missing. Some investigators promote the introduction of steroidsparing agents at the start of main therapy, or introduce these as steroids taper in sufferers at excessive risk of relapse, analogous to the therapy for autoimmune liver disease. There are additionally some data to show that sustaining lowdose steroids long term will scale back the danger of relapse. However, maintaining corticosteroids long run clearly carries well being dangers, including the event of diabetes and bone loss. Chapter 9 IgG4-Related Liver and Biliary Disease 175 There is at present no proof comparing one secondline immunosuppressive agent with another in headtohead studies, however most physicians treating IgG4related hepatopancreatobiliary illness use azathioprine at a dose of 2 mg/kg every day. Other secondline brokers which were used embrace mycophenolate, mercaptopurine, methotrexate, tacrolimus, and cyclosphosphamide. Rituximab is generally administered by two intravenous infusions of 1000 mg, 2 weeks aside. In one singlecenter analysis of 60 patients treated with rituximab, 37% skilled relapses with a median time from the first infusion to relapse of 244 days. Baseline concentrations of serum IgG4, IgE and circulating eosinophils predicted disease relapses [36]. Additional potential research of patient followup are required to perceive the longterm relapse price, which is more probably to be larger. Rituximab maintenance therapy has been proven to scale back the chance of relapse (to 11%) but carries the danger of infectious problems.
Persantine 100mg purchase with amex
Past the eighth week symptoms pink eye cheap 100 mg persantine otc, only the villi that remain in touch with the endometrium endure medications given for adhd 100mg persantine with amex. A thin placental membrane separates embryonic blood contained in the capillary of a chorionic villus from the maternal blood in a lacuna. Using lively transport and pinocytosis, numerous substances also cross the placental membrane. The flat embryonic disc turns into cylindrical, with the pinnacle and jaws growing by the end of the fourth week. The heart is now beating, forcing blood via the blood vessels, and tiny buds kind, which is able to turn out to be the upper and lower limbs. The head grows quickly and turns into rounded and erect between the fifth and seventh weeks, with the facial features growing. Prenatal Development 701 Development of the Fetal Circulation Maternal blood provides oxygen and nutrients while carrying away wastes, diffusing these substances via the placental membrane. Before week three, areas seem within the splanchnic mesoderm that are soon lined by endothelial cells and covered with mesenchyme. They are linked together with rapidly growing vascular networks that will form the guts, blood vessels, and lymphatics. Just 3�4 days later, the center is already pumping blood, though the embryo is less than one-fourth inch in length. Fetal blood contains about 50% extra oxygencarrying hemoglobin than maternal blood. Nearly half the blood carried to the fetus through the umbilical vein passes into the liver, with the remaining entering the ductus venosus, which bypasses the liver. This vessel extends to be part of the inferior vena cava, where oxygenated blood from the placenta mixes with deoxygenated blood from the lower areas of the fetal body. Much of the blood coming into the fetal right atrium is moved immediately into the left atrium through a gap within the atrial septum called the foramen ovale. The rest of the proper atrium blood passes into the right ventricle and out via the pulmonary trunk. Most of the pulmonary trunk blood enters a fetal vessel referred to as the ductus arteriosus, connecting to the descending portion of the aortic arch. Blood low in oxygen is prevented from entering the portion of the aorta branching to the guts and mind. A mixture of extremely oxygenated blood entering the left atrium and a small amount of deoxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins strikes into the left ventricle and is pumped into the aorta; some attain the myocardium and a few attain the brain. Blood from the descending aorta moves to the lower areas of the physique, with the remainder passing into the umbilical arteries resulting in the placenta. At delivery, the fetal cardiovascular system must modify when the placenta stops functioning and the new child begins to breathe. Growth During the Fetal Period Teratogens are environmental elements that trigger congenital malformations by interfering with prenatal progress or development. Among the known teratogens are chemical agents, including medication such as thalidomide and alcohol; infectious brokers, particularly German measles; and ionizing radiation (x-rays). Growth occurs quickly during this period, with body proportions beginning to seem extra like these of a standard infant. By the 12th week, the exterior reproductive organs could also be distinguished as either male or feminine. The fetus grows quickly through the fourth month, reaching up to 20 cm in size because the limbs lengthen and the skeleton continues to ossify. Growth slows through the fifth month and the decrease limbs have reached their final relative proportions. The fetus begins to develop hair on its head, and the pores and skin of the body is covered in fine hair and a combination of dead epidermal cells and sebum from the sebaceous glands. During the sixth month, the fetus positive aspects substantial weight and the eyebrows and eyelashes grow. The pores and skin is wrinkled, translucent, and reddish in look because of the various blood vessels. In the seventh month, fat is deposited in subcutaneous tissues, smoothing the pores and skin. During the ultimate trimester, mind cells type networks, organs specialize and grow, and fat continues to develop beneath the pores and skin. The last systems to mature are the digestive and respiratory methods; hence, many infants have issue respiration and digesting milk from the mother. At the tip of the ninth month or, extra precisely, after 266 days, the fetus is considered full time period. The pores and skin has misplaced its fantastic hair but continues to be coated with sebum and useless epidermal cells. Nails have developed on the fingers and toes and the skull bones are largely ossified. Maternal blood volume, the glomerular filtration rate, and nutrient necessities additionally improve. Myron Pozniak, Department of Radiology, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health. It normally happens through the third trimester, but may occur anytime after 20 weeks of gestation. Preeclampsia happens in 7% of pregnancies within the United States, with unknown causes. Risk factors embrace girls with a number of fetuses, age over 35, and history of hypertension or vascular ailments, diabetes, or lupus. It may be linked to hypertension, preeclampsia, trauma, using cocaine, infection, and multiple fetuses. Placenta previa is a condition of pregnancy by which the placenta is implanted abnormally in the uterus and covers the uterine cervix. It is the most typical cause of painless bleeding in the third trimester of being pregnant. Before hemorrhage, placenta previa may be diagnosed by ultrasonography and handled with complete mattress rest underneath shut statement. Parturition (Birth) Pregnancy ends with the birth course of, which begins hours or days before birth. A prostaglandin is synthesized that promotes these contractions as the cervix thins and opens. Nerve impulses are initiated to the hypothalamus, signaling oxytocin to be released from the posterior pituitary gland. This hormone stimulates powerful uterine contractions, aiding in the later stages of labor. Abdominal wall muscles contract, serving to to drive the fetus by way of the cervix and vagina. The fetus begins to transfer toward the cervical canal because of gravity and uterine contractions. Though the dilation stage could be of variable size, mostly it lasts for eight or more hours.
Diseases
- Antisocial personality disorder
- Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
- Lethal chondrodysplasia Moerman type
- Chromosome 7, monosomy 7q2
- Ichthyosis follicularis atrichia photophobia syndrome
- Pyropoikilocytosis
Persantine 25 mg buy free shipping
The cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum contain the nuclei of grey matter surrounded by white matter and an outer gray matter cortex medications quizzes for nurses buy persantine 25 mg without a prescription. Each cerebral hemisphere consists of the cerebral cortex nioxin scalp treatment persantine 100mg buy generic line, cerebral white matter, and basal nuclei (ganglia). The cerebral hemispheres every receive sensations from and dispatch motor impulses to the alternative aspect of the body. The cerebellum also has two hemispheres and interprets impulses from the motor cortex and sensory pathways. The limbic system is the emotional�visceral a half of the brain, and also performs a job in reminiscence. Sleep is a state of partial consciousness from which an individual can be aroused by stimuli. In most people, the left brain hemisphere controls language, whereas the best brain hemisphere controls the emotional content material of language. The meninges embrace the dura, arachnoid, and pia mater, which enclose the mind, spinal wire, and related blood vessels. The blood�brain barrier blocks certain molecules from coming into the mind, maintaining a wanted stability to the brain surroundings. The spinal twine is a two-way impulse conduction pathway and reflex middle inside the vertebral column. The central grey matter of the spinal cord is H-shaped, and both sides of its white matter has dorsal, lateral, and ventral columns known as funiculi, each containing ascending and descending tracts. The grownup brain is split into the cerebrum, diencephalon, mind stem, and cerebellum. Several sulci divide each hemisphere into the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes, in addition to the insula, which is buried deep within the lateral sulcus. The three basic regions of every cerebral hemisphere embrace the cerebral cortex, white matter, and basal nuclei. The cerebral cortex is a skinny layer of grey matter comprising the outer portion of the cerebrum and is the center of the conscious mind. The diencephalon is mostly made up of the paired gray matter buildings generally identified as the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus. The most superior area of the brain stem is the midbrain with descending areas, together with the pons and medulla oblongata. The mind stem is organized equally to the spinal wire, with deep grey matter surrounded by white matter fiber tracts. The brain stem also has nuclei of gray matter that are embedded in its white matter; this differs from the group of the spinal wire. The cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain and seems similar to the shape of a cauliflower. The cerebellum process inputs from the cerebral motor cortex, mind stem, and sensory receptors. Proprioceptors sense positions of skeletal muscles and joints and rigidity in the ligaments and tendons. Nociceptors: these respond to stimuli which may be damaging, similar to extreme heat or chilly, extreme pressure, and inflammatory chemical compounds, leading to ache. Various subtypes of chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and thermoreceptors could additionally be stimulated by these stimuli. Nociceptors are frequent within the superficial pores and skin, round blood vessel walls, inside joint capsules, and within the periostea of bones. Painful sensations are carried on two forms of fibers called kind A and kind C fibers. The myelinated sort A fibers carry fast pain sensations, such as from a vaccination or a deep reduce. The type C fibers carry gradual pain, which is described as ache that feels aching or burning. Photoreceptors: these receptors respond to light, for instance, the receptors within the retinas of the eyes. Thermoreceptors: these reply to temperature changes and are free nerve endings in the dermis, liver, skeletal muscles, and hypothalamus. Classification by Receptor Structure Most sensory receptors of the overall senses are actually modified dendritic endings. For instance, the eyes comprise sensory neurons and non-neural cells that make up their lenses, supporting walls, and associated buildings. Top picture: � Biophoto Associates/Science Source; Bottom photograph: � Donna Beer Stolz, PhD, Center for Biologic Imaging, University of Pittsburgh Medical School. They are also called the somatic senses and involve comparatively easy receptors. General sensory receptors are nerve endings of two sorts: nonencapsulated (free) or encapsulated. Free nerve endings could extend between epithelial cells and management the feeling of itching. The itch receptor of the dermis has a particularly thin diameter, and was not discovered until long after different types of receptors had been recognized. The nerve endings related to itching are activated by many various chemicals, however largely histamine, which is present in areas of inflammation. Other kinds of nonencapsulated nerve endings embrace: NonEncapsulated (Free) Nerve Endings Nonencapsulated (free) nerve endings of the sensory neurons are very common in epithelia and connective tissues. Their distal endings referred to as sensory terminals usually have small, knob-like swellings. They largely reply to temperature and painful stimuli in the pores and skin and inner tissues, apart from the brain. Pain receptors are stimulated by tissue damage but adapt to enhancing situations poorly. Pain is triggered by releases of certain chemical substances and deficiency of oxygen-rich blood (a condition often known as ischemia) or the stimulation of sure mechanoreceptors. Cold receptors are most sensitive to temperatures between 50�F (10�C) and 68�F (20�C) to produce a freezing sensation. These receptors work quickly, and sensation begins to fade away after roughly one minute of steady stimulation. Warm receptors are most sensitive to temperatures above 77�F (25�C), becoming unresponsive to temperatures above 113�F (45�C). At this temperature, ache receptors are stimulated to produce a burning sensation. Any temperatures outside the range of thermoreceptors activate the nociceptors and is perceived as painful. The nociceptors additionally respond to chemical substances which are released from damaged tissues and to pinching of the skin. A plasma membrane protein called the vanilloid receptor is essential in the detection of painful stimuli. It is opened by heat, low pH, and chemical substances similar to capsaicin, which is present in hot peppers. They are fashioned by sure free nerve endings related to enlarged tactile or Merkel cells.

Purchase persantine 100 mg on-line
Semicircular canals: the tubular inside ear constructions housing receptors that present the sense of dynamic equilibrium medicine 94 100 mg persantine cheap visa. Semicircular duct: the tubular parts of the membranous labyrinth of the interior ear; it responds to rotational actions of the top medications to treat anxiety generic persantine 100mg visa. Semilunar valves: the three-cusped valves guarding the exits type the cardiac ventricles; the pulmonary and aortic valves. Seminal vesicles: Sac-like buildings that connect to the ductus deferens close to the base of the urinary bladder; they secrete an alkaline fluid that regulates pH. Seminiferous tubules: Highly coiled constructions inside each lobule of a testis; they form a community of channels, then ducts, which join the epididymis. Semipermeable: Pertaining to the property of a membrane that permits water or solvents to cross through freely but restricts or prevents passage of supplies dissolved within the fluid. Sense organs: Complex organs that comprise the receptors for the particular senses, including hearing, imaginative and prescient, equilibrium, smell, and taste. Sensible water loss: A measurable quantity of fluid lost every day by way of the urine. Sensory input: the information gathered by the nervous system through the sensory receptors. Septum: A strong, wall-like construction that separates the left atrium and ventricle from the proper atrium and ventricle. Serous pericardium: the inside, serous portion of the pericardium, with two layers (visceral and parietal); the area between the layers is the pericardial cavity. Sertoli cells: the supporting cells of the seminiferous tubules of the testis; liable for the differentiation of spermatids and the secretion of inhibin. Serum: the clear, yellowish liquid that is still after clot formation; serum is plasma minus its clotting elements. Sesamoid bones: Those enclosed in a tendon in addition to fascial tissue, located near joints (articulations). Sex hormones: Steroid hormones corresponding to estrogens or testosterone produced by the ovaries, testes, or adrenal cortex, affecting progress or function of reproductive organs or improvement of secondary sex traits. Small cardiac vein: An inconstant vessel, accompanying the right coronary artery in the coronary sulcus, from the right margin of the right ventricle; emptying into the coronary sinus or center cardiac vein. Small cell carcinoma: A extremely malignant type of cancer, composed of small, round or egg-shaped cells with little cytoplasm; corresponding to seen in lung cancer. Smooth muscle tissue: Unstriated, involuntary muscle tissue with a "spindle"-shaped appearance; it composes hollow inner organ walls. Soft palate: the fleshy posterior extension of the hard palate, separating the nasopharynx from the oral cavity. Solute pumps: Active transporters, which transfer ions and different solutes towards the focus gradient, requiring vitality. Solutions: Homogeneous mixtures of components, which means the combination has exactly the identical composition all through; options may be gases, liquids, or solids. Solvent: the substance present in the best amount in a combination, usually a liquid. Soma: the cell body of the neuron, consisting of a spherical nucleus with a conspicuous nucleolus surrounded by cytoplasm. Somatosensory association cortex: the cortex that mostly features to combine temperature, stress, and associated data; situated just posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex. Somatosensory system: the realm of the sensory system that serves the limbs and physique wall; it receives inputs from exteroceptors, interoceptors, and proprioceptors. Somatostatin: A hormone produced within the hypothalamus that inhibits the release of somatotropin (growth hormone) form the anterior pituitary gland. It can be produced in other elements of the body, and inhibits the release of sure other hormones, including thyrotropin, adrenocorticotropic hormone, glucagon, insulin, and cholecystokinin. Shoulder separation: An harm involving partial or complete dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint. Sickle-cell anemia: A dysfunction of incomplete dominance, in which the erythrocytes assume a sickle shape, lowering blood oxygen levels. Excessive exercise or respiratory problems could cause sickle-cell disaster, blocking small capillaries and causing intense ache. Sickle-cell disaster: A scenario brought on by sickle-cell anemia; anything that lowers blood oxygen ranges, such as extreme exercise or respiratory problems, could cause the deformed erythrocytes to clump and fragment in small capillaries, resulting in intense pain. Sickle-cell trait: the trait, in individuals heterozygous for the sickling gene (Ss), of getting each normal and sickling hemoglobin. These individuals are wholesome, however can endure a disaster if blood oxygen ranges are reduced for a very long time. Sigmoid sinuses: Venous sinuses of the dura mater, steady with the straight sinus, draining into the interior jugular veins. Simple columnar epithelium: Single-layer tissue found in feminine reproductive tubes, the uterus, and most digestive tract organs; involved in secretion and absorption. Simple cuboidal epithelium: Single-layer tissue covering the ovaries and lining kidney tubules and glandular ducts; involved in secretion and absorption. Simple squamous epithelium: Single-layer tissue lining the alveoli, capillary walls, blood and lymph vessels, and physique cavities. Sinoatrial node (S-A node): A small mass of specialised tissue just beneath the epicardium in the right atrium that initiates impulses via the myocardium to stimulate contraction of cardiac muscle fibers. Skeletal muscle tissue: Voluntary muscle tissue hooked up to bones and composed of lengthy thread-like cells which have mild and darkish striations. Sliding filament mannequin: A methodology of action of muscle contraction involving how sarcomeres shorten, with thick and skinny filaments sliding past one another toward the middle of the sarcomere from both ends. Slow ache: An disagreeable sensory expertise that ravels a multisynaptic path to the mind, via slow-conducting, unmyelinated nerve fibers. Somites: Mesodermal segments of the physique of an embryo that contribute to the formation of skeletal muscles, vertebrae, and the dermis of the pores and skin. Spatial summation: the sort of summation that entails simultaneous stimuli utilized at completely different areas, cumulatively affecting the transmembrane potential. Species resistance: An innate (nonspecific) defense wherein one species is proof against certain illnesses that may have an result on other species. Spectrin: A contractile protein hooked up to glycophorin on the cytoplasmic floor of the cell membrane of erythrocytes; essential in maintenance of cell shape. Spermatids: Formed when spermatocytes divide, they comprise 23 chromosomes, and eventually mature to turn out to be sperm. Spermatocytes: Formed when spermatogonia divide, they contain forty six chromosomes but divide into major spermatocytes with 23 chromosomes, and spermatids with 23 chromosomes. Spermatogenic cells: Those that form sperm cells and line the seminiferous tubules. Spermatogonia: Undifferentiated spermatogenic cells in a male embryo; the singular form of spermatogonia is spermatogonium.
Persantine 25 mg discount on line
Some effector T cells launch chemical compounds that activate macrophages medicine grinder 100mg persantine with visa, which are killer cells that both secrete bactericidal chemical compounds and actively phagocytize invaders medicine to treat uti persantine 25mg purchase fast delivery. Many lymphocytes slip via the postcapillary venule walls of this network and occupy its areas for a short period of time. Lymphocytes can attain websites of damage or infection quickly due to their regular cycling between lymphoid tissues, circulatory vessels, and free connective physique tissues. You ought to keep in thoughts that the first lymphoid organs are solely the thymus and bone marrow. The mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue protects the epithelia of the respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems. Lymphoid Tissues and Lymphoid Organs In the immune system, lymphoid tissue is essential for 2 major causes. It incorporates lymphocytes and provides a place for them to proliferate, and it gives lymphocytes and macrophages glorious areas to conduct their surveillance of varied particles. In common, lymph nodes are hidden inside connective tissue buildings referred to as capsules. Large clusters are found near the floor of the physique within the axillary, cervical, and inguinal regions. The follicles contact the deeper cortex or paracortical area, which largely contains transitional T cells. These T cells circulate between the blood, lymph, and lymph nodes, frequently monitoring particles. The medulla of every lymph node incorporates plasma cells and B cells organized into long medullary cords. Both types of lymphocytes that exist are contained within the medullary cords, which are inward extension from the cortical lymphoid tissue. Many macrophages on the reticular fibers phagocytize international matter in lymph that flows through the sinuses. Lymph sinuses are areas inside a node that comprise complex channels via which lymph moves. There are more macrophages within the lymph sinuses than in another parts of a node. Macrophages engulf and destroy mobile debris, damaged cells, and foreign substances. Abnormal proliferation of lymphoid cells usually alters regular immune system capabilities. This may end in either impairment of immune defenses with elevated susceptibility to an infection, or abnormal immune responses as a half of various autoimmune illnesses. Hodgkin lymphoma often occurs in young adults, while non-Hodgkin lymphoma often impacts people who find themselves much older. It typically begins in a single lymph node, or a small group of lymph nodes, spreading to adjoining nodes, and finally, to different elements of the physique. Organization of the Lymphatic System 515 Lymph Node Circulation A number of afferent lymphatic vessels conducts lymph via the convex side of each lymph node. The lymph moves by way of a big subcapsular sinus into many smaller sinuses crossing the cortex and entering the medullary sinuses. It finally leaves the lymph node at its hilum though efferent lymphatic vessels. There are extra afferent vessels supplying the lymph node than efferent vessels draining it. During this slowed movement, macrophages and lymphocytes can "look at" the lymph more intently. When this occurs, the lymph node turns into swollen, infected, and tender to the contact. However, lymph nodes infiltrated by most cancers cells are normally not painful and only feel swollen. This helps in the identification of cancerous lymph nodes rather than infected ones. Describe the overall measurement of the lymph nodes and their main places in the body. Explain lymphoid follicles and the lymphocytes that dominate in their germinal facilities. Thymus the thymus is situated in the thorax, anterior to the aorta and posterior to the upper sternum. Although comparatively massive in infancy and early childhood, the thymus shrinks after puberty, changing into a lot smaller in adults. Its lymphatic tissue is changed during the later years of life by adipose and connective tissues. It continues to produce immunocompetent cells all through life, however this production declines with getting older. The thymus is divided into lobules by inwardextending connective tissues or septa. The lobules contain massive amounts of lymphocytes, including primarily inactive thymocytes. Some thymocytes mature into T lymphocytes, which depart the thymus after three weeks and supply immunity in the body. In the cortex of the thymus, lymphocytes are densely packed throughout their speedy division. These cells create the chemical and bodily environment needed for T-lymphocyte maturation. It additionally causes cardiac abnormalities, and other defects, corresponding to abnormal facial development and very extensively spaced eyes. Spleen the spleen is located in the upper left belly cavity, inferior to the diaphragm and posterior and lateral to the stomach. It differs from lymph nodes in that its venous sinuses are full of blood, not lymph. White pulp is positioned all through the spleen in small "islands," made up of splenic nodules containing many proliferating lymphocytes. Immune operate occurs within the white pulp, which is primarily made up of lymphocytes suspended on reticular fibers. Clusters of white pulp form around central arteries, which are the small splenic artery branches, making them appear as "islands" within the purple pulp. The names "white pulp" and "red pulp" mirror their look in fresh spleen tissue, not how they stain to be microscopically examined. The trabecular arteries branch extensively, and white pulp surrounds their finer branches.
Buy persantine 25 mg on line
Their axons leave the spinal twine with the ventral root alongside these from the somatic motor neurons denivit intensive treatment safe 100mg persantine. Associated sensory neuron cell our bodies lie in an enlarged region of each dorsal root treatment works persantine 25mg on line, which is identified as the dorsal root ganglion (spinal ganglion). The white matter of the spinal twine is made up of myelinated and nonmyelinated nerve fibers. These enable communication between sections of the spinal twine and between the spinal cord and mind. The tracts that carry info to the brain are known as ascending tracts and the tracts that carry information to the muscles and glands are referred to as descending tracts. The ascending tracts run up to higher centers for sensory enter and the descending tracts run down from the mind to the spinal wire or contained in the spinal cord to its lower ranges for motor output. The transverse tracts run across the spinal twine from one side to the other with commissural fibers. There are three white matter columns called funiculi on both sides of the spinal cord. They are named by their positions as the dorsal (posterior) funiculi, the lateral funiculi, and the ventral (anterior) funiculi. Each spinal tract accommodates several fiber tracts made up of axons which have related features and locations. The anterior white columns are interconnected by the anterior white commissure, which is where axons cross from both facet of the spinal cord. The lateral white column is made up by the white matter between the anterior and posterior columns on each side. They travel inferiorly by way of the vertebral canal for a protracted distance, lastly reaching their intervertebral foramina. Spinal Neuronal Pathways the primary spinal tracts or fasciculi make up multineuron pathways and connect the mind to the rest of the body. Spinal neuronal pathways are signified by decussation, relay, somatotopy, and symmetry. Most additionally encompass a chain of a quantity of neurons contributing to successive pathway tracts in the relay of data. Ascending sensory tracts, for instance, fibers that transmit inputs from sensory receptors in superior areas of the physique, lie lateral to others that convey sensory info from inferior body regions. Third-order neurons: these have cell bodies in the thalamus and send impulses to the cerebrum. There are three main types of ascending pathways on both sides of the spinal cord: the dorsal column-medial lemniscal pathways, spinothalamic pathways, and spinocerebellar pathways. The dorsal column-medial lemniscal pathways mediate exact transmission of inputs of sure sensory receptors such as for discriminative touch and vibrations. The spinothalamic pathways receive signals from many sensory receptor sorts, making multiple synapses within the brain stem. The spinothalamic pathways transmit temperature, touch, ache, and strain impulses. The spinocerebellar pathways transmit information about tendon or muscle stretching to the cerebellum so it could possibly coordinate the activities of the skeletal muscular tissues. Descending Pathways and Tracts the descending pathways transmit impulses from the mind to the spinal wire, by way of direct and indirect pathways. Upper motor neurons: these are pyramidal cells of the motor cortex as properly as neurons of the subcortical motor nuclei. Lower motor neurons: these are from the ventral horn and directly innervate skeletal muscular tissues. Direct (pyramidal) pathways originate primarily with the pyramidal neurons in the precentral gyri and ship impulses through the mind stem through massive pyramidal (corticospinal) tracts. Posterior and anterior spinocerebellar tracts Posterior funiculi Lateral and anterior funiculi Lateral funiculi Conduct sensory impulses linked to senses of touch, stress, and body movement from pores and skin, muscle tissue, tendons, and joints to the brain Conduct sensory impulses linked to senses of pain, temperature, contact, and pressure from various physique areas to the brain Conduct sensory impulses needed for coordination of muscle movements from the muscular tissues of the decrease limbs and trunk to the cerebellum Locations Functions Descending Nerve Tracts 1. Rubrospinal tracts Lateral and anterior funiculi Lateral and anterior funiculi Lateral funiculi Conduct motor impulses linked to voluntary movements from the mind to skeletal muscle tissue Conduct motor impulses linked to maintenance of muscle tone, plus exercise of sweat glands from the mind Conduct motor impulses linked to muscular coordination from the brain stem motor nuclei. Indirect pathways are most concerned in sustaining balance and posture (via the axial muscles), coarse limb movements, and the following of objects in the visible field with the head, neck, and eyes. The vestibulospinal tract and reticulospinal tract use various postural muscle tone to maintain steadiness. Flexor muscles are managed by the rubospinal tracts, whereas the superior colliculi and tectospinal tracts management head actions in relation to visible stimuli. This section focuses on mind trauma, cerebrovascular accidents, degenerative mind problems, spinal twine trauma, poliomyelitis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Trauma One of the main causes of unintended death in the United States is head injury that results in mind trauma. In a car accident, for example, the mind is broken by local injury at the site of the blow (the coup injury) and the reverse effect because the brain contacts the alternative end of the cranium (the contrecoup injury). An alteration in brain operate after a blow to the head, which is often short-term, known as a concussion. This is recognized as a contusion, which might range from the affected person remaining conscious to varying lengths of lack of consciousness. The patient is usually lucid at first after the trauma, however then develops neurological deterioration as a outcome of the hemorrhage. Treatment of intracranial hemorrhage is by way of surgical procedure to remove the localized hematoma (blood mass) and restore vessel ruptures. Traumatic head harm can also cause swelling of the mind, referred to as cerebral edema, which can worsen a mind damage and even be fatal itself. Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke) the most common nervous dysfunction is a cerebrovascular accident, which is also called a stroke or a mind attack. Deprivation of blood to a body tissue, referred to as ischemia, impairs supply of oxygen and nutrients. Usually, the survivor of a cerebrovascular accident is paralyzed on one facet of the body (hemiplegia). The most important element of a cerebrovascular accident is its long-term impact that always results in the dying of brain neurons. Neurons that are utterly deprived of oxygen disintegrate relatively rapidly, releasing an overabundance of glutamate (an excitatory neurotransmitter). In strokes, glutamate acts as an excitotoxin, which overexcites the surrounding cells till they die. High ranges of calcium ions injury mitochondria of brain cells and initiate specific protein synthesis to cause cell demise via free radicals and inflammatory agents. Stroke remedies embody plasminogen activator to dissolve blood clots and robotic surgery. Temporary episodes of reversible cerebral ischemia are often recognized as transient ischemic attacks.