Nexium
Nexium dosages: 40 mg, 20 mg
Nexium packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Generic 40 mg nexium overnight delivery
Tracheal buttons have a hole outer cannula and a stable inner cannula and prolong from the outer pores and skin into the tracheal lumen gastritis with erosion cheap nexium 40 mg mastercard. If the tube is already out gastritis symptoms chronic nexium 20 mg amex, and the specifics of the tract are unknown, extending the neck to align the stoma with the tissue tract is the first greatest position for tube replacement. Pass a pink rubber catheter (or different information catheter) into the proximal finish of the trachea. Remove the tracheostomy tube over the catheter, with only the catheter left within the trachea. This adjunct delivers intratracheal oxygen and is helpful if hypoxemia is likely to occur. Traditionally, the affected person is ventilated and correct tube placement confirmed by statement of equal chest rise and auscultation of bilateral breath sounds. Multiple research have shown quantitative capnography to be a extremely sensitive software for confirming correct placement of airway gadgets. The obstructing object may act as a ball valve and allow air to enter but restricts expiration. Place the patient on a cardiorespiratory monitor, a pulse oximeter, and continuous capnography. Be sure to have a large-bore suction catheter obtainable in case the suitable size of catheter is inadequate. Examine the tracheostomy tube to see whether or not the inner cannula is obstructed or any obvious exterior obstruction is current. Interventions Administer high-flow oxygen and encourage patients who can breathe spontaneously to cough. Thick secretions can be loosened in a critically sick patient by instilling regular saline into the tracheostomy tube, but this is not recommended for routine suctioning. First, deflate the tracheostomy cuff and provide high-flow oxygen by way of face masks if the patient is breathing spontaneously or by way of a bag-valve-mask device if the patient is unable to breathe with out assistance. This section addresses the emergency growth of late postoperative problems (occurring greater than three weeks after the operation). Management of the affected person varies relying on the type of complication that the affected person is experiencing. Rapid recognition of the problem is paramount and might drastically affect the end result. If these maneuvers are ineffective, consider more distal causes of airway obstruction, such as granulation tissue, a mass, or a clot. Dislodgement Displacement of the tracheal tube is a serious complication that may have a disastrous consequence if not acknowledged and corrected rapidly. Signs and symptoms include hypoxemia, agitation, respiratory misery, altered mental status, subcutaneous emphysema, and high airway pressure. Dislodgement can occur during affected person transfers, when traction is placed on the tube, or when the tube is manipulated for bag-valve-mask air flow or ventilator tube connection. If a tracheostomy tube is simply too long, it could turn into dislodged inferiorly, which causes the tip to either abut the mucosal wall of the trachea, or hinder it at the degree of the carina. It is necessary to know when and why the tracheostomy was positioned as a end result of such info will affect analysis and management of the patient. Blind, forceful makes an attempt at reinsertion of the tracheostomy tube in the early postoperative interval can result in the creation of a false passage and possible respiratory arrest. Preparation As for all patients with tracheostomy problems, begin with a fast major assessment and place the patient on acceptable monitoring gadgets. Continuous waveform capnography may be invaluable in determining whether or not the tracheostomy tube is placed properly. Position the patient with the neck in extension to maximize alignment of the stoma and trachea. Replacement beneath emergency circumstances may be difficult, particularly if the event occurs quickly after the tube is initially placed and earlier than a tract has fashioned (usually approximately 5 days after the procedure). Blind forceful makes an attempt at reinsertion in this circumstance could be related to the creation of a false passage and respiratory arrest. Orotracheal intubation is an alternative choice for accidental decannulation occurring before tract formation. In patients with surgical tracheostomies, traction on keep sutures positioned circumferentially around the tracheal rings (which are typically cut lengthy and sometimes taped to the anterior chest wall-not shown here) will facilitate reintubation. If the tracheostomy tube appears to be minimally displaced, attempt to reposition the tube by mild manipulation. If the tracheostomy tube is totally dislodged or no waveform is current on capnography, tube replacement ought to be tried. If the tracheostomy stoma was created less than 7 days earlier, be ready to orally intubate the patient. Stay sutures could additionally be placed to hold the stoma open and better visualize the tracheal opening. If the affected person is secure, attempt to reinsert the tracheostomy tube with the help of a gum elastic bougie or fiberoptic scope. If the tracheostomy stoma was created 7 to 30 days earlier, remove the tube and another reason for obstruction from the stoma. If the patient can ventilate independently, permit the patient to oxygenate after which reinsert the tube when prepared. If the affected person is unstable, occlude the stoma with moist gauze or other occlusive system and supply bag-valve-mask air flow. If the tracheostomy is more than 30 days old, the tube may not must be replaced. If the patient is steady and ventilating spontaneously with none indicators of distress, contact the appropriate specialty care doctor to discuss the necessity for emergency reinsertion. Once the tube is reinserted, affirm correct placement with auscultation and waveform capnography. Tube place can also be confirmed by direct visualization with a fiberoptic scope. Obese sufferers are at high threat for false passage because of their redundant neck tissue (see part on Special Populations). Subcutaneous air, crepitus, or distortion of anterior neck landmarks might indicate placement of the tracheostomy tube into a false passage. Absence of a waveform on capnography confirms misplacement of the tracheostomy tube. If a false passage is suspected, take away and replace the tracheostomy tube expeditiously. Patients might have acute respiratory complaints similar to cough, dyspnea, choking, or wheezing. Prolonged retention of a foreign body may end up in persistent respiratory signs such as wheezing, coughing, or recurrent bouts of pneumonia or bronchiectasis. To handle this problem, substitute the tube if attainable and think about bronchoscopy for retrieval of the tube fragment.
Syndromes
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Ulcerative colitis
- Heart damage
- Hold the view they are not good socially, not as good as other people, or unappealing
- Salivary gland infections
- Injury or trauma that damages the muscles
- Avoid letting your child sleep during takeoff or landing. Children swallow more often when they are awake. Also, waking up with ear pain can be frightening for the child.
- Breathing assistance, if needed
- Delirium
- Breathing tube
Discount nexium 40 mg online
Therefore emergency physicians ought to immediately observe and guide their patients when performing this testing gastritis diet virut nexium 20 mg mastercard. These values are dependent on age gastritis diet nuts buy 40 mg nexium otc, gender, ethnicity, and height and may be predicted from mathematical equations. Pulse oximetry has become the standard of care in all kinds of clinical settings. Technology Oximetry is predicated on the Beer-lambert legislation, that states the focus of an unknown solute dissolved in a solvent could be determined by mild absorption. Pulse oximetry combines the principles of optical plethysmography and spectrophotometry. Pulse oximeter sensors are usually positioned on the finger, with the sunshine centered over the nailbed, not the fats pad. However, different areas such as the toes and earlobes are used in some settings such as pediatrics. These explicit wavelengths are used because the absorption characteristics of oxyhemoglobin and lowered hemoglobin are fairly different on the two wavelengths. The majority of the sunshine is absorbed by connective tissue, skin, bones, and venous blood. A small improve in arterial blood occurs with every heartbeat, thereby resulting in an increase in light absorption. By comparing the ratio of pulsatile and baseline absorption at these two wavelengths, the ratio of oxyhemoglobin to reduced hemoglobin is calculated. Because the pulse oximeter uses solely two wavelengths of sunshine, it could possibly distinguish only two substances. Pulse oximeters measure "functional saturation": the concentration of oxyhemoglobin divided by the concentrations of oxyhemoglobin plus reduced hemoglobin. The benefit of utilizing only two wavelengths within the oximeter is that the fee, measurement, and weight of the device are reduced. Pulse oximetry can be used to assess peripheral perfusion and consider for attainable ischemia in the extremities. Vascular surgeons will use a pulse oximetry probe on a finger or toe to assess the outcomes of vascular surgery on the arm or leg. Peripheral artery occlusion from peripheral artery illness may be instructed by comparison of pulse oximetry readings in the extremities. Decreased peripheral oxygenation may be detected in sufferers with compartment syndrome, traumatic arterial injury, and external compression of the proximal circulation. Measurements of SaO2 are comparatively insensitive in detecting significant changes in PaO2 at high levels of oxygenation as a outcome of these SaO2 values fall on the plateau portion of the curve (labeled). Hence, O2 saturation is an insensitive way of detecting early compensation in patients with asthma. SaO2 correlates well with PaO2, however the relationship is nonlinear and is described by the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve. In hypoxemic patients, small changes in SaO2 symbolize massive adjustments in PaO2 as a end result of these SaO2 values fall on the steep portion of the curve. Conversely, measurements of SaO2 are comparatively insensitive in detecting important changes in PaO2 at excessive levels of oxygenation as a end result of these SaO2 values fall on the plateau portion of the curve. Currently obtainable pulse oximeters are accurate and precise when saturation ranges from 70% to one hundred pc. Testing of pulse oximeters has shown that at 75% saturation, bias is scattered uniformly between underestimation and overestimation. Procedure the location for the probe is determined by the medical situation and the forms of probes obtainable. Other sites include the earlobe, the nasal bridge, the septum, the forehead/temporal artery, and the foot or palm of an infant. More central areas could present better readings in chilly ambient temperature or throughout movement. The laptop analyzes the incoming data to establish the arteriolar pulsation and shows this parameter as beats per minute. It is important to consider serial measurements and to confirm that the measurements correlate with different clinical markers. Clinical Utility Pulse oximetry peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) provides a bonus in assessing the adequacy of oxygenation over arterial blood fuel analysis by providing continuous measurements. Rapid recognition of opposed physiologic events should enable immediate initiation of therapeutic interventions. Interpretation Patients with normal physiologic gasoline trade have an O2 saturation between 97% and 100 percent. When SaO2 falls beneath 95%, hypoxemia may be current, which can be baseline for some patients with cardiac or lung illness. B, Although the need for quick removal of the ring is clinically apparent, a pulse oximetry probe confirmed ischemia with an O2 saturation of 61%. C, When a discharged EpiPen triggered a pale finger, injection of phentolamine was thought-about. D, When pulse oximetry demonstrated a saturation of 96% (97% to 98% within the different fingers), injection was not carried out and the circulation spontaneously normalized over a period of half-hour. Pulse oximetry may be affected by quite a few extrinsic elements, and a decline in O2 saturation with serial measurements should at all times immediate an analysis of respiratory status and adequacy of circulation. Although pulse oximetry represents a major advance in noninvasive monitoring of oxygenation, clinicians should acknowledge and understand its limitations. Nonetheless a room-air SaO2 value of 97% or larger strongly guidelines towards hypoxemia and average to severe hypercapnia. During procedural sedation, monitoring of ventilation is a more fascinating aim for prevention of hypoxemia and hypercapnia than easy pulse oximetry (see section on Procedural Sedation and Analgesia beneath Carbon Dioxide Monitoring later in this chapter). Hypoventilation and the resultant hypercapnia may precede a lower in hemoglobin O2 saturation by many minutes. Supplemental O2 may mask hypoventilation by delaying the eventual O2 desaturation that pulse oximetry is designed to monitor and recognize. Severe anemia: Satisfactory readings obtained right down to a hemoglobin stage of 5 mg/dl Motion artifact: See text concerning probe websites Dyes: Transient effect except resulting in methemoglobinemia gentle artifact: Minimize by overlaying the probe with opaque materials Hypoperfusion: An insufficient pulse signal will be displayed Electrocautery: Minimize by rising the space of the sensor from the surgical web site Deep pigmentation: use the fifth finger, earlobe, or other area with lighter pigmentation Dark nail polish: Remove with acetone or place a sensor sideways on the digit Dyshemoglobinemias. Low Perfusion To operate properly, pulse oximeters require a pulsating vascular mattress. Vasoconstriction associated to hypotension, hypothermia, or the administration of vasoconstricting medication might reduce the pulsatile part to less than zero. Modern pulse oximeters have signal strength detectors and can display a message indicating an inadequate pulse signal when perfusion is compromised. Changing the situation of the sensor to an space with larger perfusion, such as an earlobe or the forehead, might enhance the pulse signal. Intravenous Dyes A variety of dyes and pigments intrude with the accuracy of pulse oximetry. Fetal Hemoglobin Full-term newborns can have as a lot as 75% of whole hemoglobin within the type of fetal hemoglobin and up to 5% within the type of carboxyhemoglobin. Although fetal hemoglobin interferes with the spectrophotometric method, pulse oximetry will remain correct.
Generic nexium 40 mg with amex
Administer anesthetic to a 2- to 3-cm area of the pores and skin and subcutaneous tissue at incision site (A) gastritis diet �� nexium 40 mg order on-line. Continue to anesthetize deeper subcutaneous A tissues and intercostal B muscular tissues (B) gastritis diet 2015 buy nexium 40 mg without prescription. Identify the rib inferior to the intercostal area the place tube might be inserted and anesthetize the periosteal floor (C). Advance the needle until a flash of pleural fluid or air enters the syringe, confirming entry into the pleural area. Open the clamp whereas contained in the pleural house and then withdraw so that every one layers of the dissected tract are enlarged. Insert a finger into the pleural space and rotate 360 degress to feel for adhesions. Use a Kelly clamp to grab fenestrated portion of the tube and introduce it via the insertion web site. Right paratracheal nodes Chapter 3 Thorax Left paratracheal nodes Bronchomediastinal lymphatic trunk Right lymphatic duct Subclavian v. Interlobular lymph vessels Inferior tracheobronchial (carinal) nodes Drainage routes Right lung: All lobes drain to pulmonary and bronchopulmonary (hilar) nodes, after which to inferior tracheobronchial (carinal) nodes. Left lung: Superior lobe drains to pulmonary and bronchopulmonary (hilar) nodes and inferior tracheobronchial (carinal) nodes. Left inferior lobe drains additionally to pulmonary and bronchopulmonary (hilar) nodes and to inferior tracheobronchial (carinal) nodes, however then largely to right superior tracheobronchial nodes, the place it follows identical route as lymph from right lung. Although the primary rib is stationary, ribs 2 to 6 are inclined to enhance the anteroposterior diameter of the chest wall, and the lower ribs mainly improve the transverse diameter. Accessory muscle tissue of inspiration that connect to the thoracic cage may also assist in very deep inspiration. During quiet expiration the elastic recoil of the lungs, relaxation of the diaphragm, and rest of the thoracic cage muscular tissues expel the air. In pressured expiration the belly muscle tissue contract and, by compressing the abdominal viscera superiorly, raise the intraabdominal stress and drive the diaphragm upward. Trachea and Bronchi he trachea is a single midline airway that extends from the cricoid cartilage to its bifurcation on the sternal angle of Louis. It lies anterior to the esophagus and is rigidly supported by 16 to 20 C-shaped cartilaginous rings. Each lobar bronchus then divides once more into tertiary bronchi supplying the 10 bronchopulmonary segments of each lung (some clinicians determine eight to 10 segments in the left lung, whereas anatomists identify 10 in every lung). Chronic restrictive lung ailments account for about 15% of noninfectious lung ailments and embody a various group of disorders with decreased compliance that trigger continual irritation, fibrosis, and the need for extra strain to inflate the stiffened lungs. Dyspnea Cyanosis Nonproductive hacking cough Diffuse pulmonary fibrosis on x-ray film Clubbing of fingers Basilar inspiratory ("Velcro") crackles Loss of weight Elevated diaphragm Cor pulmonale (late) Diffuse bilateral fibrosis of lungs with multiple small cysts giving honeycomb appearance 112 Chapter 3 Thorax Clinical Focus 3-8 Pulmonary Embolism the lungs naturally filter venous clots larger than circulating blood cells and might normally accommodate small clots because of their fibrinolytic ("clot buster") mechanisms. Saddle embolus, then again, is an emergency that can precipitate acute cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure) and circulatory collapse. Sources of pulmonary emboli Most Common Sources of Pulmonary Emboli Less Common Sources of Pulmonary Emboli Massive embolization Right aspect of heart Gonadal (ovarian or testicular) v. Lung cancer arises either from alveolar lining cells of the lung parenchyma or from the epithelium of the tracheobronchial tree. Although there are a number of sorts, squamous cell (bronchiogenic) carcinoma (about 20% of lung cancers in the United States) and adenocarcinoma (from intrapulmonary bronchi; about 37% of lung cancers in the United States) are the most common types. For instance, in Pancoast syndrome, this apical lung tumor may unfold to involve the sympathetic trunk, have an result on the decrease portion of the brachial plexus (C8, T1, and T2), and compromise the sympathetic tone to the top. Emphysema is characterised by everlasting enlargement of air spaces at and distal to the respiratory bronchioles, with destruction of the bronchiole partitions by continual inflammation. As a result, lung compliance will increase because the elastic recoil of the lung decreases, inflicting collapse of the airways during expiration. This will increase the work of expiration as sufferers try to pressure air from their diseased lungs and can lead to a "barrel-chested" look brought on by hypertrophy of the intercostal muscle tissue. She could have chronic cough and sputum manufacturing, and need accent muscles and pursed lips to help her breathe. Chapter three Thorax Connective tissue sheath (visceral layer of pretracheal fascia) Tracheal cartilage (ring) Elastic fibers Gland Small a. Lymph vessels Nerve Epithelium erior wal A nt one hundred fifteen 3 Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Connective tissue sheath (visceral layer of pretracheal fascia) Tracheal cartilages Mucosa of posterior tracheal wall exhibits longitudinal folds fashioned by dense collections of elastic fibers Superior lobar (eparterial) bronchus To superior lobe Middle lobar bronchus To middle lobe To inferior lobe Right and left main bronchi Cross section by way of trachea Posterior wall Esophageal m. Upper lobe Superior division of bronchus To Lingular bronchus superior Middle lobe lobe To lingula Lower lobe Inferior lobar bronchus To inferior lobe Inferior lobar bronchus Upper lobe l Trachealis (smooth) m. Lingula Lower lobe Intrapulmonary Extrapulmonary Intrapulmonary Normal chest x-ray with superimposed drawing of major and secondary bronchi. In situ, the guts is oriented in the middle mediastinum and has the next descriptive relationships. Inferior (diaphragmatic): some of the proper ventricle and a lot of the left ventricle. Acute angle: the sharp right ventricular margin of the heart, largely the right atrium. Obtuse angle: the more rounded left margin of the center, largely the left ventricle. Apex: the inferolateral part of the left ventricle on the fourth to fifth intercostal house. Pericardium (fibrous layer) Respiratory diaphragm Heart drawn out of opened pericardial sac: left lateral view Superior vena cava Arch of aorta Pulmonary trunk Transverse pericardial sinus Left pulmonary vv. Bleeding could additionally be attributable to a ruptured aortic aneurysm, a ruptured myocardial infarct, or a penetrating harm (most frequent cause) that compromises the beating coronary heart and decreases venous return and cardiac output. Coronary Arteries and Cardiac Veins he proper and left coronary arteries come up instantly superior to the right and left cusps, respectively, of the aortic semilunar valve. During ventricular diastole, blood enters the coronary arteries to provide the myocardium of each chamber. Although variations in the coronary artery blood supply to the various chambers of the heart are frequent, normally, the proper coronary artery provides the: Right atrium. This means that the right coronary artery provides rise to the inferior interventricular branch and the posterolateral artery, as proven in. In the remaining cases, each the proper and the left coronary arteries could contribute to this department or it could be absent and branches from each coronaries could provide this region. Inferior (posterior) interventricular (posterior descending) department of proper coronary a. Additionally, quite a few smallest cardiac veins (thebesian veins) empty venous blood into all 4 chambers of the guts, however mostly into the right atrium. Chambers of the Heart he human heart has 4 chambers, each with unique inner features associated to their perform. In both ventricles the papillary muscle tissue and their chordae tendineae provide a structural mechanism that stops the atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral) from everting (prolapsing) during ventricular systole. Pericardial reflection Ascending aorta Chapter 3 Thorax Right auricle (atrial appendage) Crista terminalis Septal leaflet (cusp) of right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve Pectinate mm. Interatrial septum Fossa ovalis Inferior vena cava Opening of coronary sinus Valve of coronary sinus Valve (eustachian) of inferior vena cava Pulmonary trunk Nonadjacent semilunar leaflet (anterior semilunar cusp) Right adjoining semilunar leaflet (cusp) Pulmonary valve Right atrium Anterosuperior leaflet (anterior cusp) Septal leaflet (cusp) Inferior leaflet (posterior cusp) Chordae tendineae Superoposterior (anterior) papillary m. Apical trabeculations Left adjacent semilunar leaflet (cusp) Conus arteriosus Septal papillary m.
Nexium 40 mg order fast delivery
Running suture underneath hymen and continued in skin after approximation of perineal body G gastritis symptom of pregnancy 20 mg nexium order. The virus is often unfold by skin-to-skin contact; the incubation interval is 3 weeks to eight months gastritis diet �� discount nexium 40 mg mastercard. Infected structures embrace the urethra, cervix, larger vestibular glands, and uterine tubes in females and the urethra, epididymis, and prostate in males. Depending on the clinical scenario, these fascial planes can inhibit or inadvertently facilitate the spread of fluids. It is essential to notice that the cavernous bodies in the female and male are homologous constructions, though they differ in measurement. Erection of the penis (and clitoris in the female) and ejaculation contain the next sequence of events: 1. Friction and sexual stimulation evoke the excitation of parasympathetic fibers (pelvic splanchnics from S2-S4), which ends up in rest of the cavernous vessels and engorgement of the erectile tissue with blood (penis and clitoris). Sympathetic fibers then initiate contraction of the smooth muscle of the epididymal ducts, ductus deferens, seminal vesicles, and prostate, in that order, to transfer sperm toward the prostatic urethra. Sperm and the seminal and prostatic secretions (released by parasympathetic stimulation) enter the prostatic urethra and combine with secretions of the bulbourethral and penile urethral glands (the sperm and the collective secretions kind the semen). In females, sexual arousal ends in lubricating secretions from the greater vestibular glands. Under sympathetic stimulation (L1-L2), the internal urethral sphincter contracts to stop retrograde ejaculation into the urinary bladder. Deep transverse perineal muscle tissue: prolong from the ischial tuberosities and rami to the perineal physique; stabilize the perineal body. Urethral rupture is more widespread and entails considered one of three mechanisms: External trauma or a penetrating damage Internal damage (caused by a catheter, instrument, or international body) Spontaneous rupture (caused by increased intraurethral strain or periurethral inflammation) Straddle injury Injury due to fracture of pelvis Injury from within (false passage) Direct exterior trauma Penetrating damage (impalement) Perforation by periurethral abscess Clinical Focus 5-23 Urine Extravasation within the Male Rupture of the male urethra can lead to urine extravasation into varied pelvic or perineal areas that are largely restricted by the perineal, pelvic, and lower belly wall fascial planes. Its prevalence will increase with age, and a few of the possible causes are illustrated. Normal erectile operate happens when a sexual stimulus causes the discharge of nitric oxide from nerve endings and endothelial cells of the corpora cavernosa, thus enjoyable the smooth muscle tone of the vessels and increasing blood move into the erectile tissues. As the erectile tissue becomes engorged with blood, it compresses the veins within the tunica albuginea so that the blood stays in the cavernous bodies. Erectile dysfunction can even happen from injury to the nerves innervating the perineum. Afferent impulses conveying stimulation/arousal sensations are conveyed by the pudendal nerve (S2-S4, somatic fibers), whereas the autonomic efferent innervation of the cavernous vasculature is via the pelvic splanchnics (S2-S4, parasympathetic fibers). Psychogenic elements agonist exercise Medial preoptic space Paraventricular nucleus Depression, anxiousness, and stress issues result in overactivity of agonists inhibiting clean m. A dual duct system (mesonephric and paramesonephric ducts) associated with the urogenital ridge develops, with one of the duct methods turning into a serious component of the reproductive system in each gender. In genetic females, the mesonephric ducts degenerate and the paramesonephric ducts 278 turn into the uterine tubes, uterus, and higher portion of the vagina. In genetic males, the mesonephric ducts persist and become the eferent ductules, duct of the epididymis, ductus deferens, seminal vesicles, and ejaculatory ducts. Like the ovaries, the testes descend inferiorly, aided by the gubernaculum and diferential development, however enter the deep inguinal ring, and ultimately pass by way of the inguinal canal to descend into the scrotum. Undescended testis is the most typical genital anomaly in males, occurring in about 3-4% of boys at delivery within the United States. However, about 50% of undescended testes at birth subsequently descend during the first 12 months of life. Development of the External Genitalia he feminine and male external genitalia develop from the genital tubercle (the phallic structures), paired urogenital folds, and labioscrotal folds. Initially these tissues are undifferentiated, however after about the twelfth week recognizable external genital features associated with each intercourse start to form. Hypospadias is much more frequent (1 in 300 male births, but this determine varies widely from country to country) and is characterized by failure of fusion of the urogenital folds, which normally seal the penile (spongy) urethra throughout the penis. Epispadias is rare (1 in a hundred and twenty,000 male births) and is characterised by a urethral orifice on the dorsal aspect of the penis. It is believed to happen from a faulty migration of the genital tubercle primordia to the cloacal membrane early in development (fifth week). Glanular hypospadias Penile hypospadias Penoscrotal hypospadias (with chordee) Scrotal hypospadias (bifid scrotum, chordee) Complete epispadias Penile epispadias Chapter 5 Pelvis and Perineum 281 5 Clinical Focus 5-26 Uterine Anomalies Incomplete fusion of the distal paramesonephric (m�llerian) ducts can result in septation of the uterus or partial or full duplication of the uterus (bicornuate uterus). If just one paramesonephric duct persists and develops, a unicornuate uterus results. These circumstances seem to be transmitted by a polygenic or multifactorial sample and carry the next risk for recurrent spontaneous abortions (15-25%), untimely labor, uterine ache, breech or transverse deliveries, and dysmenorrhea. Complete septum (with double uterus and double vagina) Partial septum Rudimentary second vagina (without exterior opening, forming cyst) Bicornuate uterus with full septum (double cervix) Double uterus Bicornuate uterus Septate uterus Partial septum Unicornuate uterus 282 Chapter 5 Pelvis and Perineum Clinical Focus 5-27 Male Circumcision (Newborn) Male circumcision is the removal of the foreskin of the penis. All circumcision strategies begin with the undiapered new child restrained on an infant (papoose) board. Placement of the bell through the baseplate may be facilitated by reaching by way of the opening with a hemostat. The stem of the bell is positioned into the top of the clamp and the thumb screw gently tightened. Clinical Focus Available Online 5-28 Ovarian Tumors Additional figures out there on-line (see inside front cover for details). Risk components include a household history of ovarian most cancers, high-fat food plan, age, nulliparity, early menarche, late menopause, white race, and higher socioeconomic standing. Papillary serous cystadenocarcinoma Uterus Clear cell carcinoma of ovary Pelvic mass (up to 30 cm) partially cystic 40% bilateral predominately Papillary projections Challenge Yourself Questions 1. Cancer of the uterine cervix reaches an advanced stage and disseminates anteriorly. Which of the next buildings is more than likely to be concerned in the unfold of the tumor Ultrasound examination reveals that she has a bicornuate uterus with a whole septum and double cervix. A 41-year-old lady presents in the clinic with a uterine prolapse (cervix at introitus) in which the cervix is seen at the vaginal opening. A 73-year-old lady is admitted to the hospital with significant abdominal ascites. When she sits upright on the facet of her bed, the intraperitoneal fluid accumulates in her pelvis. Which of the following sites represents the lowest extent of the female abdominopelvic cavity the place this fluid will acquire Vesicouterine pouch Multiple-choice and short-answer review questions available online; see inside front cover for details. A male driver has sustained extreme trauma to the pelvic area in a motorized vehicle crash, leading to a tearing of the prostatomembranous urethral junction (a tear simply superior to the external urethral sphincter). After an car crash the teenage male driver presents to the emergency division with pelvic fractures and paralysis of his urinary bladder. Which of the following constructions lies near these structures and must be preserved Sexual arousal and orgasm make use of a coordinated regulatory efort mediated by somatic and autonomic nerves, in addition to by endocrine and central nervous system enter. During male ejaculation, which of the following nerves contract the inner urethral sphincter and prevent the semen from getting into the urinary bladder A forensic pathologist is asked to characterize the bony pelvis of an unidentified and largely decomposed human body. Contraction of this muscle expels the earlier few drops of urine from the male urethra.
Nexium 40 mg cheap without prescription
Fibularis (peroneus) longus tendon Tibialis anterior tendon (cut) Plantar cuneonavicular lig gastritis translation nexium 20 mg order with mastercard. Phalangeal bones Distal Middle Proximal Joint capsule Metatarsal bone Plantar calcaneocuboid (short plantar) lig gastritis diet ������ discount nexium 40 mg without a prescription. Flexor hallucis longus tendon (cut) Flexor digitorum brevis tendon to 2nd toe (cut) Plantar metatarsal ligs. Fibularis (peroneus) brevis tendon Capsules and ligaments of metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints: lateral view Plantar lig. A affected person with footdrop should increase the knee through the swing phase of gait to avoid dragging the affected foot on the bottom or to avoid tripping. This distinctive gait pattern is recognized as "steppage" gait, and on the end of the swing part, the foot slaps all the method down to the ground. Typically, footdrop results from injury to the widespread fibular nerve or deep fibular nerve. The widespread fibular nerve is vulnerable to injury as a outcome of it lies superficially beneath the skin where the nerve passes across the fibular neck (coffee table or automotive bumper height). This nerve also may be affected by a herniated disc that compresses the L5 nerve root (L4-L5 herniated disc; see Chapter 2). Clinical Focus 6-28 Ankle Sprains Most ankle sprains contain an inversion injury when the foot is plantarflexed, placing stress on the components of the lateral collateral ligament. Often the severity of the harm occurs from anterior to posterior, involving first the anterior talofibular ligament, then the calcaneofibular ligament, and finally, if particularly extreme, the posterior talofibular ligament. The anterior drawer take a look at, during which the tibia is held regular while the heel is pulled anteriorly with the foot in about 10 to 20 levels of plantarflexion, will confirm the injury to the anterior talofibular ligament if the translation of the foot anteriorly is extreme in contrast with that of the unhurt contralateral ankle. Anterior Drawer Test for Instability of Ankle (test for tear of anterior talofibular ligament) Examiner applies backward stress on lower tibia, inflicting anterior subluxation of talus (foot firmly fixed by different hand). Talar-Tilt Sign (test for tear of calcaneofibular and anterior talofibular ligaments) Examiner firmly rotates foot in varus. Tear of calcaneofibular ligament permits excessive mobility in this path (leg firmly fastened by other hand). Synovial sheaths present safety and lubrication for muscle tendons passing from the leg to the foot. Extensor retinaculum: superior and inferior bands (tethers the dorsilexor tendons). Fibular retinacula: superior and inferior bands (tethers the ibularis tendons of the lateral compartment). Muscles, Vessels, and Nerves of the Dorsum of the Foot he dorsum (top) of the foot consists of two intrinsic muscular tissues, the extensor digitorum brevis muscular tissues and the extensor hallucis brevis muscular tissues. A dorsal venous arch drains a lot of the blood from the foot (similar to the dorsal aspect of the hand), ultimately carrying the blood to the medially situated great saphenous vein or laterally and posteriorly to the small saphenous vein. Muscles, Vessels, and Nerves of the Sole of the Foot he sole of the foot is protected by a thick layer of the deep fascia referred to as the plantar aponeurosis, which extends from the calcaneal tuberosity to individual bands of fascia that attach to the toes anteriorly. Beneath the plantar aponeurosis, the intrinsic muscle tissue of the foot are arranged into 4 layers, proven in sequence in. Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon Common tendinous sheath of fibularis longus and brevis mm. Subcutaneous calcaneal bursa (Subtendinous) bursa of calcaneal tendon Superior and Inferior fibular retinacula Extensor digitorum brevis m. Fibularis longus tendon Fibularis brevis tendon Chapter 6 Lower Limb Extensor digitorum longus m. Superior extensor retinaculum Lateral malleolus of fibula and subcutaneous bursa Inferior extensor retinaculum Tendinous sheath of extensor digitorum longus and fibularis tertius mm. Fibularis tertius tendon Tuberosity of 5th metatarsal bone Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon Tendinous sheath of flexor digitorum longus m. Subcutaneous calcaneal bursa (Subtendinous) bursa of calcaneal tendon Flexor retinaculum Tendinous sheath of flexor digitorum longus m. Fibularis (peroneus) brevis tendon Fibularis tertius tendon Extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis mm. Extensor hallucis longus tendon Extensor expansions Tendinous sheath of extensor hallucis longus m. This causes it to fracture and places rigidity on supporting ligaments of the alternative aspect. The following three types are acknowledged: Type A: Medial rotation of the talus Type B: Lateral rotation of the talus Type C: Injury extends proximally, with torn tibiofibular ligament and interosseous membrane (a variant is the Maisonneuve fracture) Type A. Avulsion fracture of lateral malleolus and shear fracture of medial malleolus caused by medial rotation of talus. Shear fracture of lateral malleolus and small avulsion fracture of medial malleolus caused by lateral rotation of talus. Disruption of tibiofibular ligaments with diastasis of syndesmosis brought on by exterior rotation of talus. Complete disruption of tibiofibular syndesmosis with diastasis caused by external rotation of talus and transmission of drive to proximal fibula, resulting in excessive fracture of fibula. Extraarticular fracture of calcaneus Avulsion fracture of anterior strategy of calcaneus attributable to rigidity on bifurcate ligament (calcaneocuboid and calcaneonavicular) Comminuted fracture of anterior process of calcaneus due to compression by cuboid in forceful abduction of forefoot Achilles tendon Bursa Avulsion fracture of tuberosity of calcaneus as a result of sudden, violent contraction of Achilles tendon Fracture of medial strategy of tuberosity of calcaneus Fracture of sustentaculum tali Fracture of body of calcaneus with no involvement of subtalar articulation Intraarticular fracture of calcaneus 10� Primary fracture line Talus pushed down into calcaneus, normally by fall and touchdown on heel Primary fracture line runs across posterior facet, forming anteromedial and posterolateral fragments. In the foot, the reference toe for adduction and abduction is the second toe, which in most individuals is the longest toe. All these intrinsic muscle tissue of the only are innervated by the medial or lateral plantar nerves (from the tibial nerve) (Tables 6. Arterial pulses may be palpated between the medial malleolus and the heel (from the posterior tibial artery) and on the dorsum of the foot just lateral to the extensor hallucis longus tendon (from the dorsalis pedis artery). Realize that most joints transfer because of the action of a number of muscular tissues working on that joint, and that this record only focuses on the more necessary of those muscular tissues for each joint. Chapter 6 Lower Limb Superficial dissection Proper plantar digital nerves of lateral plantar n. Fibrous sheaths of flexor tendons 341 First layer Proper plantar digital nerves of medial plantar n. Plantar aponeurosis (cut) Digital slips of plantar aponeurosis Medial plantar fascia Lateral plantar fascia Flexor digitorum brevis tendons overlying Flexor digitorum longus tendons Plantar metatarsal branch of lateral plantar a. Flexor hallucis longus tendon Flexor digitorum longus tendon Plantar interosseous mm. Flexor hallucis longus tendon (cut) Transverse head and Oblique head of adductor hallucis m. This deformity has a strong genetic link; males are more regularly affected, but females often have a extra severe deformity. The bones not solely are misaligned with each other but also might have an irregular form and measurement. Management could also be conservative or could require splinting, casting, and even surgery. Plantarflexion (equinus) at ankle joint Deformity of talus Tightness of tibionavicular lig. These fractures can normally be handled with immobilization, because the fragments are often not displaced. Avulsion fractures of the fifth metatarsal are common to this bone and result from stresses positioned on the fibularis brevis tendon during muscle contraction.
Elephant Climber (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose). Nexium.
- Pain relief and promoting sweating.
- Dosing considerations for Hawaiian Baby Woodrose.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Hawaiian Baby Woodrose?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Hawaiian Baby Woodrose work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96344
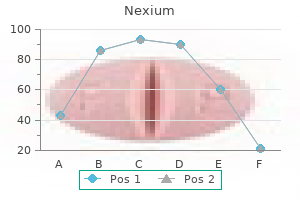
Nexium 40 mg order
Female Pelvic Reproductive Viscera he feminine pelvic reproductive viscera include the midline uterus and vagina and the adnexa (paired ovaries and uterine tubes) gastritis diet zantrex discount 20 mg nexium otc, that are positioned between the urinary bladder anteriorly and the rectum posteriorly gastritis xantomatosa 20 mg nexium with amex. External iliac vessels Superior view Chapter 5 Uterus (fundus) Median umbilical fold and lig. A double sheet of peritoneum (actually a mesentery) called the broad ligament envelops the ovaries, uterine tubes, and uterus. During embryonic development the ovaries are pulled into the pelvis by a fibromuscular band (homologue of the male gubernaculum). Because the uterine cervix initiatives into the superoanterior side of the vagina, a steady gutter surrounds the cervical opening, shallower anteriorly and deeper posteriorly, forming the anterior, lateral, and posterior fornices. Ampulla: extensive portion of the tube lying between the infundibulum and the isthmus; the similar old website of fertilization. Isthmus: proximal, slim, straight, and thickened portion of the tube that joins the body of the uterus. Coughing or straining Increased intraabdominal stress Increased intraabdominal pressure Urine loss Patient with defective fascial support of urethrovesical (U-V) junction. Bulging of anterior vaginal wall on straining Normal pubocervical fascial assist Torn pubocervical fascial sling Increased stress Closes urethra Opens urethra Increased intraabdominal stress forces urethra towards intact pubocervical fascia, closing urethra and maintaining continence. Defective fascial help allows posterior rotation of U-V junction owing to increased pressure, opening urethra and inflicting urine loss. Male Pelvic Reproductive Viscera he male pelvic reproductive viscera embody the prostate gland and paired seminal vesicles. Chapter 5 Pelvis and Perineum 245 5 Clinical Focus 5-4 Uterine Prolapse Uterine prolapse could happen when the assist constructions of the uterus, particularly the cardinal ligaments, uterosacral ligaments, and levator ani muscle, are weakened. Slight descent (1st degree) Cervix at introitus (2nd degree) Procidentia medical look Urinary bladder Uterus Characteristic Description Prevalence Age Risk factors Some descent frequent in parous ladies Late reproductive and older age groups Birth trauma, weight problems, chronic cough, lifting, weak ligaments Complete prolapse cross section Rectum Clinical Focus 5-5 Cervical Carcinoma Approximately 85% to 90% of cervical carcinomas are squamous cell carcinomas, whereas 10% to 15% are adenocarcinomas. Most carcinomas happen close to the external cervical os, where the cervical epithelium changes from easy columnar to stratified squamous epithelium (the transformation zone). Composite summary of sizes and websites Interstitial (intramural) Subserous Pedunculated, subserous Subserous, displacing uterine tube Pedunculated, submucous Characteristic Description Prevalence 30% of all ladies; 40�50% of ladies older than 50 years; most common benign tumor in girls Nulliparity, early menarche, African-American (4- to 10-fold increase) Stimulated by estrogen, oral contraceptives, epidermal development issue Intraligamentary Cervical Submucous Risk components Growth Pedunculated, submucous, protruding through external os Clinical Focus 5-7 Endometriosis Endometriosis is a progressive benign condition characterised by ectopic foci of endometrial tissue, known as implants, that grow within the pelvis-on the ovaries and within the rectouterine pouch, uterine ligaments, and uterine tubes-or within the peritoneal cavity. It typically happens between the ages of 55 and sixty five years, and danger components include the following: Obesity (increased estrogen synthesis from fats cells with out concomitant progesterone synthesis) Estrogen alternative remedy without concomitant progestin Breast or colon cancer Early menarche or late menopause (prolonged estrogen stimulation) Chronic anovulation No prior pregnancies or durations of breastfeeding Diabetes Uterine tube Early carcinoma involving only endometrium More in depth carcinoma deeply involving muscle Ovary Extensive carcinoma invading full thickness of myometrium and escaping through tube to implant on ovary Clinical Focus 5-9 Chronic Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Recurrent or persistent infections of the uterine tubes or other adnexa (uterine appendages) result in cystic dilation (hydrosalpinx) and can account for about 40% of female infertility cases. The etiology and pathogenesis are in depth and embody native uterine, ovarian, or adnexal issues, in addition to systemic and pregnancy-related issues. Because of the potential medical hazard of an ectopic being pregnant, the being pregnant is often terminated medically (if detected early enough) or surgically (often laparoscopically). Sites of ectopic implantation Tubal (ampullar) Abdominal Interstitial Tubal (isthmic) Ovarian Infundibular (ostial) Unruptured tubal being pregnant Cervical Villi invading tubular wall Chorion Characteristic Prevalence Age Causes Risk factors Description 10�15/1000 pregnancies (highest charges in Jamaica and Vietnam) >40% in 25- to 34-year-old group Uterine tube injury or poor tubal motility Tubal injury (infections), previous historical past, age (>35 years), nonwhite, smoking, intrauterine contraceptive device use, endometriosis Hemorrhage in tubal wall Lumen of tube Amnion Section through tubal pregnancy Clinical Focus 5-12 Assisted Reproduction Approximately 10% to 15% of infertile couples might benefit from various assisted reproductive methods. From 85% to 90% of all malignancies happen from the floor epithelium, with cancerous cells often breaking by way of the capsule and seeding the peritoneal floor, invading the adjoining pelvic organs, or seeding the omentum, mesentery, and intestines. Additionally, the cancer cells spread via the venous system to the lungs (ovarian vein and inferior vena cava) and liver (portal system) and via lymphatics. Risk elements embrace the following: Family history of ovarian cancer High-fat diet Age Nulliparity Early menarche or late menopause (prolonged estrogen stimulation) White race Higher socioeconomic status Routes of metastases Transdiaphragmatic communication of pleural and belly lymphatic vessels results in pleural effusion. Malignant cells in peritoneal fluid embolize to lymphatic vessels of proper hemidiaphragm. Subdiaphragmatic cell circulate Flow over omentum Flow alongside paracolic gutters Occlusion of lymphatic vessels causes ascites. Paraaortic nodes Pelvic nodes Lymphatic unfold primarily to pelvic and paraaortic lymph node chains Peritoneal seeding of free-floating malignant cells commonest mode of spread Parenchymal pulmonary metastasis Spread by way of portal v. Testes drain spermatozoa into the rete testes (straight tubules) and efferent ductules of the epididymis. Sperm mature and are stored within the epididymis, a long coiled tube about 6 meters in length if uncoiled. Prostate gland Seminal colliculus Prostatic utricle Opening of ejaculatory duct External urethral sphincter m. About three to 5 mL of semen and 100 million sperm/mL are present in each ejaculation. Pelvic Peritoneum In each sexes, the peritoneum on the decrease inside facet of the anterior stomach wall reflects of the midline from the urinary bladder because the median umbilical ligament (a remnant of the embryonic urachus). In females, the peritoneum reflects onto the superior facet of the urinary bladder, over the physique of the uterus, as the broad ligament, and onto the anterolateral side of the rectum. In males, the peritoneum displays of of the urinary bladder and instantly onto the anterolateral side Clinical Focus 5-14 Vasectomy Vasectomy presents birth control with a failure fee under that of the capsule, condom, intrauterine device, and tubal ligation. The muscular vas is identified, and a small phase is isolated between two small steel clips or sutures. The isolated phase is resected, the clipped ends of the vas are cauterized, and the incision is closed (or, in the nonincisional strategy, the puncture wound is left unsutured). Incision sites Testis (phantom view) Palpate spermatic twine by way of the skin Vasclip Site of skin incision Vas recognized by contact (causes peristaltic contraction) Small puncture website Vas being clipped with Vasclip Vas isolated in ring clamp Clinical Focus 5-15 Testicular Cancer Testicular tumors are heterogeneous neoplasms, with 95% arising from germ cells and virtually all malignant. Of the germ cell tumors, 60% show mixed histologic options, and 40% present a single histologic sample. Surgical resection often is carried out utilizing an inguinal strategy (radical inguinal orchiectomy) to keep away from spread of the most cancers to the adjoining scrotal tissues. It has a excessive incidence among Caucasians, with the best prevalence charges in Scandinavia, Germany, and New Zealand. Tunica albuginea (usually limits tumor) Seminoma (30% of germ cell tumors) Teratocarcinoma (most frequent combined tumor) Hemorrhagic necrosis Embryonal carcinoma (ill-defined, invasive masses) Clinical Focus 5-16 Hydrocele and Varicocele the commonest cause of scrotal enlargement is hydrocele, an extreme accumulation of serous fluid inside the tunica vaginalis (usually a potential space). An an infection in the testis or epididymis, trauma, or a tumor could lead to hydrocele, or it might be idiopathic. Varicocele is an abnormal dilation and tortuosity of the pampiniform venous plexus. Almost all varicoceles are on the left side (90%), perhaps as a outcome of the left testicular vein drains into the left renal vein, which has a barely higher stress, rather than into the bigger inferior vena cava, as the right testicular vein does. A varicocele is evident at bodily examination when a affected person stands, however it usually resolves when the patient is recumbent. This development can lead to urinary urgency, decreased stream pressure, frequency, and nocturia. Primary lesions invade the prostatic capsule and then spread along the ejaculatory ducts into the area between the seminal vesicles and bladder. The pelvic lymphatics and rich venous drainage of the prostate (prostatic venous plexus) facilitate metastatic unfold to distant websites. Lymph node and visceral metastases Node groups numbered in order of frequency of involvement, with relative incidence indicated by dots. Urinary bladder Carcinoma Rectum Characteristic Site Metastases Etiology Prevalence Description 90% come up in outer glands (adenocarcinomas) and are palpable by digital rectal examination Regional pelvic lymph nodes, bone, seminal vesicles, bladder, and periurethral zones Hormonal (androgens), genetic, environmental factors Increased in African-Americans and Scandinavians, few in Japan Extension of carcinoma into bladder, peritoneum, and rectal wall Chapter 5 Pelvis and Perineum 257 5 Female: superior view (peritoneum and unfastened areolar tissue removed) Medial umbilical lig. Cervix of uterus and uterine fascia Rectum and rectal fascia Presacral (potential) area (spread open) Pelvic fascia and ligs. Superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm (superior levator ani fascia) Obturator canal and obturator a. Reflection of the peritoneum in females causes a trough or pouch to form between the bladder and the uterus, known as the vesicouterine pouch.
Generic nexium 40 mg otc
Pubocervical ligaments: fascial condensations that course from the cervix to the anterior pelvic wall gastritis symptoms vs. heart attack nexium 20 mg cheap with visa, passing on both side of the female bladder gastritis symptoms burping nexium 40 mg best. Uterosacral ligaments: fascial condensations that course from the cervix posteriorly to the pelvic walls. Corresponding veins, often multiple in quantity, course with each of those arterial branches and drain into the internal iliac veins immediately or into different larger veins. Overview of Pelvic and Perineal Arteries he aorta bifurcates at concerning the L4 vertebral stage into the widespread iliac artery (1) (right and left branches), which then bifurcates into the interior iliac artery (2) and the external iliac artery (3) at concerning the L5-S1 intervertebral stage. Some anatomists divide the branches of the inner iliac artery into anterior and posterior trunks for descriptive functions. Pubic department Right Acetabular department internal Anterior and posterior branches iliac a. Superior Gluteal Artery Superficial and deep branches Right Inferior Gluteal Artery external Artery to sciatic nerve iliac a. Umbilical Artery (patent part) Artery to ductus deferens Ureteric branches Umbilical a. Superior vesical arteries Inferior Vesical Artery Superior Prostatic branches (male) vesical a. Middle Rectal Artery Vaginal (female) and prostatic Obturator (male) branches branch of Internal Pudendal Artery inferior Inferior rectal artery epigastric a. Perineal artery Labial (female) and scrotal (male) branches Urethral artery Artery of bulb (vestibule in feminine; penis in male) Dorsal artery of clitoris (female) and penis (male) Deep artery of clitoris and penis three. External Iliac Artery Inferior epigastric artery Obturator department Cremasteric artery (male) *Proximal (aortic bifurcation) Deep circumflex artery to Distal (internal pudendal artery) Ascending branch Chapter 5 Aorta Pelvis and Perineum L5 vertebra Iliolumbar a. Important portosystemic anastomoses happen between the superior rectal vein (drains into the inferior mesenteric vein of the portal system) and the center (internal iliac vein) and inferior (internal pudendal vein) rectal veins of the caval system. Because some lymph from the uterus may drain along the spherical ligament of the uterus to the inguinal nodes, physicians must be conscious that uterine most cancers may spread to these nodes in addition to the external iliac nodes. Lymph from the deep buildings of the perineum drains primarily into the inner iliac lymph nodes, as described above. However, lymph from the extra superficial structures of the perineum drains into the superficial and deep inguinal lymph nodes. As famous beforehand, lymph from the testes drains upward within the spermatic wire and follows the testicular veins to the aortic (lumbar) lymph nodes in the midabdomen (Table 5. Somatic afferent fibers convey pain, touch, and temperature from the pores and skin, skeletal muscle, and joints via nerves from these plexuses to the same relative spinal twine ranges. Inhibit contraction of each the male inner urethral sphincter for urination and the interior anal sphincter for defecation in each genders. Ischial tuberosities laterally (lateral margins are demarcated by the ischiopubic rami anteriorly and the sacrotuberous ligaments posteriorly; see. Sacral splanchnics Pelvic splanchnics Inferior hypogastric plexus Pudendal nerve he sympathetic efferent fibers typically mediate the following features: Vasoconstrict and/or keep vasomotor tone. Contract the male inside urethral sphincter and the interior anal sphincters in each genders. Visceral afferent fibers convey pelvic sensory info (largely pain) via each the sympathetic fibers (to the upper lumbar spinal twine [L1-L2] or lower thoracic ranges [T11-T12]) and parasympathetic fibers (to the S2-S4 ranges of the spinal cord). Sympathetic innervation maintains a tonic contraction of this easy muscle, besides when feces expand the rectal ampulla; then the parasympathetic stimulation relaxes this sphincter to allow for defecation. Urogenital Triangle he female urogenital triangle is divided into a superficial pouch, containing the exterior genitalia and related skeletal muscle tissue, together with the bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus, and superficial transverse perineal muscles. Communication between inside and perimuscular rectal plexuses Perimuscular rectal venous plexus Inferior rectal v. Medial to the labia majora, smaller skin folds comprise the hairless labia minora, whose boundaries define the vestibule (Table 5. Directly posterior to the vestibule is the perineal physique (central tendon of the perineum), which is a vital fibromuscular support region lying just beneath the skin halfway between the 2 ischial tuberosities and an necessary attachment level for the superficial and deep transverse perineal muscular tissues. Submucous house (internal venous plexus) Deeper half Superficial (perianal) half Peritoneum (cut edge) forming flooring of pararectal fossa Levator ani m. Ischial tuberosity Perianal area (external venous plexus) Internal anal sphincter m. Sphincter urethrovaginalis muscle: extends from the perineal physique around the lateral sides of the vagina and fuses in the midline across the anterior aspect of the urethra. Deep transversus perineal muscle tissue: extend from the ischial tuberosities and rami to the perineal physique; stabilize the perineal physique. Internal pudendal artery: arises from the internal iliac artery and, along with the pudendal nerve, passes out of the greater sciatic foramen; it then passes around the sacrospinous ligament Inferior rectal Median sacral largely occupied by the urethrovaginalis�skeletal muscle sphincter advanced surrounding the urethra and vaginal apertures. Superior to the deep pouch lies the levator ani muscle, with an intervening anterior extension of the ischioanal fossae (fat) separating the deep pouch and muscle. Vagina: distal portion passes via the deep pouch and opens into the vestibule. External urethral sphincter: the voluntary skeletal muscle sphincter of the urethra. It offers arterial branches that distribute to the perineum and include the inferior rectal, perineal, and labial branches, the artery of the bulb, and the dorsal clitoral arterial branches. Hemorrhoids can bleed; the blood could pool and clot, yielding a "thrombosed" hemorrhoid. Despite the reality that nearly each primiparous delivery results in a minimal of a minor injury to the vagina, perineum, or vulva, routine episiotomy is carried out a lot much less regularly than it was several many years in the past. When performed, episiotomies normally are both immediately in the midline by way of the perineal physique or posterolateral, to avoid the perineal body. Posterolateral Approach (one of two approaches normally used, posterolateral [shown here] or median) A. An abscess in the ischioanal fossa is proscribed in its spread superiorly by this muscle. Anterior rami of S2-S4 exit the anterior sacral foramina and then move directly over (superficial to) this muscle. Trauma to the L1-L2 sympathetic outflow would end result within the inability to contract this muscle. During a pelvic examination, the gynecologist feels a pulse adjoining to the vaginal fornix. An ultrasound examination of a 16-year-old girl shows that she has a double uterus. Failure of which of the following developmental events is responsible for this condition A 20-year-old male school pupil with testicular ache and swelling is seen in the college health clinic. Which of the next conditions is most probably the reason for the swelling and inflammation Which of the following lymph node collections is most probably to be involved first in the unfold of this tumor During a diicult supply, the physician decides to perform a posterolateral episiotomy to enlarge the vaginal opening. Which of the next buildings will be utterly or partially incised during this procedure During surgical procedure to remove an ovary and its associated lymphatics, the surgeon have to be notably aware of the shut anatomical approximation of which of the following nerves Rupture of the male urethra can lead to the extravasation of urine into numerous pelvic or perineal spaces.
Nexium 20 mg free shipping
The indications for placement of an arterial catheter fall into two major categories1 gastritis symptoms acute nexium 20 mg without prescription,2: 1 gastritis diet ������� nexium 40 mg for sale. Catheter entry removes the necessity for a quantity of arterial punctures and permits both repeated sampling or placement of sensors for steady monitoring of blood gasoline and other chemistry values. Catheter entry allows superior monitoring and moment-to-moment detection of adjustments. Some sufferers, similar to those with extreme burns, dialysis grafts or shunts, or morbid weight problems, may need ongoing monitoring of perfusion, which may best be completed by arterial catheterization. The arterial blood pressure defines cardiac arrest and serves as a definitive end point for resuscitative efforts. Intraarterial cannulation with steady blood stress measurement remains an accepted standard in critically unwell patients. Intraarterial monitoring of blood pressure better reflects the drive of systemic perfusion and is doubtless certainly one of the most necessary determinants of cardiac work. Cultures carried out on blood obtained from an indwelling arterial line have a sensitivity and specificity much like that of cultures performed on blood obtained from a venipuncture site. The preliminary correlation between noninvasive values and acid-base status through arterial sampling is commonly necessary in critical illness to set a baseline or confirm a development. The response of trauma and post-cardiac arrest patients to acute resuscitative efforts may be extra simply monitored with the usage of arterial catheterization. If completely essential, a single arterial puncture of the readily compressible radial artery is preferred. There are stories of patients with bleeding complications who require transfusion. Some sufferers have suffered compression neuropathies secondary to hematomas on the puncture site. The presence of severe arteriosclerosis, with or without diminution in circulate, is a relative contraindication to arterial puncture. In hemodynamically unstable patients with superior heart problems, the advantages of invasive monitoring could nonetheless outweigh its dangers. Avoid puncturing a selected arterial web site when infection, burn, or different injury to cutaneous defenses exists in the overlying skin or via or distal to a surgical shunt. For pediatric arterial sampling, use a needle with a barely shorter size within the vary of 22- to 24-gauge on the identical sites as in adults. Fully eject the heparin by way of the needle instantly before skin puncture to decrease heparin-related errors. Although the syringe may appear devoid of heparin, enough heparin remains within the needle and syringe to provide anticoagulation. A falsely Vented plunger Pre-heparinzed syringe Arterial Versus Venous Analysis Arterial sampling has been the standard strategy to evaluating acid-base abnormalities in critically unwell patients, especially those being maintained on a ventilator. Additionally, the plunger is vented, which permits air in the syringe to escape by way of the plunger because the pattern is collected. To use this kind of syringe, pull again the plunger to the specified volume earlier than arterial puncture. The frequency responses of tubing, transducers, and other components of the monitoring system affect the accuracy of systolic and diastolic pressure measurement. Failure to recognize recording system artifacts will result in errors in interpretation of the strain. Various catheter types have demonstrated related frequencyresponse characteristics, but some studies have discovered different complication rates. The incidence of thrombosis also will increase with elevated duration of catheter placement. In contrast, a higher threat for thrombosis was seen in the femoral artery than in the radial artery in a research involving a pediatric population. Shorter catheters are ideal for peripheral artery cannulation, whereas use of a longer catheter and the Seldinger technique is preferable for the femoral artery. For arterial cannulation in adults, use a 16- to 18-gauge catheter for the femoral artery and a 20-gauge catheter for the radial artery. Small children and infants require a 22- to 24-gauge catheter, which can need to be inserted percutaneously via the Seldinger technique or through a femoral cutdown. Based on patient measurement, older pediatric sufferers usually require 20- to 22-gauge catheters. The tubing that connects the catheter to the pressure transducer has a big impact on accuracy of the monitoring system. The higher the frequency response of the whole system, the extra accurate the dedication of systolic and diastolic stress; nevertheless, artifact additionally becomes extra of an issue. The arterial fluid wave is received by an electromechanical transducer that modifications the mechanical stress wave into an electrical sign that could be displayed on the monitor. When the lever reaches the reference mark on the barrel of the device, the tip of the guidewire is at the opening of the needle lumen. A steady methodology of flushing the strain tubing is required to preserve patency of the catheter lumen throughout intraarterial pressure monitoring. A three-way stopcock through which the tubing is intermittently flushed with saline (a minimal of every 15 to 30 minutes) is a simple, efficient method. Anaerobic storage at room temperature for 20 minutes ends in no significant change. A 1-l bag of regular saline is pressurized to 250�300 mm Hg with a metered blood pump (not shown). The transducer device is a sterile, inexpensive, totally assembled monitor that can be used during patient transfer. A saline flush solution could be injected manually via a syringe on the proximal or distal port. Because probably the most frequent complication of arterial catheterization is bleeding, the ability to control hemorrhage must also be thought of. For these causes, the radial and femoral arteries are favored due to their good collateral blood flow and ease of compression in case of hemorrhage. Current pressure-monitoring setups embody not only built-in stopcocks but in addition in-line flushing plungers to facilitate clearance of blood after sampling. Intravascular transducers were initially seen as an enchancment over the exterior electromechanical transducers in use because the mid-1970s. Despite anecdotal stories of fibrin deposition on these gadgets, no elevated incidence of thrombus formation has been famous. If local anesthesia is to be given, take care to use solely a small amount of local anesthetic as a result of a big wheal might obscure the coronary heart beat. Isolate the arterial pulsation with the index and middle fingers of the gloved, nondominant hand and identify the course of the vessel.
![MAT deficiency[disambiguation needed]](http://healthdept.sp.gov.lk/purchase/Nexium/lekmywpi/galqd2.jpg)
Nexium 40 mg buy online
The cuffed mask is designed to kind a seal across the glottis when the gadget is positioned properly gastritis zittern 40 mg nexium buy overnight delivery. Since then it has been used greater than 200 million instances and has been described in additional than 2500 educational papers gastritis diet ppt nexium 40 mg online. Using this methodology permits the strongest muscles of the arms to perform a jaw thrust, which pulls the face into the masks to create a seal. To keep away from gastric inflation, ventilate with a small volume (500 mL or 6 to eight mL/kg) and avoid high peak stress through the use of a protracted inspiratory time (1 second). Some authors imagine that improper approach is to blame for the various reported failures of cricoid strain. It might present a more secure and dependable means of ventilation than bag-mask air flow. Advantages embrace a deal with that makes placement easier and allows the operator to carry as a lot as improve the seal in opposition to the laryngeal inlet if wanted. Keep the posterior of the mask firmly utilized to the soft palate and posterior pharynx until firm resistance is felt. Frequently, solely half the maximum cuff volume is adequate to get hold of an excellent masks seal. Attach a bag and ventilate the patient while using chest rise, breath sounds, and capnography to confirm adequate gasoline exchange. After each adjustment maneuver, assess the standard of bag ventilation and masks seal. Open the mouth widely and place the posterior surface of the device in opposition to the exhausting palate, instantly posterior to the upper incisors. Initially inflate the cuff with solely half of the maximum quantity, and improve inflation as needed. This manuever aligns the masks with the glottis and will provide for higher ventilation. Attach a bag and ventilate the patient, with chest rise, breath sounds, and capnography used to verify adequate fuel trade. The best approach to guarantee correct air flow is to optimize the insertion approach by carefully following the aforementioned instructions. Listen for an audible cuff leak to ensure that a good masks seal has been achieved. Adjust the cuff quantity if essential to improve the mask seal and guarantee optimal air flow. Cuff overinflation could trigger a leak, however deflation and repositioning might improve the seal. This technique can be utilized in combination with any of the maneuvers simply mentioned. In fasted anesthetized patients, the incidence of aspiration is very low, approximately 2 per 10,000 instances. Size three is yellow and designed for patients four to 5 ft in height, dimension 4 is pink and designed for sufferers 5 to 6 feet in peak, and size 5 is purple and designed for patients taller than 6 toes. Introduce the tip of the gadget into the nook of the mouth while rotating the tube forty five to 90 degrees in order that the blue orientation line on the tube is touching the nook of the mouth. As the tip passes beneath the base of the tongue, rotate the tube again to the midline so that the blue orientation line faces the ceiling. The gadget is properly positioned posterior to the larynx, with the distal end within the proximal esophagus. The distal cuff is inflated within the proximal esophagus and the bigger proximal cuff is inflated on the base of the tongue. The proximal portion of the tube is on the lip line and the distal aperture (between the cuffs) is aligned with the glottic opening; oxygen flow from the system to the glottis is depicted by the white arrows. The actual pathology was not decided however was thought to be a pharyngeal or esophageal perforation. Inflate the cuffs with the minimum quantity essential to create a great seal (see the product brochure for maximum cuff volumes). The most serious complication is tracheal placement, which occurred in 10% of cases in a single study and might be considerably underappreciated and underreported. Because an post-mortem was denied, the exact damage was by no means confirmed and should have been associated to other interventions throughout resuscitation. The longer lumen or tube is used for air flow when the tip is within the esophagus. The massive proximal cuff or balloon is designed to occlude the pharynx by filling the area between the base of the tongue and the soft palate. Because the King is easier to use and confirmed to be an efficient and dependable main and rescue airway device, the Combitube is used less frequently than beforehand. The producer recommends the smaller 37-Fr device for patients from 4 feet to 5 ft 6 inches tall and the larger 41-Fr device for patients taller than 5 ft 6 inches. Studies recommend that the smaller 37-Fr Combitube can be utilized safely in sufferers as a lot as roughly 6 toes tall. To insert the Combitube, maintain the system in the dominant hand and gently advance it caudally into the pharynx while grasping the tongue and jaw between the thumb and index finger of the nondominant hand. A, Approximately 95% of placements are esophageal, so start air flow via the longer (blue) airway tube. When the distal tip is in the esophagus, ventilation occurs by way of the vent holes between the distal and proximal cuffs (white arrows). It is important to recognize this shortly, and use the brief (white) tube for ventilations. The large pharyngeal balloon serves to securely seat the Combitube in the oropharynx and creates a closed system in the case of esophageal placement. Because approximately 95% of placements are esophageal, begin ventilation through the longer (blue) airway tube. Alternatively, use a Wee-type aspirator gadget on the shorter (clear) lumen to confirm that the tip is in the esophagus before air flow via the longer (blue) lumen. Easy aspiration with the Wee-type system indicates tracheal positioning of the tube and requires altering the air flow to the shorter (clear) tracheal lumen. Use a extra caudal, longitudinal course of insertion versus an anteroposterior direction of insertion. The Combitube must also be maintained within the true midline position throughout insertion to avoid blind pockets in the supraglottic area, which might forestall passage of the tube. There are many strategies and gadgets that can be utilized to handle emergency airways. In difficult conditions, providers will most likely have one of the best success when primary expertise are carried out excellently. Complications Inappropriate balloon inflation and incorrect Combitube placement can result in air leaks during air flow. Combes X, Jabre P, Margenet A, et al: Unanticipated difficult airway management within the prehospital emergency setting: potential validation of an algorithm. Meier S, Geiduschek J, Paganoni R, et al: the impact of chin carry, jaw thrust, and continuous optimistic airway pressure on the scale of the glottic opening and on stridor rating in anesthetized, spontaneously breathing kids. Guildner C: Resuscitation-opening the airway: a comparative research of strategies for opening an airway obstructed by the tongue.
Order 40 mg nexium with mastercard
Confirmation ought to be tried by noting multiple characteristics of the vessel (compressibility gastritis symptoms lower back pain 20 mg nexium safe, form xenadrine gastritis buy 20 mg nexium mastercard, anatomic location, etc. Once the vessel has been confirmed because the vein, the operator must take great care to make certain that the position of the tip of the needle is obvious always. Most issues happen when the tip of the needle is deeper or more medial than the operator realizes, thus putting it in proximity to other structures. An intensive discussion of each method can be found in the primary ultrasound chapter (see Chapter 66), and each approach has its drawbacks in determining position. In the transverse methodology, the angle of method could be tough to verify and trigger the tip of the needle to be deeper than the operator realizes. In the longitudinal method, the medial to lateral orientation of the needle may be troublesome to appreciate. Additionally, slight actions of the transducer may end in lack of the suitable picture. A combination of these two, or an oblique method, may reduce these difficulties. They could be discovered at the level of the inguinal crease on the medial side of the thigh. Similar to vessels within the neck, the femoral vein is extra oval or triangular in form. Though not evident on this image, slight pressure will cause collapse of the vessel. It will also sometimes improve in size when the decrease a part of the leg is squeezed. The vascular bundle may must be followed inferiorly or superiorly to determine probably the most optimum location for puncture. Variant anatomy or variations in volume status (either depletion or overload) could make the vessels difficult to distinguish from one another. The tip of the needle could also be difficult to follow within the transverse approach and result in an inadvertent puncture of the posterior wall of the vessel. When the artery lies deep to the vein, arterial puncture or cannulation could outcome. In the longitudinal strategy, the medial to lateral position of the needle may be tough to appreciate and result in unintentional arterial puncture. The subclavian artery, not seen in this image, will be seen as a similar-appearing vessel deep to the vein. Subclavian Vein the subclavian vessels may be imaged from both a supraclavicular or an infraclavicular strategy. The vein can be identified by its variation with respiration and alter in measurement with the Valsalva maneuver. In the infraclavicular strategy, the transducer is placed beneath the clavicle at its most lateral aspect, in a sagittal or slightly oblique orientation, following the position of the clavicle. In this view, the vessels shall be seen in cross section or a barely oblique aircraft. The pleura may also be seen deep to the vessels as an echogenic vertical line that slides backwards and forwards with respiration. This will enable a shallow angle to be used and thereby minimize the possibility of damaging deeper constructions such as the lung. Once a flash of blood has been obtained, the ultrasound transducer could be put aside and the procedure continued as described beforehand. The subclavian artery and vein lie in close opposition to the pleura, so pneumothorax is a more frequent complication. Using a long-axis method (in which the needle is launched from the top of the transducer rather than from the middle) provides the advantage of visualizing the entirety of the needle in its course towards the vein. A shallow angle can be used, and the connection of the needle to the pleura may additionally be appreciated. Twist open the pliable clamp and place it over the catheter at a website a couple of centimeters from the insertion web site. B Suture right here the rubber clamp is covered with a blue plastic fastener, and each the clamp and fastener are sutured to the pores and skin to safe the catheter. Stapler Tent the pores and skin here after which staple C To avoid a needlestick, the blunt end of the needle is used to pass the suture via the holes of the fastening units. E this Biopatch is a chlorhexidine-containing hydrophilic masking placed at the site the place the catheter enters the pores and skin to deliver local antisepsis for 7 days. The ideas of the catheters are appropriately placed in the superior vena cava (arrows). Obtain a chest movie as quickly as possible to examine for hemothorax, pneumothorax, and the place of the tip of the catheter. Because small amounts of fluid or air might layer out parallel to the radiographic plate with the affected person within the supine place, take the movie in the upright or semi-upright place each time potential. In sick patients, a rotated or oblique projection on a chest radiograph could additionally be obtained, and the clinician may be confused about the correct place of the catheter. A misplaced catheter tip is usually obvious on a properly positioned normal posteroanterior chest radiograph. Although this complication is uncommon, if not specifically considered it might be missed by each clinicians and radiologists. If such patients are steady and hemodynamically monitored, radiography may be deferred safely in the absence of obvious issues or medical suspicion of malposition. Although the catheter may have been positioned intravascularly in a venous anatomic variant, it was determined to take away this line and substitute it with a brand new catheter. Redirection of Misplaced Catheters Improper catheter tip position occurs generally. Complications of improper positioning embrace hydrothorax, hemothorax, ascites, chest wall abscess, embolization to the pleural space, and chest ache. An unusual complication attributable to improper tip position is cerebral infarction, which can happen following inadvertent cannulation of the subclavian artery. Loop formation, lodging in small neck veins, tips directed caudally, and innominate vein place are frequent problems. If the catheter is getting used for fluid resuscitation, the malposition could also be tolerated for a while. If vasopressors or medications are infused, correct positioning of the tip of the catheter is extra critical. One technique is to insert a 2-Fr Fogarty catheter through the lumen of the central line and advance it 3 cm beyond the tip. Deflate the balloon and advance the central line over the Fogarty catheter, which is then withdrawn. Another anecdotal strategy is to withdraw the catheter till solely the distal tip remains within the cannulated vessel. This measurement is best appreciated by evaluating the size of the indwelling catheter with another unused catheter.