Isoptin
Isoptin dosages: 240 mg, 120 mg, 40 mg
Isoptin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Purchase 40 mg isoptin amex
When a xenobiotic crosses this unstirred water layer and the acid mucolayer blood pressure medication bananas generic isoptin 40 mg on line, it reaches the floor epithelium arrhythmia in 7 year old isoptin 40 mg generic otc. The two major pathways for substances to enter the membrane are transcellular (through the cells) and paracellular (between the cells) (Gad, 2007). Transcellular transport mechanisms may be passive corresponding to in diffusion, filtration, osmosis, or facilitated diffusion. Active transcellular transport could also be direct or oblique such as by endocytosis, pinocytosis, phagocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis, or exocytosis (Kapp, 2007). Paracellular transport pathways allow the passive motion of gear through intercellular epithelial cell areas regulated by apical tight junctions. Villus peak and crypt depth decrease aborally by way of the gut, whereas the variety of goblet (mucus) cells will increase. The digestive and absorptive surfaces of the intestine are markedly elevated by the presence of villi and microvilli on the enterocytes. Villus epithelial cells are current on basement membranes (not seen) on a core of lamina propria. Some of these metabolic actions are current in the gut microflora that could be modified by dietary manipulation (Betton, 2013). In the lamina propria, the arterioles generate resistance to blood move, the precapillary sphincters decide perfusion, and molecular trade occurs across capillaries. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Gastrointestinal Toxicity 147 (Tepperman and Jacobson, 1981). Constant supply of oxygen and other vitamins to the villus and elimination of absorbed supplies are important capabilities of the mesenteric circulation. Autoregulation of blood circulate by villus vessels exceeds that of deeper mucosal or muscular vessels (Tepperman and Jacobson, 1981). Regulation of mesenteric circulation is via the sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric nervous systems; by intrinsic sensory neurons; and by autoregulation (interstitial cells of Cajal). Norepinephrine, adenosine triphosphate, and neuropeptide-Y are vasoconstrictors launched instantly onto blood vessels by the sympathetic nervous system. At excessive concentrations, capsaicin causes neuronal degeneration (Buck and Burks, 1986; Buck et al. Topical application of capsaicin to gastric mucosa causes dilation of submucosal arterioles, presumably by preliminary release of peptides from sensory neurons (Chen et al. Prior therapy with a neurotoxic (peptide-depleting) dose of capsaicin blocks the vasodilator response. Endogenous nitric oxide additionally mediates the vasodilation that accompanies acid secretion (Holzer et al. Intimate contact with the absorptive surface of the intestinal mucosa is affected by segmenting or mixing contractions. Contractions of the round muscle happen roughly randomly however are considerably mounted by the electrical sluggish waves or electrical management exercise generated in the interstitial cells of Cajal. Propulsive contractions can occur, including random migrating clustered contractions associated with contractile rings that move distally from 5 to 30 cm propelling content material aborad (Sarna and Otterson, 1989). Toxic brokers that induce excessive migrating clustered contractions might velocity propulsion. Pharmaceuticals that alter intestinal motility embody atropine, morphine, clonidine, papaverine, and isoproterenol (Gad, 2015). The cell junctions of the large intestinal epithelium are a lot tighter than those of the small gut. As a outcome, massive intestinal enterocytes absorb sodium ions more fully than within the small intestine (Spainhour, 2007). Rhythmic segmentation permits retropulsion however not peristalsis permitting the colon to operate as a storage organ (Saur, 2010). Orthograde and retrograde contractions are thought to happen in the proximal and middle colon (Sarna, 1991). A variety of drugs and therapeutic chemical compounds could alter the colon and or its features by direct contact or systemic mechanisms (Ernest, 2010). The microbiota throughout the colon hydrolyzes some remaining digesta and xenobiotics by way of bacterial b-glucuronidase. Intestinal microbes facilitate enterohepatic circulation of phenytoin, phenacetin, diethylstilbestrol, digitoxin, and warfarin. The colon slowly propels its contents aborally, holds residual materials in the distal colon, and expels its contents throughout defecation (Sarna, 1991). Since the colonic mucosa lacks villi, the absorptive area of the colon relative to the small gut is small and absorption is slow. Transit of contents by way of the colon is 2�10 h in small species and 30�50 h in people. Progenitor cells, positioned within the intestinal crypts, give rise to all different epithelial cell sorts lining the crypts and overlaying the villi. These pathways contain typical ligand�receptor interactions the place the ligand is a transmembrane protein expressed in a single cell kind that binds with a notch receptor. This binding interaction ends in modifications of gene expression within the cell expressing the receptor, such as facilitating its differentiation into an absorptive enterocyte. This ligand�receptor binding appears to result in cells organizing into groups of cell varieties as wanted for his or her differentiation into specific tissues and organs. A combination of Notch and Wnt alerts is important for proliferation of enterocyte precursors, but differentiation of cell sorts is unbiased of Wnt. In a neonatal piglet that has not achieved climax flora, the epithelial turnover price is approximately 7 days. The immature, just lately produced cells, aside from the enteroendocrine and Paneth cells, mature as they slide along the basement membrane to the villous tip extrusion zone the place senescent cells turn out to be a half of the fecal mass by a process of apoptosis termed anoikis. The migration fee relies on many components, one of which is adaptation to intestine microflora. Crypt cells have secretory features (secretory part, NaCl) and may be concerned in IgA and IgM transport. They harbor a floor glycocalyx that contains the digestive and absorptive enzymes. These vesicles contain alkaline phosphatase and catalase that are bacteriocidal in addition to membrane attachment websites for some pathogens. Enterocytes are linked to each other by an apical junctional complex composed of more than 40 transmembrane proteins and other molecules. They present negative suggestions inhibition to the progenitor cells by secreted chalones. The absorptive cells are pinocytotic early in life for colostrum absorption and passive switch of antibody in some species. The colonic mucosa is covered by relatively flat mucus-secreting cells and crypts. Mucus exerts a variety of protecting results together with trapping of bacteria with resultant passage within the fecal mass, lessening of shear forces of particulate matter on the enterocytes, and housing bacteriophages that scale back the bacterial inhabitants of the intestine by 104.
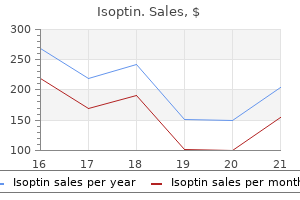
Isoptin 40 mg purchase line
Generation of gut-homing T cells and their localization to the small intestinal mucosa heart attack 2013 isoptin 40 mg for sale. Identification of a chemokine network that recruits FoxP3(�) regulatory T cells into chronically infected intestine hypertension journal articles isoptin 40 mg order with amex. Recent progress in understanding the phenotype and function of intestinal dendritic cells and macrophages. Direct demonstration in intestinal secretions of an IgA memory response to orally administered Shigella flexneri antigens. The higher chemotactic community for lymphocyte trafficking: Chemokines and beyond. Migration and performance of FoxP3 � regulatory T cells in the hematolymphoid system. Homeostatic regulation of intestinal epithelia by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Intraepithelial lymphocytes: Their shared and divergent immunological behaviors within the small and enormous intestine. Retinoic acid decreases adherence of murine myeloid dendritic cells and increases production of matrix metalloproteinase-9. An immunomodulatory molecule of symbiotic micro organism directs maturation of the host immune system. The common mucosal immune system: from primary principles to enteric vaccines with relevance for the feminine reproductive tract. Human intestinal epithelial cells are broadly unresponsive to Toll-like receptor 2-dependent bacterial ligands: Implications for host-microbial interactions within the gut. Antigen sampling across epithelial limitations and induction of mucosal immune responses. Lamina propria dendritic cells in the physiology and pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Generation of T follicular helper cells is mediated by interleukin-21 however unbiased of T helper 1, 2, or 17 cell lineages. A protective perform for interleukin 17A in T cell-mediated intestinal irritation. Interactions among dendritic cells, macrophages, and epithelial cells within the gut: Implications for immune tolerance. Mucosal interplay amongst commensal and pathogenic micro organism: Lessons from flagellin and Toll-like receptor 5. M cells as ports of entry for enteroinvasive pathogens: Mechanisms of interplay, penalties for the disease process. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Small intestine lamina propria dendritic cells promote de novo era of Foxp3 T reg cells by way of retinoic acid. Intestinal IgA synthesis: A primitive type of adaptive immunity that regulates microbial communities in the intestine. Expansion of alpha beta T-cell receptor-bearing intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes after microbial colonization in germ-free mice and its independence from thymus. A elementary role for interleukin-21 in the era of T follicular helper cells. Neuroimmune interactions: potential goal for mitigating or treating intestinal radiation damage. Isolation and characterization of resident macrophages from guinea pig and human gut. A evaluate of the physiological and immunological functions of biliary epithelial cells: targets for primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis and drug-induced ductopenias. The interaction of intestinal epithelial cells and intraepithelial lymphocytes in host protection. Role of mast cells in intestinal mucosal perform: Studies in fashions of hypersensitivity and stress. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in mucosal homeostasis on the intestinal epithelial barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. These micro organism are deeply involved in host energy metabolism, biotransformation, immune system, improvement, and so on. Although intestine microbiome has massive variety and can be affected by many components like sex, age, food regimen, and xenobiotics, the human gut microbiota are dominated by 5 bacterial phyla: Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Verrucomicrobia (Tremaroli and B�ckhed, 2012). Since the intestine is the primary location of food digestion, nutrient adsorption, and xenobiotic metabolism, the biotransformation in gastrointestinal tract is highly associated to our well being and multiple illnesses, such as weight problems, diabetes, and cancers (Gill et al. The giant gene pool and diversity of gut bacteria enable them to have powerful functionality to process many substrates in intestine. However, these plant polysaccharides are important power sources of gut micro organism and the merchandise of fermentation may be sequentially absorbed by human as substances of power source or signaling molecules between micro organism and host (Flint et al. For instance, bile acids are primarily synthesized in liver, then released into the intestine tract to digest food, take in cholesterol, and lipid-soluble nutritional vitamins and then back to human body by way of colon epithelial cells absorption, which is recognized as hepatoenteral circulation (Cowen et al. In this course of, micro organism can biotransform major bile acids to secondary bile acids by a sequence of reactions together with deconjugation, dehydrogenation, and dehydroxylation (Ridlon et al. The products of bile acid biotransformation carried out by bacteria are closely related to host metabolism and ailments. Gut tract can also be incessantly uncovered to xenobiotics, together with drugs, heavy metals, and other hazardous substances. Gut microbiota can change the forms of xenobiotics, which may significantly alter the toxicity of xenobiotics, like arsenic and mercury (Syversen and Kaur, 2012; Rowland, 1988; Van de Wiele et al. In some cases, similar to activation of medication and detoxification of heavy metals, the pretreatment of xenobiotics by intestine bacteria could presumably be helpful to host (Gingell et al. On the other hand, bacteria-metabolized xenobiotics could produce extra toxic metabolites than parent compounds to host body (Rowland et al. Gut micro organism can also re-activate xenobiotics that are already detoxified by host and excreted to intestine, which impedes the toxin efflux and prolongs the interval of xenobiotic motion (Rowland, 1988; Sousa et al. This article briefly discusses three major areas of gut biotransformation: meals fiber digestion, bile acid biotransformation, and xenobiotic metabolism, such as drug and heavy metals (B�ckhed et al. It is certainly not a whole record of biotransformation reactions by intestine microbiome. Germ-free animals are powerful instruments to explore how the presence of gut bacteria influences xenobiotic metabolism and host physiological conditions under specific treatments (Swann et al. However, the interspecies difference causes totally different physiological situations and intestine microbiome profiles. And, human subjects are very tough to control and standardize the experimental circumstances.
Isoptin 120 mg online
Each of these actions is associated with exact changes in muscle contractions blood pressure wrist monitor 40 mg isoptin with visa. The length of the system varies amongst species pulse pressure fitness isoptin 40 mg buy discount on line, shorter tracts in carnivores, and longer extra complicated tracts in herbivores. In addition, herbivores require a fermentation chamber to digest cellulose, the forestomachs in ruminants and camelids or an enlarged cecum in equids, rodents, and lagomorphs. Caustic substances, some pathogens, heat and electricity could lead to thermal and chemical erosions or ulcerations of the oral mucosa, however mucus membranes heal quickly. At varied places throughout the tract, extraintestinal substances are added to the ingesta. Saliva also incorporates a bacteria-rich flora and no less than in humans, opiorphin, an analgesic. The lining epithelium is keratinized in swine, equids, ruminants, rats, and mice and nonkeratinized in carnivores and humans. The muscularis is striated in ruminants and dogs, clean in equids (distal third) which might be unable to vomit, and variably combined in different species. Mice and rats, that have primarily striated muscle of their esophagus, are additionally unable to vomit (Treuting et al. Submucosal mucus glands are current all through the esophagus in swine, canine, and people and at the pharyngeal junction in cats, equids, and ruminants. The robust muscular contractions of the esophagus, together with its poor blood supply and lack of serosa, mean that healing from caustic or penetrating wounds renders a poor prognosis for a functional return to normalcy. Insofar as therapy for caustic toxin ingestion what burns going down may even burn coming again up, so typically speaking induction of vomition is contraindicated (Gelberg, 2013). The contracted musculature of the upper esophageal sphincter relaxes to allow movement of the swallowed bolus into the proximal portion of the esophagus. Relaxation of the sphincter and subsequent restoration of tone require precise management by regulatory techniques that might be disrupted by toxins. When the bolus has entered the higher esophagus, an aborally progressing entrance of contraction of the round muscle layer begins at the top of the esophageal physique, seemingly as a continuation or extension of the forceful contraction of the upper esophageal sphincter that follows its rest (Conklin and Christensen, 1994). A ring of contraction above the swallowed bolus moves down the esophagus, propelling the bolus toward the stomach. While the bolus remains to be progressing through the mid-portion of the esophagus, the contracted ring of circular muscle that varieties the decrease esophageal sphincter relaxes and is totally relaxed by the time the bolus reaches the gastroesophageal junction. The proximal abdomen (fundus and higher corpus) typically relaxes, whereas the swallowed bolus continues to be in the esophageal body and has not yet handed the decrease esophageal sphincter (receptive relaxation). After the bolus has entered the stomach, the fundus and corpus muscles relax in order that a large volume can be stored in the upper abdomen without considerably rising intragastric strain (accommodation). As the volume within the abdomen increases, a subjective sensation of satiation develops (Burks and Villar, 1980). These fatty acids are directly absorbed into the bloodstream together with sodium and chloride. Most medical illness of the forestomachs pertains to disruptions in coordinated motility and adjustments in pH. Equids and a few rodents have stomachs that are divided into proximal stratified and aboral glandular parts. Swine have solely a small stratified portion that directly surrounds the esophageal os. The abomasum/C3 capabilities much like the stomachs of monogastric mammals (Gelberg, 2016). The secretory gastric, small intestinal, and colonic mucosae are lined by a single layer of columnar epithelial cells. The mucosal floor of the abdomen is covered by mucus-secreting cells and, in the fundus and corpus, gastric crypts. The glandular abdomen (abomasum, C3) is responsible for enzymatic and hydrolytic digestion of ingesta. There are three types of exocrine cells within the stomach: parietal, chief, and mucus. Mucus cells of the floor and gastric pits produce bicarbonate and an unstirred protecting layer on the cell surface. Enteroendocrine cells (G cells) of the gastric pits produce serotonin, gastrin, ghrelin, somatostatin, endothelin, histamine, enteroglucagon, and different hormones. Although the reason for ulcers, apart from caustic agents and those attributable to bacteria that may survive the extremely low pH of the abdomen (Helicobacter spp. Gastric ulcers induced by alcohol consumption are dose associated with effects starting from a decrease in mucus production and bicarbonate secretion to leakage of bicarbonate and electrolytes to vascular harm (Rousseaux and Haschek, 2010). Anecdotal proof suggests that a propensity in the course of ulcer formation could additionally be hereditable (Gelberg, 2016). Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Gastrointestinal Toxicity 145 Tobacco products increase gastric reflux, pepsinogen-1, and basal acid output while lowering mucus production and pancreatic bicarbonate secretion resulting in duodenal ulceration (Hojgaard et al. Mucus secretion is lowered as a outcome of decreases in total mucus neck cell numbers and neck cell mucus volume. Gastric mucosa damaged by publicity to high concentrations of sodium chloride may be repaired over a period of 6 h by migration of epithelial cells from the glands (Svanes et al. Rapid epithelial restitution of the superficial mucosa is doubtless one of the main defense mechanisms of the abdomen, small gut, and colon (Feil et al. Preservation of the basement membrane in the area of damage is crucial for prevention or repair of lesions. The liquid component of a mixed meal usually empties faster than the solid component. Low pH or high osmolarity tends to lower the speed of gastric emptying (Read, 1994). Effective gastric emptying requires coordinated propulsive contractions within the antrum that progress to the pyloric canal along with properly timed relaxation of the upper duodenum (Lin, 1994). Some drugs and toxins cut back the speed of gastric emptying by producing contractions of the duodenum that abolish the antral�duodenal strain gradient required for efficient emptying (Burks, 1994; Malbert et al. Because the alimentary lumen is markedly acidic in the stomach and slightly alkaline within the gut, the degree of ionization of xenobiotics varies by the pKa(s) of the molecule. Nonionized varieties cross cell membranes more readily and can pass into the mucosa depending on the local pH. Each villus consists of 2000�8000 epithelial cells and is surrounded by 6�14 crypts of Lieberkuhn. They produce bacteriocidal cryptdins, lysins, peptidases, and lysozymes which will serve to defend crypt cells. Paneth cell perform and microbial composition range amongst strains of mice suggesting a genetic influence of the host (Sonnenberg et al. Paneth cells reside within the lower portion of the crypt and have a life span of roughly 21 days.
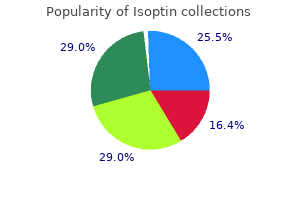
40 mg isoptin cheap otc
Several types of intrinsic neurons are also current in the adrenal medulla (Holgert et al arteria spanish buy isoptin 240 mg without a prescription. These embody large neurons which would possibly be usually present in clusters and appear to be postganglionic sympathetic neurons (Dagerlind et al lipo 6 arrhythmia buy isoptin 240 mg fast delivery. Tracer studies have demonstrated that adrenal medullary neurons project axons into the splanchnic nerve (Dagerlind et al. Because of the complexity of the adrenal nerve provide, surgical denervation for experimental purposes is difficult to obtain, and the results of different procedures may be difficult to evaluate (Kanamatsu et al. The presence of abundant secretory granules is demonstrated by immunoreactivity for CgA. For most functions, fluorescence and different histochemical methods may now get replaced by immunohistochemical approaches that allow retrospective analysis of catecholamine-synthesizing capability in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections (Lloyd et al. Immunohistochemical research of the adrenal medulla have been facilitated (Tischler, 1995a,b) by the development of microwave antigen retrieval (Shi et al. In some cases, immunohistochemistry may additionally be utilized to instantly reveal shops of catecholamines or different fragrant amines (Lloyd et al. Immunohistochemistry can be employed to acquire details about the relative numbers of secretory granules inside individual cells in a tissue part by staining for chromogranin A (CgA) or other granule constituents. Various immunohistochemical markers have been used to localize the nonchromaffin cell types within the adrenal medulla. Sustentacular cells and Schwann cells, for example, could be recognized by immunoreactivity for S-100 protein, a widely distributed glial marker (Cocchia and Michetti, 1981). The innervation of the adrenal medulla may also be visualized immunohistochemically, thereby eliminating the need for enzyme histochemistry to reveal acetylcholinesterase activity (Coupland, 1965) for that purpose. A highly delicate marker for visualizing axon terminals within the adrenal medulla is vesicular acetylcholine transporter (Tischler et al. Other markers which have been studied include choline acetyltransferase (Murabayashi et al. The pharmacology and molecular biology of those transporters have been extensively reviewed (Henry et al. Further regulation of secretion could also be provided in an autocrine or paracrine method by substances secreted by chromaffin cells themselves, or by the extracellular breakdown products of these substances. Possible examples embrace inhibitory effects of enkephalin, substance P, or chromogranin fragments (Feldman and Eiden, 2003; Mahapatra et al. Both neural and nonneural alerts have been implicated within the improvement of adrenal medullary pathology. Adrenal medullary peptides and amines coexist in the same cells and in the identical secretory granules. There are additionally species variations within the prevalence of various regulatory peptides and granins. Different strains of rats have been reported to have differing content of CgB (Hansen et al. In addition, the adrenal medulla is innervated by axons that contain nitric oxide synthase (Marley et al. Nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors cooperatively stimulate the secretory response by increasing Ca2 � flux and activating protein kinase C. Chromaffin cells utilize Ca2 � from each extracellular fluid and intracellular shops as a second messenger (Garcia-Sancho and Verkhratsky, 2008). Following neural stimulation, extracellular Ca2 � may enter a chromaffin cell both immediately through a nicotinic cholinergic receptor channel or via a voltage-gated channel. Chromaffin cells categorical a number of forms of voltage-gated Ca2 � channels (Fox et al. Ca2 � may be released from intracellular stores within the endoplasmic reticulum and different organelles via ryanodine/caffeine receptors (Pan et al. Studies suggest that Ca2 � could have an effect on completely different mobile features relying upon its route of entry into the cell, its intracellular localization, and its local focus (Garcia-Sancho and Verkhratsky, 2008). Increased cytosolic Ca2 � results in migration of secretory granules to the cell membrane and to Ca2 �-mediated exocytosis. Small, synaptic-like vesicles, which appear to be the main locus of the vesicle membrane protein synaptophysin (Winkler, 1997), could make the most of a considerably different secretory equipment. The intracellular signaling events that regulate hormone secretion exert each short- and long-term effects on different cell capabilities. Chromaffin cell capabilities could be additional modified by steroid hormones from the adrenal cortex (Schinner and Bornstein, 2005) and extracellular matrix (Doupe et al. In addition, a person growth issue can generally produce either proliferation or neuron-like differentiation, relying on its concentration (Powers et al. These observations counsel that messages converging on the exterior of a chromaffin cell utilize each parallel and convergent intracellular pathways to coordinate their effects. Toxic Responses of the Adrenal Medulla 193 Both strain- and age-dependent differences in adrenal medullary physiology have been described in rats. Under resting conditions, normal younger grownup rats of generally studied strains apparently have comparable levels of plasma catecholamines. However, marked differences have been demonstrated between strains in response to stress (McCarty and Kopin, 1978). Some strain differences may reflect variations in cholinergic innervation of the adrenal medulla. The practical regulation of the rat adrenal medulla undergoes two age-dependent transitions, associated predominantly to modifications in innervation. The first occurs after the tip of the primary week of life, with the onset of splanchnic nerve activity. This interval is marked by will increase in catecholamine and neuropeptide synthesis (Coulter et al. Nerve exercise in Wistar rats four hundred days old is more than twice that of rats a hundred days old (Ito et al. However, age-related differences within the composition of chromaffin granules have been reported (Santer and Hann, 1993). Mitoses are readily recognized in histological sections of postnatal rat adrenals, but are rare after the age of 60 days. Adult rat chromaffin cells have been subsequently regarded for many years as basically postmitotic and terminally differentiated. Cell kinetic research based on incorporation of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) in vivo estimate a renewal fee of approximately 1% per day for grownup rat chromaffin cells (Verhofstad, 1993). These and even larger variations could be attributable to variations in animal maintenance, such as group housing versus solitary housing (Tischler et al. Inter-experimental comparisons should therefore be made with caution, particularly for older research without rigorously managed maintenance conditions.
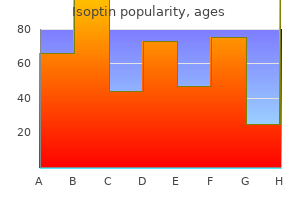
240 mg isoptin generic fast delivery
An early physiological apoptotic wave arteria rectalis inferior cheap isoptin 240 mg with amex, which happens among the many germ cells through the first division and differentiation of germ cells blood pressure of 170100 order isoptin 240 mg overnight delivery, is necessary for the development of normal mature spermatogenesis (Russell et al. Adult values for spermatogenic characteristics corresponding to testicular weight, daily sperm production per individual, Sertoli cell quantity per particular person, seminiferous tubule volume, and seminiferous tubule diameter are achieved. To optimize the potential for producing offspring, the male adapts to his setting. Examples of adaptation to improve reproductive success include seasonal breeding to permit for maximal manufacturing of spermatozoa in the course of the mating season and mating groups to enable for passage of genetic material from one male to numerous females. There are also numerous different environmental factors that affect reproductive potential in the grownup male. Either an elevated or decreased environmental temperature can be detrimental to spermatogenesis. Exposure to environmental pollution following industrialization of the world is blamed for the decline within the adult reproductive capacity of quite a few animal species and humans (Bendvold, 1989; Bendvold et al. These might intrude with gonadal growth in males and have been proposed as an important reason for a decreased variety of spermatozoa in human ejaculate, elevated male reproductive tract anomalies, and situations of male tract cancers. In reality, current findings present an overlap in sperm concentration, motility, and morphology between fertile and infertile males (Winker and Rudiger, 2006). Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a standard clinical finding in growing older people and canine with probably detrimental results on life. Impotence increases with aging and limits the natural deposition of semen in the feminine reproductive tract. Not only is there a reduction within the variety of sperm cells, but there are additionally changes in motility of sperm cells and increases in abnormal forms (Blackman, 1990). As measured by a decline in serum testosterone concentrations, endocrine perform of the testis declines with age. There are various stories on the consequences of age on Leydig cell number (de Kretser and Kerr, 1994). In the human there are stories of decreased, increased, and no distinction in older men in comparability with young men. However, most knowledge assist an age-related decline in Leydig cell number with or without an effect on spermatogenesis (Kaler and Neaves, 1978; Neaves and Johnson, 1985; Neaves et al. The stallion demonstrates a rise in Leydig cell number as a lot as 20 years of age (Johnson and Neaves, 1981). A decrease in sexual activity is associated with the decline in serum testosterone focus (Austin and Short, 1982). There can additionally be decreased fertilizing capacity of the spermatozoa produced by the aged male (Bishop, 1970). A decline within the number of Sertoli cells per testis is present in aged people and rats (Johnson, 1986b; Wang et al. Additional adjustments seen in the seminiferous tubules associated with advanced age are elevated thickness of the encompassing boundary tissue because of a reduction within the whole length of the seminiferous tubule (de Kretser et al. The increased thickening of the boundary tissue could cause a lowered move of vitamins or hormone indicators to and from the seminiferous epithelium (Johnson, 1986b). The reason for the age-related decline in reproductive potential is complicated and should range among species. The need for information on the results of aging on the reproductive organs of humans is becoming more and more important as couples wait later in life to have youngsters. As the effects of male reproductive toxicants interact with the getting older course of, the complexity of male reproductive aging increases. Courtship contains numerous patterns of behavioral exercise to inform the opposite intercourse that one is physiologically able to copulate. Also, these behaviors arouse 52 Anatomy and Physiology of the Male Reproductive System and Potential Targets of Toxicants sexual curiosity within the potential partner. The premating ritual of the peacock is a outstanding display of courtship signals directed at its companion. Mammals have more delicate, but still distinct, courtship alerts to get the eye of their partners. The mare, however, squeals, urinates, strikes or kicks, and lifts her tail earlier than she receives the stallion. When near males, receptive feminine rats wiggle their ears and dart about to get attention. Likewise, receptive feminine monkeys undertake a attribute mating place that attracts the males. In ferrets and minks, the vulva swells enormously, and in canine, more moderate vulvar swelling occurs at the time of estrus. The scent of estrus female dogs attracts dogs from the entire neighborhood, even when saved indoors. If the male is simply too hungry, if there are predators present that have to be prevented, or if animals have been conditioned by electrical shock to not mate in a given environment, animals could not mate (Herbert, 1972). In addition, sexual habits relies on the suitable hormonal secretions of both sexes. Alterations in hormonal status (as in endocrine disturbances or toxicant-induced well being alterations) can cut back fertility by lowering libido and rising the failure of males to display regular sexual behavior. It ought to help within the understanding of mechanisms that drive male reproductive processes and enhance the design of experiments to take a look at the effect and severity of potential toxicants on numerous aspects of male reproductive anatomy and physiology. Insulin augmentation of testosterone production in a main culture of rat testicular cells. Insulin-like progress components as intraovarian regulators of granulosa cell progress and function. Quantitative testicular histology and comparisons between daily sperm production as determined histologically and by daily sperm output. A critical evaluation of methods for evaluation of spermatogenesis from seminal traits. Detection of alterations in testicular and epididymal perform in laboratory animals. Fertility of bovine spermatozoa from rete testis, cauda epididymidis, and ejaculated semen. Daily spermatozoal manufacturing, epididymal spermatozoal reserves and transit time of spermatozoa via the epididymis of the rhesus monkey. Anatomy and Physiology of the Male Reproductive System and Potential Targets of Toxicants fifty three Anway, M. Molecular characterization of the genital organizer: Gene expression profile of the mouse urethral plate epithelium. Changes within the pituitary-testicular axis with age monographs on endocrinology: the pituitary and testis. Direct inhibitory impact of glucocorticoids upon testicular luteinizing hormone receptor and steroidogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone and its agonist inhibit testicular luteinizing hormone receptor and steroidogenesis in immature and adult hypophysectomized rats. Effects of expression of human or bovine progress hormone genes on sperm manufacturing and male reproductive performance in 4 traces of transgenic mice.
Syndromes
- Grades 1 and 2 involve a smaller amount of bleeding. Most of the time, there are no long term problems as a result of the bleeding.
- Damage to the blood vessel as the needle and catheter are inserted
- Activated charcoal, especially if other substances were also taken
- Occur in single lesion or clusters, often at the site of skin injury
- Numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness
- Bladder cancer
- Cultures from the cervix for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and other organisms
- Diarrhea, worse on high-fat diet
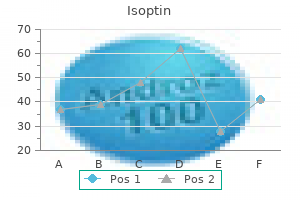
Isoptin 240 mg generic
Toxicological Sciences: An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology arteria radialis 240 mg isoptin generic free shipping, 76 heart attack news cheap 240 mg isoptin amex, 190�200. Diethyldithiocarbamate and structurally-related compounds and the uptake and launch of noradrenaline within the coronary heart of the rat. Effects of tetramethylthiuram disulfide and structurally-related compounds on the dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity within the rat and hamster. Divalent cation inhibition of hormone launch from isolated adenohypophysial secretory granules. Peripheral administration of metastin induces marked gonadotropin launch and ovulation in the rat. Evidence that atrazine and diaminochlorotriazine inhibit the estrogen/progesterone induced surge of luteinizing hormone in female Sprague�Dawley rats with out changing estrogen receptor motion. Toxicological Sciences: An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology, 79, 278�286. An inhalation reproductive toxicity research of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (D4) in female rats utilizing multiple and single day publicity regimens. Maturation of the inhibitory suggestions motion of oestrogen on follicle-stimulating hormone secretion within the immature feminine rat: a job for alpha-foetoprotein. Ovarian follicular development resulting in first ovulation and accompanying gonadotrophin ranges as studied in the unilaterally ovariectomized rat. Aging alters norepinephrine release in the medial preoptic space in response to steroid priming in ovariectomized rats. Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion by kisspeptin/dynorphin/ neurokinin B neurons within the arcuate nucleus of the mouse. The Journal of Neuroscience: the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 29, 11859�11866. Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone pulse generator activity in the hypothalamus of the goat. Epidermal growth issue tyrosine kinase receptors and the neuroendocrine control of mammalian puberty. Distribution of 63Ni in rabbit tissues following intravenous injection of 63NiCl2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 86, 2506�2510. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the estrogenic, androgenic, and progestagenic potential of two cyclic siloxanes. Toxicological Sciences: An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology, 96, 145�153. Early hormonal modifications during valproate or carbamazepine therapy: a 3-month examine. Identification of drug-induced hyper- or hypoprolactinemia within the feminine rat based on basic and reproductive toxicity research parameters. Delayed adverse results of neonatal publicity to polymeric nanoparticle poly(ethylene glycol)-block-polylactide methyl ether on hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis improvement and performance in Wistar rats. Effects of cadmium chloride on ovulation and on induction of sterility within the feminine golden hamster. Subchronic toxicity research on perfluorooctanesulfonate potassium salt in cynomolgus monkeys. Toxicological Sciences: An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology, 68, 249�264. Effect of neonatal prolactin deficiency on prepubertal tuberoinfundibular and tuberohypophyseal dopaminergic neuronal activity. A two-generation reproductive toxicity examine of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (D4) in rats uncovered by whole-body vapor inhalation. The Journal of Neuroscience: the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 19, 2037�2050. Development of a technique for and evaluation of pulsatile luteinizing hormone secretion in juvenile and grownup male mice. Distribution of 14C-atrazine following an acute lactational exposure within the Wistar rat. Effect of Environmental Toxicants on the Neuroendocrine Control of Female Reproduction 321 Stoker, T. The dithiocarbamate fungicide thiram disrupts the hormonal control of ovulation in the feminine rat. Characterization of pregnancy outcome following thiram-induced ovulatory delay within the female rat. Delayed ovulation and being pregnant end result: effect of environmental toxicants on the neuroendocrine management of the ovary(1). The effects of atrazine metabolites on puberty and thyroid function within the male Wistar rat. Toxicological Sciences: An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology, sixty seven, 198�206. Abnormal fertilization is liable for reduced fecundity following thiram-induced ovulatory delay within the rat. Toxicological Sciences: An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology, eighty four, 38�48. Release of norepinephrine within the preoptic area prompts anteroventral periventricular nucleus neurons and stimulates the surge of luteinizing hormone. Sexual differentiation of kisspeptin neurons liable for sex distinction in gonadotropin release in rats. Lack of pulse and surge modes and glutamatergic stimulation of luteinising hormone release in Kiss1 knockout rats. In vitro simulation of prepubertal adjustments in pulsatile luteinizing hormone launch enhances progesterone and 17 beta-estradiol secretion from immature rat ovaries. Neurokinin B and dynorphin A in kisspeptin neurons of the arcuate nucleus participate in era of periodic oscillation of neural exercise driving pulsatile gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion within the goat. The Journal of Neuroscience: the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 30, 3124�3132. Acute effects of adrenergic receptor blocking medicine and neuroleptic brokers on pulsatile discharges of luteinizing hormone in the ovariectomized rat. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone in peripheral plasma and hypothalamus of normal and ovariectomized rats. Changes in ovarian luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone receptor content and in gonadotropin-induced ornithine decarboxylase activity throughout prepubertal and pubertal improvement of the female rat. Vaginal cyclicity, sexual receptivity, and consuming habits of the feminine rat following remedy with chlordecone. Gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor mediated inhibition of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons is suppressed by kisspeptin-G protein-coupled receptor 54 signaling.
Isoptin 120 mg buy amex
The levels are forty mg for each men and women pulse pressure heart rate buy discount isoptin 40 mg, infants to thirteen years heart attack telugu movie review discount 240 mg isoptin mastercard, and forty five mg for ages 14 and older. It ought to be famous that health-care suppliers can prescribe intakes higher than the Tolerable Upper Intake Level; for example, to appropriate iron deficiency anemias. Information on thresholds of total-body shops and hepatic concentrations of iron associated with liver cirrhosis and fibrosis are mentioned in subsequent sections. The physique lacks an efficient means to rid itself of excess iron; thus, the homeostatic mechanisms for iron can easily be overcome in iron overload circumstances. As a consequence, conditions or exposures that markedly elevate whole-body iron can result in a wide spectrum of symptoms and pathologies. In people who survive, medical indicators of hepatic morbidity embody jaundice, elevated serum transaminase actions, and extended prothrombin time. Histological findings are usually most pronounced in periportal areas and include steatosis and hemorrhagic necrosis of the hepatic parenchyma with minimal infiltration of inflammatory cells. Mitochondria are critical intracellular targets; damage of those organelles ends in clinical hepatotoxicity. Treatment of overdosage can be achieved through gastric lavage and supportive measures, and in some circumstances the iron chelator, desferrioxamine, is indicated (Robertson and Tenenbein, 2005). The term is derived from elevated pigment in tissues due to iron, which was initially believed to originate from blood. This illness entails the deposition of extreme iron in parenchymal cells of many organs, including the liver, which finally results in cell injury. Other conditions which would possibly be associated with iron overload, elevated liver iron burdens, and hepatotoxicity in people are referred to as acquired (secondary) iron overload illnesses (Kuntz and Kuntz, 2006). In these circumstances, the extreme intestinal absorption of iron occurs secondary to other underlying defects. Secondary iron overload ailments include anemias as a outcome of faulty erythropoiesis, such as thalassemia major; persistent liver diseases, similar to alcoholic cirrhosis; and different inherited or congenital defects, such as porphyria cutanea tarda and neonatal iron overload. Excessive iron ingestion, either therapeutic or dietary, can even end in clinically significant iron overload and produce hepatotoxicity. Liver is the necessary thing organ of iron disposition and the expression of iron regulatory genes and proteins that maintain iron homeostasis. Dysregulation of these features leads to disruption of iron homeostasis inflicting continual liver harm (Anderson and Shah, 2013). More detailed dialogue of iron overload ailments, together with iron hepatic metabolism, genetic components, clinical pathologies, scientific diagnoses, mechanisms of liver damage, and therapy, could be present in several glorious treatises (Adams and Barton, 2007; Fowler, 2008; Kuntz and Kuntz, 2006; Ramm and Ruddell, 2005). Even with the remedy, common life expectancy can be decreased by roughly 5 years (Little, 1996). Because the body lacks a mechanism to rid itself of extra iron, a rise in whole-body and hepatic iron beyond normal capability overwhelms iron homeostatic mechanisms and ends in harm to organs, together with the liver. As the disease progresses, iron deposits in midzonal and centrilobular hepatocytes, bile duct epithelia, and Kupffer cells. When the storage capability of lysosomes has been exceeded, inflammatory reactions, single-cell necrosis, and activation of macrophages occur. In people with chronic iron overload circumstances, extreme iron accumulation in the liver leads to progressive fibrosis and fibrosclerosis, which can ultimately lead to cirrhosis and hepatic carcinoma (Adams and Barton, 2007; Kuntz and Kuntz, 2006). In people, hepatic iron ranges typically must surpass a critical or threshold concentration of 4000 mg g� 1 wet weight (normally 200 mg g� 1) for the development of fibrosis or cirrhosis to occur. In addition to the optimistic correlations between hepatic iron levels and hepatotoxicity, other proof that implicates iron because the proximate toxicant in iron overload ailments stems from studies by which lowering the hepatic iron concentration, by way of either venesection or chelation remedy, has resulted in clinical improvement (Bacon and Britton, 1989; Salgia and Brown, 2015). Desferrioxamine and Deferasirox are the chelators of option to deal with both acute and chronic iron overload. Iron chelation has additionally been proposed for the remedy of iron overload-related cancers (Buss et al. Both oblique and direct strategies can be found for the analysis of symptomatic individuals. Direct strategies for the determination of elevated iron shops include checks which are invasive and noninvasive. Various fashions of iron overload and hepatotoxicity have been studied in experimental animals. Hepatotoxicity can be constantly demonstrated, whereas fibrosis and cirrhosis are tougher to reproduce in these experimental fashions. Iron-rich diets are incessantly used to examine iron overload and iron-induced liver damage and fibrosis (Das et al. Hereditary hemochromatosis is brought on by mutations within the hereditary hemochromatosis protein (Hfe), transferrin-receptor 2 (TfR2), hemojuvelin (Hjv), hepcidin, or ferroportin genes. Various genetic models with these gene mutations have been created to research iron overload-induced hepatotoxicity. Disruption of each Hfe and TfR2 triggered extra severe hepatic iron overload with extra advanced lipid peroxidation, irritation, and portal fibrosis than was observed with the disruption of both gene alone (Delima et al. Several mechanisms of hepatic injury resulting from chronic iron overload have been postulated (Kuntz and Kuntz, 2006; Ramm and Ruddell, 2005). These mechanisms include: (1) induction of lipid peroxidation and reactive oxygen intermediates, (2) lysosomal membrane fragility and leakage, most probably because of iron-catalyzed peroxidation of lipids, (3) peroxidative damage to mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum that leads to dysfunction of those organelles, (4) fibrogenic effects of iron overload by way of a quantity of mechanisms including direct stimulation of collagen synthesis or activation of stellate cells, and (5) a mix of any of the above. Metabolic issues, hemolytic conditions, alcohol abuse, and different types of persistent liver disease can all contribute to acquired (or secondary) hemochromatosis. In a study using a dietary iron overload mannequin, lipid peroxidation was noticed in vivo in rats fed ferrocene (Dresow et al. In research on patients with hemochromatosis, elevated levels of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal adducts, shaped on account of membrane lipid peroxidation, have been found in liver biopsies. Adduct ranges decreased following venesection therapy, which decreased hepatic iron levels (Houglum et al. Decreased ranges of serum and liver antioxidants are found in iron-overloaded animals and hemochromatosis patients, offering additional proof for the position of lipid peroxidation in iron-induced hepatotoxicity (McCullough and Bartfay, 2007). Although initially helpful due to sequestration of labile iron and promoting its biliary excretion, iron accumulation ultimately results in lysosomal damage. Lysosomal fragility has been demonstrated in iron-overloaded sufferers (Seymour and Peters, 1978) and in iron-overloaded rats (Hultcrantz et al. In rats, experimental iron overload induced by dietary iron carbonyl brought on hepatic lysosomes to become pleomorphic, increased the fragility and decreased the fluidity of lysosomal membranes, and elevated intralysosomal pH (Myers et al. In isolated mitochondria, peroxidative injury has been associated with swelling and lysis, inhibition of enzymes concerned in glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and inhibition of oxidative respiration (Bacon and Britton, 1989; Thakerngpol et al. Disruption of calcium homeostasis might play a task in toxicity observed after iron overload, as dietary iron overload has been proven to improve the discharge of mitochondrial Ca2 � (Masini et al. Treatment of isolated hepatocytes with ferric-hydroxyquinoline caused mitochondria to bear mitochondrial permeability transition, resulting in the release of cytochrome c and potentially selling apoptotic cell demise (Rauen et al. Ferrocene-induced iron-overloaded mice had mitochondria dysfunction, along with overproduction of oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation (Liu et al. The improvement of hepatic fibrosis noticed in iron overload may result, a minimal of partially, from iron-induced perturbation of collagen biosynthesis (Weintraub et al. Hepatocytes in mice treated with carbonyl iron or iron dextran have marked overexpression of cyclin D1, a protein concerned in cell cycle regulation, which might contribute to preneoplastic proliferation (Troadec et al.
Discount isoptin 120 mg without a prescription
Early menopause blood pressure medication help lose weight 40 mg isoptin discount fast delivery, association with tobacco smoking blood pressure pills 240 mg isoptin order with mastercard, coffee consumption and other life-style factors: a cross-sectional research. Methoxychlor immediately affects ovarian antral follicle progress and atresia by way of Bcl-2- and Bax-mediated pathways. Methoxychlor metabolites might cause ovarian toxicity by way of estrogen-regulated pathways. Effects of chosen endocrine disruptors on meiotic maturation, cumulus growth, synthesis of hyaluronan and progesterone by porcine oocyte-cumulus complexes. Molecular goal of endocrine disruption in human luteinizing granulosa cells by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: inhibition of estradiol secretion because of decreased 17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase cytochrome P450 expression. Wnt4/5a signalling coordinates cell adhesion and entry into meiosis throughout presumptive ovarian follicle growth. Simultaneous effect of lead and cadmium on granulosa cells: a cellular model for ovarian toxicity. Effect of co-exposure to lead and cadmium on antioxidant status in rat ovarian granulose cells. Follicle progress is inhibited by benzo-[a]-pyrene, at concentrations consultant of human exposure, in an isolated rat follicle culture assay. Cellular interactions that management primordial follicle improvement and folliculogenesis. Bone morphogenetic protein-4 acts as an ovarian follicle survival factor and promotes primordial follicle development. Kit ligand and basic fibroblast development factor interactions in the induction of ovarian primordial to major follicle transition. Basic fibroblast progress issue induces primordial follicle development and initiates folliculogenesis. Platelet-derived growth factor modulates the primordial to primary follicle transition. Actions of anti-mullerian hormone on the ovarian transcriptome to inhibit primordial to main follicle transition. The pesticide heptachlor impacts steroid hormone secretion in isolated follicular and luteal cells of rat. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, a hundred and forty four, 76�84. Lead accumulation in human ovarian follicular fluid, and in vitro impact of lead on progesterone production by cultured human ovarian granulosa cells. TrkB receptors are required for follicular development and oocyte survival in the mammalian ovary. Direct actions of kit-ligand on theca cell progress and differentiation during follicle growth. Kit ligand actions on ovarian stromal cells: effects on theca cell recruitment and steroid production. Estrogen receptor alpha overexpressing mouse antral follicles are sensitive to atresia induced by methoxychlor and its metabolites. Bisphenol A inhibits follicle progress and induces atresia in cultured mouse antral follicles independently of the genomic estrogenic pathway. Bisphenol A and reproductive well being: replace of experimental and human evidence, 2007�2013. Ablation of Bcl-2 gene expression decreases the numbers of oocytes and primordial follicles established in the post-natal feminine mouse gonad. Ovarian development in Wistar rat handled prenatally with single dose diisobutyl phthalate. Oocyte-specific deletion of Pten causes untimely activation of the primordial follicle pool. Neonatal exposure to bisphenol A or diethylstilbestrol alters the ovarian follicular dynamics in the lamb. Estrogen regulation of thecal cell steroidogenesis and differentiation: thecal cell-granulosa cell interactions. Ah receptor agonists as endocrine disruptors: antiestrogenic activity and mechanisms. In utero and lactational publicity to 2,three,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and a pair of,three,4,7,8-pentachlorodibenzofuran reduces progress and disrupts reproductive parameters in female rats. Neurotrophin-4/5 and neurotrophin-3 are current inside the human ovarian follicle however seem to have different paracrine/autocrine functions. Effects of 1-bromopropane, 2-bromopropane, and 1,2-dichloropropane on the estrous cycle and ovulation in F344 rats. Cigarette smoking accelerates the event of diminished ovarian reserve as evidenced by the clomiphene citrate problem test. Ovarian endocrine disruption underlies untimely reproductive senescence following environmentally relevant continual exposure to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist 2,three,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Follicle-stimulating hormone induces useful receptors for fundamental fibroblast growth think about rat granulosa cells. Prenatal publicity to chromium induces early reproductive senescence by increasing germ cell apoptosis and advancing germ cell cyst breakdown within the F1 offspring. Cadmium stimulates transcription of the cytochrome P450 facet chain cleavage gene in genetically modified steady porcine granulosa cells. The position of neurotrophin receptors in feminine germ-cell survival in mouse and human. Involvement of apoptosis in 4-vinylclohexene diepoxide-induced ovotoxicity in rats. Enhanced expression of Bax in small preantral follicles during 4-vinylcyclohexene diepoxide-induced ovotoxicity within the rat. Higher affinity of the carboxyl-terminal truncated forms for heparan sulfate proteoglycans on the ovarian granulosa cell. Nobox is a homeobox-encoding gene preferentially expressed in primordial and growing oocytes. Effects of methoxychlor treatment of pregnant mice on feminine offspring of the handled and subsequent pregnancies. Neonatal exposure to technical methoxychlor alters pregnancy consequence in feminine mice. Rapid induction of ovarian granulosa cell tumors by 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene in neonatally estrogenized mice. Similarity of bisphenol A pharmacokinetics in rhesus monkeys and mice: relevance for human publicity. Follistatin288 regulates germ cell cyst breakdown and primordial follicle assembly in the mouse ovary. Hippo signaling pathway reveals a spatio-temporal correlation with the scale of primordial follicle pool in mice. Notch2 is required in somatic cells for breakdown of ovarian germ-cell nests and formation of primordial follicles. Vascular endothelial progress factor stimulates the primary to secondary follicle transition in bovine follicles in vitro.
Buy isoptin 240 mg with amex
Apoptosis pattern elicited by several apoptogenic brokers on the seminiferous epithelium of the adult rat testis prehypertension early pregnancy 40 mg isoptin buy mastercard. The rate of 2 hypertension in african americans isoptin 120 mg buy low cost,5-hexanedione intoxication, not whole dose, determines the extent of testicular damage and altered microtubule assembly within the rat. In vitro functional screening as a method to establish new plasticizers devoid of reproductive toxicity. Epidemiologic proof on biological and environmental male factors in embryonic loss. Chronic administration of 4-tert-octylphenol to grownup male rats causes shrinkage of the testes and male accessory intercourse organs, disrupts spermatogenesis, and will increase the incidence of sperm deformities. Effects of busulfan on murine spermatogenesis: cytotoxicity, sterility, sperm abnormalities, and dominant deadly mutations. Induction of apoptosis in the germ cells of adult male rats after publicity to cyclophosphamide. High-resolution mapping of chromatin packaging in mouse embryonic stem cells and sperm. Sperm function in staff exposed to N,N-dimethylformamide within the synthetic leather trade. Role of epididymal inflammation within the induction of dominant deadly mutations in Fischer 344 rat sperm by methyl chloride. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, eighty three, 8087�8091. Quantitative evaluation of spermatogenesis of the rat: A revised model for the renewal of spermatogonia. Immunocytochemical localization of proteins utilized in the formation of outer dense fibers and fibrous sheath in rat spermatids: An electron microscope examine. Shedding gentle on the controversy surrounding the temporal decline in human sperm counts: a systematic review. Transcriptome evaluation of highly purified mouse spermatogenic cell populations: gene expression signatures change from meiotic-to postmeiotic-related processes at pachytene stage. Impact of the chemotherapy cocktail used to deal with testicular most cancers on the gene expression profile of germ cells from male BrownNorway rats. Insights into function of bromodomain, testis-specific (Brdt) in acetylated histone H4-dependent chromatin remodeling in mammalian spermiogenesis. Molecular determinants of nucleosome retention at CpG-rich sequences in mouse spermatozoa. Glycolysis and sperm motility: does a spoonful of sugar help the flagellum go spherical A biochemical foundation for 1,2-dibromo-3-chloropropane-induced male infertility: inhibition of sperm mitochondrial electron transport activity. Towards an understanding of the genetics of human male infertility: lessons from flies. Genome-wide analysis identifies adjustments in histone retention and epigenetic modifications at developmental and imprinted gene loci in the sperm of infertile males. Regulation of meiotic cell divisions and dedication of gamete high quality: impression of reproductive toxins. Genome-wide locations of potential epimutations associated with environmentally induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease utilizing a sequential machine studying prediction approach. The presence of macrophages and inflammatory responses in an in vitro testicular co-culture model of male reproductive improvement enhance relevance to in vivo conditions. Outer dense fibres of human spermatozoa: partial characterization and possible physiological features. Effects of environmental toxicants on the efferent ducts, epididymis and fertility. Spermatogonial intercellular bridges in whole-mounted seminiferous tubules from normal and irradiated rodent testes. Application of three-dimensional culture techniques to study mammalian spermatogenesis, with an emphasis on the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Stage-specific gene expression is a elementary characteristic of rat spermatogenic cells and Sertoli cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, one hundred and five, 8315�8320. International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, 22, 305�329. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 2647�2652. Multiple glycolytic enzymes are tightly certain to the fibrous sheath of mouse spermatozoa. Chromatin reworking in spermatids: a delicate step for the genetic integrity of the male gamete. Ozone therapy prevents the toxicity of an environmental combination of estrogens on rat fetal testicular development. Hypothyroidism protects di(n-butyl) phthalate-induced reproductive organs damage in Sprague-Dawley male rats. Mouse pachytene checkpoint 2 (trip13) is required for completing meiotic recombination but not synapsis. Identification of differentially expressed genes of primary spermatocyte towards spherical spermatid isolated from human testis utilizing the laser seize microdissection method. Endpoints of spermatotoxicity in the rat after short period exposures to fourteen reproductive toxicants. The relationship between abnormity of synaptonemal complicated and male fertility impairment in human. Development of a short-term fluorescence-based assay to assess the toxicity of anticancer medicine on rat stem/progenitor spermatogonia in vitro. Analysis of aneuploidy in spermatozoa from testicular biopsies from males with nonobstructive azoospermia. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase-S, a sperm-specific glycolytic enzyme, is required for sperm motility and male fertility. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, a hundred and one, 16501�16506. Dose-dependent results of Sertoli cell toxicants 2,5-hexanedione, carbendazim, and mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in grownup rat testis. Pattern and kinetics of mouse donor spermatogonial stem cell colonization in recipient testes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 228�233.
120 mg isoptin best
Anticoagulation and inhibition of nitric oxide synthase affect hepatic hypoxia after monocrotaline exposure hypertension meds cheap isoptin 40 mg amex. Cytokine-associated drug toxicity in human hepatocytes is related to signaling community dysregulation heart attack questions to ask doctor purchase isoptin 120 mg with amex. Structural and useful differentiation of sinusoidal endothelial cells throughout liver organogenesis in people. Mitochondrial dysfunction happens earlier than transport or tight junction deficits in biliary epithelial cells exposed to bile from methylenedianiline-treated rats. Distinct populations of hepatic stellate cells in the mouse liver have completely different capacities for retinoid and lipid storage. New technologies and screening strategies for hepatotoxicity: Use of in vitro fashions. Hemodynamic flow improves rat hepatocyte morphology, operate, and metabolic activity in vitro. Antibiotic-associated acute vanishing bile-duct syndromedA pattern associated with extreme, extended, intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatic oval cell response to the choline-deficient, ethionine supplemented model of murine liver damage is attenuated by the administration of a cyclo-oxygenase 2 inhibitor. Development and characterization of human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cholangiocytes. Extracellular heat shock proteins, cellular export vesicles, and the Stress Observation System: A type of communication during injury, infection, and cell harm. Gene expression profiles throughout hepatic stellate cell activation in culture and in vivo. Direct motion versus requirement for hepatocyte activation in numerous mouse strains. Embolization by sinusoidal lining cells obstructs the microcirculation in rat sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype is maintained by paracrine and autocrine regulation. Sinusoidal endothelial cells prevent rat stellate cell activation and promote reversion to quiescence. The use of liver spheroids as an in vitro model for studying induction of the stress response as a marker of chemical toxicity. Inductive angiocrine indicators from sinusoidal endothelium are required for liver regeneration. Divergent angiocrine alerts from vascular niche balance liver regeneration and fibrosis. Transcriptomic responses generated by hepatocarcinogens in a battery of liver-based in vitro fashions. Human recombinant vascular endothelial growth factor reduces necrosis and enhances hepatocyte regeneration in a mouse model of acetaminophen toxicity. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes and endothelial cells in multi-component hydrogel fibers for liver tissue engineering. Long-term in vitro perform of grownup hepatocytes in a collagen sandwich configuration. Liver microvascular architecture: An insight into the pathophysiology of portal hypertension. The enhanced value of combining typical and "omics" analyses in early evaluation of drug-induced hepatobiliary harm. The liver sinusoidal endothelial cell: A cell kind of controversial and confusing id. Effects of dexamethasone or celecoxib on biliary toxicity after hepatic arterial infusion of 5-fluorodeoxyuridine in a canine model. Drug-protein adducts: An industry perspective on minimizing the potential for drug bioactivation in drug discovery and development. Critical evaluate of preclinical approaches to examine cytochrome p450-mediated therapeutic protein drug-drug interactions and recommendations for finest practices: A white paper. The endothelin antagonist bosentan inhibits the canalicular bile salt export pump: A potential mechanism for hepatic adverse reactions. High-throughput cellular microarray platforms: Applications in drug discovery, toxicology and stem cell analysis. A new xenobiotic-induced mouse model of sclerosing cholangitis and biliary fibrosis. Pathogenesis of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury and medical perspectives. Resveratrol enhances the sensitivity of cholangiocarcinoma to chemotherapeutic brokers. Recent advances on the mechanisms regulating cholangiocyte proliferation and the importance of the neuroendocrine regulation of cholangiocyte pathophysiology. Lipoproteins and the liver sieve: the role of the fenestrated sinusoidal endothelium in lipoprotein metabolism, atherosclerosis, and cirrhosis. Evaluation of using imaging parameters for the detection of compound-induced hepatotoxicity in 384-well cultures of HepG2 cells and cryopreserved primary human hepatocytes. Determination of liver specific toxicities in rat hepatocytes by excessive content imaging during 2-week a quantity of therapy. Generation of liver disease-specific induced pluripotent stem cells along with efficient differentiation to functional hepatocyte-like cells. Molecular identification and functional characterization of Mdr1a in rat cholangiocytes. Knockout of alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide reduces cholangiocyte proliferation in bile duct ligated mice. Knockout of secretin receptor reduces massive cholangiocyte hyperplasia in mice with extrahepatic cholestasis induced by bile duct ligation. Hepatic sinusoids in liver harm, inflammation, and fibrosis: New pathophysiological insights. Dose metric issues in in vitro assays to enhance quantitative in vitro-in vivo dose extrapolations. A correlation between the in vitro drug toxicity of medicine to cell traces that express human P450s and their propensity to trigger liver damage in people. Induced pluripotent stem cell derived macrophages as a cellular system to examine salmonella and other pathogens. Regulation of drug-induced liver harm by sign transduction pathways: Critical function of mitochondria. Lipids promote survival, proliferation, and maintenance of differentiation of rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in vitro. Basement membrane and matrix metalloproteinases in monocrotaline-induced liver harm.