Grifulvin V
Grifulvin V dosages: 250 mg, 125 mg
Grifulvin V packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Generic 250 mg grifulvin v with visa
Evaluation of recent native anesthetics obtained by way of the manipulation of the enantiomeric ratio of bupivacaine on the central nervous system of the rat fungus life cycle buy grifulvin v 125 mg with mastercard. Enantioselective actions of bupivacaine and ropivacaine on coronary vascular resistance at cardiotoxic concentrations antifungal garlic generic grifulvin v 250 mg overnight delivery. Structure-affinity relationships and stereospecificity of a number of homologous collection of local anesthetics for the beta2-adrenergic receptor. Differences in cardiotoxicity of bupivacaine and ropivacaine are the end result of physicochemical and stereoselective properties. Effects of levobupivacaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine on tail-flick response and motor function in rats following epidural or intrathecal administration. Comparative ventricular electrophysiologic effect of racemic bupivacaine, levobupivacaine, and ropivacaine on the isolated rabbit heart. Comparative somatic and visceral antinociception and neurotoxicity of intrathecal bupivacaine, 18. Chapter 3: Properties, Absorption, and Disposition of Local Anesthetic Agents 87 33. Stereoselectivity of bupivacaine in local anesthetic-sensitive ion channels of peripheral nerve. In vitro antagonism of recombinant ligand-gated ion-channel receptors by stereospecific enantiomers of bupivacaine. Stereoselective block of cardiac sodium channels by bupivacaine in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Is comparative cardiotoxicity of S(�) and R(+) bupivacaine related to enantiomerselective inhibition of L-type Ca(2+) channels Stereoselective urinary excretion of bupivacaine and its metabolites throughout epidural infusion. High-performance liquid chromatographic separation and nanogram quantitation of bupivacaine enantiomers in blood. Plasma concentrations of the stereoisomers of prilocaine after administration of the racemate- implications for toxicity Racemisation of Rbupivacaine: A key issue within the built-in and economic course of for the manufacturing of levobupivacaine. Determination of the minimal native analgesic concentrations of epidural bupivacaine and lidocaine in labor. Minimum native analgesic dose: Effect of different volumes of intrathecal levobupivacaine in early labor. Minimum native analgesic doses of ropivacaine, levobupivacaine, and bupivacaine for intrathecal labor analgesia. Relative analgesic potencies of ropivacaine and bupivacaine for epidural analgesia in labor: Implications for therapeutic indexes. Relative analgesic potencies of levobupivacaine and ropivacaine for epidural analgesia in labor. Minimum native analgesic focus of extradural bupivacaine increases with development of labour. Effect of epidural epinephrine on the minimal local analgesic concentration of epidural bupivacaine in labor. Minimum local analgesic dose of intrathecal bupivacaine in labor and the effect of intrathecal fentanyl. Intrathecal sufentanil and epidural bupivacaine for labor analgesia: Dose-response of particular person agents and together. Continuous infusion epidural analgesia in parturients receiving bupivacaine, chloroprocaine, or lidocaine: Maternal, fetal, and neonatal results. Partition coefficients (noctanol/water) of N-butyl-p-aminobenzoate and different native anesthetics measured by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Fast and direct methodology for measuring 1-octanolwater partition coefficients exemplified for six native anesthetics. Barrier properties of the spinal meninges are markedly decreased by freezing meningeal tissues. Calculation of the permeability coefficient ought to take into account the reality that most drugs are weak electrolytes. Effect of epinephrine on epidural, intrathecal, and plasma pharmacokinetics of ropivacaine and bupivacaine in sheep. Epidural, intrathecal, pharmacokinetics, and intrathecal bioavailability of ropivacaine. Spinal biopharmaceutics of e bupivacaine and lidocaine by microdialysis after their simultaneous administration in rabbits. Cerebrospinal fluid bioavaile capability and pharmacokinetics of bupivacaine and lidocaine after intrathecal and epidural administrations in rabbits using microdialysis. Effect of epinephrine on lidocaine clearance in vivo: A microdialysis study in people. Studies on the period of local anaesthesia: Structure/activity relationships in a collection of homologous local anaesthetics. Influence of dextran on the absorption of adrenaline-containing lignocaine solutions: A protecting mechanism in local anaesthesia. Measured octanol:buffer partition coefficients and pKa values of clinically used medication. True oil/water partition coefficients of procaine and lidocaine and estimation of their dissociation constants in natural solvents. Pleural permeability to native anesthetics: the influence of focus, pH, and native anesthetic combinations. Alkalinization of mepivacaine accelerates onset of interscalene block for shoulder surgery. Transient neurologic symptoms after spinal anaesthesia utilizing isobaric 2% mepivacaine and isobaric 2% lidocaine. Prospective study on incidence and functional impression of transient neurologic symptoms related to 1% versus 5% hyperbaric lidocaine in short urologic procedures. Possible mechanism of irreversible nerve harm brought on by local anesthetics: Detergent properties of native anesthetics and membrane disruption. Uptake of bupivacaine, etidocaine, lignocaine and ropivacaine in n-heptane, rat sciatic nerve and human epidural and subcutaneous fat. The partition coefficient as a predictor of native anesthetic efficiency for spinal anesthesia: Evaluation of five local anesthetics in a mouse model. The effect of the structural variation on the local analgetic properties of the most generally used teams of drugs. Structure activity relationships in differential nerve block at excessive and low frequency stimulation.
Diseases
- Hyperhidrosis
- Epiphysealis hemimelica dysplasia
- Multiple pterygium syndrome lethal type
- Upington disease
- Whipple disease
- African trypanosomiasis
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Bartter syndrome, classic form
- David syndrome
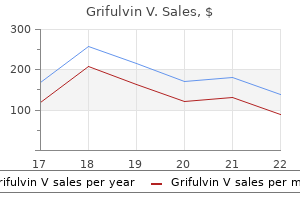
125 mg grifulvin v with amex
A commonplace dental cartridge with 1:a hundred fungus gnats in drains purchase grifulvin v 250 mg with amex,000 epinephrine contains 18 g of epinephrine fungus under my toenail discount grifulvin v 250 mg overnight delivery. Levonordefrin is discovered solely in dental cartridges containing mepivacaine, in a focus of 50 g/mL (1:20,000). A normal dental cartridge with 1:20,000 levonordefrin accommodates ninety g of levonordefrin. Al- though levonordefrin is a relatively weaker adrenergic agonist than epinephrine, consideration must be given to the truth that the 1:20,000 concentration is five instances higher than the standard concentration of epinephrine. Therefore, fewer cartridges containing levonordefrin could additionally be safely used in comparison with cartridges containing epinephrine. Table 18-3 gives usually accepted dosages for vasoconstrictors in wholesome patients, as well as in these with cardiovascular compromise. The mucosa of the oral cavity is highly vascularized, and the systemic uptake of vasoconstrictors following intraoral injection may be rapid. A single dental cartridge of lidocaine 2% with 1:100,000 epinephrine can double the resting epinephrine titer inside minutes (8,9). Furthermore, the intraoral administration of eight dental cartridges of a 1:one hundred,000 epinephrine resolution might produce plasma epinephrine concentrations equivalent to these present during heavy exercise (10). It is necessary to restrict the amount of vasoconstrictor-containing native anesthetic options to patients with severe anxiety and/or heart problems. Caution also wants to be exercised in patients taking nonspecific -adrenergic blockers, adrenergic neuron blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and phenothiazine derivatives. Somatic impulses, including thermal, touch, and ache, are transmitted from the pores and skin of the face and brow, mucous membranes of the nasal surfaces and oral cavity, the teeth, the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and anterior parts of the cranial dura. Proprioceptive impulses are carried from the tooth, periodontium, hard palate, and temporomandibular joint. The trigeminal nerve carries afferent impulses from stretch receptors in the muscles of mastication. Additionally, visceral efferent fibers innervate the muscles of mastication, the tensor tympani and tensor veli palatine muscles, muscles of the attention, and facial muscles. The trigeminal nerve is split into the ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) divisions. Chapter 18: Neural Blockade of Oral and Circumoral Structures 433 Anatomy of the Ophthalmic Division (V1) the ophthalmic division is completely sensory, and is the smallest of the three trigeminal divisions. It exits the skull and enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure, the place it divides into its three main branches: the frontal, nasociliary, and lacrimal nerves. These nerves supply the eyeball, conjunctiva, lacrimal gland, parts of the mucous membranes of the nose and sinuses, and the skin of the brow, eyelids, and nose. The branches inside the pterygopalatine fossa are: Pharyngeal branch: Mucosa of pharynx Middle and posterior palatine: Tonsil and soft palate Greater palatine: Mucosa of posterior palate Nasopalatine department: Septal mucosa by way of incisive canal to the anterior onerous palate Posterior and superior lateral nasal branch: Lateral walls of nasal cavity Posterior superior alveolar branch: Second and third maxillary molars, as well as palatal and distobuccal root of first molar, alveolus, and overlying buccal soft tissue. It exits the skull via the foramen rotundum and enters the pterygopalatine fossa, whence it progresses forward into the inferior orbital fissure and passes into the orbital cavity. Here, it turns barely laterally in the infraorbital groove on the orbital floor of the maxilla. As it continues ahead, it passes through the infraorbital canal and exits onto the front of the maxilla via the infraorbital foramen. The branches of the maxillary nerve (V2) and associated areas of sensory innervation occur (a) inside the pterygopalatine fossa, (b) within the infraorbital groove and canal, and (c) as terminal branches to the face. Although most dental professionals entry the maxillary nerve via intraoral strategies, extraoral methods are also possible in chosen circumstances. The needle is inserted by way of mucous membrane in the area of the tooth or enamel to be anesthetized. Soft tissues of the oral cavity could additionally be satisfactorily anesthetized with native infiltration. Because in many areas of the oral cavity the mucosa is adherent to the underlying periosteum, care should be taken to avoid depositing massive volumes of answer. Large volumes may strip the periosteum from the underlying bone or end in pressure-induced soft tissue ischemia and resultant tissue slough; this injection into tightly adherent tissues can be extremely painful. The maxilla is healthier suited for this type of injection due to the porosity of the maxillary bone, which allows diffusion of the anesthetic resolution. A dose of 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic answer should be injected slowly, al- lowing about 5 minutes for optimum effect. The maxillary incisors, cuspids, and bicuspids may be anesthetized in this method. Maxillary molars may require other techniques, as a result of these tooth are multirooted and divergent, and the overlying bone is dense. Intraoral and Extraoral Approaches for the Infraorbital Nerve Block (Block of the Anterior and Middle Superior Alveolar Nerves). The infraorbital nerve block is helpful for providing anesthesia of the lower eyelid, lateral inferior portion of the nostril and vestibule, and the upper lid and mucosa. The anterior superior alveolar nerve branches from the infraorbital nerve in the anterior part of the infraorbital canal and innervates the maxillary incisors, cuspid enamel (including their bony support), and surrounding labial delicate tissue. The patient is instructed to look instantly forward whereas the operator palpates the supraorbital and infraorbital notches. When the infraorbital notch is identified, the palpating finger ought to comply with the vertical line inferiorly about 0. A 4-cm, 25gauge needle is then inserted alongside the imaginary vertical line Chapter 18: Neural Blockade of Oral and Circumoral Structures 435 till the foramen is reached. The thumb in place over the foramen ought to be used to maneuver the needle into place, in order that it contacts the bone on the entrance to the foramen. The skin over the infraorbital foramen should be massaged to promote the spread of the anesthetic solution into the foramen. To anesthetize the anterior and middle superior alveolar nerves that offer the tooth, the solution must enter the infraorbital foramen and circulate proximally by way of the infraorbital canal. Instrumentation of the teeth in question will reveal success or failure of the block. The extraoral strategy to the infraorbital nerve is completed by first identifying the infraorbital ridge of the maxillary bone and palpating the infraorbital foramen, positioned approximately 2 cm from the lateral surface of the nose. The anterior portion of the canal within the orbit is often covered with a skinny plate of bone, so that needle insertion should occur zero. This nerve block offers anesthesia of the third and second maxillary molars, and two-thirds of the first maxillary molar, in addition to supporting hard and buccal gentle tissues. Since the primary maxillary molar has twin innervation by way of the center superior alveolar nerve, the posterior superior alveolar nerve block should typically be coupled with infiltration over the mesiobuccal root to present whole pulpal anesthesia. The posterior superior alveolar nerve arises from the maxillary nerve earlier than it enters the physique of the maxilla. Supraorbital notch, pupil of the eye, infraorbital notch, infraorbital body, bicuspid tooth, and psychological foramen lie on a straight vertical line.
Purchase grifulvin v 250 mg online
The impact of the latter is presumably to right the acidosis brought on by ischemia fungus in grass buy cheap grifulvin v 125 mg, thereby facilitating tissue uptake of the lidocaine fungus gnats larvae cannabis 125 mg grifulvin v cheap mastercard. Weight and Height In adults, plasma concentrations of local anesthetics after epidural and different nerve blocks are correlated poorly with body weight and peak (149,199,266,298�300). Despite this, and acknowledging that dosage changes must be made for the extremes of body weight, numerous dosage suggestions continue to embody whole body weight as a major factor (167). Age the results of aging on the assorted elements of neural blockade and their mechanisms are complicated because of concurrent age-related anatomic and physiologic adjustments that lead to related local and systemic pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic changes. The fraction of dose absorbed rapidly was smaller with elevated age with ropivacaine and levobupivacaine (but was unaffected with bupivacaine) (174�177). This was in all probability associated to the differences in local disposition and systemic uptake mediated by way of agerelated modifications in epidural blood move and the effective vasoactivity of the local anesthetic agents. The introduction of ropivacaine and levobupivacaine appears to have coincided with a resurgence of curiosity of neural blockade in infants and kids (302). They noted that two of the principle elements producing variations between younger immature and older pediatric sufferers derive from the relatively lower resting ranges of 1 -acid glycoprotein (the main binding protein) through the first 6 to 9 months of life, and the maturation of the hepatic metabolizing enzyme system responsible for drug clearance (303,303a,304). Observed Tmax knowledge in infants and youngsters are topic to the beforehand mentioned caveat about blood sampling. Nevertheless, the out there information suggest a considerably faster systemic absorption of most native anesthetics than in adults (303,305,306). Depot Formulations Several supply systems based mostly upon local anesthetic-loaded liposomes, polylactide microspheres, or cyclodextrin inclusion complexes have been shown to prolong epidural and subarachnoid block in animals by offering a depot from which local anesthetic is slowly launched. This sluggish local launch also wants to be accompanied by a decrease within the rate of systemic drug absorption. Thus, decrease and more extended plasma concentrations of lidocaine and bupivacaine have been measured in animals after injection of liposomal and other formulations in comparability with aqueous options (125,289�293). In people, dextran (6%�10%) has been shown to attenuate markedly the systemic absorption rate of lidocaine and epinephrine after injection into the scalp (81,295). However, no convincing proof showed that neuraxial blockade to T6�T7 with tetracaine influenced the general disposition of etidocaine administered intravenously (171). Direct actions of local anesthetic brokers on vascular smooth muscle are complex, being each drug- and concentration-dependent (188). Physical and Pathophysiological Factors An overview of the influence of patient-related variables on the disposition of the principal local anesthetic agents was thought-about as a basis for revision of the maximum really helpful doses of local anesthetics (166,167,297). Interpretation of results of research, however, is somewhat hampered by inconsistency in experimental design, notably in blood sampling and processing. Disease and Surgery Changes in native perfusion related to altered hemodynamics as a outcome of illness or surgical procedure could modify the absorption of native anesthetics and therefore length of anesthesia. For instance, acute hypovolemia slows lidocaine absorption after epidural injection in dogs (308) and prolongs anesthesia in sufferers present process thoracotomy with regional block (309). Conversely, a decreased period of brachial plexus block in patients with persistent renal failure was instructed to reflect a hyperkinetic circulation and enhanced systemic uptake of local anesthetic (310) however this speculation has not been substantiated by the outcomes of subsequent studies (311�313). It seems that the primary effects of renal and hepatic illness are on the systemic disposition of the brokers. In pregnant ladies, a small proportion of the dose also crosses the placenta into the fetus. In people, such research with native anesthetics are usually performed with low enough doses to keep away from toxicity, and with peripheral blood sampling strategies. More invasive studies to characterize poisonous doses, as well as to research the regional pharmacokinetics of the agents and relevant regional physiology, are primarily carried out in massive animals, normally canines, pigs, and sheep. Some pharmacokinetic information describing the systemic disposition of some frequent local anesthetics in healthy human subjects are given in Table 3-6; these have been derived from compartment mannequin evaluation. In some research, the systemic disposition of a stable (nonradioactive) isotopically labelled native anesthetic has been used to compute the systemic absorption rate (see the earlier section Agents), and these have been found experimentally to not differ to concurrently determined values with native agent (173,180). Compartment models-in which the drug is identified as being in one of three locations: in a "central compartment" containing sampled blood (along with extremely perfused regions), in other regions that have identifiably decrease perfusion and drug tissue-to-plasma distribution coefficients (and are lumped collectively as "peripheral compartments"), or already eliminated-are one, perhaps more readily visualized, method. However, there are a number of attainable compartment fashions, and a failing of this technique is that it is in all probability not possible to help one such model unequivocally, or even to determine the "appropriate" mannequin, from the data obtained. Pharmacokinetic and clinical pharmacological research with mepivacaine and prilocaine. Chapter 3: Properties, Absorption, and Disposition of Local Anesthetic Agents seventy three Distribution the Role of the Lung the first capillary mattress to be exposed to native anesthetic once it has entered the systemic circulation is that within the lungs. This extremely perfused maze-like structure acts to (temporarily) sequester an considerable quantity of drug because of its massive surface space for drug uptake and favorable tissue-to-blood distribution coefficient. Several methods have been used to examine lung uptake of native anesthetic agents; most are adaptable to other tissues as properly. Drug binding in blood or plasma is especially determined ex vivo using equilibrium dialysis or ultrafiltration (114,333). At equilibrium, the concentration of unbound, nonionized drug will be the same on both aspect of the membrane, but total drug concentrations will differ relying on the relative capacities of the binding sites related to the two aqueous phases and any pH gradient. The in vitro fashions are used to infer the relationships between certain and unbound drug concentrations existent in vivo; the mechanism has been used to clarify, for instance, the unequal distribution of native anesthetic agents across the placenta (333,334). However, both models produce results that depend to some extent upon methodological variables, in order that data are better used for comparative than absolute functions. Most importantly, the fractional binding of a drug in plasma usually decreases as drug concentrations increase-an indication of saturability of binding websites. The internet flux of levobupivacaine across the lungs was measured from the product of the pulmonary arterial� aortic levobupivacaine concentration gradient and the cardiac output. The net flux is constructive (net inflow blood to lungs) when the gradient is optimistic, the lung and blood concentrations are equal when the gradient is zero, and adverse (net efflux from lung to blood) when the gradient is adverse. A concentration gradient at regular state, or an space under the plasma drug concentration�time curve distinction at non-steady state, supplies evidence of clearance. Direct measurement of drug concentrations in lung tissue samples taken serially both repeatedly or discretely in several subjects have been used to demonstrate lung uptake (323,324). Isotopically labeled agents also have been used with acceptable imaging methods to show the time course of lung (and other tissue) uptake (325). Direct determination of uptake and metabolism has been assessed by perfusion of the agent in a medium applied to isolated laboratory rodent lungs either by single-pass or recirculation, or by incubation of agent in preparations of lung tissue. Others have also found a larger uptake of prilocaine than of mepivacaine and bupivacaine in the isolated perfused rat lung, with little evidence of pulmonary metabolism (329). The rank order of uptake in rat lung slices was discovered to be bupivacaine >etidocaine >lidocaine (330). Other research using the dye comparison method found that the lung extraction in rabbits is levobupivacaine >ropivacaine (328). There can additionally be proof for modest enantioselectivity of distribution: Rutten et al. The extravascular pH of the lung is low relative to plasma pH, and this encourages ion trapping of native anesthetic (331). Other fundamental drugs, corresponding to propranolol, might compete with native anesthetics for pulmonary binding sites, thereby decreasing their first-pass extraction.
125 mg grifulvin v buy otc
In some instances fungus gnats in house 125 mg grifulvin v order overnight delivery, this is because of the event of regionally excessive drug blood focus fungus gnats coffee grounds buy discount grifulvin v 250 mg line. Extent and Rate of Absorption In the absence of local metabolism, all of a dose deposited perineurally will finally turn out to be absorbed into the systemic circulation. The focus gradient is the primary driving drive for dissipation of drug both from its (heterogeneous) perineural website of administration into local tissues and uptake into the blood. Concentration gradients drive the trade of drug between blood (strictly, plasma water) and tissues (strictly, extracellular fluids), including regions that excrete and metabolize drug. This pattern also can normally be represented by the sum of exponentials, during which the drug focus approaches zero as time will increase due to its excretion and/or metabolism lumped together as elimination (see systemic disposition, which is discussed later within the text). Conversely, a perineural administration displays the concurrent whole-body disposition of drug whereas arriving and once within the systemic circulation. More latest technical developments have allowed utility to quite lots of topics undergoing epidural and subarachnoid blocks, in which a concurrent small dose of deuterium-labeled agent is administered intravenously (172�177). The two forms of the f In which drug concentration in some kind is said to time in an exponential product, in order that the rate of change of focus is proportional to how much drug is present at any nominated time (referred to as first-order kinetics). Conceptual mannequin of native anesthetics injected perineurally used to calculate the speed of systemic absorption utilizing the numerical deconvolution technique. The necessary assumption is that the systemic disposition of the drug, as revealed by intravenous administration, remains the identical when the drug is run perineurally. With the secure isotope technique, the intravenous disposition is set concurrently with the neural blockade. Such pharmacokinetic calculations present a mathematicalstatistical description of a practical course of whereby the drug acts a tracer; nonetheless, the description has bodily components. Thus, their vascular absorption charges shall be directly associated to blood circulate and inversely to local tissue binding (distribution coefficient). Important native determinants of systemic absorption include those affecting the tissue distribution, including the location of injection, the lipophilicity and vasoactivity of the agent, the presence of components corresponding to vasoconstrictors, other formulation factors supposed to modify local drug residence and release, the affect of nerve block, and (patho)physiologic features of the patient. Tmax for a particular type of nerve block tends to happen at about the identical time as a result of the early absorption is dominated by the quicker absorption rate fixed, which has similarities for all brokers. However, the half-life of the drug in plasma is dominated by the slower absorption fee fixed, and this is usually slower than the elimination price constant. The real anatomic scenario is, nevertheless, much more complicated than a simple two-pool mannequin. Overall, for a given blood sampling website, Cmax and Tmax are inversely related in that the higher the Tmax then the lower the value of Cmax. Extensive information on Cmax and Tmax of the amide local anesthetics after numerous routes of injection have been tabulated elsewhere (145,178). So too have information on (poly)exponential equation exponents and coefficients describing the rate(s) of systemic absorption after epidural administration (171�178). Agent Differences between agents must be assessed underneath comparable conditions relating to drug administration, topic selection, and subject preparation. Inspection of Cmax and Tmax after epidural injection of plain solutions of the amide native anesthetics, and allowing for differences in sampling regimens, reveals that the increment in peak complete blood drug focus per 100 mg of dose is about 0. Although differences in disposition kinetics contribute to this order, it seems that, regardless of comparable times of peak concentrations, net absorption of the longer-acting, more lipophilic agents is slower. Each patient additionally had a concurrent intravenous dose of stable isotope-labeled local anesthetic to decide the systemic disposition. From the combined knowledge, the charges of systemic absorption of the agent was decided by numerical deconvolution. Simultaneous investigation of absorption and disposition kinetics using secure isotopes. The effect of age on systemic absorption and systemic disposition of bupivacaine after subarachnoid administration. Pharmacokinetica of bupivacaine throughout postoperative epidural infusion: Enantioselectivity and function of protein binding. Epidural anesthesia with bupivacaine: Effects of age on neural blockade and pharmacokinetics. Differences within the net absorption charges of the varied brokers have implications for their accumulation throughout repeated and continuous administration. Whereas systemic accumulation is more marked with the short-acting amides, extensive local accumulation is predicted for the longer-acting compounds, despite their longer dosage intervals (171,181,182). For prilocaine and for articaine, a excessive systemic clearance, rather than gradual absorption, is accountable primarily for the comparatively low blood drug concentrations (12,183). Although the rate of systemic absorption of native anesthetics is controlled largely by the extent of native binding, their relative intrinsic vasoactive properties could additionally modulate local perfusion and therefore uptake. However, the results are a posh operate of drug, dose, enantiomer, and kind and tone of blood vessel, and their relevance to the overall relative absorption of drugs after peripheral and central nerve blocks is troublesome to consider (172). Nevertheless, it has been instructed, for instance, that an increase in epidural blood circulate (whether mediated locally or by change in cardiac output or both), with assumed increase in the systemic absorption price of bupivacaine, is an important factor resulting in regression of anal- gesia during the steady epidural infusion of bupivacaine (184). Furthermore, the vasodilatory impact of bupivacaine on cerebral pial, cutaneous, and epidural blood vessels contrasts strikingly with the relative web vasoconstrictor effect of ropivacaine and levobupivacaine, a distinction that may contribute to their relative anesthetic profiles (185�187a). Others, however, have found the effects on cutaneous blood vessels to be biphasic: vasodilatory at excessive concentrations and vasoconstrictive at low concentrations-clearly, the choice of exploratory mannequin and circumstances is crucial in evaluating the net results (188,189). Although R-bupivacaine was found to be two to three times stronger than S-bupivacaine in blocking nerve fibers in vitro (190), this intrinsic difference in motion could additionally be modulated in vivo by the dominant stereoselective effects on blood vessels. Thus, the S-enantiomer amide native anesthetics are longer appearing than the R-enantiomers after separate subcutaneous injection, apparently reflecting a higher vasoconstrictor activity and, due to this fact, a presumed slower systemic absorption (14,191). Similar logic concerning the higher vasoconstrictor exercise of ropivacaine than bupivacaine has been used to rationalize the slower obvious rate of ropivacaine absorption. Display of fraction of dose absorbed into the systemic circulation plotted as a operate of time after epidural injection of chosen amide local anesthetics, as decided by the secure isotope technique in comparable affected person populations. The curves characterize bi-exponential functions fitted to the speed of systemic absorption. Pharmacokinetics of lidocaine and bupivacaine in surgical sufferers following epidural administration. Effect of age on the clinical profile and systemic absorption and disposition of levobupivacaine after epidural administration. Site of Administration Anatomic features, such as vascularity and the presence of tissue and fat that may bind native anesthetics, are major influences on their fee of distribution inside, and elimination from, specific websites of injection. As revealed by imaging or dyes at numerous websites of native anesthetic injection, different features, such because the presence of septa or different fibrous tissues (and any resultant pressure gradients), additionally contribute to distribution of resolution and thus spread of anesthesia (131,193�196). This is pertinent to all procedures of neural blockade, but notably so for the central neuraxis, where the detailed anatomy is complicated and obscured from the anesthesiologist, variable between people, and still largely unresolved with respect to the resultant block (197,198). As indicated earlier, arterial plasma drug concentrations precede and exceed these in peripheral venous plasma, whatever the agent. A research with epidural ropivacaine found that the forearm arteriovenous gradient diminished exponentially, with the distinction essentially extinguished about 1 hour after administration (201), as can be anticipated from the time needed for drug focus within the tissues to equilibrate with that in the venous blood. However, different conclusions might need been reached had the same study been performed by figuring out the drug arteriovenous concentration gradient in a lower limb as a outcome of the block itself would have influenced the venous tone of the higher and lower limbs in a unique way (171). Concurrent administration of common anesthetics and some medications can alter the time programs of arterial and venous plasma drug concentrations through local and systemic cardiovascular effects, and this can be noticed when information from surgical patients and nonsurgical sufferers or wholesome volunteers are compared.
Evergreen (Periwinkle). Grifulvin V.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Preventing brain disorders, tonsillitis, sore throat, intestinal swelling (inflammation), toothache, chest pain, wounds, high blood pressure, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Periwinkle?
- Dosing considerations for Periwinkle.
- How does Periwinkle work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96484
Buy grifulvin v 250 mg with mastercard
The patient could expertise such symptoms even when comparatively closely sedated (94) antifungal nappy cream generic grifulvin v 125 mg online. Chapter 15: Intravenous Regional Neural Blockade 381 After using the above-mentioned doses antifungal pills for ringworm discount 250 mg grifulvin v, the tourniquet cuff could normally be launched in one step, and the tourniquet is immediately eliminated to permit unobstructed circulation to the skin. However, if for some cause the cuff must be deflated sooner than 20 minutes after local anesthetic injection, or if the patients has a disease that will improve the risk of cardiotoxicity, the cuff may be deflated and reinflated in cycles until affirmation of no complications is made. Indications include, for example, repositioning of painful fractures of the elbow and forearm and minor operations of the hand or foot. Intravenous regional analgesia: A helpful method of manufacturing analgesia of the limb. Centripetal paralysis arising out of arrested blood-flow to the limb, including notes on a type of tingling. Experimental studies on intraneural microvascular pathophysiology and nerve perform in a limb, subjected to temporary circulatory arrest. Effect of ischemia on peripheral nerve-evoked potential: Experimental and clinical study. Major Limb Replantation and Postischemia Syndrome: Investigation of Acute Ischemia-induced Myopathy and Reperfusion Injury. The pathophysiology of skeletal muscle ischemia and the reperfusion syndrome: A evaluation. Effect of the strategy of exsanguination on the quality of anaesthesia and prilocaine plasma concentrations. A comparative study of carticaine and prilocaine in regional intra� venous analgesia (German). Comparison of ropivacaine and lidocaine for intravenous regional anesthesia in volunteers: A preliminary research on anesthetic efficacy and blood level. The cuffs are pressurized to 50 to 75 mm Hg above the systolic arterial stress, and the switching-between-cuff precept is practiced, as in adults. The local anesthetic dose has to be modified according to the size of the extremity and the child, ranging from 10 to 15 mL (lidocaine or prilocaine 5 mg/mL) in a 3- to 4-yearold baby to 25 to 30 mL in a 11- to 12-year-old youngster. Risk components for prilocaine-induced methaemoglobinaemia following peripheral regional anaesthesia. Clinical chemistry of prilocaine and clinical evaluation of methaemoglobinaemia induced by this agent. Controlled study on intravenous regional anesthesia using high and low concentration prilocaine (German). Clinical pharmacology and the utilization of articaine for local and regional anaesthesia. Comparison of 2-chloroprocaine and prilocaine for intravenous regional anaesthesia of the arm: A medical study. Comparison of wound infiltration with ketorolac versus intravenous regional anesthesia with ketorolac for postoperative analgesia following ambulatory hand surgery. Experimental research on intravenous regional anaesthesia using radioactive lignocaine. Distribution and elimination of local anaesthetic brokers: the role of lung, liver and kidney. Methemoglobin formation and oxygen transport following intravenous regional anesthesia utilizing prilocaine. Costs and effectiveness of rofecoxib, celecoxib, and acetaminophen for stopping pain after ambulatory otolaryngologic surgery. A double-blind potential comparison of rofecoxib vs ketorolac in lowering postoperative pain after arthroscopic knee surgery. Comparison of propofol with thiopentone for therapy of bupivacaine-induced seizures in rats. A comparability of the consequences of propofol and sevoflurane on the systemic toxicity of intravenous bupivacaine in rats. Successful resuscitation of a patient with ropivacaine-induced asystole after axillary plexus block using lipid infusion. Improved intravenous regional anesthesia for surgery of the hand, wrist, and forearm. Influence of premedication on lignocaineinduced acute toxicity and plasma concentrations of lignocaine. For the purposes of this chapter, the thorax and stomach might be thought-about individually. The nerve provide to the thorax is derived from the anterior main rami of T1 to T6. The nerve supply of the belly wall is derived from the anterior major rami of T6 to L1. Nevertheless, other postoperative opposed events corresponding to pain, nausea and vomiting, and urinary retention may impair affected person consolation, recovery, and rehabilitation after minor and main surgical procedures. In addition, rising proof means that acute postoperative occasions might lead to long-term consequences. For instance, uncontrolled postoperative ache is said to the event of persistent pain syndromes (1); to postoperative myocardial ischaemia and infarction, that are threat factors for dying from cardiac causes within the following months (2); and to postoperative cognitive decline, which could be persistent (3). As postoperative pain is usually the predominant symptom, it may be thought-about an necessary outcome of surgical procedure. Pain is a key part within the alteration of lung function after thoracic and higher abdominal surgery. This highlights the importance of offering efficient postoperative analgesia to reduce pulmonary complications and attenuate the stress response. Minor surgeries, such chest and belly wall procedures, are often performed on an outpatient foundation. Postoperative analgesia in this setting is commonly not optimum (4), with related adverse affected person outcomes (4). Peripheral nerve blockade has explicit benefits over other analgesic methods similar to neuroaxial blocks and systemic opioids (5). Studies have examined the consequences of intercostal blocks on lung volumes and gas move charges following either abdominal or thoracic surgical procedure. Most authors have used peak expiratory move as a measure of the maximal expiratory effort that may be generated by a patient. When in contrast with opioid analgesia, intercostal block leads to larger peak expiratory flows (6). In healthy volunteers, Jakobson discovered that bilateral intercostal nerve blocks with 0. Total lung capability, compelled vital capacity, and peak expiratory move, all decreased by 4%. Functional residual capacity decreased by 8%, and peak expiratory airway strain decreased by 7%. Epidural analgesia is taken into account by many to be the best method of ache reduction after major surgical procedure. Although efficient, unwanted side effects embody hypotension, urinary retention, incomplete (or failed) block, and, in uncommon circumstances, paraplegia.
Grifulvin v 250 mg generic amex
On the seventh postoperative day fungus killing soap purchase grifulvin v 250 mg free shipping, coagulation parameters had been normalized in order to antifungal by mouth grifulvin v 250 mg low price safely remove the epidural catheter. Thus, the increased risk for thromboembolic phenomenon in patients requiring anticoagulation therapy must be considered when assessing the risk-benefit ratio of applying epidural strategies in sufferers present process cardiovascular surgical procedure. In summary, the efficiency of regional anesthetic techniques in patients undergoing cardiac surgical procedure, though rising in recognition, stays extremely controversial due to perceived hematoma threat and lack of clinical advantages, thus prompting numerous editorials by acknowledged experts within the field of cardiac anesthesia (209�214). One of the principle reasons such controversy exists (and doubtless will proceed for some time) is that the numerous clinical investigations concerning this topic are suboptimally designed and utilize a broad array of disparate methods that forestall clinically useful conclusions all can agree on (215,216). On the other hand, most clinicians consider that the use of regional anesthetic techniques is comparatively safe in patients with regular coagulation undergoing vascular surgical procedures that require a lesser diploma of anticoagulation than that required for cardiac surgical procedure. The American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management within the Perioperative Setting reports that the literature helps the administration via a single route of two analgesic brokers that act by completely different mechanisms to provide superior analgesic efficacy with equal or decreased antagonistic effects (1). The literature suggests that two routes of administration, in comparison with a single route, may be more effective in providing perioperative analgesia. The listing of factors in Table 22-5 is presented in no explicit order; obviously, relying on specific scientific conditions (surgical process, patient comorbidity), sure elements will be more essential than others. One should remember that morbidity and mortality following cardiovascular surgery is profoundly influenced by maintenance of perioperative hemodynamic stability. It is extremely difficult (if not impossible) to decide precisely how important attaining enough postoperative analgesia actually is in relation to all of those scientific factors surrounding a patient undergoing cardiovascular surgery. A clear link between "enough" or "high-quality" postoperative analgesia in sufferers following cardiovascular surgical procedure has but to be established (220�222). Although subsequent analysis has elucidated the distinction between additivity and synergy, the basic technique behind such mixtures ("multimodal" or "balanced" analgesia) stays unchanged: enhanced analgesia with minimization of adverse physiologic results. Opioids have been used for a few years within the treatment of postoperative ache in sufferers following cardiovascular surgical procedure with good outcomes. Neural blockade strategies (used as part of a multimodal analgesic approach) certainly supply unique benefits to these sufferers. One ought to strive for an method that uses a selection of different therapies (mul- timodal therapy), each counteracting ache through completely different mechanisms. Preemptive analgesia, whereas intriguing, wants further examine to determine its role in affecting postoperative analgesia and outcome (223�226). Last, the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management in the Perioperative Setting presents sound advice (1). It recommends that anesthesiologists who manage perioperative pain should make the most of analgesic therapeutic options solely after thoughtfully contemplating the dangers and benefits for the individual patient. This capacity includes the power to acknowledge and treat adverse effects that emerge after initiation of therapy. Whenever potential, anesthesiologists should employ multimodal pain management therapy. Dosing regimens should be administered to optimize efficacy whereas minimizing the chance of adverse occasions. The selection of treatment, dose, route, and period of remedy should always be individualized. Practice pointers for acute ache management in the perioperative setting: An up to date report by the American Society of Anesthesiologist Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Effects of epidural anesthesia and analgesia on coagulation and outcome after major vascular surgery. Postoperative myocardial ischemia: Therapeutic trials utilizing intensive analgesia following surgery. Halothane-morphine in contrast with high-dose sufentanil for anesthesia and postoperative analgesia in neonatal cardiac surgery. A systematic evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of fast-track cardiac anesthesia [Review article]. Postoperative pain, expectation and expertise after coronary artery bypass grafting. Analgesic administration, pain intensity, and affected person satisfaction in cardiac surgical patients. Persistent ache after cardiac surgical procedure: An audit of high thoracic epidural and primary opioids analgesia therapies. Severe incisional pain and lengthy thoracic nerve damage after port-access minimally invasive mitral valve surgery [Case report]. Endoscopic vein harvest for coronary artery bypass grafting: Technique and outcomes. Postoperative myocardial ischemia in sufferers present process cardiac artery bypass graft surgery. Prognostic importance of postbypass regional wall-motion abnormalities in patients present process coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Neuronal and adrenomedullary catecholamine launch in response to cardiopulmonary bypass in man. Systemic hypertension associated with coronary artery bypass surgical procedure: Predisposing factors, hemodynamic traits, humoral profile, and therapy. Epidural anesthesia and analgesia: Their function in postoperative outcome [Review article]. The effect of ache on healthrelated quality of life in the immediate postoperative interval. Use of a continuous local anesthetic infusion for ache administration after median sternotomy. Improved pain management after cardiac surgical procedure: Results of a randomized, double-blind, scientific trial. Local anesthetic infusion pump techniques opposed occasions reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Pain management after thoracic surgical procedure, a evaluate of present strategies [Review article]. Extrapleural regional versus systemic analgesia for relieving postthoracotomy ache: A scientific study of bupivacaine compared with metamizol. A comparative analysis of intrapleural and thoracic epidural analgesia for postoperative ache reduction after minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass surgery. Regional anesthesia for major cardiac and noncardiac surgery: More than only a strategy for effective analgesia Intrathecal and epidural anesthesia and analgesia for cardiac surgical procedure [Review article]. Noradrenergic exercise and silent ischaemic in hypertensive sufferers with secure angina: Effect of metoprolol. Effects of thoracic epidural anesthesia on coronary arteries and arterioles in patients with coronary artery disease. Cardiac sympathetic nerve exercise and progressive vasoconstriction distal to coronary stenosis: Feed-back aggravation of myocardial ischemia.
Discount 250 mg grifulvin v with visa
Persistent pain has additionally lately been reported after cesarean section in approximately 12% of patients at 10 months after surgery (71) antifungal acne grifulvin v 250 mg discount without prescription. As talked about earlier on this chapter and discussed at length in Chapters 31 via 33 fungus gnats jump order grifulvin v 250 mg amex, peripheral and central sensitization may happen following surgical procedure, ultimately leading to chronic ache with hyperalgesia and allodynia. Patients present process thoracic surgical procedure underneath basic anesthesia have been randomized to receive both steady epidural block earlier than surgical incision or at completion of surgical procedure. Postoperative pain was less within the group that acquired continuous epidural block previous to surgical incision. This group also had decrease postoperative pain scores and the next proportion of pain-free sufferers at 3 and 6 months after surgical procedure (73). Postoperative central nervous system problems are usually marked by deficits in cognition and reminiscence. These problems embody a variety of postoperative states including delirium or dementia (impairment in cognitive function), amnesia (impairment in memory), and sedation (impairment of consciousness). The etiologies of those disorders are complex and could also be distinct for particular issues. However, psychological operate sometimes reaches a nadir in the early postoperative period, with a recovery to preoperative ranges by 1 week following surgical procedure in most patients (74,75). Delirium is a particularly problematic subset of postoperative cognitive dysfunction as it could contribute to a minimum of an additional 17. Delirium could happen in 9% to 11% of elderly sufferers present process elective noncardiac surgery (78,79) and as many as 36. Higher levels of postoperative pain severity are associated with a higher incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction (especially delirium) (82,83). However, the impact of postoperative analgesia on mental perform has not been rigorously investigated as trials in this area usually lack management of the postoperative analgesic regimen. Chapter 7: Neural Blockade: Impact on Outcome 151 Patient-oriented Outcomes Patient-oriented ("nontraditional") outcomes, such as affected person satisfaction, quality of life, and high quality of recovery, are necessary, legitimate outcomes which have been widely utilized in other areas of medicine and are becoming more important in the field of anesthesiology and perioperative care. Although many diverse patient-oriented outcomes exist, a quantity of features of regional anesthesia and analgesia. Although provision of analgesia is a commonly acknowledged goal for postoperative pain management, the presence of analgesic agent�related unwanted effects, typically from opioids or local anesthetics, differ amongst analgesic strategies and could additionally be an essential influence on patientoriented outcomes. Patient satisfaction has turn out to be an necessary consequence measurement and indicator of high quality of medical care. Although assessing affected person satisfaction may appear intuitively straightforward, the concept of patient satisfaction incorporates many dimensions and domains and is sort of complex, embracing various theories, definitions, and concepts regarding patient satisfaction still not clearly codified by consensus. Appropriate methods to assess affected person satisfaction should utilize validated survey instruments that have been psychometrically constructed (85). For example, patients who received epidural anesthesia for elective cesarean part had greater maternal satisfaction (using a validated instrument) compared with those that have been randomized to obtain spinal anesthesia, due partially to the elevated unwanted effects. Complications A number of problems could happen with neuraxial anesthesia and analgesia. These are discussed intimately in the context of perioperative care in Chapters 12 and 20, and in relation to ache management in Chapter 50. In light of these critical antagonistic results, clinicians should fastidiously weigh the risks and advantages of contemplated neuraxial strategies on an individual basis. The incidence of neuraxial opioid-induced respiratory depression is dose-dependent and is reported to happen in roughly 0. Risk components for the development of respiratory depression after administration of neuraxial opioids embody increasing dose, increasing age, concomitant use of systemic opioids or sedatives, and possibly extended or in depth surgical procedure, presence of comorbidities, and thoracic surgery (91). A potential sequence of 4,185 patients with thoracic epidural catheters reported a zero. Epidural hematoma is probably considered one of the most feared issues of neuraxial methods. Although epidural vessel puncture could occur in up to 12% of epidural catheter placements (96), the development of symptomatic epidural hematomas is rare, with an estimated incidence of roughly 1:one hundred fifty,000 after epidural anesthesia/analgesia (97). Epidural abscess formation is luckily relatively uncommon, with a reported incidence of zero. Although an epidural catheter provides a route of entry into the epidural area, epidural abscesses are more probably to outcome from hematogenous quite than direct unfold (100) and are rare with routine postoperative use (101). Peripheral Nerve Analgesia and Outcomes Peripheral nerve blocks and catheter placement for steady local anesthetic infusion have turn into more and more in style in acute postoperative pain administration. Peripheral methods provide more focused and restricted sensory and motor block than central neuraxial analgesia and supply lowered danger of catastrophic problems similar to spinal hematomas and abscesses. The quantity of residency coaching devoted to regional anesthesia and peripheral nerve blocks has steadily elevated within the United States as a mirrored image of this elevated curiosity and the potential advantages. A survey of American anesthesiology residency program administrators in 2002 indicated that just about 60% of programs now provide a particular peripheral nerve block rotation (102). A review of medical case logs submitted from residents to the Residency Review Committee for Anesthesiology demonstrated a development in use of regional anesthesia strategies from 21% of circumstances in 1980 to 30% of instances in 2000 (103). Single-shot Peripheral Nerve Blocks Although excellent proof exists for elevated curiosity and coaching in peripheral nerve blocks, there stays little proof that these methods have an effect on medical outcomes. Conceptually, single-shot peripheral nerve blocks would supply limited means to scale back the mechanisms of major perioperative issues described up to now. Duration of analgesia after a single injection of long-acting local anesthetic is at most about 12 hours (104), whereas maximal postoperative pain after major surgical procedure has an average duration of 3 days (40). Mean and most ache scores for continuous perineural versus systemic opioid analgesia after a wide range of surgical procedures. Pain scores have been considerably decrease for perineural analgesia forever points. Chapter 7: Neural Blockade: Impact on Outcome 153 nerve blocks are temporally inadequate to have an effect on ongoing pain and subsequent outcomes. As discussed earlier, cardiopulmonary problems are essentially the most frequent supply of major morbidity (23) and often happen later than 12 hours into the postoperative period. Postoperative myocardial infarction remains the leading explanation for main postoperative morbidity, and sufferers stay at risk for a minimum of 24 hours after surgery (36). Although much less severe however extra frequent than cardiac issues, postoperative pulmonary issues could additionally be associated with significantly longer increments of hospital keep (9). The most necessary postoperative ventilatory change is the delayed decrease in functional residual capability. Because this lower is maximal at 24 to forty eight hours after surgery, single-shot peripheral nerve blocks are temporally inadequate to have an result on pulmonary end result. In addition, the restricted spatial concentrating on of conduction block with peripheral neural blockade, although usually a beautiful characteristic, can also prohibit potentially beneficial results on postoperative pathophysiology. For instance, blocks restricted to the periphery have minimal direct effects on sympathetic activation, which is an important contributor to cardiovascular (105) and gastrointestinal (106) morbidity, in addition to limited effects on phrenic afferent stimulation, which can be detrimental to pulmonary operate (9). Finally, the power of peripheral nerve blocks per se to have an effect on consequence could additionally be diluted by the frequent use of adjunct analgesics. This multimodal method might profit the patient but lessens potential contribution of peripheral nerve blocks per se upon consequence.
Grifulvin v 250 mg low price
On the opposite hand antifungal katzung grifulvin v 250 mg cheap mastercard, related umbilical artery-toumbilical vein focus ratios noticed for the assorted brokers argue against large differences of their equilibration charges in the fetus anti fungal additive grifulvin v 125 mg without prescription. As a results of ion trapping, fetal acidosis will increase both the cord-to-maternal ratio of unbound drug and the speed of placental transfer of local anesthetic (334,510, 515�519). Systematic studies performed in sheep at time period have discovered comparable placental transmission, along with fetal tissue concentrations of bupivacaine, levobupivacaine, and ropivacaine (324). Some diploma of enantioselectivity is conceivable and could be Enzyme-inducing Agents the systemic clearance of unbound lidocaine was discovered to be about 25% greater in sufferers with epilepsy than in controls (499,500). This is presumed to be a consequence of the enzymeinducing properties of the anticonvulsant. Long-term remedy with phenytoin also induces the synthesis of 1 -glycoprotein, leading to elevated plasma binding of lidocaine (500). In contrast, the enzyme inducer rifampicin seems not to influence 1 -acid glycoprotein ranges and plasma lidocaine binding in people (501) however was discovered to markedly improve the clearance of ropivacaine in each smokers and nonsmokers (485a). Other Drugs Administration of inhibitors of plasma pseudocholinesterase, for instance, neostigmine and echothiophate, ought to be avoided in sufferers receiving ester-type local anesthetics, as ought to acetazolamide, which blocks hydrolysis by the purple cell esterase (439). Many primary medication have been shown to displace lidocaine from plasma binding sites, but solely when added at supratherapeutic concentrations. Placental Transfer Esters After maternal injection, 2-chloroprocaine seems in each maternal and twine plasma in very low concentrations (62,502). An intermediate window will exist in which the body burden to the newborn, whose capability to eliminate the drug may be impaired, is relatively high. The interpretation of this difference with respect to relative rates of equilibration of the medicine in fetal tissues is complicated by the potential of differential extraction on first move via the fetal liver. Thus, the next extraction ratio of lidocaine would amplify its transplacental gradient during infusion, thereby accelerating drug transfer to the fetal circulation. If these findings may be extrapolated to people, they counsel that back-transfer, which was noticed with bupivacaine, may be exploited after an inadvertent injection within the mom by delaying supply to cut back the burden of drug within the neonate. In contrast, a major fetal clearance of lidocaine would possibly help to protect against toxicity, and the lack of net back-transfer of this agent would counsel no benefit in delaying supply. This response was then shown to be a posh perform of chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, the physiologic penalties of neural blockade, and the (patho)physiologic status of the patient. With every revision, some brokers have waned in use and new agents have been introduced-and the emphasis has shifted to safer regional anesthesia. Although the utmost tolerated doses could differ, all local anesthetic agents are doubtlessly poisonous, no matter claims, and that is clearly evident by the continual publication of case reviews of incidents even with the "safer" chiral caines. The actual issue is the separation between the utmost tolerated dose and the minimum efficient dose wanted for the process, and here the brokers differ little-but sufficient to help make choices. Knowledge of the chemical and physicochemical properties offers rationale for these choices. Xylocaine: A New Synthetic Drug, Inaugural Dissertation for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy. Stockholm, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences of the University of Stockholm, 1948. Local Anesthetics, International Encyclopedia of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Vol. Anaesthetic brokers for superior regional anaesthesia: A North American perspective. Protein binding of prilocaine in human plasma: Influence of focus, pH and temperature. The influence of lactic acid on the serum protein binding of bupivacaine: Species differences. The influence of diazepam on the serum protein binding of bupivacaine at normal and acidic pH. The affect of acidosis on the distribution of lidocaine and bupivacaine into the myocardium and mind of the sheep. Hydrophobic and ionic factors in the binding of local anesthetics to the major variant of human 1-acid glycoprotein. I: Relationships between binding, physicochemical properties and anesthetic exercise. Cerebrospinal fluid and spinal cord distribution of baclofen and bupivacaine throughout slow intrathecal infusion in pigs. Analgesic period and kinetics of liposomal bupivacaine after subcutaneous injection in mice. Determination of native tissue concentrations of bupivacaine released from biodegradable microspheres and the impact of vasoactive compounds on bupivacaine tissue clearance studied by microdialysis sampling. Prolongation of epidural anesthesia in the rabbit with using a biodegradable copolymer paste containing lidocaine. Epidural administration of liposome-associated bupivacaine for the management of postsurgical pain: A first research. A mannequin to consider the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic variables of extended-release merchandise using in vivo tissue microdialysis in people: Bupivacaine-loaded microcapsules. The dose response and effects of dexamethasone on bupivacaine microcapsules for intercostal blockade (T9 to T11) in wholesome volunteers. Noninvasive percutaneous induction of topical analgesia by a brand new sort of drug carrier, and prolongation of native pain insensitivity by anesthetic liposomes. Celiac plexus block: A roentgenographic, anatomic research of approach and spread of resolution in sufferers and corpses. Influence of volume on the spread of native anesthetic-methylene blue solution after injection for intercostal block. High volume and low focus of anaesthetic resolution in the perivascular interscalene sheath determines quality of block and incidence of issues. Epidural, cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma pharmacokinetics of epidural opioids (part 2): Effect of epinephrine. Pharmacokinetic nature of tachyphylaxis to lidocaine: Peripheral nerve blocks and infiltration anesthesia in rats. The results of extracellular pH with and with out bicarbonate on intracellular procaine concentrations and anesthetic effects in crayfish big axons. Differential sensitivity of A and C nerve fibres to long-acting amide local anaesthetics. Chapter three: Properties, Absorption, and Disposition of Local Anesthetic Agents 89 143. Effects of acute blood strain reduction by sodium nitroprusside on serum lidocaine levels. Bupivacaine (Marcaine): An analysis of its tissue and systemic toxicity in humans. Intraindividual and interindividual variability within the disposition of the local anesthetic ropivacaine in wholesome topics. Acute toxicity of native anesthetics: Underlying pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic concepts. Cardiovascular, central nervous system effect of lengthy acting local anaesthetics in man. Cerebral and hemodynamic results of lidocaine by accident injected into the carotid arteries of sufferers having carotid endarterectomy.
Grifulvin v 125 mg buy free shipping
Nerves in cross-section often seem spherical or oval on ultrasound and reveal different echogenicity-hypoechoic (dark fungus gnats effect on cannabis cheap grifulvin v 125 mg mastercard, displaying the neural component) or hyperechoic (bright fungus gnats killer generic 250 mg grifulvin v overnight delivery, displaying the connective tissue component). Electrical stimulation by way of a metal-reinforced epidural catheter primed with saline (a conducting medium) can affirm proper catheter placement in the epidural space. A positive check is indicated by a segmental motor response, unilateral or bilateral, in a dermatome congruent with the epidural insertion stage induced by a stimulating current between 1 and 10 mA (1 Hz and 0. Depending on the catheter tip location, electrical stimulation might cause anal sphincter contraction (S2�S4) with a caudal catheter, leg contraction with a lumbar catheter, intercostal or abdominal muscle contraction with a thoracic catheter, and higher limb contraction with a cervical catheter. It is important to join the cathode lead of the stimulator to the steel hub of an adapter connected to the epidural catheter and the anode (ground) lead on the body. This take a look at is reportedly 80% sensitive but the positive predictive worth is around one hundred pc (no false-positive) (62). It is essential to note that a higher current (10 to 15 mA) may be required for catheter stimulation (63), though a current of higher than 15 mA is usually not really helpful. Conversely, a motor response occurring at lower than 1 mA likely indicates intrathecal or subdural catheter placement or the catheter in shut proximity to a nerve root. A transverse sonogram showing a block needle (arrows) involved with the ulnar nerve (arrowhead) within the axilla; needle is advanced using the in-plane needle method. Needle imaging throughout advancement supplies real-time visible steerage to minimize random needle motion as the block needle is superior toward the target nerves. Needle-to-nerve contact is further confirmed by nerve motion with or without concomitant electrical stimulation. Those ultrasound probes most helpful for superficial scanning (within three to 4 cm deep;. Ultrasound scanning for the brachial plexus in the interscalene, supraclavicular, infraclavicular, and axillary regions and its peripheral branches and that for the femoral nerve and popliteal sciatic nerve is technically simple. Preliminary consequence data showing benefits of ultrasoundguided brachial plexus blocks include shortened process time, faster block onset, improvement in block high quality, extended block length, and a lower in block-related problems. Scanning the sciatic nerve in the gluteal area and lumbar plexus in the psoas compartment in adults and older children may be difficult because of the deep areas of those nerves. It is essential to realize that the success of ultrasound-guided nerve block demands: (a) correct nerve imaging technique, (b) proficiency in monitoring needle advancement in real time, (c) recognition of needle-tonerve contact, and (d) a enough quantity of local anesthetic deposit around the goal nerve. Although ultrasound technology for nerve imaging is advancing rapidly, a number of technical limitations stay. Accurate needle tracking throughout development could be tough within the absence of an echogenic needle tip design. A main concern of patients when discussing regional anesthesia for their surgery is that they will have to remain awake. This approach to the management of sufferers with nerve blockade may be traced again to the earliest days of surgery when there have been no, or too few, anesthesiologists. Surgeons performed the nerve blocks first, then they proceeded with the surgical procedure. Gaston Labat (73), a surgeon and the "Father of Regional Anesthesia," acknowledged in his early writings the importance of sedative supplementation of regional anesthesia. Even extra important are his comments relating to excessive noise within the operating room, pointless dialog that may be misinterpreted by the affected person, and avoidance of the surgeon querying the affected person about his degree of sedation or consolation. Many patients could be content material with little or no sedation if the operating room environment were quiet and nonthreatening. This could additionally be because of a full abdomen, troublesome airway, or excessive threat (poor physical status), all components that Chapter 8: Perioperative Management of Patients and Equipment Selection for Neural Blockade 175 impose severe risks beneath general anesthesia. Clearly, these patients ought to be awake or sedated just sufficient to present anxiolysis and a cooperative perspective. Specific pharmacologic agents will be discussed later, but it is a situation during which "vocal anesthesia" (reassuring conversation) or music by way of headphones could be very useful. The antithesis of the high-risk, barely sedated affected person is the pediatric or in any other case overly anxious patient who will probably become uncooperative or agitated intraoperatively. It is a uncommon patient, nevertheless, who should be denied any type of supplementation simply as a matter of precept. Surgical Considerations Frequently, the determinant of supplemental drugs and methods is the situation or anticipated period of the surgical process, or each. In common, the nearer the surgical process is to the head and neck, the more complicated the anesthetic administration. Unfortunately, as the surgical group occupies the area at the head of the patient, the anesthesiologist is most likely going dislocated to areas extra distant, requiring vigilance and caution in balancing sedation with airway management and security. One should additionally evaluation if and what medicine were given within the pre-block period because many are of quick period. A continuum of needed sedation and analgesia have to be maintained all through the perioperative interval. However, one should complement solely to the degree and period essential to restore the contribution of the regional method to general anesthetic satisfaction. A last factor overlooked by anesthesiologists and surgeons alike is total consolation for the affected person. The period of the surgical procedure affects the whole vary of supplemental pharmacology. Extremely short procedures may require no supplemental medication, whereas lengthy procedures will probably require both sedation and analgesia. Depending on surgical position, most patients will turn out to be progressively more uncomfortable from lying still on an working table. Although excessive sensory ranges of spinal or epidural anesthesia provide their very own analgesia, low levels of block and peripheral nerve blocks have restricted areas of analgesia. A ready resolution to this downside for healthy patients receiving epidural or spinal anesthesia is to produce the next stage of sensory blockade. For instance, a T11 spinal anesthetic could be adequate for lower extremity surgical procedure. However, if no vital opposed physiologic results are anticipated, then a T6 degree would supply patient comfort up to the mid-thorax with out use of large doses of systemic analgesics. Drugs and Techniques Specific agents or strategies for intraoperative supplementation of regional anesthesia include the entire gamut of anesthesia follow. Other sufferers are ambivalent about the want for or desirability of sedation and defer to the anesthesiologist. A thorough explanation to the affected person of the anesthetic and surgical happenings might be useful in their choice. Reassurance that the anesthesiologist will be in fixed attendance and capable of enhance ranges of supplementation as required or desired is essential. Techniques for distraction differ, but are designed to prevent anticipation of pain and worry by the patient. Office practitioners of native or nerve block anesthesia become adept at these methods of "vocal anesthesia. First is an intensive data of the neural components concerned in the surgical process and of the regional block to be performed. For example, the use of an intercostal nerve block is extraordinarily helpful because the anesthetic approach for placement of a gastrostomy feeding tube. One must appreciate, nevertheless, that the intercostal nerve block supplies only somatic sensory blockade of that portion of the stomach wall.