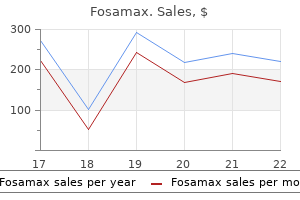
Fosamax
Fosamax dosages: 70 mg, 35 mg
Fosamax packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Discount fosamax 35 mg line
Although it has mechanisms to avoid the immune response women's health center of lynchburg va generic 35 mg fosamax, the massive variety of secreted substances trigger considerable injury to host tissues women's health clinic darwin discount 35 mg fosamax free shipping. This rash is the hallmark of scarlet fever, a toxemia almost completely related to pharyngeal infections. Impetigo, an an infection of essentially the most superficial pores and skin layers, seems as a cluster of small vesicles on a pink base that breaks right down to honeycolored crusts. Erysipelas is a raised, shiny red patch of skin with a sharply demarcated but quickly advancing margin. Deep infections corresponding to myositis and necrotizing fasciitis are accompanied by excruciating pain and often some proof of overlying pores and skin necrosis. The diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis, then again, is more confounding. To determine the cause for pharyngitis, physicians carry out rapid strep checks on a throat swab in the workplace after which tradition the organism on blood agar plates. The fast strep tests depend on detection of the group A carbohydrate antigen from organisms obtained from the throat swab. An different remedy is a single-dose injection of long-acting penicillin (benzathine penicillin) that persists within the bloodstream for an adequate period. In the school-aged population, early recognition and treatment of pharyngeal and pores and skin infections can decrease unfold to different kids. At least 24 hours of antibiotic therapy ought to be completed earlier than a child is allowed to return to faculty. The mortality fee in infants is roughly 5%, and a lot of surviving infants with neonatal infection have long-term issues such as seizures, deafness, developmental delay, and motor deficits. In general, the capsular polysaccharides are poor antigens for exciting a protecting immune response. Therefore, there was nice interest in creating a protein-carbohydrate conjugate vaccine, much like the Haemophilus influenzae kind b and pneumococcal vaccines, for use in females of childbearing age. The a-hemolytic Streptococcus pneumoniae is another major pathogenic streptococcus described in Chapter thirteen. The viridans streptococci are a diverse assortment of primarily -hemolytic species found in the oral cavity that produce a greenish discoloration upon growth on blood agar ("viridis" is Latin for green). Another medically vital group includes nutritionally variant streptococci which are troublesome to develop within the laboratory as a outcome of they require supplemental cofactors for growth in artificial media. They may cause a damaging form of endocarditis that results in extra problems than do infections with other streptococci. However, as various antibiotic classes have been used with far more frequency, the enterococci demonstrated their amazing adaptability by developing resistance to each sort of antibiotic. Thus, in the 1990s this normally harmless commensal bacterium became one of the feared nosocomial (hospital-acquired) infections, because it developed resistance to the last-line antibiotic in opposition to Gram-positive organisms, vancomycin. Transmission is primarily via the palms of well being care staff, but additionally can contain inanimate objects (fomites) corresponding to mattress rails, pc keyboards, draperies, and devices. Despite having low overall virulence, enterococci possess some virulence traits similar to biofilm formation and cytolysin manufacturing. Antibiotics like penicillins normally kill bacteria as a result of they disrupt their cell wall synthesis. Enterococci are additionally intrinsically proof against aminoglycosides by resisting their penetration into the cytoplasm. However, bacterial killing can be achieved by utilizing a combination of a penicillin and an aminoglycoside. In this mixture, the penicillin damages the cell wall and facilitates the entry of the aminoglycoside. This situation, in which the combination of two antibiotics produces a larger effect than the sum of their individual actions, is identified as antibiotic synergy. The enterococci are also capable of genetic transfer by way of conjugative elements (transposons, plasmids) and bacteriophage, which may lead to uptake of novel resistance genes or extrinsic resistance. In this fashion, enterococci might acquire absolute resistance to penicillins or aminoglycosides that negates the benefits of antibiotic synergy. These embrace linezolid, a bacterial protein synthesis inhibitor; daptomycin, a novel bacteriocidal lipopeptide that inserts into the bacterial membrane and causes cytoplasmic leak; tigecycline, a tetracycline by-product; and dalfopristin�quinupristin, a combination of two synergistic agents that additionally inhibit bacterial protein synthesis but has restricted use because of toxicity and rising resistance. Although all these drugs are welcome additions to the antimicrobial armamentarium, bacterial isolates with resistance to every of them have already been observed. While both of those organisms remain vulnerable to penicillins, the beforehand innocuous enterococci have emerged as important nosocomial pathogens, primarily due to their ability to purchase antibiotic resistance as new courses of antibiotics are introduced and abused in hospital settings. Enterococci may act as reservoirs for antibiotic resistance within the commensal microbiota. Typing group A hemolytic streptococci by M precipitin response in capillary pipettes. Encounter: Pneumococcus generally colonizes the human nasopharynx and is transmitted between people by contact and respiratory droplet spread. Entry: Bacteria are introduced into the nasopharynx; colonization precedes an infection or illness. Spread and Multiplication: Pneumococci resist phagocytic clearance by expression of a polysaccharide capsule. Organisms could unfold to other elements of the respiratory tract or into the bloodstream. Damage: Infection is characterized by an acute inflammatory response, resulting in respiratory tract infections, including otitis media, sinusitis, chronic bronchitis, and pneumonia, as properly as invasive infections such as bacteremia and meningitis. Diagnosis: the diagnosis is suspected when Gram-positive diplococci are seen in sterile tissue and body fluids. Treatment: Usually treatable with all kinds of antibiotics; nonetheless, pneumococci have developed increased resistance to penicillin and other commonly used antibiotics. Prevention: Immune protection is dependent upon antibody to the pneumococcal capsule (opsonins) and neutrophils (phagocytes). However, pneumococci categorical a number of capsular types; consequently, multiple capsule types are combined to be used in vaccines. It commonly colonizes the mucosal floor of the nasopharynx without causing disease, except host factors allow it to achieve entry to normally sterile sites such as the lung, where it is in a position to trigger an acute inflammatory response. The presence of a thick layer of surface polysaccharide, nevertheless, inhibits in any other case effective host clearance capabilities involving complement- and antibody-mediated phagocytosis. Progress in treating illness caused by this major pathogen has been eroded by the acquisition and widespread dissemination of antibiotic resistance. He felt that his signs have been resolving till he abruptly developed a shaking chill, cough, and severe pain on the best side of his chest that worsened with respiration. When he was seen in the emergency department 2 days later, he appeared acutely unwell and had a temperature of 40�C. His respiration was shallow, with diminished breath sounds over the proper facet of the thorax, indicating consolidation of the air areas of the lung. This pattern of respiration, during which the patient is reluctant to move one side of the chest because of inspiratory ache, is a condition known as splinting and signifies inflammation of the pleura (lining of the thoracic cavity and lungs) or pleurisy. A Gram stain of the sputum showed many neutrophils and lancet-shaped Gram-positive diplococci. Blood was obtained for tradition, and treatment for a communityacquired pneumonia was begun with the fluoroquinolone antibiotic, levofloxacin.
Cheap 35 mg fosamax mastercard
The normal microbiota of the intestine performs a task in human diet and metabolism breast cancer zazzle discount fosamax 70 mg without prescription, with the extent of its influence being extrapolated again from experiments done in animals 7 menstrual dwarfs generic 70 mg fosamax fast delivery. It is increasingly clear that the huge and metabolically energetic biomass residing within the large gut plays a role in the dietary stability of the host. Digestion of advanced polysaccharides is carried out by our microbiota, and several intestinal bacteria, similar to E. The metabolism of several key compounds entails their excretion from the liver into the large gut and their return from there to the liver. This enterohepatic circulatory loop is particularly necessary for intercourse steroid hormones and bile salts. Members of the intestinal bacterial microbiota make glucuronidases and sulfatases that deconjugate the compounds. Keeping Out Invaders In some sites of the physique, the normal microbiota helps hold out pathogens. Commensal micro organism have the bodily benefit of previous occupancy, especially on epithelial surfaces. Some commensal micro organism produce substances that inhibit newcomers, similar to antibiotics or deadly proteins referred to as bacteriocins. This reduces occupancy of sites on the intestinal mucosa and permits the pathogen to achieve a foothold. When the normal microbiota is worn out with antibiotics, both exogenous and endogenous microorganisms are given the opportunity to cause disease. For example, after mice are given certain antibiotics, the infecting oral dose of a Salmonella strain decreases virtually a millionfold. Patients treated with antibiotics which are significantly efficient within the intestine could undergo from diarrhea caused by toxins produced from the overgrowth of a particular organism, Clostridium difficile. Severe infections with this bacterium lead to a serious illness called pseudomembranous colitis (see Chapter 20). This organism is a minor member of the normal microbiota but can develop to a big population density when its neighbors are suppressed. Good and Bad Conversion of Ingested Compounds Compounds we ingest may be chemically remodeled by the various metabolic activities of the gut microbiota. Some compounds become carcinogens only after being modified, which might happen by way of the motion of microbiota in the large gut. For instance, the artificial sweetener cyclamate (cyclohexamine sulfate) is transformed to the active bladder carcinogen cyclohexamine by bacterial sulfatases. Evidence does implicate the normal microbiota as a threat issue for some cancers, however the significance is tough to assess; consequently, it is a topic of appreciable scrutiny (Box 2-1). On the opposite hand, the microbiota also detoxifies some potential carcinogens by degrading them. Nitrosamines present in some processed foods, or generated from the usage of nitrite to cure meals, could be damaged down by the motion of the microbiota. Similarly, carcinogenic heterocyclic amines-which could be present in cooked meat-are acted on by the normal microbiota and made much less toxic. Traditionally, our information of the role of the conventional microbiota in vitamin and prevention of disease has come from finding out animals reared beneath sterile conditions-the so-called germfree animals. Rats and mice resemble humans in lots of physiological properties but differ in essential details. A small mammal may be reared in the germfree situation if it is positioned in a sterile chamber after a cesarean delivery. The germfree chamber is provided with gloves and ports to enable manipulation and the trade of meals and different materials without breaking the sterile barrier. Many species of animals breed underneath these situations, and large colonies could be established. In basic, rodents thrive under germfree situations as lengthy as their diets are supplemented with vitamins. One of the extra fascinating traits of germfree animals is that the histology of their intestines is kind of completely different. The most seen difference is in the lamina propria, which has only some lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages. By distinction, in conventional animals, the identical tissue is heavily infiltrated with these cells. This discovering means that the "regular" gut is in a constant state of persistent inflammation. Investigators are making use of rules of microbial ecology to study the diversity and group construction of assorted websites within the human physique. The strategy is to acquire samples from essentially the most closely colonized sites-nose, mouth, intestine, vagina, and skin-and carry out huge sequencing analysis. Bioinformatics strategies of this metagenome sequencing knowledge allows the position of the sequences into taxonomical items without the want to tradition the constituent organisms. This "Human Microbiome Project" goals to catalogue the microbiota of these websites in individuals over time to decide the wholesome state, and then to correlate this state with adjustments in the microbiota that occur in various illness states, including in metabolic problems, inflammatory bowel illness, and different poorly understood persistent situations. We additionally carry viruses, fungi, protozoa, and infrequently worms, however within the healthy individual, these microorganisms are present in smaller numbers than are the micro organism. In the early days of microbiology, it was thought that most micro organism of the physique have been aerobes or facultative anaerobes. Only by using particular techniques of anaerobic cultivation has it been realized that in the gingival pocket or in feces, strict anaerobes outnumber the others by a hundred to 1 or more. Furthermore, the small quantity of oxygen that diffuses into deeper tissue layers can readily be used by host cells or by actively metabolizing aerobes and facultative anaerobes. Thus, anaerobic circumstances can be discovered a fraction of a millimeter beneath the floor. Table 2-2 exhibits the distribution and prevalence of distinguished bacteria in selected elements of the human physique. It must be understood that the organisms listed, though essentially the most frequently encountered, symbolize solely a minute fraction of the number of genera and species represented. When counted by culture-based methods, 300 to 500 species are estimated, but knowledge from metagenome and different culture-independent analyses indicate that the culturebased estimates are low by perhaps an element of 10. Newborn babies turn out to be colonized very quickly by a varied microbial microbiota, especially in their intestines. In animals and probably in humans, organisms appear based on a selected time sequence. Little is understood about why species range of their colonizing capability and in their capability to compete with others. It appears probably that particular properties of micro organism, similar to their pili, allow them to attach and survive in numerous microenvironments throughout the gut. Thus, the microbiota is different at the base of the intestinal crypts, within the mucus that covers the villi, and within the lumen of the gut. Normally, the intestinal microbiota of one particular person is remarkably fixed, though this could change with antibiotic use or in sure disease states. This stability suggests that successful colonizers are outfitted with highly effective devices to withstand the problem from newly ingested microorganisms.
Cheap 35 mg fosamax amex
Humans acquire infection by ingesting eggs in the feces of contaminated carnivores pregnancy yoga pants 35 mg fosamax order with amex, similar to canines or wolves (1) breast cancer fundraising ideas fosamax 70 mg discount with visa. The larvae cross from the gastrointestinal tract to the tissues (3), where they turn into cysts containing daughter cysts and scolices (heads) from which tapeworms can develop under the suitable circumstance (4). As indicated by the open arrow and strong line under step four, this an infection is a lifeless end in people. The tissue cysts that develop within the animals are equivalent to those in people (5, 6), but when the animals finally die in the pasture (often from unrelated causes), canines or wolves might eat their stays and ingest the tissue cysts. In the canine intestine, the ingested heads (scolices) might develop into adult tapeworms (7�9), which finally produce eggs (1) to full the cycle. Comparative epidemiology of two tissue-invasive tapeworm infections: cysticercosis (caused by the pork tapeworm Taenia solium) and echinococcosis, or cystic hydatid disease (caused by Echinococcus granulosus). In pork tapeworm, the definitive host is the human, not the pig, as a end result of solely people harbor the grownup tapeworms. Pigs are an intermediate host, since they develop solely the tissue invasive type of infection (cysticercosis) after ingestion of eggs from feces of contaminated people. Humans also develop the tissue-invasive stage of infection after ingesting eggs from human feces. Although tapeworm carriers can infect themselves with eggs from their very own feces, many humans purchase cysticercosis instantly by ingestion of fecally contaminated food and by no means really harbor tapeworms themselves. The definitive host for the tapeworm that causes echinococcosis is the canine (dog, wolf, or fox). Intermediate hosts that harbor the tissue-invasive types turn into contaminated by ingesting eggs from canine feces. In humans, tissue-invasive illness with both tapeworm is considered a dead-end an infection, since people are rarely cannibalized (to full the Taenia life cycle), and human remains are buried or incinerated in most cultures (making completion of the echinococcal life cycle improbable). When a cyst dies, its contents leak into the encompassing tissues and induce a host inflammatory response. However, even small cysticerci in the brain may cause cerebral dysfunction, including seizures, elevated intracranial stress, and blindness. Cysticerci thus provide an excellent instance of the correlation between the location and the severity of a disease. Cysticerci may cause symptoms when the parasites die and displacement of normal tissue is magnified by the host inflammatory response. That usually occurs 5 to 10 years after an infection, however signs could not turn out to be obvious until as a lot as 50 years after the preliminary infection. Praziquantel and albendazole are each efficient within the treatment of cysticercosis. The fluidfilled cysts collapse, and the parasite is ultimately resorbed by the host or calcified. During therapy, central nervous system signs might transiently worsen because of the inflammatory response to dying cysticerci. The anthelmintic drug albendazole administered over a interval of weeks can kill rising echinococcal cysts as properly. Alternatively, surgical removal of a large cyst can cure the infection, although great care have to be taken to avoid spillage and dissemination of the an infection. Examination of her esophagus and abdomen with a fiberoptic gastroscope revealed dilated veins within the esophagus that have been oozing large amounts of blood. Because viable eggs of Schistosoma mansoni have been found in her stool, she was treated with praziquantel. Nevertheless, and regardless of the potential hazard of needle puncture, procedures for aspiration of cysts have been developed that are safe and effective. Quite typically, sufferers with echinococcosis are found after their cysts have died. The infective stage of the parasite emerges from the snails and swims in water until it finds an appropriate host. They are able to burrowing through the skin of people standing, swimming, or walking in contaminated water, like the rice paddies by which Mr. In the human physique, the cercariae lose their tails and change into types known as schistosomula, which may enter the bloodstream. The parasites then move by way of the pulmonary circulation to the portal venous system, where they mature. After several weeks, pairs of male and female adults move to the venous plexuses of the massive gut (S. The mating worms remain locked together, copulating within the venous system for 10 years or more. Schistosomes Schistosomiasis is a crucial and customary disease in tropical areas. Schistosomiasis produces quite lots of clinical syndromes, relying on the anatomic location of the adult worms and the eggs they release. Under the microscope, his urine confirmed the presence of Schistosoma haematobium eggs. At cystoscopy, his bladder had a cobblestone sample, in keeping with the granulomatous modifications seen in schistosomiasis. Over a few years of infection, that process leads to the pathological modifications of schistosomiasis, corresponding to periportal fibrosis within the liver. Fibrotic changes within the bladder and ureters could cause ureterovesical obstruction and recurrent secondary bacterial infections of the bladder, leading sometimes to Gram-negative septicemia. As in other helminthic infections that invade the tissues, eosinophilia and elevated IgE levels are common in persons with schistosomiasis. Two important anomalous host�parasite interactions are central to the pathogenesis of schistosomiasis: � Profound fibrotic reactions to schistosome eggs, in all probability mediated by cytokines, account for the necessary pathology of the disease and its long-term problems. Essentially, the parasite camouflages itself with those host proteins to evade the host immune response. The life cycle is accomplished when the eggs are released into recent water, the place they hatch and penetrate the suitable snail intermediate host. Humans purchase schistosomiasis by publicity of unprotected skin to water containing infectious cercariae (1). The cercariae penetrate unbroken pores and skin (2), lose their tails, and turn into schistosomula (3). They then travel all through the bloodstream, cross the lungs (4), and mature (5) within the venous system of the liver to grownup worms (6). After a interval of 6 to eight weeks, pairs of grownup worms travel to the venous plexuses of the bladder (S. Eggs released into contemporary water hatch to miracidia (8), which invade the snail intermediate host where they mature to sporocysts (9). In such sufferers, serologic testing for antischistosomal antibodies could also be priceless. Serologic testing is most helpful in individuals who have had single, defined exposures in endemic areas.
70 mg fosamax
Sputum Gram stain (and possibly blood smear) may present Gram-negative bacilli with attribute bipolar staining menopause headaches 70 mg fosamax buy otc. Treatment of pneumonic plague should be began within 24 hours of onset of signs women's health clinic melbourne fosamax 35 mg buy on line, or mortality approaches one hundred pc. Because pneumonic plague can unfold from person to individual by droplet transmission, sufferers with this type of disease have to be treated in respiratory isolation. In addition, individuals in shut contact with the affected people ought to receive prophylactic antimicrobial remedy. Tularemia Tularemia, the illness attributable to the Gram-negative bacterium Francisella tularensis, occurs naturally throughout North America and Eurasia. As with plague, transmission of the infection amongst these animals occurs by way of the bites of ticks, flies, and mosquitoes. Human an infection is acquired by arthropod bites, handling infectious animal tissue, ingestion of contaminated meals or water, and inhalation of aerosols. Virulence factors include an antiphagocytic capsule and the enzyme citrulline ureidase. The Japanese studied the disease of their bioweapons program in Manchuria (1932 to 1945), and the Russian Biopreparat program developed aerosolized forms of F. In humans, tularemia can present in varied ways depending on the route of transmission and the site of entry into the body (see Table 57-2). The analysis of a bioterrorist attack with tularemia would be difficult given the nonspecific presentation. Lymphadenopathy, the hallmark of naturally occurring tularemia, is probably not present, and commonplace microbiological testing of sputum might miss F. The treatment of selection for pneumonic, septic, or typhoidal tularemia is an aminoglycoside antibiotic. Ciprofloxacin and doxycycline are also effective and can be preferred in a mass casualty setting. Smallpox the final naturally occurring case of smallpox was recognized in 1977 in Somalia. Thus, a case of smallpox wherever on the planet today could solely arise as a result of a clandestine laboratory accident or a bioterrorist attack. A bioterrorist might provoke a smallpox epidemic by aerosol launch or by sending deliberately contaminated individuals into an unsuspecting population. In its most pathogenic kind, variola causes disfiguring pores and skin eruptions, fever, and a mortality fee of 30% or more in unvaccinated persons. Natural an infection occurs when virus from respiratory droplets or skin lesions comes into contact with the oropharyngeal or respiratory mucosa. The infectious dose is assumed to be very small, but historical outbreaks suggest that close contact is usually required to spread the illness. After migration to regional lymph nodes, an asymptomatic viremia transmits virus all through the body. A nonspecific prodrome of fever, malaise, and prostration with headache and backache follows an incubation interval that averages 12 to 14 days (ranging from 7 to 17 days). Within 2 to 4 days of fever onset, the patient develops a maculopapular rash on the mucosa of the mouth, pharynx, face, and arms that spreads to the trunk and legs. Over the next several days, the rash turns into vesicular after which pustular because it covers the whole physique. If the patient survives, lesions kind crusts after 2 weeks and leave disfiguring scars. The patient is most contagious through the first week of rash, but transmission continues to happen until all scabs have fallen off (about 3 weeks). Mortality is usually associated with toxemia, most likely the outcomes of circulating immune complexes and soluble variola antigens, or, less often, encephalitis or secondary bacterial pneumonia. Differentiating smallpox (variola) from the more common chickenpox (varicella) could be challenging, but several discriminating options make correct diagnoses possible (Table 57-3). Note early involvement of the face, arms (including the palms), and ft (including the soles). Vaccination with live vaccinia virus has been one of the only ways to forestall smallpox disease because the late 1700s, and mass vaccination would most probably happen in a widespread outbreak. During an outbreak, an infection management measures could be of paramount significance in stopping the unfold of smallpox. All health care workers caring for smallpox patients would be vaccinated as soon as attainable, and sufferers with suspected an infection can be positioned in high-level isolation. Vaccine administered within 4 days of publicity to smallpox can significantly decrease morbidity and mortality. Public well being officials would immediately begin contact tracing to establish different potential cases and candidates for vaccination. Person-to-person spread of Ebola virus has been the cause for several devastating outbreaks in Africa. Marburg virus and possibly Lassa fever additionally spread via person-to-person contact, though aerosol unfold was implicated in an outbreak of Lassa fever in Nigeria in 1969. After an incubation interval of 2 to 21 days, infected individuals develop fever, myalgias, headache, retro-orbital pain, and prostration. A maculopapular rash and/or conjunctivitis may be present with Lassa fever and yellow fever. The mortality price varies from less than 1% for Rift Valley fever to greater than 70% from Ebola or Marburg virus. The more than likely route of dissemination in a bioterrorist attack could be aerosolization. Botulinum toxin acts on the neuromuscular junction to forestall launch of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contraction. The medical symptoms that end result are manifestations of impaired muscle contraction. Large amounts of weaponized botulinum toxin had been additionally produced within the former Soviet Union and in Iraq. Contamination of the water supply with botulinum toxin is impractical given that enormous amounts of toxin can be required, and commonplace water purification methods. Botulinum toxin exists in seven distinct antigenic types (A by way of G) that make convenient epidemiologic markers in an outbreak. Chapter 57: Biological Agents of Warfare and Terrorism 571 to present inside hours. The classic triad of botulism is (1) descending flaccid paralysis with distinguished bulbar signs, (2) regular body temperature, and (3) regular mental standing. The bulbar signs include the "4 Ds": diplopia (double vision), dysarthria (difficulty forming words), dysphonia (difficulty intoning words), and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing). Paralysis may progress to involve the muscle of respiration, in which case, dying outcomes from asphyxiation or secondary an infection (aspiration pneumonia). In addition to foodborne botulism (see Chapter 76), the toxin can be launched from C.

Buy fosamax 70 mg visa
Targeting Virulence Mechanisms: Novel Approaches to Antimicrobial Discovery the approach favored for many years in developing antimicrobial compounds has been to target the growth of microbes throughout an infection women's health big book of exercises free download buy 35 mg fosamax overnight delivery. Resistance to growth-inhibiting antibiotics and the speedy spread of resistance genes to beforehand susceptible microbial populations are severe concerns among physicians and within the general inhabitants women's health center kalamazoo mi fosamax 35 mg buy cheap on-line. An active space of analysis and growth for identifying new antimicrobial compounds is in targeting virulence mechanisms in order to block their perform during an infection. Many virulence traits-including specialized secretion mechanisms, regulatory pathways, assembly, construction, and function of extracellular organelles and toxins-are conserved throughout pathogenic species, offering the potential for broad-spectrum efficacy of compounds focused at these traits. Thus, fundamental analysis into virulence mechanisms of pathogens mentioned in succeeding chapters is prone to pay off with new therapeutic brokers. Macrolides: Resistance by Target (Ribosome) Modification the macrolide antibiotics and their derivatives are represented in medical medication by erythromycin, clindamycin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin. Like tetracyclines, macrolides may be transported out of the bacterial cell by efflux pumps, making a low degree of resistance. For example, most of the antibiotics that inhibit fungal ribosomes are additionally active towards human ribosomes and are therefore too toxic to use. In common, therapeutic agents against fungi, viruses, and animal parasites are often fairly poisonous. Especially interesting examples are the polyenes (see Chapter 50), which bind more avidly to ergosterol in the membranes of fungi than to ldl cholesterol in the membranes of upper eukaryotes. They are totally artificial, very like the sulfonamides described earlier in this chapter. Consequently, preexisting resistance genes similar to those who encode -lactamases, aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes, or ribosomal methylases sixty four Part 1: Principles appreciable. For instance, yeasts are about 200-fold extra sensitive to the polyene antibiotic amphotericin B than are cultured human cells. Nevertheless, the efficacy of amphotericin B is proscribed by toxicity to blood cells and harm to membranes of kidney cells. To some extent, this toxicity has been limited by conjugating the drug to lipid complexes. The imidazoles are one other group of agents with larger specificity for a fungal goal than for a similar goal within the host. These antifungal agents can be used topically to deal with native infections or systemically to deal with invasive disease. Thus, when tetracycline is given with penicillin, it blocks protein synthesis, preventing the cell growth required for penicillin to trigger lysis. Drugs can show synergism in toxicity in addition to in antimicrobial action (an example is the heightened harm to the kidney by the joint administration of vancomycin and an aminoglycoside). Finally, in a hospital setting, the principle sources of drug resistance are the members of the resident microbiota (not bacterial flora). Therefore, the choice to administer a number of medicine and which of them to select should be ruled by the spectrum of multidrug resistance of the dominant organisms in that hospital. A potent argument for counteracting drug resistance in microorganisms could be made for the administration of a quantity of antibiotics at once. Mutations conferring resistance to some antibiotics occur with frequencies of 106 to 109 per era. Thus, due to the fast development of bacteria in human an infection, outgrowth of resistant mutants can simply happen and turn into a significant scientific risk. However, two antibiotics given simultaneously can theoretically cut back the possibility that a bacterium will utterly evade antibiotic destruction. For instance, assume that resistance to drug A arises with a frequency of 106 per technology. If drug B has an analogous frequency of resistant mutants and is given simultaneously, the prospect of a single bacterium changing into immune to both antibiotics is 106 � 106, or 1012, which is vanishingly small. An wonderful example of this idea presently in apply is mixture therapy with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Treatment of active tuberculosis with a single agent is invariably associated with medical failure and the emergence of drug-resistant strains. Synergism: the effectiveness of the drugs collectively is larger than that of both drug alone. For instance, enterococci are naturally tolerant to penicillins and immune to gentamicin. Some of the genes that result in antibiotic resistance are chromosomal and thus are inherent within the genome of the species. But many resistance genes are plasmidborne and are in all probability acquired from different micro organism (see Table 5-1). Resistance genes, both chromosomal and on plasmids, predate the use of antibiotics. Such genes have been found in strains saved earlier than the introduction of the medicine or in isolates from areas the place antibiotics have by no means been deliberately introduced. The selective pressure of the widespread use of antibiotics has resulted in an growing frequency of resistant bacteria. In broad terms, the unfold of resistance genes increases with the usage of medicine in a particular geographic space or medical heart. Multiple resistance genes might accumulate in a given pressure by the effective mechanism of gene transposition. This process may lead to the emergence of "supergerms," microorganisms resistant to a lot of antimicrobial brokers. Near-supergerm status has been achieved by occasional isolates immune to 15 or more antibiotics. Particular examples are strains of enterococci immune to most obtainable antibiotics. In contrast, meningococci, group A streptococci, and the spirochete of syphilis remain almost as prone to penicillin today as they had been when the drug was first used. Certainly, the struggle between efficient therapy and Chapter 5: Biological Basis for Antibacterial Action 65 drug resistance is unlikely to abate, but the battles must continue to be fought and won. The various can be to hand over what many physicians and historians of science regard as a key distinction between fashionable medication and the Dark Ages. The Rationale for revising the medical and laboratory requirements institute vancomycin minimal inhibitory focus interpretive criteria for Staphylococcus aureus. Largely, our sanitary way of life determines the extent to which we encounter exogenous microorganisms, together with potential pathogens. Thus, defenses towards infectious diseases begin with the means in which we have an effect on the environment and one another. For instance, youngsters who reside in crowded, inadequately ventilated housing and eat a food regimen missing in protein usually have a tendency to contract infectious diseases such as tuberculosis than are different kids. The cause is twofold: poor nutrition diminishes the effectiveness of physique defenses, and crowding makes the encounter with tubercle bacilli more frequent. The adults in such households could have already got tuberculosis and, in close quarters, turn into ready sources of contagion. Defenses against such occasions are clear: good diet, sufficient housing, and remedy of the ill.
Fosamax 70 mg order overnight delivery
Both pathways thus pregnancy clothes fosamax 70 mg generic on line, result within the inhibition of protein synthesis and there by menstruation 19th century buy fosamax 70 mg line, successfully block viral replication. Certain cell-mediated reactions are additionally the a part of the innate defenses against viral infections. Therefore, these two innate defense mechanisms appear to work collectively to shield the host from viral an infection. Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity are various methods, how the antibodies against the viral components defend the host. Small quantity of antibody in the blood, can neutralize the virus earlier than it reaches its goal cells within the nervous system. The antibodies block the receptor molecules on the viruses, thus, preventing their attachment to the complementary tissues. Immunity in Parasitic, Viral, Bacterial and Fungal Infections In some circumstances, antibodies could block viral penetration by binding to epitope which are essential, to mediate fusion of the viral envelope with the plasma membrane. Uncoating with its launch of viral nucleic acid, into the cytoplasm, could be inhibited if the virion is roofed by antibody. If the induced antibody is of complement-activating isotypes, lysis of enveloped virions can ensue. Antibody and complement can even operate as an opsonizing agent to facilitate Fc or C3b receptor-mediated phagocytosis of the viral particles. Humoral immunity does play a major protecting function in polio and in variety of different viral infections. Passively administered antibody can protect people against a quantity of infections including measles, hepatitis A and B. Both pathways thus end result within the inhibition of protein synthesis and thereby effectively block viral replication. Antibody-mediated destruction of the virus depends on the activation of the complement resulting in lysis or phagocytosis following opsonization, but certain viruses develop strategies, to overcome complement-mediated destruction. For instance, vaccinia virus secretes protein that binds to C4b component of the complement and inhibit the classical complement pathway. The finest instance is influenza virus, which undergoes antigenic variation, producing a different pressure. Viral Evasion of Host Defense Mechanism Despite sufficient immune response produced against the viral components, virus evades the defense mechanism of the host and establish infection. The advantage of such proteins is that they permit Immunity in Parasitic, Viral, Bacterial and Fungal Infections 251. Different levels of host protection are enlisted relying on the variety of organisms and their virulence. If the inoculum dimension is small and the virulence of the organisms are low, they are often eradicated by phagocytic cells of the innate defense system. On the opposite hand, if the scale of the inoculums is bigger and the organisms are extra virulent, then the position of specific immune response comes. Whenever, the bacteria acquire entry to the tissues, their capability to fight the organisms and to get rid of relies upon upon the immune response generated towards the microbial antigens. In most cases, the immune reponse is generated against the components of the bacteria and the molecules secreted by them. Immune response is also generated towards the organ of motility (flagella), the organ of adhesion (fimbriae) and likewise the capsules. Specific antibodies to flagella and fimbriae additionally have an result on their ability to function correctly. The bacteria after successfully evading the innate protection mechanisms (mechanical barrier, antibacterial substances, phagocytosis, and so forth. The resulting increased vascular permeability leads to the exudation of serum, which incorporates complement parts, antibodies, clotting elements, in addition to phagocytic cells. Anaphylatoxins (C3a, C5a) generated by complement activations, further improve the vascular permeability increasing blood move to the world. Antibodies acquired by both immunization or previous an infection or given passively, neutralize the bacterial exotoxins. The antibody in opposition to enzymes interferes with the power of the enzyme to interact with substrates. Antibody can interfere the conventional functioning of bacteria, if in numerous ways when it binds directly to bacteria. Direct binding impacts the exercise of specific transport systems, there by depriving the micro organism of its energy supply and different important chemicals. Invasion of the micro organism may additionally be inhibited by proscribing the motility, when antiflagellar antibodies are produced. Specific antibody can agglutinate the bacteria, thus proscribing the dissemination of the organism. Antibody that binds to accessible antigens on the surface of a bacterium together with C3b element of complement, act as an opsonin and will increase the phagocytosis and clearance of the bacterium. In some bacteria, notably gram-negative micro organism, complement activations can lead directly to the lysis of the organism. Antibody-mediated complement activation additionally produce sure localized effector molecules, which help to amplify the inflammatory response. For example, the complement cut up merchandise (C3a, C4a and C5a) act as anaphylatoxin to induce mast cell degranulation and thus, vasodilation and extravasation of neutrophils and lymphocytes from blood to tissues. Humoral Immunity Attachment and invasion are necessary processes, which pathogenic micro organism adopt to set up the an infection. Certain antibodies similar to secretory IgA, intrude with the attachment molecule (agresin) and prevent colonization of pathogenic bacteria. Many organisms produce disease through their exotoxins (diphtheria, tetanus, botulism, etc). [newline]Cell-mediated Immunity Ultimately, all bacteria shall be engulfed by macrophages both to kill the micro organism or to remove after extracellular killing. The microbial products (muramyl dipeptide and trehalose dimycolate) and chemotactic factors (formyl methionyl peptide) are the Immunity in Parasitic, Viral, Bacterial and Fungal Infections 253. Complement activation on bacterial floor leads to complement-mediated lysis of micro organism; three. Antibody and the complement break up product C3b bind to micro organism, serving as opsonins to increase phagocytosis; 4. C3a and C5a, generated by antibody-initiated complement activation, induce native mast cell degranulation, releasing substances that mediate vasodilation and extravasation of lymphocytes and neutrophils; 5. The endotoxin current within the cell wall of gram-negative micro organism and numerous carbohydrate polymers, similar to -glucans, are additionally potent macrophage activators. Intracellular micro organism induce a cellmediated immune response, particularly delayed type of hypersensitivity. In many circumstances, the immune response brings in regards to the destruction of the host tissue. Evasion of Host Defense Mechanisms Establishment of bacterial an infection includes four major steps. Host protection mechanisms act at every of those steps and many micro organism have evolved methods to circumvent a few of these host defenses (Table 18. Among 70,000 or so species of fungi, solely a small numbers are pathogenic for people.
Fosamax 35 mg cheap online
Let N be the number of micro organism and t the time menstrual zine fosamax 35 mg cheap with visa, then dN/dt = Nk where k is the expansion price fixed breast cancer hoodies fosamax 70 mg buy discount on line. By integration, we obtain the regulation of growth: N t = N zero e kt the place Nt is the variety of micro organism at time t, and N0 is the initial variety of micro organism at t = 0. The regulation of growth describes a geometric progression, which holds for many situations. In some circumstances resulting in cell dying (for instance, sterilizing warmth or antiseptic chemicals), the decrease in viable bacteria could also be described by the same equation but with a adverse fixed. Growth in the Real World If balanced growth went unchecked, a single bacterium dividing twice an hour would produce a mass as large as that of the Earth in just 2 days. Instead, when micro organism grow to a certain density, they either exhaust required nutrients or they accumulate poisonous levels of metabolites. Bacteria within the inoculum sometimes resume progress slowly (lag phase, hours zero to 5). When foodstuff is exhausted or toxic material accumulates, they enter the stationary part (hours 10 onward). During the stationary phase, bacterial cultures might lose their viability, as mirrored within the viable depend, typically without dropping cell integrity (maintaining a continuing total count). For aerobic micro organism, crowding results in the exhaustion of oxygen, which is poorly soluble in water. Toxic metabolites could additionally be hydrogen peroxide, which is the case for some anaerobes that lack catalase, or acids shaped by fermentation, which ends up in a pH too low to be appropriate with development. Which of these elements truly slows down progress first depends on the strain of bacteria and on the composition of the culture medium. The explosiveness of exponential growth implies that even a small variety of micro organism can rapidly initiate an infection. An example of unhampered development that results in harmful illness is acute bacterial meningitis in a baby. Bacteria that trigger this disease, such as the meningococci, grow so quickly in the affected person that the physician must intervene with great pace to avoid a fatal end result. For instance, tubercle bacilli divide every 24 hours or so even under optimal conditions. In the tissues of the body (as well as in the environment), bacteria are often stressed by dietary limitations or by the damaging motion of the defense mechanisms. Instead, although they stop internet growth, they continue some artificial actions that allow them to make specific constituents wanted for adaptation. Energy and building blocks are provided by turnover of cell material not needed within the stationary part. Major sources of amino acids are the ribosomes and preexisting proteins not tremendously used underneath these situations. This means of feeding on itself offers bacteria adaptability and postpones death, which might otherwise happen by random degradative events within the absence of artificial actions. Bacteria are uncovered to countless injuries and have developed particular adaptive mechanisms to cope with many of them. Other protecting responses are turned on when bacteria are starved for the source of carbon, nitrogen, or phosphorus; when the temperature is raised abruptly; or when anaerobic cultures are suddenly exposed to oxygen. In every case, the fast rate at Chapter 3: Biology of Infectious Agents 35 which the bacteria implement their coping mechanism is a tribute to the powers of bacterial adaptation. First, nongrowing bacteria are nonetheless immunogenic and might elicit immune responses with both useful and detrimental results. Second, manufacturing of poisons typically begins or accelerates when bacteria enter the stationary section. In some circumstances, we can fathom the rationale for this timing, because toxin manufacturing could present micro organism with vitamins. For example, some streptococci make enzymes that lyse purple blood cells and proteases that degrade hemoglobin. This leads to the manufacturing of metabolically inert spores terribly immune to chemical and physical insults. The cytoplasmic contents that are launched generally include large quantities of poisons. This happens in tetanus, gasoline gangrene, and other ailments attributable to sporulating bacteria. The relationship between microbial progress and pathogenesis is far from easy but should be kept in mind when trying to perceive the etiology and course of infections. The reason is in all probability going financial: stopping the flow of substrates at the very starting of the pathway eliminates waste of unusable metabolites. Regulation of Enzyme Synthesis Feedback inhibition suffices to cease the synthesis of leucine in the leucine-fed culture. If this have been all, the organisms would still synthesize the biosynthetic enzymes for leucine, at a value of appreciable energy. This is wasteful and would possibly place the organisms at a selective drawback vis-�-vis more-efficient ones. To keep away from such an pointless expenditure, the cells rapidly turn off the synthesis of the enzymes of the leucine biosynthetic pathway. Two such mechanisms of regulation of gene expression used to change operons on and off are mentioned right here. The operons involved in the biosynthesis of amino acids, such as leucine, are typically regulated by a mechanism referred to as attenuation. Another mechanism for turning on or off the synthesis of enzymes is discovered within the case of many enzymes concerned in the utilization of sugars. Inefficient strains are rapidly lost in competitors with others that use their resources more successfully. There are important exceptions to this statement, however usually, it illustrates the financial system and effectivity of the bacterial way of life. We know an excellent deal about the mechanisms bacteria use to adapt to changing environmental circumstances. As extra info is gathered, it becomes evident that numerous mechanisms function a certain means underneath specific circumstances. Within seconds, the endogenous synthesis of leucine shall be stopped, and the cells will use the exogenously supplied leucine exclusively. From the viewpoint of the economy of the bacteria, this is fascinating as a end result of it saves the metabolic power expended for biosynthesis of leucine. The same phenomenon would happen if other amino acids, purines, pyrimidines, or other metabolites had been added. Transcription stops when a termination stem and loop construction involving sequences C and D is fashioned. In the absence of lactose, as within the case of a tradition rising solely on glucose, the synthesis of -galactosidase is unnecessary and wasteful. In the presence of lactose, however, the repressor undergoes a conformational change to render it incapable of binding to the operator.