Fertomid
Fertomid dosages: 50 mg
Fertomid packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Cheap fertomid 50 mg without a prescription
The histologic classification breast cancer volleyball shirts discount 50 mg fertomid overnight delivery, biological traits and histogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinomas menopause essential oils generic fertomid 50 mg line. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma with preliminary supradiaphragmatic presentation: natural historical past and patterns of disease development. Embryonal "Botryoid" rhabdomyosarcoma of the larynx: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of two instances. A examine of thirty-nine circumstances utilizing polymerase chain response and in situ hybridization. Fine structure of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with particular reference to the anaplastic kind. Malignant tumours in patients with a history of a number of laryngeal papillomas: the significance of irradiation. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity in patients aged forty five years and under: a descriptive analysis of 116 instances identified within the South East of England from 1990 to 1997. Polymorphous lowgrade adenocarcinoma arising in the nasal cavities with an related undifferentiated carcinoma. Expression of cell cycle and apoptosis-related proteins in sporadic odontogenic keratocysts and odontogenic keratocysts associated with the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Laryngeal angiosarcoma: a clinicopathologic research of five circumstances with a evaluation of the literature. The significance of "optimistic" margins in surgically resected epidermoid carcinomas. Intraoral salivary duct carcinoma: case report with immunohistochemical observations. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors of the head and neck: evaluation of prognostic elements. Alveolar and extraalveolar granular cell lesions of the new child: report of case and evaluation of literature. Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in Epstein-Barr-virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Odontogenic ghost cell carcinoma: report of four new instances and evaluation of the literature. Oncocytic papillary carcinoma with lymphoid stroma (Warthin-like tumour) of the thyroid: a distinct entity with beneficial prognosis. Sialoblastoma and epithelial tumors in youngsters: their morphologic spectrum and distribution by age. Salivary epithelial-myoepithelial carcinomas of intercalated ducts: a clinical, electron microscopic, and immunocytochemical examine. Fine-needle aspiration of metastatic nonlymphomatous tumors to the most important salivary glands: a clinicopathologic examine of 40 instances cytologically identified and histologically correlated. The affect of alcohol consumption on worldwide developments in mortality from upper aerodigestive tract cancers in males. Immunohistochemical elements of basal cell adenoma and canalicular adenoma of salivary glands. Lymphoepithelial carcinoma of the larynx and hypopharynx: study of eight circumstances with relationship to Epstein-Barr virus and p53 gene alterations, and evaluation of the literature. Laryngeal osteosarcoma: a clinicopathologic analysis of four cases and comparison with a carcinosarcoma. Malignancies arising in oncocytic schneiderian papillomas: a report of 2 cases and evaluation of the literature. Solitary plasmacytoma and extramedullary plasmacytoma of the paranasal sinuses and soft palate. Mallofre C, Cardesa A, Campo E, Condom E, Palacin A, Garin-Chesa P, Traserra J (1993). Expression of cytokeratins in squamous cell carcinomas of the larynx: immunohistochemical evaluation and correlation with prognostic elements. Epidemiological considerations of cancer of the gallbladder, bile ducts and salivary glands within the rubber industry. Odontoma syndrome: report of an uncommon case with multiple multiform odontomas of each jaws. Malignant mucosal melanoma of the top and neck: evaluate of the literature and report of 14 patients. Phenotype and genotype of advanced premalignant head and neck lesions after chemopreventive therapy. Frequent microsatellite alterations at chromosomes 9p21 and 3p14 in oral premalignant lesions and their worth in cancer danger assessment. Diet and cancer of oral cavity and pharynx: a case-control study in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Regulation of gene expression within the olfactory neuroepithelium: a neurogenetic matrix. Primary T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the larynx with subsequent cutaneous involvement. Increased proliferation of osteoblastic cells expressing the activating Gs alpha mutation in monostotic and polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Fine mapping of a putatively imprinted gene for familial non-chromaffin paragangliomas to chromosome 11q13. A human adenolymphoma showing the chromosomal aberrations del (7)(p12p14-15) and t(11;19) (q21;p12-13). Impact of the in vitro approach used on the cytogenetic patterns in pleomorphic adenomas. Martinelli M, Martini F, Rinaldi E, Caramanico L, Magri E, Grandi E, Carinci F, Pastore A, Tognon M (2002). Simian virus 40 sequences and expression of the viral giant T antigen oncoprotein in human pleomorphic adenomas of parotid glands. Highly aggressive brown tumour of the maxilla as first manifestation of major hyperparathyroidism. Cytogenetic similarities between two kinds of salivary gland carcinomas: adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma. Expression of p16 protein and hypermethylation standing of its promoter gene in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck. Sebaceous lymphadenoma of the lip: report of a case of minor salivary gland origin. Primary malignant melanoma of the nasal cavity: a clinicopathologic examine of nine cases. Adenocarcinomas of major and minor salivary gland origin: a histopathologic evaluation of remedy failure patterns. Matsumura S, Murakami S, Kakimoto N, Furukawa S, Kishino M, Ishida T, Fuchihata H (1998). Matsuno A, Nagashima T, Matsuura R, Tanaka H, Hirakawa M, Murakami M, Tamura A, Kirino T (1996). Matsushita H, Matsuya S, Endo Y, Hara M, Shishiba Y, Yamaguchi H, Kameya T (1984). Primary mucosal malignant melanoma of the larynx: case report and evaluate of the literature.
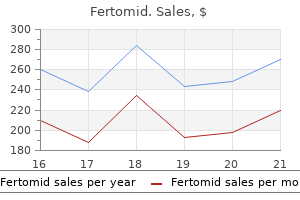
Order 50 mg fertomid amex
Maxillary and mandibular involvement might result in premenstrual dysphoric disorder 50 mg fertomid discount mastercard displacement of tooth menopause kit joke buy fertomid 50 mg without a prescription, malocclusion and, not often, root resorption 1759. Lesions extending to the orbit may cause visible impairment, while temporal bone lesions may produce hearing loss. Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia (mandible, base of skull) with extreme deformity of the mandible. Radiograph displaying expansile osteolysis with irregular opacities of the mandible, extending into the ascending ramus up to the mandibular condyle. A Trabeculae of woven bone without osteoblastic rimming embedded in a monotonous cell wealthy stroma. A Extension of Sharpey fibers from trabeculae into stroma on polarized microscopy. C In long-standing fibrous dysplasia focal lamellar remodelling could occur in the absence of osteoblastic rimming. Characteristically, bundles of collagen fibres oriented perpendicular to the bone surface, appropriate with Sharpey-fibers, can be demonstrated 1018,2067,2176. In lengthy standing lesions some osteoblastic rimming and "maturation" to lamellar bone may happen. In eight of 11 cases clonal chromosomal aberrations have been described, including both structural and numeric adjustments. Repeated chromosomal modifications have solely been documented up to now for trisomy 2 and rearrangements of 12p13, in three cases every 527. Surgical interventions may be essential for useful causes or severe disfigurement 2710. Very hardly ever, sarcoma development, predominantly osteosarcoma, has been reported preferentially in craniofacial bones and even within the absence of prior irradiation 220,2213, 2522,2835. Synonyms Periapical cemental dysplasia, periapical osseous dysplasia, focal cemento-osseous dysplasia, periapical cementoma. Clinical features / Imaging the condition happens in various scientific varieties that bear completely different names. A similar restricted lesion occurring in a posterior jaw quadrant is named focal osseous dysplasia, formerly referred to as focal cemento-osseous dysplasia 2502. However, the variation in appearances of mineralized materials distinguishes each lesions, fibrous dysplasia almost completely consisting of woven bone 2401. Histogenesis Osseous dysplasia is taken into account to originate from the periodontal ligament 2861. In distinction to large cell tumour of bone, about 1/3 of patients are younger than 20 years 1239. Molar and premolar areas are extra usually affected than the anterior components or the ascending ramus 2460. Clinical options / Imaging Most cases present as asymptomatic incidental findings. Some, nevertheless, present with ache or paraesthesia, swellings, or loosening of tooth. Disappearance of the lamina dura, root resorption or, more typically, tooth displacement are additional findings 452,967,1244,2460, 2782. Histopathology the lesion consists of spindle-shaped fibroblastic or myofibroblastic cells 643,1920, loosely arranged in a fibrous, sometimes fibromyxoid, vascularized tissue with haemorrhagic areas, haemosiderin deposits, macrophages, lymphocytes, granulocytes and, hardly ever, plasma cells. Especially in the haemorrhagic areas, evenly dispersed or small clusters of osteoclast-like large cells are found 84,452,771. In addition, traversing collagen bundles are current, often accompanied by metaplastic bone formation, giving the lesion a considerably lobular appearance. Clusters of multinucleated giant cells close to small foci of haemorrhage accompanied by mononuclear cells. More recently, antiangiogenic therapy with interferon alpha has been successfully applied 1241. Well marginated hypodense osteolysis with vestibular cortical destruction but no cortical thinning. B Well circumscribed lesion, demarcated from adherent gentle tissues (top) and mandibular bone (left). Epidemiology Cherubism is a familial illness affecting 100% of males and as a lot as 70% of females. Generally, analysis is made in early childhood (14 months to 4 years) or, in milder types, in pre-adolescence. With rising age, particularly after cessation of bone growth, the lesions regress 2608. Usually the mandible is affected more extensively, beginning on the angle at the time of permanent molar eruption. The course of may lengthen into the ascending ramus without affecting the condyle, and the mandibular body. In the maxilla, each tuberosities are affected initially followed by involvement of the anterior and inferior parts of the orbits 76,479. Clinical options / Imaging Symmetrical swellings and an indolent medical course are attribute. Bilateral maxillary enlargement might lead to retraction of the facial pores and skin including the lower eyelids, leading to scleral publicity and the typical "trying towards Heaven" appearance (cherubs on Renaissance paintings) 479,1236. Other penalties are tooth displacement and delay in tooth eruption, loosening of teeth, speech alterations and visible impairment. Affected bones are expanded by bilateral, well-delineated multilocular radiolucencies with a "soap bubble" look. With advancing age, the initially fibrous tissue is replaced by bony constructions, leading to sclerosis 76. Histopathology Initially, fibrous tissue and giant cells resembling osteoclasts are current, giving an impression that could be almost indistinguishable from central big cell lesion 1287,2840. Although a uncommon discovering, perivascular cuff-like collagen deposits are thought to be characteristic for cherubism 990. A Genetics Cherubism is an autosomal dominant familial illness and has been mapped to chromosome 4p16. Prognosis and predictive factors With time, particularly after puberty, the lesions regress 1286. Before puberty, surgical procedure ought to be carried out only in cases of severe useful disturbances 1362. A Bilateral expansile multilocular osteolytic lesions of both mandibular angles and the ascending ramus. Most lesions are believed to be reactive, however, an association with trauma is unlikely, particularly for maxillary ones 150. Borders are well delineated however perforations of the cortices could additionally be current and extensions into the delicate tissues do happen.
Diseases
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Cardiac and laterality defects
- Cystic fibrosis
- Western equine encephalitis
- Pointer syndrome
- Edwards Patton Dilly syndrome
- Endocardial fibroelastosis
50 mg fertomid best
The take a look at is used diagnostically to show blocked muscle lactate manufacturing and exaggerated manufacturing of ammonia in these issues menopause weight fertomid 50 mg discount line. If a mitochondrial myopathy is suspected women's health new zealand magazine fertomid 50 mg discount free shipping, a handgrip check can additionally be helpful diagnostically. Oxygen extraction is compromised in situations with respiratory chain insufficiency, and due to this fact desaturation of venous oxygen is impaired or even absent in these situations. Testing of labor capability A cycle ergometer check is the gold commonplace to check the oxidative capacity of a person, and thus the best goal measure of whether or not an individual has train intolerance. A maximal oxygen uptake of two commonplace deviations beneath the norm for a given age and gender is clearly irregular. At the beginning of exercise and through strenuous exercise, muscle operate relies upon International Neurology, Second version. When performed appropriately, topics need to reach close to their maximal predicted heart fee at exhaustion. Otherwise, a low oxidative capacity could very nicely simply be a query of underperformance. In contrast to the shortage of specificity of a maximal cycle test, a lower constantrate cycle depth protocol could be diagnostically useful in sufferers with muscle glycogenoses. As with the handgrip test, blunted or absent lactate responses and exaggerated ammonia responses could be measured throughout exercise in these situations, and in sufferers with myophosphorylase deficiency (McArdle disease) and a few sufferers with phosphoglucomutase deficiency, a secondwind phenomenon develops throughout train. The secondwind phenomenon denotes a sudden, spontaneous marked improvement in train capability after 7�8 minutes of exercise, and is brought on by an enhanced uptake and oxidation of glucose and fatty acids. The impact of an intravenous or oral complement of glucose/sucrose on work capability throughout cycle exercise may additionally be simply noticed in McArdle disease, debrancher deficiency, and phosphoglucomutase deficiency. Thus, in a examine of 77 sufferers with myoglobinuria seen in a nonspecialty clinic, almost all had acquired causes; alcohol was the commonest, adopted in order of frequency by limb immobilization with compression, generalized seizures, direct trauma, and drug abuse. Low bodily health decreases the period and intensity of exercise that can be sustained with out muscle harm. Hypokalemia and hypophosphatemia dispose to myoglobinuria, probably due to depolarization of the muscle membrane. Hypo or hyperthermia and infections, which often might produce myoglobinuria alone, can also act as potentiating factors. In 77 muscle biopsies from patients with mostly recurrent myoglobinuria studied in a neuromuscular clinic, 47% had an identifiable enzyme deficiency suitable with a metabolic myopathy, when apparent extrinsic components had been dominated out beforehand. Under regular circumstances, myoglobin is excreted in minimal quantities in urine (less than 5 ng/mL). Myoglobin consists of eight helical segments, and with its single heme group has the next affinity for binding oxygen than hemoglobin. Thus, adult transgenic mice missing myoglobin expression have normal life expectancy and might train, because of adaptive responses similar to increased vascularity and overexpression of hypoxiainducible transcription factors. Rhabdomyolysis is usually used interchangeably with myoglobinuria, and describes the dissolution or disruption of striated muscle that results in lack of muscle proteins, including myoglobin, to the extracellular house. Common to all etiologies of myoglobinuria is direct damage to the sarcolemma, often related to failure of power provide to maintain sarcolemmal transport functions, which inevitably will result in a rise in intracellular calcium. This triggers muscle contraction and the necessity for extra vitality, whereas calciumdependent proteases and phospholipidases will begin to break down essential protein constructions of the muscle, and lysosomes will digest the protein debris. Thus, disruption of sarcolemmal integrity starts a vicious circle which will finish with disintegration of the muscle fiber. Causes of myoglobinuria Myoglobinuria has many intrinsic in addition to extrinsic causes. The enzyme defect in this condition is often complete, and therefore train capability is severely lowered. Most other muscle glycogenoses are related to some residual enzyme exercise, and consequently the train depth that provokes myoglobinuria is much higher than in McArdle disease, and the frequency of attacks is lower than in McArdle illness. Disorders of fatty acid oxidation these disorders comprise more than 25 enzyme deficiencies of fats metabolism, but many primarily give rise to hepatic manifestations with hypoglycemia, encephalopathy, and seizures. Less than eight of the disorders give rise to myopathic symptoms and myoglobinuria. Two other issues of fatty acid oxidation related to frequent attacks of 518 Part thirteen Neuromuscular Disorders Table 126. Mitochondrial issues Besides the specific mitochondrial disorders talked about in Table 126. The underlying mechanism is probably energy failure, as in other metabolic myopathies, but the low incidence of myoglobinuria in these conditions signifies that vitality failure alone is probably not the one factor responsible. As with disorders of fatty acid oxidation, buildup of acylcarnitines can also play a role in disruption of the sarcolemma. Muscular dystrophies Recurrent myoglobinuria is being increasingly recognized in quite lots of muscular dystrophies, particularly with the appearance of higher molecular characterization of these muscle diseases. Recurrent myoglobinuria was first recognized in the dystrophinopathies, and may in Becker muscular dystrophy be the presenting symptom. However, myoglobinuria can also be the presenting symptom in 20% of sufferers with limbgirdle muscular dystrophy varieties 2I and 2L, and has also been noticed in sarcoglycanopathies. Acquired causes of myoglobinuria Drugs and toxins Drugs and toxins most likely account for greater than 75% of all cases of myoglobinuria in adults. The commonest compounds concerned are alcohol, illicit medication (particularly ecstasy, amphetamines, cocaine, opiates), and cholesterollowering brokers (particularly statins). Trauma Myoglobinuria is unfortunately nonetheless a significant factor in natural and manmade disasters involving compression of musculature. This consists of trauma sustained during traffic accidents, falls, struggle, or different violence. It also contains compression after long immobility, and therefore overlaps with alcohol abuse, compression after prolonged, extreme generalized seizures, and on account of compartment syndromes, which may be both traumatic or exercise induced. Chapter 126 Exercise intolerance and myoglobinuria 519 Infections A number of viral and bacterial brokers may trigger myoglobinuria (Table 126. The commonest infectious etiologies are influenza viruses A and B, streptococci, staphylococci, legionella, and salmonella. The pathogenesis of myoglobinuria continues to be unclear, however could embrace direct invasion of myocytes by the infectious agent, toxic results, hyperthermia, and drug therapy in critically ill sufferers, particularly together with muscle relaxants and steroids. Treatment and prevention the mainstay of remedy effort in any case of myoglobinuria is to avoid renal failure. It is therefore necessary to maintain enough blood stress and keep away from hypovolemia. Thus, saline infusion is necessary to preserve urine output and as a method to dilute poisonous products launched from the necrotizing musculature. Myoglobin crystallizes at low pH, and it could subsequently be necessary to alkalinize the urine. Disturbances of plasma calcium and phosphate or potassium ranges have to be corrected, and if a compartment syndrome is present, fasciotomy could additionally be wanted.
Fertomid 50 mg cheap free shipping
Wipe the again of the slide clean women's health clinic stephenville tx fertomid 50 mg with visa, and place in a draining rack for the smears to air-dry (protect from direct sun light) menstrual 3 times in 1 month fertomid 50 mg order on-line. Most are soil saprophytes, but some are human pathogens accountable to cause actinomycosis nocardiosis and actinomycetoma. Large group of gram constructive bacilli with an inclination to form chains and filaments. Endogenous members of the bacterial flora within the mouth and lower gastrointestinal tract Actinomycosis Chronic Etiology: Actinomyces israeli Actinomyces naeslundii Characteristics. Gram optimistic, facultative anaerobe substrate filaments that grow in co2 enriched condition Pathogenesis and clinical options. Infection is initiated by trauma that introduces these endogenous micro organism into the mucosa 1. Cervico facial actinomycosis 270 suppurative and granulomatous infection with interconnecting sinus tracts that comprise sulfur granules Medical Bacteriology Fluctuant mass with draining fistula in jaw area, and should lengthen to involve bone and lymphnodes within the head and neck 2. Thoracic actinomycosis Resemle subacute pulmonary infection with extension to chest wall and ribs 3. Diagnosis: Specimen: Tissue, pus, sputum Smear: Gram-positive filaments with lobulated sulfur granules Culture: Thioglycolate broth or blood agar incubated anaerobically or co2 enriched condition Biochemical reacrion: Catalase positive/negative Treatment: Penicillin Clindamycin + Surgery Erythromycin Nocardiosis Etiology: Nocardia asteroides complex N. Aerobic gram constructive, partially aci fast bacilli Pathogenesis and cloinical options: Route of transmission: Inhalation Usual presentation is subacute or continual pulmonary an infection with dissemination to the mind and skin Lab. Spirochete include protoplasmic cylinder bounded by a cell wall and outer membrane. There is an axial filament or endoflagella between the cell wall and outer membrane. Not cultured in synthetic media, in fertilized eggs and tissue culture, but the saprophytic Reiter pressure grows in anaerobic culture. Remain viable in the blood or plasma store at 4 0c no much less than for twenty-four hrs (transmitted via blood transfusion) Antigenic construction. Manifests maculopapular rash condylomata lata and white patches 274 Medical Bacteriology in the mouth. There may be syphilitic meningitis, Primary and secondary syphilis are wealthy in spirochete from the site of the lesion and patients are highly infectious. Early latent stage: Relapse of signs and signs happen, and patients are infectious. Tertiary stage: Manifesting with gumma(granulomatous lesion) in bone, skin and liver; meningovascular syphilis, syphilitic paresis, tabes dorsalis, syphilitic aortitis and aortic aneurysm. One third of circumstances seems spontaneously cured throughout main and secondary syphilis but no clear evidence 2. Out come: Abortion Fetal demise Still start Early neonatal death Organ damage: Congenital syphilis triad. Non-treponemal antigen tests Antigen- Cardiolipin from beef coronary heart 276 Medical Bacteriology 1. Positive outcome revert to negative with in 618 months of effective remedy of syphilitic an infection Principle: Antigen and antibody (Reagin) reaction ends in clumping after aggitation. It may give quantitative outcomes, and valuable in establishing a analysis and in evaluating impact of treatment 2. Complement fixation take a look at: Wasserman test; Kolmer test Principle: Reagin-containing sera (mixture of IgM and IgA) repair complement in the presence of "cardiolipin-cholestrol-lecithin complex" antigen. Add diluted serum containing antibody to the sensitized gelatin particle in a microdilution tray. Positive result when agglutination occurs Treatment: Penicillin Tetracycline Erythromycin Control measures: Treatment of instances and display contacts Practice safe sex with condoms Health training T. Tightly coiled, thin, versatile spiraled spirochetes forming one polared hooked ends. Fatty acid oxidation is main supply of vitality Antigenic structure: Lipopolysaccharide: Determine the specificity of human immune response to the organism and serologic classification of leptospirae Pathogenesis and scientific options: Essentially zoonotic infection and humans are unintentional host Source of infection is contaminated foood and water with leprospia spp. Antigenic construction: Group-specific antigens Species-specific antigens Clinical Features: Clinical illness is as a result of of the invasion and multiplication of rickettsiae within the endothelial cells of small blood vessels. These are: Typhus group Scrub typhus group Spotted fever group headache, malaise, pores and skin rash and Table 2. It causes epidemic or louse-borne typhus and the milder recrudescence kind, Brill-Zinser illness. Clinical Features: It is transmitted by self-inoculation of the organism by scratching after chunk by contaminated louse(Pediculous humanus corporis and pediculous humanus capitis). The illness manifests with sudden onset of fever, headache, malaise, prostration and skin rash. Epidemics of the disease are associated with overcrowding, cold climate, lack of washing services and gasoline, famine and warfare. The illness is milder than louse-borne typhus and occurs in those people living or working in highly rat-infested space. Laboratory analysis: Specimen: Serum for serological exams the serological checks to diagnose typhus are: 1. The smallest dwelling micro-organism capable of free dwelling in nature self-replicating on laboratory media. Highly pleomorphic because of absence of inflexible cell wall, as an alternative bounded by a triple-layered "unit membrane". Have enzyme methods and make their very own proteins, lipids, nucleic acids and vitamins. The elementary physique is reorganized into reticulate physique in the host cell which is specifically adapted for intracellular growth. The reticulate physique grows and divides many times to type inclusions within the host cell cytoplasm. With in 24-48 hours of developmental cycle, the reticulate bodies rearrange them selves into infective elementary our bodies and released after host cell rupture. Antigenic construction: Group-specific antigen Species-specific antigen Chlamydia trachomatis. Appearance in iodine stain Brown inclusions in host cell cytoplasm because of glycogen matrix surrounding the particle. Incubation interval is 3-10 days Route of transmission is through oblique contact like eye-toeye by contaminated fingers or sharing towels. It manifests as a persistent keratoconjunctivitis producing scarring and deformity of the eyelids, corneal vascularization and opacities which may result in blindness. Culture: Mac coy cells or embryonated eggs Serology: Immunofluorescent exams Treatment: Erythromycin Tetracycline Control measures. Male - non-gonococcal urethritis Epididymitis 290 Conjunctival scraping from higher tarsal Medical Bacteriology. Females- Urethritis Cervicitis Pelvic inflamatory diseases If sophisticated in females, it causes infertility and ectopic pregnancy. Neonatal inclusion conjunctivitis and neonatal pneumonia Transmission is during passage via the contaminated start canal. Laboratorydiagnosis: Specimen: Endocervical scraping Culture: mac coy cells Serology: Enzyme immunoassay for group-specific antigen. On the idea of their life habits, microorganism is assessed as saprophytes or parasites.
Fertomid 50 mg without prescription
Look for the looks of capsule swelling Treatment: Amoxicillin Chloramphenicol Thid technology Cephalosporins Prevention and control: Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: Immunization of people with kind particular polysaccharide vaccine Biochemical response to diagnose streptococci pregnancy 0-2 weeks fertomid 50 mg buy on line. Optochin take a look at under the 100X goal microscope 191 Medical Bacteriology Table 2 women's health center templeton fertomid 50 mg buy. Cutaneous anthrax (Malignant pustule): ninety five % of anthrax presentation Characterized by a black necrotic lesion with a particular edematous margin onhands, arms, face or neck with regional lymphadenitis associated systemic signs. Intestinal anthrax: Presents with abdominal ache, vomiting, and bloody diarrhea Bacteremic and intestinal anthrax are rare to occur Laboratory diagnosis: Specimen: Fluid or pus from skin lesion, Blood, sputum Smear: Non-capsulated gram-positive rods with centrally positioned spores from culture Large capsulated gram-positive rods with out spores from major specimen. Non-hemolytic,massive, dense, grey-white irregular colonies with colony margin of "Medussa Head" or "curled-hair lock" look due to composition of parallel chaining of cells. Biochemical response: Gelatin-stab culture: Gelatin liquefaction Growth along the observe of the wire with lateral spikes longest near the floor Providing "inverted fur tree" look. Ocular infection Ocular disease following trauma from non-sugical penetrating objects 196 Medical Bacteriology Manifests with keratitis, endophthalmitis, and panophthalmitis Treatment: Clindamycin + Aminoglycosides 2. Genus: Clostridium Characteristics: � � � � � Clostridia are anaerobic, spore-forming motile, gram-positive rods. They inhabit human and animal gut, soil, water, decaying animal and plant matter Spores of clostridia are wider than the diameter of organism and positioned centrally, subterminally and terminally Species of medical significance: C. It causes cell lysis as a result of lecithinase motion on the lecithin which is present in mammalian cell membrane. Clostridial meals poisoning It causes secretory diarrhea because of launch of enterotoxin within the intestine Self-limiting diarrhea just like that produced by B. Saccharolytic property showing reddening of the meat with a rancid odor as a end result of carbohydrate decomposition. Proteolytic property displaying blackening of the meat with disagreeable odor because of protein decomposition. Nagler reaction: Lecithinase C activity- Opacity within the egg-yolk medium due to lecithin break down 199 Medical Bacteriology Procedure: 1. Treatment: Penicillin Prompt and extensive wound debridement Polyvalent antitoxin Prevention and management Early debridement enough contaminated wound cleansing and 200 Medical Bacteriology Closridium difficile General traits. Not incessantly discovered in the wholesome grownup, but is found usually within the hospital setting. Human feces are the expected supply of the organism Pathogenesis and clinical options: Administration of antibiotics like ampicillin, clindamycin and cephalosporins ends in killing of colonic normal flora and proliferation of drug resistant C. Dignosis: Identification of toxin A and B in feces by latex agglutination test Treatment: Dicontinuation of offending medication Administration of metronidazole or vancomycin 201 Medical Bacteriology Clostridium tetani General characteristics: � � � � World broad in distribution in the soil and in animal feces Longer and thinner gram-positive rods with round terminal spores giving attribute "drum-stick" look. Tetanolysin: Hemolytic property Pathogenesis and Clinical manifestation: Infection of devitalized tissue (wound, burn, harm, umblical stamp, surgical suture) by spores of C. Muscle spasm and rigidity Laboratory analysis: the bacteria can be cultured in a media with anaerobic atmosphere. The toxin is absorbed from the gut and acts by blocking the discharge of acetylcholine at synapses and neuromuscular junction and manifests with flaccid paralysis and visual disturbance, lack of ability to swallow, and speech issue Death is secondary to respiratory failure or cardiac arrest 2. Diagnosed by demonstration of the organism or toxin from the stool 204 Medical Bacteriology three. Treatment: Administration of intravenous trivalent antitoxin (A,B,E) Mechanical ventilator for respiratory support Prevention and management. Diphteria toxin causes respiratory tract epithelial destruction tesulting in formation of necrotic epithelium with pseudomembrane formation over the tonsils, pharynx, and larynx. Distant toxic damage contains parenchymal degeneration and necrosis in coronary heart muscle, liver, kidney, adrenal glands and peripheral and cranial nerves. Wound/skin diphteria occurs mainly in the tropics and types membrane-covered wound that fails to heal. Blood tellurite agar: Produce characteristic grey-black colonies as a result of their capability to reduce potassium tellurite to tellurium Characteristics of C. Gel-precipitation (Elek) test: a filter paper strip previously immersed in diphteria antitoxin is included into serum agar; the pressure of C. Incubate at 37 0c for 1-2 days, and observe for strains of precipitation in the agar indicating toxin-antitoxin interaction. Schick check: a pores and skin check to demonstrate immunitydue to immunization or natural an infection Method: Intradermal injection of toxin into the anterior aspect of one forearm and heat-inactivated toxin into the other. Reactions as a outcome of the toxin are slower and longer lasting than these resulting from hypersensitivity. Listreriolysin(hemolysin) Pathogenesis and medical options: Transmitted to people through ingestion of poorly coooked meat and unpasteurized milk and milk products 1. Swine is major reservoir Pathogenicity and clinical options: Most human circumstances of illness are associated to occupational exposure, i. Diagnosis: Specimen: Blood Culture: Shows -hemolysis on Blood agar Biochemical response. Produce acid from sugar fermentation Treatment: Penicillin G 212 Medical Bacteriology 2. Neisseria gonorrhoea Antigenic structure: antigenically heterogeneous and capable of changing its surface buildings. Pili: Hair-like appendages extending from bacterial floor and improve attachment to host cells and evade human defense. IgA1 protease:Splits and inactivates main mucosal IgA(IgA1) Clinical manifestation: Route of an infection: Sexual contact Male. Gonococcal urethritis If complicated: Urethral stricture Gonococcal epididymitis Gonococcal epididymo-orchitis Infertility. Gonococcal salpingitis If compicated: Gonococcal tubo-ovarian abscess 215 Responsible to harm Medical Bacteriology Pelvic peritonitis Infertility Infant (When delivered by way of the infected birth canal). Gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum If untreated and complicated results in blindness Laboratory diagnosis: Specimen: Urethral swab, cervical swab, eye swab Smear: Gram-negative intracellular diplococci More than 5 polymorphs per high power subject. Drug of choice: Ceftriaxone Ciprofloxacin Prevention and management � � � � � � Avoid a quantity of sexual associate Using mechanical safety methods (condom) Early analysis and immediate therapy of instances Contact tracing Screening of excessive threat population groups Ophthalmic ointment application of erythromycin or tetracycline to the conjunctiva of all new borns 217 Medical Bacteriology Neisseria meningitidis Characteristics: � � Gram-negative intra mobile diplococci. Capsular carbohydrate It is necessary for serogrouping of meningococci and there are thirteen serogroups. The most essential serogroups associated with disease in humans are A, B, C, Y and W135. Outer membrane protein Analogous to por protein of gonococci and liable for the formation of por in the meningococcal cellwall 20 recognized serotypes It meningococci. Lipopolysaccharide Responsible for the toxic effects found in meningococcal disease Clinical manifestation. Meningococcemia: Meningococcal septicemia is responsible for serotype specificity of Table 2. Laboratory analysis: Specimen: Cerebrospinal fluid, blood Smear: Gram-negative intracellular diplococci 219 Cloudy. Serology: Latex agglutination test/ Hemmagglutination test Treatment: Penicillin Penicillin-allergic Prevention and control. Rifampicin is used as prophylactic drug to scale back the service state throughout epidemics and given to home maintain and other shut contacts. The major species of medical significance are: Medical Bacteriology Clinical options: the bacteria causes illness mostly in younger children. Acute pyogenic arthritis Laboratory prognosis: Specimen: Cerebrospinal fluid, sputum, blood, pus Smear: Gram-negative brief rods.
Syndromes
- Bleeding
- Getting plenty of exercise
- Manage the diarrhea
- Abnormally heavy menstruation
- Weakened immune system
- Diflorasone acetonide
- Chronic conduction system disease
- Did the breathing problem start suddenly?
Fertomid 50 mg best
Occasionally womens health group tulsa purchase fertomid 50 mg with mastercard, the first symptoms might observe an episode of coughing menopause sweating purchase 50 mg fertomid with mastercard, sneezing, or straining. Wasting and weakness of the small muscles of the arms are widespread early signs, but, alternatively, the patient may notice lack of feeling within the palms or the resulting accidents. The index of clinical suspicion for syringomyelia ought to be raised in children with scoliosis, as its incidence is 50% in these kids. Sensory indicators Sensory signs are often probably the most prominent medical function and manifest as a consequence of the progressive lesion in the central region of the spinal wire. It interrupts decussating sensory fibers derived from several consecutive dorsal roots. As these fibers conduct ache, heat, and chilly sensitivity, these types of sensation are impaired while others are preserved. Accordingly, pain and temperature sensory loss with preservation of position, vibration, and touch (dissociated sensory loss) is characteristic. It normally appears alongside the ulnar border of the hand, forearm, and arm, and on the higher part of the chest and again on one side, in a "halfcape" (unilateral) distribution, with a decrease border across the chest wall. When the lesion is situated centrally, or has prolonged from one aspect of the twine to the other, the realm of dissociated sensory loss is bilateral. As the lesion extends upward and downward in the cord, the realm of sensory impairment reaches the radial facet of the hand, forearm, and arm and downward over the thorax. On reaching the higher cervical segments, the lesion begins to involve the spinal tract and nucleus of the trigeminal nerve, with the formation of the world of dissociated sensory loss extending in a concentric method from behind forwards on the face. The progressive extension of the spinal lesion later causes compression of the lateral spinothalamic tracts on one or either side, resulting in lack of sensation of pain, heat, and cold over the lower components of the body. Pain is a prominent function in 50�90% of adult sufferers with established syringomyelia. Patients sometimes current with complaints of radicular pain (often in a bandlike distribution), headache, neck, or interscapular ache. In addition to the more frequent scientific pain syndromes, approximately 40% of sufferers with syringomyelia expertise important dysesthetic ache, which is variously described as a burning sensation, pins and needles, or stretching of the skin. Other common characteristics include dermatomal patterns of hypersensitivity, in addition to trophic changes corresponding to shiny or shiny pores and skin, coldness, paleness, and irregular sweating. Motor signs the earliest motor manifestations are often muscular weakness and losing in the small hand muscular tissues because of compression or destruction of the anterior horn cells. As the lesion extends, the wast- ing spreads to contain forearms and later the arms, shoulder girdles, and higher intercostals. In contrast to motor neuron illness, fasciculation and severe wasting are uncommon. Extension of the lesion to the posterolateral medulla typically entails the nucleus ambiguus, inflicting paresis of the taste bud, pharynx, and vocal cord, sometimes leading to laryngeal stridor. Compression of the corticospinal tracts in the spinal cord causes weak spot, with slight spasticity and extensor plantar responses in most cases in the later levels. The tendon reflexes are exaggerated in the decrease limbs, however are diminished and lost early within the upper limbs, significantly on the side of the dissociated anesthesia. Loss of sweating or excessive sweating may happen, usually over the face and higher limbs. Neuropathic osteoarthropathy, also called Charcot neuroarthropathy (usually with involvement of the shoulder and elbow), is exhibited in 20% of patients. The scars of former accidents are usually evident on the palmar surface of the fingers. When the syrinx is related to a Chiari malformation, the latter can also be readily demonstrated on sagittal Tlweighted pictures that embrace the level of the foramen magnum. Treatment An etiologydriven strategy is beneficial within the diagnosis and administration of syringomyelia. In the absence of signs, syringomyelia should in all probability not be handled, however carefully monitored. Protection of analgesic areas and early therapy of cutaneous lesions to have the ability to promote healing are essential. Chapter one hundred sixty Syringomyelia 637 Surgical intervention stays controversial and is individualized to these sufferers with progressive spinal twine injury to maximize residual function. In instances involving a Chiari malformation, the principle aim of surgical procedure is to provide more room for the cerebellum on the base of the skull and higher cervical spine. Successful surgical procedure should stabilize the condition and should lead to a modest enchancment in signs. Idiopathic syringomyelia: Retrospective case sequence, complete evaluation, and update on management. This chapter will spotlight common causes of neurological deficits occurring in infancy and persevering with via adulthood. Intraventricular hemorrhage Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy Perinatal asphyxia happens in untimely and term newborns. Diagnosing asphyxia is based on wire blood acidosis, low Apgar scores, such as 6 or under, or different metabolic abnormalities that may recommend injury to other organs besides the mind. In a state of extended hypoxicischemic injury, cardiac output fails, systemic hypotension occurs, and cerebral blood circulate decreases. Healthy brain vasculature is prepared to compensate by autoregulation to preserve sufficient blood circulate to the brain. However, untimely brains and infants with cardiorespiratory illness have poor autoregulation. The cerebral circulation is strain passive, which means that a fluctuating arterial blood pressure causes an associated fluctuating sample of cerebral blood flow velocity as a result of the poor ability of the cerebral vessels to compensate for these alterations. As a end result, ranges of many neurotransmitters are unbalanced, together with glutamate, excitatory amino acids, and aspartate, and there may be an inflow of sodium, calcium, and chloride into cells. Sequelae of hypoxicischemic harm are decided by the extent and area of the ischemia. A world hypoxicischemic injury produces infarction within the watershed areas of the mind, whereas a extra focal harm from localized vascular compromise results in focal infarction. Often, the basal ganglia, a region by which energetic metabolism will increase susceptibility to periods of relative ischemia, is injured and will produce a concomitant motion dysfunction corresponding to dystonia or athetosis with spasticity. The incidence has been reported to be as high as 50% in the United States for births less than 35 weeks gestational age. Internationally, the incidence of hemorrhage is immediately related to the incidence of prematurity. The germinal matrix is very mobile and highly vascularized and helps the differentiation of glial cells until about 32 weeks of gestation. The capillary mattress within the subependymal germinal matrix consists of skinny endotheliallined vessels missing a developed adventitia. The combination of poor autoregulation and fragile vessels predisposes untimely infants to intraventricular and periventricular hemorrhage in this area. The periventricular white matter adjoining to the germinal matrix turns into ischemic from hypoperfusion and hemorrhagic from ventricular blood impairing venous drainage. Chronic obstruction from arachnoiditis impairs outflow of the fourth ventricle, inflicting hydrocephalus.
Cheap 50 mg fertomid
The scientific signs and signs are non-specific and the microscopical options are thought of in Chapter 5 pregnancy x-rays order 50 mg fertomid. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma Lesions involving the oral and oropharyngeal minor glands fashioned 17 menses generic fertomid 50 mg with visa. They normally form a painless mass of lengthy duration and there could also be a historical past of recent fast growth, often with ulceration. Tumour presenting as a firm swelling on the lateral aspect of the junction between the onerous and taste bud. B Plasmacytoid, or hyaline myoepithelial cells are sometimes a conspicuous characteristic of pleomorphic adenomas of minor glands. Both basal cell adenoma and canalicular adenoma can show multifocal tumours and evidence of duct transformation inside salivary gland lobules. Mucinous adenocarcinoma is very rare while clear cell carcinoma is a controversial entity; each are discussed in Chapter 5. Oral pleomorphic adenomas are related microscopically to tumours elsewhere however incessantly lack encapsulation, especially in the palate. Cases of intraoral pleomorphic adenoma with florid pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of the overlying mucosa have been reported following incisional biopsy 2541. Basal cell adenoma About 20% of basal cell adenomas contain the oral cavity and the upper lip and buccal mucosa are the most typical websites 669. Cystadenoma these lesions are unusual and kind 7% of benign minor gland tumours 668. Of these, 30% arose in the lips, 23% within the cheek, 20% within the palate and 26% in other oral and oropharyngeal sites. Canalicular adenoma and duct papillomas arise nearly exclusively in the minor salivary glands and are discussed intimately in Chapter 5. Pleomorphic adenoma these amount to 40-70% of minor gland tumours, the massive majority of instances being situated within the palate, lips and buccal mucosa 2711. They not often exceed three sphere cm in diam- Myoepithelioma the minor glands are the widespread website for and myoepitheliomas account for about 42% of all of these tumours. They show the identical range of morphological variation described in Chapter 5, but predominantly plasmacytoid tumours have a predilection for the palate of youthful individuals 546. During the course of the illness or initially, mucosal membranes similar to oral mucosa, lymph nodes and visceral organs could also be affected, typically without pores and skin involvement. They are notably frequent in distal extremities and could also be accompanied by lymphoedema. The disease is usually indolent, lymph node and visceral involvement occurs infrequently. A variant of endemic illness, a lymphadenopathic kind in African kids is quickly progressive and highly deadly. It develops in a couple of months to several years after the transplantation of solid organs or immunosuppressive therapy for a vari- Table 4. The disease could resolve entirely upon withdrawal of immunosuppressive treatment though immunosuppressive therapy though its course is considerably unpredictable. Early lesions of the skin or the mucosa are uncharacteristic and current with refined vascular proliferation 2216. In the patch stage, vascular spaces are increased in number, of irregular form, and should dissect collagen fibres within the superficial corium. Endothelial cells lining the areas are flattened or more oval, with little atypia. Admixed are sparse lymphocytes and plasma cells; incessantly, extravasated erythrocytes and deposits of hemosiderin surround the vas- cular buildings. Slits lined by attenuated endothelial cells between collagen bundles are also seen. Slit-like spaces, lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltration and extravasated erythrocytes are additionally noticed. There is more extensive angio-proliferation with vascular areas exhibiting jagged outlines. Inflammatory infiltrate is denser and extravascular purple cells and siderophages are quite a few. Hyaline globules (likely representing destroyed pink blood cells) are incessantly found. Nodular stage is characterized by welldefined nodules of intersecting fascicles of spindle cells with only delicate atypia and quite a few slit-like spaces containing pink cells. The lumina could also be both empty or contain proteinaceous fluid, lymphocytes and sometimes a few erythrocytes. Epidemiology Lymphangiomas are frequent paediatric lesions, which most frequently present at start or during the first years of life. Lymphangiomas seem principally in the head and neck area however may be present in some other a half of the body. Etiology Early or even congenital appearance in life and lesional architecture are in favour of a developmental malformation, with genetic abnormalities playing an extra function in cystic lymphangioma of the neck in association with Turner syndrome 416. Clinical options the lesion presents as a considerably circumscribed painless swelling, which is delicate and fluctuant on palpation. In oral involvement, the tongue is the site of predilection, the vast majority of lymphangiomas being located on the dorsal surface of the anterior a half of the tongue. The size may range from pinhead dimensions to massive lesions involving the whole tongue and surrounding structures. With increasing calibre the vessels may purchase pericytes and easy muscle, respectively. Current interest is centred on treating these lesions with sclerosing brokers 2117, interferon 1953 or bleomycin 2903A. There is an exceedingly uncommon case report of a squamous cell carcinoma arising in a lymphangioma of the tongue 203. A staging system of lymphatic malformations of the head and neck primarily based on the anatomic location has proven to be of relevance in predicting prognosis and consequence of surgical intervention 561,991. Macroscopy Lymphangiomas type a multicystic or spongy mass, the cavities of which contain watery to milky fluid. Histopathology Lymphangiomas are characterized by thin-walled, dilated lymphatic vessels of different measurement, which are lined by a flat- A B Lymphangioma of the tongue 195. Epidemiology In 1995, nineteen cases of the beforehand undescribed entity were reported. Clinical options Most tumours presented as an otherwise asymptomatic, sluggish rising solitary nodule within the anterior dorsal tongue. Macroscopy the reduce surface has a gelatinous consistency with occasional foci of haemorrhage.

Fertomid 50 mg line
The altering image of neoplastic disease within the western and central Canadian Arctic (1950-1980) womens health online cheap 50 mg fertomid with mastercard. Occupational publicity to wood menstruation explained 50 mg fertomid purchase mastercard, formaldehyde, and solvents and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nerve sheath tumors of the paranasal sinuses: electron microscopy and histopathologic analysis. Salivary gland choristoma of the middle ear: report of a case and review of the literature. Hirabayashi H, Koshii K, Uno K, Ohgaki H, Nakasone Y, Fujisawa T, Syouno N, Hinohara T, Hirabayashi K (1991). Extracapsular unfold of squamous cell carcinoma in neck lymph nodes: prognostic factor of laryngeal most cancers. Thyroid transcription factor-1, but not p53, is helpful in distinguishing moderately differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma of the larynx from medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. Calcifying odontogenic cyst related to odontoma: a possible separate entity (odontocalcifying odontogenic cyst). Hirunsatit R, Kongruttanachok N, Shotelersuk K, Supiyaphun P, Voravud N, Sakuntabhai A, Mutirangura A (2003). Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor polymorphisms and threat of nasopharyngeal cancer. A case of complicated odontoma related to an impacted decrease deciduous second molar and analysis of the 107 odontomas. Second main most cancers following laryngeal most cancers with particular reference to smoking habits. In: Recent Advances in Human Tumor Virology and Immunology: Proceedings of the First International Cancer Symposium of the Princess Takamatsu Cancer Research Fund, Nakahara W, Hirayama T, Ito Y, eds. Molecular and biomarker analyses of salivary duct carcinomas: comparison with mammary duct carcinoma. National Cancer Data Base report on most cancers of the top and neck: acinic cell carcinoma. Granular cell tumor of the larynx in a six-year-old baby: case report and review of the literature. A comparison of the Chinese 1992 and fifth-edition International Union Against Cancer staging techniques for staging nasopharyngeal carcinoma. A review of ninety-two circumstances with reevaluation of their nature as cysts or neoplasms, the character of ghost cells, and subclassification. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: histopathological sorts and association with Epstein-Barr Virus. Human papillomavirus types 11 and 16 detected in nasopharyngeal carcinomas by the polymerase chain response. Horinouchi H, Ishihara T, Kawamura M, Kato R, Kikuchi K, Kobayashi K, Maenaka Y, Torikata C (1993). Congenital sialolipoma of the parotid gland first reported case and evaluate of the literature. Hosaka N, Kitajiri S, Hiraumi H, Nogaki H, Toki J, Yang G, Hisha H, Ikehara S (2002). Extraosseous calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor: report of two cases and evaluate of the literature. Nasal chondromesenchymal hamartoma in children: report of 2 instances with evaluation of the literature. Cytogenetics of undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts from southern Chinese. Carcinoma of the nasal and paranasal areas in rats fed Cantonese salted marine fish. Sinonasal clean muscle cell tumors: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 12 circumstances with emphasis on the low-grade end of the spectrum. Genetic variations detected by comparative genomic hybridization in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas from completely different tumor sites: development of oncogenetic timber for tumor progression. Three new circumstances of salivary duct carcinoma within the palate: A radiologic investigation and review of the literature. Detection of recurrent chromosomal gains and losses in primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma by comparative genomic hybridisation. Genome wide detection of oncogene amplifications in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by array based mostly comparative genomic hybridization. Malignant nerve sheath tumors of the top and neck: 4 case studies and evaluation of the literature. Relative paucity of gross genetic alterations in myoepitheliomas and myoepithelial carcinomas of salivary glands. Review of the literature and report of 33 new circumstances, together with 4 cases related to the lymphoepithelial lesion. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the parapharyngeal space: case report and evaluate of the literature. Malignant myoepithelioma of the larynx with huge metastatic spread to the liver: an ultrastructural and immunocytochemical study. Case report: congenital salivary gland analage tumor presenting with neonatal respiratory misery. Ectomesenchymal chondromyxoid tumor of the anterior tongue with myxoglobulosislike change. Intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma arising in affiliation with a squamous odontogenic tumour of the mandible. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma: a report of two instances arising in websites of earlier irradiation. A case of Weber-Christian illness accompanied by a nasal symptom (a clinicopathologic case report). Ito K, Tsukuda M, Kawabe R, Nakagawa C, Matsushita K, Kubota A, Furukawa M, Kameda Y, Ito T (2000). Benign and malignant oncocytoma of the salivary glands with an immunohistochemical evaluation of Ki-67. Adenosquamous carcinoma of the tongue: report of a case with histochemical, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study and review of the literature. Report of the Workshop on Nasal and Related Extranodal Angiocentric T/Natural Killer Cell Lymphomas. Primary combined squamous and small cell carcinoma of the larynx: a case report and review of the literature. Correlating imaging and histopathology of an odontogenic keratocyst within the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.
50 mg fertomid purchase fast delivery
This signifies that genetically feminine embryos and genetically male embryos are phenotypically indistinguishable pregnancy joint pain fertomid 50 mg order on-line. The main sex cords prolong into the medulla of the gonad and lose their connection with the floor epithelium because the thick tunica albuginea forms women's health center of lebanon pa 50 mg fertomid generic. The mesoderm between the seminiferous cords offers rise to the interstitial (Leydig) cells, which secrete testosterone. The seminiferous cords remain as solid cords till puberty, when they purchase a lumen and are then known as seminiferous tubules. The testes originally develop throughout the stomach however later endure a relative descent into the scrotum as a result of disproportionate development of the upper belly area away from the pelvic region. The gubernaculum is a band of fibrous tissue alongside the posterior wall that extends from the caudal pole of the testes to the scrotum. Remnants of the gubernaculum in the adult male serve to anchor the testes inside the scrotum. The peritoneum evaginates alongside the gubernaculum to form the processus vaginalis. Later in improvement, many of the processus vaginalis is obliterated besides at its distal end, which stays as a peritoneal sac referred to as the tunica vaginalis of the testes. The cranial portion of the paramesonephric ducts run parallel to the mesonephric ducts. The caudal portion of the paramesonephric ducts fuse within the midline to type the uterovaginal primordium. Vestigial remnants of the paramesonephric duct (called the appendix testis) could additionally be discovered in the adult male. The mesonephric ducts develop within the male as part of the urinary system because these ducts are crucial in the formation of the definitive metanephric kidney. The mesonephric ducts then proceed to additionally form the epididymis, ductus deferens, seminal vesicle, and ejaculatory duct. A few mesonephric tubules in the area of the testes type the efferent ductules of the testes. Vestigial remnants of the mesonephric duct (called the appendix epididymis) may be found within the grownup male. Vestigial remnants of mesonephric tubules (called the paradidymis) also could also be found in the grownup male. A proliferation of mesoderm across the cloacal membrane causes the overlying ectoderm to stand up in order that three constructions are visible externally: the phallus, urogenital folds, and labioscrotal swellings. The phallus types the penis (glans penis, corpora cavernosa penis, and corpus spongiosum penis). Hypospadias is usually associated with a poorly developed penis that curves ventrally, generally recognized as chordee. The proper photograph exhibits chordee, where the penis is poorly developed and bowed ventrally. The undescended testes may be found in the belly cavity or in the inguinal canal. This demonstrates as a scrotal enlargement that transilluminates because of persistence of tunica vaginalis. Congenital inguinal hernia happens when a big patency of the processus vaginalis stays in order that a loop of gut might herniate into the scrotum or labia majora. Intersexuality is classified according to the histological look of the gonad and ambiguous genitalia. Treatment contains instant infusion of intravenous saline and long-term steroid hormone replacement, both cortisol and mineralocorticoids (9 -fludrocortisone). The masculinization of feminine exterior genitalia is clear with fusion of the labia majora and enlarged clitoris (see arrow to inset). This is caused most commonly by mutations in genes for androgen steroid biosynthesis. The epididymis, ductus deferens, seminal vesicle, and ejaculatory duct are regular. As this child neared puberty, testosterone levels elevated and clitoral enlargement ensued. The testes may be discovered in the labia majora and are surgically removed to circumvent malignant tumor formation. These individuals present as normal-appearing females, and their psychosocial orientation is female despite their genotype. Even although the developing male fetus is uncovered to normal ranges of androgens, the shortage of androgen receptors renders the phallus, urogenital folds, and labioscrotal swellings unresponsive to androgens. They seen that his testicles appeared to be swollen once they were altering his diaper a week in the past. The fluid accumulates in the scrotum, becomes trapped, and causes the scrotum to enlarge. A hydrocele is normally harmless and in most cases resolves within a couple of months after birth. A hematocele might have additionally been thought of, but a hematocele is usually as a outcome of trauma, and blood would have been seen on fluid collection. Inguinal hernias usually accompany hydroceles, however there was no bulge detected on bodily examination. The first signal of development is the formation of the respiratory diverticulum within the ventral wall of the primitive foregut during week 4. The lung bud divides into two bronchial buds that branch into the main (primary), lobar (secondary), segmental (tertiary), and subsegmental bronchi. The respiratory diverticulum initially is in open communication with the foregut, however ultimately they become separated by indentations of mesoderm-the tracheoesophageal folds. When the tracheoesophageal folds fuse in the midline to type the tracheoesophageal septum, the foregut is split into the trachea ventrally and esophagus dorsally. The foregut is split into the trachea ventrally and the esophagus dorsally by the tracheoesophageal folds, which fuse to kind the tracheoesophageal septum. Both lateral views and cross-sectional views are shown (dotted traces point out the extent of cross section). Curved arrows indicate the motion of the tracheoesophageal folds as the tracheoesophageal septum types between the trachea and esophagus. Clinical features embody extreme accumulation of saliva or mucus within the nostril and mouth; episodes of gagging and cyanosis after swallowing milk; stomach distention after crying; and reflux of gastric contents into lungs, inflicting pneumonitis. The main bronchi additional subdivide into lobar (secondary) bronchi (three on the right aspect and two on the left aspect, corresponding to the lobes of the adult lung). The lobar bronchi additional subdivide into segmental (tertiary) bronchi (10 on the proper facet and 9 on the left side), which further subdivide into subsegmental bronchi.
Buy 50 mg fertomid amex
Association between intellectual functioning and age in kids and younger adults with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Further outcomes from a metaanalysis menstruation in children buy fertomid 50 mg visa. Survival in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Improvements in life expectancy since 1967 and the influence of house nocturnal air flow women's health clinic flinders fertomid 50 mg cheap line. Details of the derepression machinery, other transcripts of the repeat and their operate, and the pathways of downstream genes resulting in the weak muscular tissues of their characteristic sample have yet to be worked out. Mean onset of the disease is in the second decade, with a large variation from childhood to late maturity. The illness is attributable to a lack of epigenetic repression of the D4Z4 repeat array on chromosome 4q35. Epigenetic derepression of D4Z4 is characterized by hypomethylation of the repeat and histone modifications. The resulting chromatin leisure may be brought about by discount of the number of repeats from 11�150 to 1�10. The mechanism of repeat reduction seems to be intrachromosomal gene conversion with out crossover in the majority of circumstances. Initial complaints are often as a result of shoulder muscle weakness (80%), while these caused by ankle dorsiflexor (10%), pelvic girdle (5%), and facial (5%) muscle weakness are less generally talked about. On scientific examination almost invariably shoulder girdle weakness is current, which is often asymmetric. At age 60 approximately twothirds of all gene carriers have developed ankle dorsiflexor weak point and 50% pelvic girdle weakness. Dysphagia and dysarthria are rare features; lingual hypoplasia and facial immobility have been reported in extreme circumstances. Respiratory operate is expounded to the severity of the disease, however lower than 1% of sufferers require ventilatory help. Cardiac muscle involvement has been debated for a very lengthy time; conduction defects such as proper bundle branch block happen slightly more frequently than in the regular inhabitants. Muscle pain (50�80%) and fatigue (35� 60%) are uncared for signs within the older literature. Subclinical hightone listening to loss (75%) and retinal vasculopathy with telangiectasis (60%) only hardly ever lead to deafness or visible loss, except within the infantile kind (onset before age 10 years). The latter represents the more severe finish of the clinical spectrum, often with marked facial weakness and early wheelchair dependency. Because of the genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity in this group of problems, this illness is now known as myotonic dystrophies. Difficulties in sucking and swallowing and severe respiratory distress are frequent. Survivors could have delayed motor and speech growth, psychological retardation, arthrogryposis, and talipes. The wasting and weak point of wrist extensors, finger extensors, and intrinsic hand muscle tissue could be the earliest indicators of the illness. In the lower extremities distal weak spot and wasting involve mainly the anterior tibial and peroneal muscle tissue, leading to foot drop. Disease progression is very gradual, with gradual involvement of the proximal limb and truncal muscular tissues. Grip and percussion myotonia are common options that affect bulbar, tongue, or facial muscles, inflicting problems with talking, chewing, and swallowing. Sudden demise attributable to Epidemiology Myotonic dystrophy sort 1 is the commonest inherited muscular dystrophy in adults, with an estimated prevalence of 1/8,000 in most American and European populations. Cardiomyopathy and congestive heart failure happen far less frequently than conduction disturbances. The most prevalent echocardiographic changes are mitral valve prolapse and septal and myocardial fibrosis. Testicular atrophy with hypotestosteronism, oligospermia, decreased libido or impotence, and sterility are frequent manifestations. Diaphragmatic and intercostal muscle weak point could additionally be the purpose for impaired pulmonary very important capacity and impaired most expiratory pressure, resulting in alveolar hypoventilation and continual bronchitis. Skull abnormalities embody hyperostosis, enlargement of the paranasal sinuses, decrease in sella turcica measurement, and prognathism. Central nervous system involvement features a gentle to moderate diploma of mental retardation, dysexecutive syndrome, paranoid character changes, cerebral ventricular enlargement, and non specific focal whitematter lesions in addition to diffuse graymatter atrophy. These signs lead slowly however progressively to intellectual and social deterioration. Excessive daytime sleepiness, a common drawback, may be mistaken for narcolepsy and is associated with a disturbance of the nighttime sleep pattern. Centrally mediated hypoventilation, a sleeprelated breathing dysfunction, is characterised by an absence of the standard hyperpnea as a response to elevated carbon dioxide focus. This is associated with an abnormal sensitivity to barbiturates, morphine, and different medicine that depress the ventilatory drive. In these sufferers the seek for cataracts is helpful for identifying the transmitting particular person. A median survival of 59�60 years has been reported for the grownup kind myotonic dystrophy and of 35 years for the congenital sort. The sufferers have much less symptomatic distal, facial, and bulbar weakness, and fewer pronounced scientific myotonia. Cardiac conduction alterations are primarily restricted to firstdegree atrioventricular and bundle branch block. However, sudden death, pacemaker implantation, and extreme cardiac arrhythmias have been described in small numbers of patients. Patients with premutations are asymptomatic or current a number of gentle signs, similar to cataracts, however are at danger of having children with bigger, pathologically expanded repeats. Children may inherit repeat lengths considerably longer than these current within the transmitting father or mother, a phenomenon generally identified as genetic anticipation during which illness severity increases and/or age of onset of illness decreases from one era to the subsequent. In each illnesses, affected muscle tissue show a excessive number of central nuclei and a markedly increased variation in fiber diameter. Symptomatic remedy by a multidisciplinary rehabilitation staff for the progressive muscle weakness consists of regular physiotherapy and light-weight orthoses, which stabilize the ankle and knee joints. Pacemaker insertion is strongly really helpful for patients with superior conduction system abnormalities, as are house respirators for sufferers with respiratory insufficiency. Hypersomnia could additionally be treated with methylphenidate or modafinil and despair by imipramine or amitriptyline. Carbamazepine or mexiletine together with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs or Tylenol ameliorates pain in some sufferers. Chapter 113 Myotonic dystrophies 475 Further reading Cardani R, Mancinelli E, Sansone V, et al.