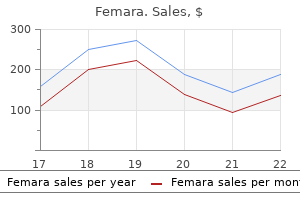
Femara
Femara dosages: 2.5 mg
Femara packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Femara 2.5 mg buy cheap
This outstanding fact was revealed by making genetically labeled clones of cells in the creating retina menstruation depression femara 2.5 mg buy discount on-line, and analyzing the adult retina to see how the clones matched to specific cell varieties pregnancy 23 weeks femara 2.5 mg generic free shipping. The possibility that each ommatidium came from a single "ommatidioblast" was quickly ruled out as clones incessantly break up by way of single ommatidia. In this technique, as we shall see, signaling between the postmitotic cells is what specifies cell fate. The mechanism controlling retinal cell destiny diversification within the Drosophila retina can be likened to a crystallization course of. At the front of this wave is a narrow groove fashioned by apical constriction of the attention disc cells. This moving groove, called the morphogenetic furrow, is the place ommatidial differentiation begins. As the morphogenetic furrow advances, cells in its wake manage themselves into regularly spaced clusters that foreshadow the crystalline ommatidial sample. Initially, all cells at the morphogenetic furrow are equal potential photoreceptor progenitors. Then, through a process of Notch-mediated lateral inhibition (Chapter 1), frequently spaced cells are singled out for sturdy Ato expression and neural differentiation. The two cells that first receive this signal activate the transcription factor Rough and become R2 and R5. R2 and R5 then additionally start to sign themselves, and assist R8 recruit the following neighbors, who turn out to be R3 and R4 which specific the transcription factors Svp and Spalt. Photoreceptors R2 and R5 (grey), R1, R3, R4, and R6 (blue), R7 (orange), and R8 (purple). In these images, the morphogenetic furrow (brighter red) initiates on the posterior (left) margin and traverses the disc toward the anterior (right) fringe of the epithelium leaving a pattern of ommatidial preclusters expressing the neural marker (Elav) in green. As each cell is recruited into the ommatidium it in turn will generate a new signal and the method repeats itself. The last photoreceptor cell kind to be part of the photoreceptor cluster inside every ommatidium is the ultraviolet receptor R7 (Ready, 1989). The first of those was called sevenless (sev), a mutant in a gene coding for a transmembrane receptor that alerts through a multistep phosphorylation pathway known as the Ras-Raf pathway (Rubin, 1991; Hafen et al. Another mutant with Generation of Neural Diversity Chapter four ninety nine a sevenless phenotype known as bride of sevenless (boss), was then discovered to encode a transmembrane protein that binds and activates the Sev receptor (Reinke and Zipursky, 1988). Genetic studies with these genes suggest that when an uncommitted cell expressing Sev touches R8, it gets an extra burst of Ras signaling that drives the R7 fate by turning on R7 specific transcription factors such as Deadpan. After the photoreceptors are all decided, the next cells that be part of the cluster turn into cone cells, and the final cells to join become the pigment cells. Thus cells are sequentially assimilated into ommatidial clusters as the wave of neurocrystallization progresses throughout the developing eye. Up to this level in our story, it may appear that the fates of neural cells should be predictable consequences of both intrinsic or extrinsic influences or a combination of the two. So it got here as fairly a shock to discover that within the Drosophila eye there are two kinds of ommatidia, and that these two varieties are stochastically distributed all through the retina. This stochasticity is underneath the management of an intrinsic "coin-flipper," a gene referred to as spineless. Whether spineless flips on or off in a selected R7 appears to be beneath the management of the vicissitudes of enhancer and silencer parts within the chromatin surrounding the spineless locus (Wernet et al. In quite lots of different techniques, together with the human retina and the mammalian olfactory neuroepithelium, stochastic mechanisms are also at work. Stochastic mechanisms produce strong distributions of fates whose percentages can simply be tuned, similar to by altering the likelihood of spineless firing within the Drosophila retina, toward evolutionarily essential environmental alerts (Losick and Desplan, 2008). These cells then migrate alongside stereotypic pathways through the embryo (see Chapter 3), go away the cell cycle, and start to differentiate. Crest cells give rise to a variety of differentiated cell types including the sympathetic and parasympathetic peripheral nervous system, the sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglia the peripheral glia (Schwann cells), and plenty of nonneural cell varieties, corresponding to adrenal chromaffin cells, melanocytes, cartilage, and tooth. The insert is an electron micrograph via a single side and reveals a cross part of the photoreceptor array. Notice that the central photoreceptor R7 is missing in every side of the mutant eye. The left panel reveals the stochastic distribution of the two types of R7 cell (one that has the photopigment Rh3 (blue) and one that has Rh4 (red) in the retina depending on whether the R7 expresses Spineless or not (see text). The proper panel exhibits, in a unique eye, the two kinds of R8 cell (one the has the Rh5 (blue) and Rh6 (green)) are additionally arranged stochastically. The R8 cells, however, make their decisions based on the selection of the overlying R7 cell. In basic experiments, Nicole Le Douarin and colleagues transplanted the premigratory crest between completely different anterior-posterior positions (Le Douarin et al. She used quail embryos as donors and chick embryos as hosts as cells from these two species can be readily distinguished. When rostral crest cells had been transplanted into the trunk region, the transplanted crest cells migrated alongside the trunk pathways and differentiated into adrenergic neurons. Similarly, trunk crest cells that have been transplanted to the rostral area gave rise to cholinergic neurons. Other transplantation experiments, showing similar switching of phenotypes, confirmed that crest cells display nice flexibility in fate choice, which seems to be decided largely by responding to local environmental cues. The "educational" hypothesis implied above is that the setting influences destiny selection in neural crest cells, but a "selective" speculation might also be thought-about, specifically that all crest cells generate a full complement of different progenitor types, however that as a outcome of environmental components like Wnt, only the appropriate types survive in each area. To test if Wnt in this system is educational or selective, single premigratory crest cells have been individually cultured in vitro with or without Wnt in the medium. Without Wnt, the cells proliferated and gave rise to clones of cells that contained a mix of crest-derived cell types. In the Wnt treated cultures, cells additionally proliferated however gave rise to clones composed of only sensory neurons (Lee et al. There was minimal cell demise in either case excluding a selective mechanism and favoring instead an instructive one. The place where the migratory crest cells encounter explicit components is very important in shaping applicable cellular choices for explicit elements of the physique (Groves and Anderson, 1996; Anderson et al. A single progenitor cell is injected with a lineage tracer, and its progeny are followed as they migrate out of the neural tube. Some could turn out to be sensory neurons, whereas others turn into Schwann cells or neurons of the autonomic nervous system. Environments these cells move via on their migration routes affect their destiny choice. Similarly, trunk crest cells which are transplanted anteriorly give rise to cholinergic neurons. Neurotransmitter selection in these cells, like the choice of opsins in Drosophila photoreceptors, is thus a really late facet of cell fate which may be influenced by the interactions with other cells such as target cells (Francis and Landis, 1999; Spitzer, 2017). The decision of a neural crest cell to decide to a glial fate is regulated by another secreted protein known as Neuregulin-1 (Nrg-1) (Britsch et al. Clonal dilutions of migrating crest cells have been cultured within the presence or absence of added Nrg-1.
Femara 2.5 mg order fast delivery
Alternatively pregnancy zantac generic 2.5 mg femara free shipping, if we already know the narrow-sense heritability pregnancy 0 negative blood type femara 2.5 mg buy on line, we will predict the mean phenotypes of offspring. If we rearrange the realized heritability equation as follows: X O - X = hN2 (X P - X) 24. Animals with a imply weight of 540 kg are used as parents and produce offspring which have a mean weight of 535 kg. What is the narrow-sense heritability (hN2) for body weight in this inhabitants of cows More particularly, the query is about utilizing heritability to predict the phenotypes of offspring. Quantitative traits usually exhibit a continuum of phenotypic variation that follows a traditional distribution (see determine 24. Genetic variance and environmental variance could contribute additively to phenotypic variance. Genetic variance and environmental variance may exhibit interactions and associations (see figure 24. Broad-sense heritability takes under consideration several varieties of genetic variation that may have an effect on phenotype, together with the additive results of alleles, results due to dominant/recessive relationships, and results because of epistatic interactions. Narrow-sense heritability is heritability that is because of the additive results of alleles. Polygenic inheritance and environmental factors might produce a continuum of phenotypes for a quantitative trait (see figures 24. Starting with a genetically numerous population, selective breeding can normally modify a trait in a desired path until a variety restrict is reached (see figure 24. The correlation coefficient is computed because the covariance divided by the product of the standard deviations. To start to clear up this problem, you first must calculate the means and commonplace deviations for each group: weights of 20 offspring. To solve this downside, you first must calculate the imply weight of the offspring after which use the equation above. Heritability within the slim sense takes under consideration all types of genetic variance. Heritability is a measure of the amount that genetics contributes to the finish result of a trait. She begins with a herd having a mean weight of 595 kg and chooses people to breed that have a imply weight of 625 kg. Twenty offspring are obtained, having the following weights in kilograms: 612, 587, 604, 589, 615, 641, 575, 611, 610, 598, 589, 620, 617, 577, 609, 633, 588, 599, 601, and 611. More specifically, the question is about calculating the realized heritability primarily based on the outcomes of crosses. One strategy to solve this downside is to recall the definitions of heritability and narrow-sense heritability. Heritability is a measure of the quantity of phenotypic variation that is as a end result of of genetic variation; it applies to the variation of a selected population raised in a specific surroundings. At the molecular stage, explain why quantitative traits often exhibit a continuum of phenotypes inside a inhabitants. Two totally different kinds of potato crops produce potatoes with the identical imply weight of 1. One selection has a very low variance for potato weight, and the opposite has a a lot higher variance. If you were a potato farmer, would you somewhat elevate a spread with a low or excessive variance If you had been a potato breeder and also you wished to develop potatoes with a heavier weight, would you select the variety with a low or excessive variance When a correlation coefficient is statistically important, what do you conclude concerning the two variables If the allele frequencies in the inhabitants are equal for both kinds of alleles. Would you conclude that the setting is unimportant in the consequence of this trait It is frequent for plant breeders to take two totally different, extremely inbred strains, which are the product of many generations of selective breeding, and cross them to make hybrids. Many stunning sorts of roses have been produced, significantly in the last few many years. These newer varieties typically have very striking and showy flowers, making them desirable as horticultural specimens. Why is a heritability worth valid just for a particular population of people raised in a particular surroundings What is the distinction between broad-sense heritability and narrow-sense heritability Why is narrow-sense heritability such a useful concept within the field of agricultural genetics Nearly the entire phenotypic variation for this trait in this group of chickens is due to genetic variation. In a pretty large inhabitants of individuals residing in a commune in the southern United States, everyone cares about good nutrition. [newline]All of the members of this population eat very nutritious foods, and their diets are similar to each other. How do you assume the heights of people in this commune population would examine with these of the overall inhabitants within the following categories When artificial selection is practiced over many generations, eventually a plateau is reached in which additional selection has little impact on the outcome of the trait. Discuss whether or not a natural population of wolves or a domesticated population of German shepherds is more prone to have a higher heritability for the trait of size. Height (cm) 159 162 161 175 174 198 172 180 161 173 Weight (kg) 48 50 fifty two 60 64 eighty one fifty eight seventy four 50 fifty four following sizes: zero. You mate them after which determine the thorax lengths of 30 offspring (half male and half female): 0. In a pressure of mice, the average 6-week physique weight is 25 g and the narrow-sense heritability for this trait is zero. What could be the typical weight of the offspring if mother and father with a imply weight of 27 g had been chosen What parental mean weight would you want to choose to obtain offspring with an average weight of 26. A hazard in computing heritability values from research involving genetically related individuals is the likelihood that these individuals share more similar environments than do unrelated individuals. A large, genetically heterogeneous group of tomato vegetation was used as the original breeding stock by two completely different breeders, named Mary and Hector.
Femara 2.5 mg purchase overnight delivery
Oral hypoglycemic agents What are the indicators and signs of diabetic ketoacidosis What is the term used to describe a rise in blood glucose often between 4 and eleven am as a result of women's health big book of exercises free download 2.5 mg femara cheap free shipping the release of development hormone breast cancer 3 day 2015 femara 2.5 mg cheap amex, cortisol, glucagons, and epinephrine What is the time period used to describe a rebound rise in morning blood glucose secondary to a low overnight blood glucose Hypoglycemia Confusion; diaphoresis; tremors; tachycardia; seizures; coma; lethargy Diaphoresis, as this is a cholinergicmediated response Endocrine Agents 159 What is the name of the incretin mimetic that will increase insulin secretion, slows gastric emptying, and decreases meals intake Other than blood glucose discount, regular insulin may additionally be used for what condition Exenatide Pramlintide Insulin Hyperkalemia; insulin causes an intracellular shift of potassium; insulin is given in combination with glucose to forestall hypoglycemia in this state of affairs For every of the next oral hypoglycemic brokers, state which drug class it belongs to What drug with constructive inotropic and chronotropic activity can be used to stimulate the heart during a b-blocker overdose Which kind of diabetes insipidus is characterized by insensitivity to vasopressin within the amassing ducts Which type of diabetes insipidus is characterized by insufficient secretion of vasopressin from the posterior pituitary gland Nephrogenic Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Neurogenic diabetes insipidus Lithium; demeclocycline; vincristine; amphotericin B; alcohol Demeclocycline Thiazide diuretics in combination with amiloride; chlorpropamide; clofibrate 1. Heat intolerance; nervousness; fatigue; weight loss with increased urge for food; increased bowel movements; palpitations; irregular menses; proximal muscle weak point; moist skin; nice hair; hyperactive deep tendon reflexes; tachycardia; widened pulse stress; tremor Growth retardation in children; slowing of physical and mental exercise; weight achieve; cold intolerance; constipation; weak spot; melancholy; dry skin; chilly pores and skin; coarse skin; coarse hair; bradycardia; muscle cramps; delayed relaxation of deep tendon reflexes; hyponatremia High fever; dehydration; delirium; tachycardia; tachypnea; nausea; vomiting; diarrhea; coma A extreme, life-threatening hypothyroid state precipitated by an acute insult; symptoms: altered mental status, hypercapnia from hypoventilation, bradycardia, hypotension, hyponatremia, hypoglycemia Propranolol What are the indicators and signs of hypothyroidism Triiodothyronine (T3) T3 (up to five times extra active) 164 Zoom Review: Pharmacology What is the half-life of T4 When a hypothyroid patient is began on levothyroxine therapy, how lengthy will the drug take to reach a steady state What antiarrhythmic agent can doubtlessly cause both hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism (more commonly hypothyroidism) Radioactive iodine (I) Hypothyroidism virtually inevitably outcomes; different attainable problems embody hypocalcemia as a end result of removal of the parathyroid glands along with the thyroid Thionamides (propylthiouracil and methimazole) Iodide; lithium Propylthiouracil; methimazole 131 What are the medicine of option to deal with hyperthyroidism What drugs block the conversion of T4 to T3 in the periphery by inhibiting 5-deiodinase Zona reticularis (inner) 166 Zoom Review: Pharmacology Name the steroid hormones produced by every of the next layers of the adrenal cortex: Zona glomerulosa Zona fasciculata Zona reticularis What is the main precursor of all steroid hormones What is the first mechanism by which corticosteroids enhance the neutrophil depend List the antagonistic results of glucocorticoids: What drug inhibits glucocorticoid synthesis by inhibiting 11-hydroxylase activity What antifungal can be used to decrease cortisol levels in Cushing disease and may trigger gynecomastia as an opposed impact What diuretic blocks mineralocorticoid receptors and in addition inhibits the synthesis of aldosterone and androgens. What are the makes use of of testosterone and its derivatives (danazol; stanozolol; nandrolone; oxandrolone) What antifungal drug inhibits the synthesis of androgens and can be used as an antifungal What medicine act as androgen receptor blockers and are used within the remedy of prostate cancer Flutamide; bicalutamide 170 Zoom Review: Pharmacology What is the mechanism of motion of leuprolide Exemestane Breast cancer in postmenopausal girls Fertility drug How do estrogens have an result on serum lipids What drug acts as a progesterone antagonist and is used in mixture with prostaglandin E1 as an abortifacient Metformin in combination with iodinated distinction supplies can lead to lactic acidosis and decreased renal function. This is especially concerning in patients who could have already got a point of renal impairment, similar to diabetics. Additionally, preexisting renal impairment together with oral distinction can lead to increased serum levels of metformin, leading to toxicity. Proper kidney operate needs to be documented as properly before the treatment is resumed. A 24-year-old lady with no significant past medical history is being evaluated at a prenatal go to. What medication used to treat male sample baldness have to be prevented round pregnant girls Finasteride, a 5-reductase inhibitor has been proven to be efficient to treat some circumstances of male sample baldness. Some sufferers will buy the inexpensive model of the drug and cut up the tablets to get the appropriate dose. This is a hazardous apply round pregnant females since even contact with crushed or broken tablets can result in birth defects, notably abnormalities of the male external genitalia. In gentle of the potential opposed effects, the obstetrician might substitute finasteride with topical minoxidil, which opens potassium channels and stimulates hair development by an unknown mechanism. A 19-year-old man presents to his main care physician with complaints of increasing fatigue. He believes just lately he has contracted the flu as a result of he has had nausea and vomiting, in addition to muscle pain. He states that he has to be careful not to get up too quickly, as this makes his dizziness worse. What different diagnostic test would be appropriate presently, and what can be the probably outcomes On physical examination, the hyperpigmentation of Addison illness may be distinguished from a suntan by examining areas unlikely to be uncovered to sun, such because the axilla. Skin creases also are inclined to be darkly pigmented in Addison disease, as seen in this affected person. The affected person is on continual prednisone therapy to control his rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. The affected person is famous to have a rounded face and shoulders, and linear discolorations on his stomach. A note is made within the chart to think about adding a medication to his perioperative regimen. Side effects of high dose, prolonged steroid use can result in Cushing syndrome characterized by belly adiposity, moon facies, abdominal straie, buffalo hump, and glucose intolerance. Adrenal insufficiency could additionally be of concern in periods of stress, such as from an operation, and supplemental steroid administration could also be needed. This web page intentionally left blank Chapter 10 Anti-inflammatory Agents and p-Aminophenol Derivatives (Acetaminophen) Eicosanoids (inflammatory mediators) are synthesized from what chemical compound What drug is administered early to mitigate the second-phase symptoms of anaphylaxis, from the slowreleasing substances of anaphylaxis Which adverse results of celecoxib have sparked debates about whether it ought to be pulled from the market or not Blood exams are ordered which return normal, including normal liver function tests.
2.5 mg femara generic visa
When these neurons are genetically ablated womens health vcu generic femara 2.5 mg fast delivery, the affected mice are constrained to walking very slowly breast cancer 8 cm femara 2.5 mg generic on line. Some of these neurons are the Renshaw cells that present suggestions inhibition onto motor neurons. When activated, they shorten burst intervals and safe reciprocal flexor-extensor exercise (Gosgnach et al. More dorsal nonetheless, within the V0 area, are commissural inhibitory and excitatory interneurons that specific Dbx1. Mutant dbx1 mice often make synchronous rather than alternating left-right bursts of motor exercise, leading to mice that hop rather than stroll (Lanuza et al. In the next most dorsal region (dl6) are the commissural interneurons that specific the transcription issue Dmrt3. The position of these neurons is partially revealed by the strange proven fact that Icelandic horses, which have five natural gaits somewhat than the three or 4 of most other breeds, have a truncated Dmrt3 protein (Andersson et al. Indeed, electrophysiological studies from spinal cords of dmrt3 mutant mice show disorganized motor stepping actions. While many different types of interneurons are recognized, their roles in locomotion are yet to be studied intimately. From a developmental viewpoint, it goes to be significantly attention-grabbing to explore how these transcription components management the connectivity and network properties of these neurons. Simultaneous imaging of each the Mauthner cell (top of each panel) and considered one of its segmental homologues (bottom of every panel). The first is that circuits are sometimes established with electrical synapses, and optimistic suggestions causes all the elements of the circuit to burst collectively. The later growth of chemical, and significantly inhibitory, signaling changes the relationships between components of the circuit so that not all parts fire together. Circuits by which neurons have particular part relationships to each other are refined, generating extra helpful exercise patterns for the developing animal. The second feature is, as Coghill surmised nearly a century in the past, that circuits are in-built progressive stages. The rostrocaudal axis of the spinal cord is patterned by Hox genes (see Chapters 2 and 4), and the locomotor circuitry can be specialised along this axis by the action of transcription factors. A rooster flaps its wings synchronously yet moves its legs in an alternating gate. In Drosophila, loss and acquire of perform experiments with the Hox genes, Ubx and AbdA, that are expressed in thoracic and abdominal segments, show that these genes are essential and adequate to dictate the formation of the region-specific motor community involved in peristaltic larval locomotion (Dixit et al. More than a century in the past, Ross Harrison (1904) raised salamander embryos in an anesthetic solution throughout the interval when bending, coiling, "S," and early swimming actions emerge. He then transferred the embryos to anesthetic-free answer, and found that the embryos have been in a position to swim soon after the anesthetic was washed out. He reported that after a quick period, the beforehand drugged animals had been indistinguishable from controls. However, for as much as 2 h instantly after drug withdrawal, the embryos moved and swam more slowly and fitfully, suggesting a delay in motor improvement. If early activity in a motor circuit is necessary for the conventional emergence of coordinated behavior, how would possibly this be achieved This adjustment is dependent upon negative feedback, which leads to the relative upkeep of the suitable exercise levels in the circuit (Gonzalez-Islas and Wenner, 2006). A hint about how such a mechanism could additionally be achieved within the swim circuit comes from experiments in Xenopus tadpoles. Here, serotonin released from hindbrain neurons will increase the period of rhythmic swimming bursts. The serotonergic enter is tuned, remarkably, by the spontaneous exercise of these neurons. The calcium that accompanies every spike lowers the expression of Lmx1b, a transcription factor controlling the synthesis of serotonin (Demarque and Spitzer, 2010). Each larva has about 24 h to find food after hatching or else it starves to death. They swim usually, and electrophysiological information from ventral roots on reverse sides of the spinal twine show the expected alternating sample of exercise. When the chick hatches, instead of walking, it jumps in the rhythm of flapping wings. These motor episodes are poorly organized at first, but over the subsequent hour and a quarter, they become increasingly coordinated, creating left-right synchronization and sequential activation of segmental muscular tissues in neighboring segments. A temperaturesensitive dominant unfavorable mutant of the shibire gene, which encodes vesicle recycling protein, was used to shortly and reversibly block all synaptic exercise in the whole nervous system both earlier than the early interval of episodic uncoordinated movements or just after the emergence of coordinated movements. However, blocking synaptic exercise for simply 1 h initially of episodic uncoordinated movements, triggered a major delay within the development of coordinated peristaltic waves. This was outlined, subsequently, as a sensitive period for the development of crawling circuitry. As the delay was almost the same length as the block, the outcomes recommend that the entire program must be run via so as to generate the coordinated movements. To higher perceive the significance of particular patterns of exercise during this period, Crisp et al. In agreement with the shibire work, when these exercise patterns had been ontogenetically imposed before or after the sensitive period, the stimulation protocol had little effect on the event of the coordinated crawling program. Summary diagram displaying sequence of electrical, morphological, and behavioral growth. Vertical bars point out episodic activity within the motor system as revealed by muscle contractions (Crisp et al. Therefore the query arises whether, as in Drosophila, these earliest actions, or the circuit activity that produces them, may be substrative, getting ready the nervous system for the formation of a extra mature motor community. This reveals that cholinergic activity is important throughout a transient period of growth to mediate correct meeting of spinal locomotor circuits (Myers et al. They then appeared at the results of these treatments on the motor neurons and found a quantity of kinds of errors in connectivity. This correlated with the mispositioning of their cell somas throughout the spinal twine into inappropriate motor pool areas. Two necessary steering cues have been also affected: the Ephrin receptor, EphA4, which is involved in dorsal vs ventral axon pathfinding decisions within the plexus, and polysialic acid, which is important in defasciculation (see Chapters 5 and 6). Increasing the frequency of spontaneous bursting episodes by remedy with a glycine reuptake inhibitor additionally had dramatic effects on the wiring of motor neurons. This remedy disrupted the fasciculation of axons of the identical motor pool resulting in the aberrant intermingling of axons from totally different motor swimming pools and subsequent innervation errors. Limb muscles tended to be innervated by a mix of their very own and overseas motor neurons (Hanson and Landmesser, 2006). Similar results have been obtained when channelrhodopsin was used to drive extra frequent bursting. Motor neurons have been once more positioned in the mistaken motor pools, and there have been long-term results on coordination when the stimulation was terminated.
Diseases
- Hyperinsulinism in children, congenital
- Graham Boyle Troxell syndrome
- FRAXA syndrome
- Brachydactyly dwarfism mental retardation
- WAGR syndrome
- Donnai Barrow syndrome
- Winship Viljoen Leary syndrome
- Oligophernia
- Urban Schosser Spohn syndrome
- Thiolase deficiency
Generic femara 2.5 mg on line
Researchers have identified two various varieties of genetic changes that diminish the operate of tumor-suppressor genes: A mutation can happen particularly inside a tumor-suppressor gene to inactivate its function women's health center bismarck north dakota femara 2.5 mg buy on-line. For instance women's health kissing tips buy discount femara 2.5 mg, a mutation could inactivate the promoter of a tumor-suppressor gene or introduce an early stop codon in the coding sequence. In some circumstances, chromosome loss could contribute to the progression of most cancers because the lost chromosome carries one or more tumorsuppressor genes. Many cancers start with a benign genetic alteration that, over time and with extra mutations, progresses to malignancy. Furthermore, a malignancy can proceed to accumulate genetic adjustments that make it even more troublesome to treat. For instance, some tumors could purchase mutations that trigger them to be proof against chemotherapeutic brokers. In 1990, Eric Fearon and Bert Vogelstein proposed a series of genetic adjustments that lead to colorectal most cancers, the second most typical cancer in the United States. Additional genetic adjustments involving the lack of different tumor-suppressor genes and the activation of an oncogene (namely, ras) lead finally to the event of a carcinoma. Among several types of tumors, researchers have identified a lot of genes that are mutated in cancer cells. Though not all of those mutant genes have been directly shown to affect the growth price of cells, such mutations are more probably to be present in tumors because they provide some type of progress advantage for the cell inhabitants from which the most cancers developed. For example, sure mutations could enable cells to metastasize to neighboring places. Researchers have estimated that about 300 totally different proteinencoding genes may play a job within the development of human most cancers. Since the approximate genome measurement of humans is about 22,000 protein-encoding genes, this remark signifies that over 1% of those genes have the potential to promote most cancers if their function is altered by a mutation. In addition to mutations within specific genes, different frequent genetic changes associated with cancer are alterations in chromosome construction and quantity. If tumor-suppressor genes are on these lacking chromosomes, their function is lost as well. If this chromosome carries proto-oncogenes, the expression of these genes may be overactive. Finally, tumor cells often have chromosomes with translocations (these are designated as marker chromosomes within the figure). Such translocations might create fused genes (as within the case of the Philadelphia chromosome discussed earlier in this section), or they may place two genes close collectively so that the regulatory sequences of 1 gene have an result on the expression of the other. The bottom set, from a tumor cell, is extremely abnormal, with missing copies of some chromosomes and an additional copy of chromosome 7. Translocated chromosomes (designated marker chromosomes in this figure) are manufactured from fused pieces of different chromosomes. As mentioned beforehand, about 5�10% of all circumstances of cancer contain inherited (germ-line) mutations. These familial forms of cancer occur as a result of individuals have inherited mutations from one or both dad and mom that give them an elevated susceptibility to developing most cancers. For instance, von Hippel-Lindau disease and familial adenomatous polyposis are examples of syndromes for which genetic testing to identify at-risk family members is taken into account the usual of care. Most inherited forms of cancer involve a defect in a tumor-suppressor gene (Table 22. In these instances, the person is heterozygous, with one regular and one inactive allele. At the level of a human pedigree, a predisposition for developing most cancers is inherited in a dominant trend as a end result of a heterozygote reveals this predisposition. The cancers listed are these in which it has been firmly established that a predisposition to develop the disease is often as a end result of germ-line mutations in the designated gene. Normal cells in an affected particular person are heterozygous, whereas cancer cells in the same individual have misplaced their heterozygosity. Therefore, at the cellular degree, most cancers is recessive because both alleles must be inactivated for it to occur. When contemplating the function of epigenetic adjustments and human disease, an affiliation can arise in three frequent ways: the epigenetic adjustments instantly contribute to the illness signs. Conversely, the illness symptoms may arise first, and then they trigger subsequent epigenetic changes to happen. In common, correlation coefficients are fairly helpful in identifying associations between two variables. Even so, research studies that identify associations are very helpful as a outcome of they provide the motivation to perform further analysis to determine if a cause-and-effect relationship exists. Researchers have recognized many examples during which epigenetic adjustments are related to a selected disease. These embrace Alzheimer illness, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and asthma. For these diseases, further research is required to decide if these epigenetic modifications are directly contributing to the illness symptoms. The function of epigenetics and disease has been most extensively studied with regard to most cancers. We will first discover the forms of epigenetic changes which may be associated with most cancers, and then study how abnormalities in epigenetic changes could arise. One of probably the most lively fields in genetics involves the examine of how epigenetic changes contribute to human ailments. We are most likely seeing only the "tip of the iceberg" in our present understanding of this matter. Many medical research have recognized correlations between epigenetic adjustments and specific ailments. Researchers analyze the info to decide if such a correlation is statistically vital. When a statistically important correlation coefficient is obtained, how can we interpret its that means Such a result suggests a real association-changes within the two variables follow a pattern. For instance, in a positive correlation, when one variable will increase, the opposite variable additionally increases. Abnormalities in Chromatin Modification Are Common in Cancer Cells Three common types of chromatin modifications are often found to be irregular in most cancers cells. For instance, hypermethylation-an abnormally excessive level of methylation, usually at CpG islands, is commonly observed. This hypermethylation might promote cancer by inhibiting the expression of tumor-suppressor genes. As described in Chapter 17, the covalent modification of histones can have an effect on the expression of genes, both activating or inhibiting transcription depending on the sample of modification. Variation within the covalent modification of histones has been proven to occur at specific genes in most cancers 22. Depending on the particular kind of modification, such adjustments may enhance the expression of oncogenes or inhibit the expression of tumor-suppressor genes.
Purchase 2.5 mg femara overnight delivery
Hormone remedy can enhance the dimensions of brain nuclei pregnancy zits buy femara 2.5 mg cheap, each by increasing afferent innervation and promoting dendritic progress women's health center tulane femara 2.5 mg purchase online. Although most female songbirds tend to not vocalize throughout mating, feminine tropical wrens do sing a "duet" with the males. In fact, when the music repertoire of a female wren Behavioral Development Chapter 10 339 turns into comparatively giant, its song-control nuclei attain a dimension much like that of males (Brenowitz and Arnold, 1986). However, female vocal conduct, termed rapping, is assumed to trigger the entire copulatory repertoire (Tobias et al. When the feminine frog is unreceptive, it produces a ticking sound, but when it is ready to lay eggs, it begins to rap. This name stimulates males to vocalize much more vigorously and to attempt copulation. In Xenopus, both sexes have the identical central networks for vocalization behavior, and circulating testosterone is necessary for the male-specific vocalizations (Yu and Yamaguchi, 2009). Sex-specific differentiation has been observed on the level of vocal motor neuron membrane properties, and this may result in completely different output patterns for males and females (Yamaguchi et al. Male fruit flies acknowledge females based mostly on an olfactory cue, called a contact pheromone, and males perform a stereotyped courtship conduct after they detect this sign. The male orients in the course of a feminine, taps her stomach, flutters his wings in song, and places his proboscis (the mouthparts) on the genitals. How does the central nervous system create this advanced set of sexspecific behaviors Whenever the enhancer is activated by a transcription factor, a reporter gene throughout the enhancer lure is expressed. The enhancer lure line may also be used to drive the expression of native genes, corresponding to transformer (green). An enhancer trap system has been used to specific a feminizing signal (transformer) in olfactory neurons that process the contact pheromone (Ferveur et al. Genetic males that express transformer had been introduced with flies of either sex to see whether they selectively courtroom the female, as regular males do. The behavior of reworked animals may be because of their failure in discriminating the feminine pheromone. When the enhancer entice approach was used to make male flies that secrete solely feminine pheromones, these flies had been courted as if they have been females (Ferveur et al. Thus, 340 Development of the Nervous System in flies, particular brain regions must have a gender if animals are to precisely interpret sensory data and produce sexually acceptable motor responses. A separate tack has been used to explore the genes which should be expressed in male or female nerve cells so as to produce correct sexual behaviors (Hall, 1994; Manoli et al. For example, a sex-specific splice-form of the transcription factor, fruitless, is expressed in about 500 neurons of male flies only, and mutations of this gene also trigger males to court docket each other. A mutation of the dissatisfaction gene leads virgin females to resist males during courtship, they usually fail to lay mature eggs (Finley et al. Most mutations that affect sexual activity in flies are also discovered to affect other behaviors. Mutations of the period gene affects circadian rhythms, but in addition they change the temporal properties of the courtship music. Depending on the exact mutation, the interval between wingbeats may be shorter or longer than regular, giving the track the next or decrease frequency, respectively. A notably compelling instance of genetic dedication of brain sexual dimorphism was found in a uncommon zebra finch gynandromorph. Thus the genetic sex of songbird brain cells appears to play a role of their differentiation (Agate et al. These outcomes recommend that intrinsic genetic alerts bias nervous system development within the absence of gonadal alerts. In truth, some diencephalic neurons specific a sex-specific phenotype in vitro, even when explanted before experiencing the rise in plasma testosterone ranges. Tyrosine hydroxylaseexpressing neurons are 30% bigger in males, and the quantity Behavioral Development Chapter 10 341 of prolactin-expressing neurons is two to 3 times greater in female tissue, much like grownup animals (Kolbinger et al. Furthermore, mice can be genetically engineered to carry an active copy of the Sry gene on an autosome. When mesencephalic neurons have been explanted at embryonic day 14, the variety of dopaminergic neurons was larger in Sry-/- genetic males than genetic females, even though each teams had female gonads. Further characterization of Sry-/- genetic males indicated that genes on the sex chromosomes, apart from Sry, are liable for a quantity of behavioral or neural traits (Arnold and Chen, 2009). Thus, aggression is greater in genetic males, even after they develop with ovaries, and genetic females show a extra speedy response to painful stimuli, even after they develop with testes. Taken together, these experiments present that the vertebrate nervous system develops no less than some sex-specific traits due to expression of genes on the sex chromosomes. In mammals, maternal care is often higher, beginning with the in utero environment and continuing through postnatal lactation. This can be true on the genetic degree the place sex chromosomes provide the strongest parental affect, as mentioned above. As discussed earlier in the chapter, lots of of genes are inactivated within the germ cells produced by every parent via a process known as genomic imprinting (Wilkinson et al. Such canonical genomic imprinting is comparatively outstanding within the mind (Babak et al. When each alleles are regular and the male allele is imprinted, then the offspring is regular (top, left). However, if the female carries a mutation and the male allele is imprinted, then the offspring will categorical solely the mutated protein and may be impaired (top right). A greater proportion of maternal genes are expressed throughout development, while a greater share of male genes are expressed in maturity. In this situation, genomic imprinting by the mother or father is believed to enhance the probability that her or his genes shall be passed on. An example of this concept is the allocation of resources between mom and offspring. At least 1300 genes which are expressed in the mouse mind display some extent of bias in the direction of the maternal or paternal allele (Gregg et al. Many of those genes are expressed in mind areas associated with feeding, mating, social interactions, and reward studying. When contemplating all imprinted genes within the fetal mind, 61% p.c are maternal in origin, indicating that the mom exerts a main affect over mind development. Thus, maternal bias is larger for the X chromosome, and paternal bias may be greater for autosomes. Furthermore, noncanonical imprinting has been reported to be mind region-specific, and should affect conduct (Bonthuis et al. Genomic imprinting can have a tremendous influence on developmental disorders of the nervous system. Both copies include genes for necdin (Ndn) and the ubiquitin protein ligase E3A (Ube3a).
Femara 2.5 mg buy discount on-line
For example breast cancer 77 year old femara 2.5 mg on line, the partitions of the main arteries such because the aorta menstrual discomfort femara 2.5 mg cheap visa, the big artery that leaves the guts, are sometimes affected. X-Linked Dominant Inheritance Relatively few genetic disorders in humans follow an X-linked dominant inheritance pattern. In most cases, males are more severely affected than females, probably as a end result of females carry an X chromosome with a traditional copy of the gene in question. Also, as a end result of their dominant nature and severity, persons with some of the problems listed in Table 22. For these X-linked dominant problems by which the offspring can reproduce, the next sample is usually noticed: 1. Therefore, a female heterozygous for an X-linked recessive allele passes this trait on to 50% of her sons, as proven within the following Punnett sq. for hemophilia. This term refers to the phenomenon in which a specific sort of illness may be attributable to mutations in two or extra completely different genes. For instance, blood clotting involves the participation of several different proteins that take part in a mobile cascade that results in the formation of a clot. Hemophilia is often caused by a defect in one of three totally different clotting components. For instance, a human pedigree would possibly include individuals with X-linked hemophilia and other individuals with hemophilia C. A geneticist who assumed that all affected individuals had defects in the same gene can be unable to clarify the ensuing sample of inheritance. However, for uncommon illnesses which would possibly be poorly understood at the molecular stage, locus heterogeneity might obscure the sample of inheritance. For hemophiliacs, frequent accidents pose a risk of extreme inner or external bleeding. This disease has additionally been known as the "royal disease," because it has affected many members of European royal families. The sample of X-linked recessive inheritance is revealed by the next observations: 1. Pictured are Queen Victoria and Prince Albert of Great Britain with some of their descendants. Thousands of human genetic illnesses follow simple Mendelian patterns of inheritance. Recessive diseases are normally attributable to loss-of-function mutations, whereas dominant diseases may be attributable to haploinsufficiency, gain-of-function mutations, or dominant-negative mutations. Explain how haplotypes are analyzed to establish disease- causing alleles in people. Assuming full penetrance, which kind of inheritance pattern is according to the pedigree shown right here Haplotypes Exhibit Genetic Variation To establish disease-causing alleles, researchers typically depend on the identified chromosomal places of genes and molecular markers which were characterised in human populations. A diseasecausing allele may be identified because of its proximity to one other recognized gene or its proximity to molecular markers. As discussed in Chapter 21, researchers can characterize chromosomes at the molecular level and decide the exact places of genes and molecular markers on each chromosome. These sites could presumably be within explicit genes or they could be molecular markers used in mapping studies. The term haplotype, which is a contraction of haploid genotype, refers to the linkage of alleles or molecular markers on a single chromosome. By comparison, haplotypes are more likely to change over the course of some generations as a result of crossing over. However, the chance of fixing a haplotype depends on the gap between the alleles or molecular markers. If sites 1, 2, three, and 4 were very shut collectively alongside this chromosome, the haplotypes proven on this determine can be prone to stay the identical after a number of generations. For example, a great-great-great grandchild of particular person 2 may inherit the haplotype 1A 2B 3B 4C or 1C 2C 3C 4A. In contrast, the inheritance of both haplotype would be a lot less probably if the sites were far apart and will incessantly recombine by crossing over. This example considers 4 sites on a chromosome which will exist in numerous variations, designated A, B, or C. Although a wide range of approaches may be followed, the hunt typically begins with household pedigrees. This approach is predicated on two assumptions: the disease-causing allele had its origin in a single individual generally known as a founder, who lived many generations ago. When the disease-causing allele originated within the founder, it occurred in a region of a chromosome with a specific haplotype. By comparing the transmission patterns of many molecular markers with the incidence of an inherited illness, researchers can pinpoint explicit markers that are carefully linked to the disease-causing mutant allele. The molecular markers designated 1A, 2C, 3B, and 4B are very close to the situation of this mutant allele. In succeeding generations, the disease-causing allele would be extra more probably to be current in individuals with haplotype 1A 2C 3B 4B than in those without this haplotype. Due to their shut proximity, it will be unlikely that a crossover would separate the 2C marker and the disease-causing allele from each other and create a special haplotype. The phenomenon of linkage disequilibrium is frequent when a disease-causing allele arises in a founder and the allele is carefully linked to different markers on the same chromosome. Nancy Wexler, whose own mom died of this disorder, has studied Huntington illness amongst a population of associated people in Venezuela. A particular molecular marker, called G8, is present in 4 totally different versions, named A, B, C, or D. In this Venezuelan population, pedigree analysis revealed that the G8-C marker, which is situated close to the tip of the brief arm of chromosome four, is kind of all the time related to the mutant gene causing Huntington disease. Once a disease-causing mutant gene has been localized to a brief chromosomal region, the next step is to determine which gene within the region is responsible for the illness. One method to determine a diseasecausing allele is chromosome walking, a technique during which a researcher starts at a selected molecular marker, corresponding to G8-C, and constructs a series of clones until the gene of interest is reached. In this instance, the new mutation occurred in a region with a specific haplotype: 1A 2C 3B 4B. The letters inside every symbol point out the forms of the G8 marker (A, B, C, or D) the person carries. Therefore, researchers can analyze the 1-Mb region to which a gene has been mapped to decide if a mutant gene on this region is answerable for a illness. In the human genome, a 1-Mb area normally incorporates about 5 to 10 completely different genes, although the quantity can differ greatly. As the scientific community explores the capabilities of genes experimentally, the data are published in the analysis literature and placed into databases. In some circumstances, this information might assist to slender down the listing of candidate genes. For example, if the disease of interest is neurological, researchers might discover that only sure genes within the mapped region are expressed in neurons.

Buy generic femara 2.5 mg on-line
These studies recommend that the coordination of mammalian terrestrial locomotion may undertake the primitive swim circuitry found in ancestral vertebrates to coordinate left and proper sides menstrual heavy bleeding 2.5 mg femara overnight delivery. Images emphasize key levels of zebrafish embryo development earlier than and after hatching (52 h) breast cancer 4th stage survival rate femara 2.5 mg buy on line. CiAs are so named due to their major ascending axon, nonetheless, additionally they have a secondary descending one. Successive images at completely different time points (hours postfertilization famous in respective images) illustrate the expansion of the descending axon (at thin and thick white arrows), in addition to the elaboration of the dendrites. Even in people, the precursors to mature locomotion may be seen lengthy before infants take their first steps. When infants are positioned on a delicate downhill slope, one can elicit left-right motor coordinated movements even at precrawling phases. The spinal circuits that control repetitive leftright actions in walking or swimming are conserved in vertebrates, largely as a end result of the mechanisms that generate spinal neuron cell types and their connectivity are also conserved. Subsequently, the movements of many species turn out to be fairly complex, such because the completely different gaits of a horse or the fine finger movements of a piano participant. Descending pathways from the cortex convey movements beneath voluntary management and coordinate the consequences of motor learning. Genetic methods that make use of the transcription elements that outline each domain allow studies of the physiological contributions of each cell type. Optogenetic stimulation of these cells reveals that they modulate the excitability of the swimming networks (Wyart et al. Lhx3-expressing interneurons sit within the V2 area, immediately above the motor neurons. In mice, these neurons are involved in left-right alternation during working (Crone et al. Engrailed1-expressing interneurons of the V1 domain are the subsequent most dorsal neurons and are required for producing "quick" bursting. This suggests that there have been both motor neuron innervation errors, as nicely as altered inputs to these motor neurons (Kastanenka and Landmesser, 2010, 2013). Clearly, the activity patterns, projections, and molecular steerage components are extraordinarily sensitive to the early spontaneous bursting exercise patterns within the twine as either too little or too much bursting exercise leads to serious alterations of normal motor neuron exercise and connectivity. In zebra-fish embryos, blocking spontaneous calcium spikes in single primary motor neurons results in characteristic pathfinding errors of the axons, whereas silencing the spikes in all of the motor neurons had no effect, suggesting that there may be an element of competition in this system (Plazas et al. This 328 Development of the Nervous System work reveals that the spontaneous waves of bursting exercise seen in the motor system are essential in wiring up the nervous system, simply because the spontaneous waves of exercise within the retina before eye opening are important within the normal formation of connections within the thalamus and visible cortex of mammals (see Chapter 8). In reality this "spontaneous" exercise plays an necessary position within the maturation of synaptic connections (see Chapter 9). Nonetheless, the nervous system is still fairly immature when animals first start to hear, scent, see, steadiness, style, and feel. Studies of sensory perception are among the most difficult experiments within the area of developmental neuroscience. Neonatal animals, together with human infants, tend to be sluggish, sleepy, cranky, inattentive, and forgetful. Fetal listening to was first demonstrated by monitoring a reflex, the attention blink response, using ultrasound imaging (Birnholz and Benacerraf, 1983). By analyzing the sound evoked responses from 236 fetuses, listening to onset was discovered to occur between 26 and 28 weeks of gestation, properly before delivery. Although humans start to hear in utero, they remain less sensitive to sound for over a yr after start. Behavioral thresholds had been obtained from infants by conditioning them to produce a head turn in response to a goal sound. Although 3-month infants can study this task, scoring their efficiency is hard because head-turning habits is considerably variable at this age. Using this approach, it was found that human auditory thresholds proceed to enhance beyond the first 12 months of life (Olsho et al. As thresholds decrease, most animals become extra conscious of greater sound frequencies. This is due, in part, to a physical change in the cochlea: a place along the basilar membrane responds to greater frequencies as animals mature. In truth, 15-day-old rat pups can be trained to suppress exercise after they hear a eight kHz tone, however when examined three days later they suppress exercise to a better frequency. That is, the higher sound frequency apparently feels like eight kHz to the rat as a outcome of its cochlear frequency map has shifted (Hyson and Rudy, 1987; R�bsamen, 1992). The sound stimulus must remain on for about 1 s, or be repeated many times, if the infant is to make an appropriate head orientation response (Clarkson et al. In distinction, adults want only a millisecond of sound, similar to a finger snap, to find the supply. Although infants can determine whether or not a sound source is coming from the left or the best, they remain very poor at localizing the exact position of a sound. Rat pups can flip towards a noise a couple of days after the ear canal opens, however the share of correct turns toward the sound increases over the subsequent week (Kelly et al. Adults can focus narrowly on a stimulus of interest and ignore different stimuli which might be distracting. On the opposite 25% of trials, topics are presented with frequencies which are greater or lower than 1000 Hz. To enhance the sensitivity of this procedure, an grownup observer watches the infant and judges whether or not the toddler heard the stimulus primarily based on any response that the infant makes (left). Using this observer-based procedure, the auditory thresholds of 3- and 12-month-old infants was obtained (right). The plot exhibits that absolute threshold continues to enhance even after the first postnatal year. In distinction, infants detect all the tones equally well (Bargones and Werner, 1994). Thus, attentional systems differ between infants and adults, and such nonsensory factors have a big influence on the event of sensory notion. Absolute sensitivity is a measure of the minimum change in stimulus magnitude that could be detected: the softest contact, the quietest sound, the dimmest gentle. Discrimination is a measure of the flexibility to perceive a distinction between two comparable stimuli: sky-blue vs turquoise, center C vs C sharp, margarine vs butter. If the maturation of all perceptual expertise could presumably be attributed to specific neural mechanisms, then these skills would all develop at the same pace. Rather, totally different perceptual expertise reach an adult-like state at very different postnatal ages (Sanes and Woolley, 2011). The ability to detect a tone within the presence of a second, nearby tone (called frequency resolution) matures first for low frequencies, and is adult-like by 6 months (Spetner and Olsho, 1990; Schneider et al. Furthermore, the response often took a number of seconds to emerge, and the head motion was quite slow (right).