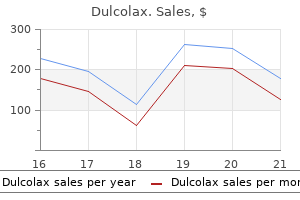
Dulcolax
Dulcolax dosages: 5 mg
Dulcolax packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Discount 5 mg dulcolax fast delivery
A easy change (B) medicine pouch generic 5 mg dulcolax overnight delivery, a negative autoregulatory switch (A) top medicine generic dulcolax 5 mg with visa, and a positive autoregulatory change (C) respond with different kinetics to an inducing signal. Now, nonetheless, we recognize that the degrees of gene expression vary substantially amongst people in a inhabitants and even between two copies of the same gene in the same cell. We due to this fact outline noise as the variation in gene expression underneath seemingly uniform situations. The existence of noise signifies that stochasticity influences the level of expression of particular person genes. Stochasticity signifies that a process is characterised to some extent by randomness. As we shall see later, some regulatory motifs are designed to deal with noise, and other motifs are designed to exploit it. Noise in gene expression comes from two sources-intrinsic and extrinsic; both lead to differences in gene expression in a inhabitants. Intrinsic noise refers to variation in the stage of expression of particular person genes within a cell and is as a result of of stochastic events throughout the machinery for gene expression. A basic experiment that demonstrates intrinsic noise uses Escherichia coli cells harboring two copies of the identical gene. One copy of the gene is joined to a reporter encoding a pink fluorescent protein and the other to a reporter encoding a green fluorescent protein. Absent intrinsic noise, each gene copies ought to produce equal quantities of the red and green fluorescent proteins, and therefore the cells ought to be yellow. What is observed as an alternative is that many cells are conspicuously red and others conspicuously green. Extrinsic noise refers to differences in gene expression between cells in a seemingly homogeneous inhabitants or to changes in gene expression in the identical cell over time. In this case, the level of expression of both genes in an individual cell varies in unison, rising for a interval after which falling. This implies that the overall capability of individual cells to support the expression of some or all genes fluctuates with time. Returning to negative autoregulation, we see that this regulatory motif helps cells cope with noise by allowing cells to compensate for variations within the degree of expression of the autoregulated gene. As we will see later, other regulatory motifs additionally help cells meet the challenge of coping with varied sources of stochasticity, such because the fluctuations in signals that trigger gene expression. Because both the clone and the cat from which it was derived are genetically identical, one might need expected that the cats would have identical coat patterns. Positive Autoregulation Delays Gene Expression Positive autoregulation occurs when an activator protein stimulates the transcription of its own gene. Thus, "steady state" refers to a situation during which the level of the gene product varies solely negligibly over time. The necessary point is that the time required to reach regular state after a gene is switched on is longer for the case of positive autoregulation than for the case of unfavorable autoregulation or for no suggestions in any respect. Or, to be more precise, the time at which half-maximal accumulation happens is longer for optimistic autoregulation than 780 Chapter 22 for the choice regulatory switches. This is because the speed of manufacturing, which will increase over time, depends on the accumulation of the activator in the first place. Positive autoregulation can be helpful in organic processes that unfold slowly, corresponding to growth, which may profit from the slow accumulation of proteins concerned in morphogenesis. Thus, the s factors in addition to the products of the genes they management accumulate slowly because the manufacturing of sG and sK is dependent upon their very own synthesis. It is the idea for an excessive type of regulatory change often identified as a "bistable change," as we shall explain later. Some Regulatory Circuits Persist in Alternative Stable States A well-studied instance of a bistable change is the circuit that governs whether B. Cooperation among ComK molecules certain at the promoter creates a nonlinear response, which is hypersensitive to small, stochastic modifications in the degree of ComK. As we saw in Chapter 18, Box 18-4 within the case of the l repressor (which is itself liable for a basic instance of bistability to which we shall return later), cooperativity of this kind imparts nonlinearity on the output of the swap as a operate of the focus of the activator. In other phrases, the output is highly delicate to adjustments in the level of ComK (the opposite of robustness). Whether or not cells have the potential to turn on comK is governed by a regulatory pathway operating on the level of the proteolytic stability of the ComK protein. This may be vividly seen using cells harboring a fluorescent reporter (the gene for the green fluorescent protein) for ComK-directed gene exercise. Thus, noise in the expression of the comK gene leading to small variations within the ranges of ComK between cells allows the activator to reach a threshold focus in some cells and not others. This instance of constructive autoregulation illustrates how noise in gene expression may be exploited to drive cells in to alternative states. Although numerous examples of bistable switches are present in micro organism, bistability is certainly not restricted to microbes. A double-negative-feedback loop that could be stably maintained in a single state or one other dictates whether a typical precursor cell will express one set of receptors or the opposite. Rather, upstream alerts dictate during which path the swap is thrown, whereas the double-negativefeedback loop subsequently locks the swap in its predetermined state. Like bistable techniques, excitable techniques involve a self-reinforcing circuit that causes a large and stereotypical response to a small perturbation. In cells harboring the modified gene alone, no bistability is observed, and the extent of ComK-directed gene expression will increase in a more or less uniform method in response to growing ranges of inducer, exhibiting a unimodal distribution of expression levels among cells within the inhabitants at any give focus of inducer (Box 22-1. However, in cells harboring both the modified gene and the traditional autoregulated gene, increasing concentrations of inducer trigger the cells to bifurcate in to a subpopulation displaying a low level of ComK activity and a subpopulation exhibiting a excessive stage of ComK exercise (Box 22-1. Strictly speaking, the usage of the time period "bistability" requires that a change present a property called hysteresis. When exposed to a magnetic subject, the fabric turns into magnetized and, importantly, remains so even when the external magnetic area is eliminated. Now let us return to our example of cells harboring both ComK and a modified copy of ComK that responds to an inducer. Now think about what happens when we lower the extent of inducer such that much less and fewer ComK is produced from the engineered copy of the gene. The switch governing the decision between the lysogenic and lytic modes of propagation of bacteriophage l can also be hysteretic. Note that the cells in a and b harbored a fusion of the gene for the green fluorescent protein to a promoter under the control of ComK. A basic instance of an excitable system in biology is the action potential of a neuron. Neurons show a resting potential (typically � 70 mV) in which the focus of cations is barely larger exterior the cell than inside, resulting in a net unfavorable charge within the cytoplasm. Should the resting potential rise above a threshold (� 55 mV), protein channels in the membrane often identified as voltage-gated ion channels open, permitting sodium ions to flow in to the cell. This inward circulate of positive ions causes the membrane potential to rise still higher, triggering extra channels that had not but opened to allow sodium ions in to the cell. Eventually, this cascade of channel openings culminates in a peak of constructive voltage (40 mV) contained in the cell. Excess sodium ions are then pumped out of the neuron, restoring the membrane to its authentic resting state.
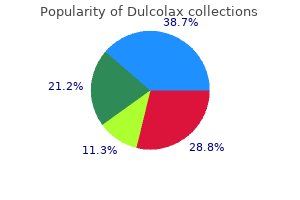
Effective dulcolax 5 mg
Children may additionally be taken care of at home either in a spica or on a Thomas splint treatment management company dulcolax 5 mg with mastercard. This is a properly acknowledged harm associated with a dorsiflexing drive suddenly utilized to the answers 417 approach medicine 906 cheap dulcolax 5 mg overnight delivery. Non-operative treatment is safer in older patients and those with danger factors for wound issues, including smoking, diabetes and steroid use. Surgery is often offered to younger, athletically energetic patients or patients who current late, as in this case. This affected person presented at 2 weeks and is probably at excessive risk of a poor result with non-operative therapy, so should be handled by surgical procedure until there are contraindications. The differential diagnosis of an acute monoarthritis on this affected person includes, in approximate order of chance: a. Alternatively, he may have acquired Chlamydia infection with subsequent reactive arthritis; gastrointestinal signs could be unrelated or due to sexually acquired proctitis � chlamydial or gonococcal, or both, as a outcome of twin infection is widespread. If he has contracted gonorrhoea, the arthritis may be a post-infectious one somewhat than the classical reactive arthritis that follows Chlamydia an infection. Lastly, his gastrointestinal signs may be the first presentation of inflammatory bowel disease and the arthritis related to this; this would not explain any of his genitourinary symptoms and is, subsequently, a less doubtless possibility. Taking in to account the inversion injury that brought on the fracture, care must be taken to exclude an associated ankle fracture or ligament damage. There could additionally be a disruption of a number of the components of the lateral ligament complicated or a fracture of the lateral malleolus. It is normally required in patients with lots of pain or in older patients who find crutches and partial weight-bearing difficult. Occasionally, the fracture fragment shaped by the base of the metatarsal is considerably displaced by the pull of the peroneus brevis (inserted on the base) and in these instances screw fixation could additionally be considered. Fractures of the shaft of the fifth metatarsal on the junction of the proximal 418 drawback - orientated section must be considered in a patient who may have consumed considerable quantities of alcohol throughout their vacation and, thus, increased the prospect of developing gout. This will assist to exclude septic arthritis and gout, whereas the presence of sterile cellular fluid will affirm an inflammatory arthritis. To identify any organism that might trigger reactive arthritis, a stool sample ought to be cultured for Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, Yersinia and Escherichia coli, and a urethral swab or first-pass urine tested for Chlamydia, ideally using a sensitive nucleic acid amplification approach. In cases of extreme persistent signs a disease-modifying drug, such as sulfasalazine or methotrexate, could also be launched, however this is rarely required within the first 6�12 weeks of management. This affected person has hypermobility of her knees and probably also has hypermobility at a quantity of different websites (see Chapter 1 on the way to score hypermobility). They might undergo pain and occasional swelling within the joints, but not necessarily instantly after overstretching or injury. Exercise is the most important treatment, encouraging aerobic exercise particularly. The differential diagnosis would include gout, particularly with the appearance of lumps that might be tophi. Chronic tophaceous gout might develop after long-term diuretic use, particularly in aged girls. In the absence of the lumps, psoriatic arthritis might produce the same scientific look. If you look closely on the picture, nonetheless, you can also see some small dark lesions, which symbolize small-vessel vasculitis. The mixture of arthritis, lumps and vasculitis strongly helps a prognosis of seropositive nodular rheumatoid arthritis. Typically, nodules are introduced on by method of methotrexate in sufferers with rheumatoid arthritis. This might sound like a reason not to use methotrexate, but actually most patients choose the appearance of nodules to the pain of inflammatory joint illness and are keen to accept the appearance of nodules as a suitable side-effect. In pathological terms, rheumatoid nodules are non-caseating chronic granulomata with pallisading histiocytes and lymphocytes round a central space. The antibiotic alternative would clearly depend upon his possible drug allergic reactions, however, within the circumstances, Staphylococcus aureus is a extremely doubtless candidate, as is Streptococcus. You would proceed to aspirate the joint day by day, till the effusion settled, after which start some physiotherapy to try to regain joint range of movement. The present suggestion is a minimum of two weeks of intravenous antibiotic remedy followed by an additional four weeks of oral antibiotic therapy. You can be guided by the blood and synovial fluid culture outcomes with regard to the selection of antibiotic. If it was a staphylococcal an infection you may elect to cease benzylpenicillin and introduce fusidic acid as a substitute so that you just had two medication working against that organism (flucloxacillin and fusidic acid). Most patients reply nicely to antibiotic therapy initiated early, but there are some potential sequelae. About 30% of sufferers would be anticipated to have residual loss of joint range of movement on account of the an infection. There is a small risk of bacteraemic spread with liver abscesses or lung abscesses. In this case, septic arthritis has to be very high on the differential analysis listing, as does acute crystal arthritis. Ask a few household historical past of this sort of condition (relevant for both gout and pseudo-gout). Ask about the presence of other co-morbid circumstances, similar to hypertension, that might require the patient to take diuretic remedy (a potent explanation for hyperuricaemia) or the presence of diabetes or other endocrine and metabolic disorders, many of which predispose to pseudo-gout. Occasionally, sufferers with reactive arthritis (see Chapter 16) can current in this way and, due to this fact, an enquiry in to current changes in dietary habits with related diarrhoea or overseas travel, and any change in sexual partners and/or the presence of urethral discharge, are the related questions to ask. Pregnancy normally has an immunosuppressive impact on joint disease, so many sufferers with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis experience remission or vital enchancment throughout being pregnant. However, you also needs to contemplate the potential of an infection, especially viral infections, similar to parvovirus B19, which can be damaging to the fetus. Treatment on this patient would in all probability be with systemic corticosteroids and low-dose aspirin. Use of steroids at significant doses will increase the chance of congenital cleft lip and cleft palate, particularly if given in the first trimester. Combined management between rheumatologists and obstetricians could be very important for this patient. Central disc herniation with cauda equina syndrome due to the rapid onset of bilateral neurological trouble and probable urinary retention. The image is certainly one of a profound lower motor neurone lesion affecting lots of the sacral nerves. Central disc herniation is rare (1�2% of all disc herniations) and incessantly misdiagnosed. There may be very little ache and profound sphincter disturbance or severe sciatica, bilateral lower-limb neurological deficit and relative sparing of sacral roots 2, 3 and 4. The key sign is perineal numbness, the presence of which calls for urgent investigation. Because the normal bladder sensation is lost, the patient may be oblivious of their urinary retention, so it is very important be mindful of the chance and to search bladder distension by palpation and percussion of the lower stomach. On the axial view the theca and nerves (lighter colour) are displaced and compressed by the disc material (dark).
5 mg dulcolax free shipping
Research carried out with chimpanzees living in a wildlife sanctuary has proven that the introduction of 1 nut-cracking chimp can lead shortly to the spreading of that ability throughout the colony (Marshall-Pescini & Whiten medications an 627 5 mg dulcolax cheap overnight delivery, 2008) medicine tour buy dulcolax 5 mg otc. The most refined type of social studying is teaching, which involves the teacher modifying his or her conduct in order that the "scholar" purchase new knowledge. Teaching requires that the learner recognize the attitude of the trainer and that the teacher be delicate to the knowledge, motivations, and emotions of the learner. Although we regularly speak of nonhuman animals educating their offspring, instructing in the animal world is rare. It has been shown in meerkats (Thorton & McAuliffe, 2006), dolphins (Bender et al. Mother chimpanzees make exaggerated movements while cracking nuts when within the presence of their infants (Boesch, 1991). This reflexive motion, referred to as gaze following, helps us perceive what the opposite person is pondering about and, in conversations, helps us to know what he or she is talking about (Richardson et al. Beginning within the latter half of their first yr of life, human infants reflexively are inclined to take a glance at no matter their caregiver is looking at (Brooks & Meltzoff, 2002; Woodward, 2003). Such gaze following ensures that the infants pay consideration to the same objects and occasions in their environment that their elders attend to , which can be crucial things to find out about for survival in their culture. Consistent with this idea, researchers have discovered that infants who show essentially the most reliable gaze following learn language quicker than those that exhibit less gaze following (Brooks & Meltzoff, 2008). Presumably, in the course of our evolution, the benefits of cuing others in to our ideas outweighed the advantages of deception. Many have suggested that human minds had been shaped by natural selection to be particularly attentive to social relations- to infer the goals, intentions, and thoughts of others-that permitted our ancestors to more effectively cooperate and compete with, and especially be taught from one another (Shaf to et al. But now we flip to some narrower forms of specialised learning, both in humans and different animals. When individuals have a look at faces like this, even in images, they reflexively shift their very own eyes within the direction at which the observed eyes are wanting. Play Exploration Social Learning In line with a principle originated by Karl Groos, young mammals appear to play in ways that assist them to develop essential survival abilities. Human children play not just at abilities that are essential to people everywhere, but in addition at those distinctive abilities that are essential to the culture in which they develop. Exploration is more primitive than play, occurring in lots of extra species and at all ages. Curiosity motivates exploration of novel objects and places, but is balanced by fear. Latent learning experiments present that exploration alone, without exterior reward, produces helpful data. Stimulus enhancement, aim enhancement, and emulation are easier types of observational learning than imitation. The most refined type of social studying is instructing, which humans do readily however is uncommon (though not nonexistent) on other animals. Animals can learn many different things by way of classical conditioning, operant conditioning, play, exploration, and statement. But natural selection has also endowed animals with specialised studying skills which have quite limited domains of operation. These could additionally be finest regarded as adjuncts to particular species-typical behavior patterns. Special Abilities for Learning What to Eat For some animals, learning what to eat is a comparatively easy matter. Such animals have evolved special mechanisms for studying to establish healthful meals and to keep away from potential poisons. Food-Aversion Learning: How It Differs from Typical Classical Conditioning If rats turn into ill after consuming a novel-tasting meals, they subsequently avoid that food. Similarly, individuals who by likelihood get sick after consuming an uncommon meals usually develop a long-term aversion to the meals (Bernstein, 1991; Logue, 1988). For years as a toddler, I (Peter Gray) hated the style and scent of a selected breakfast cereal, as a outcome of once, a couple of hours after I ate it, I occurred to develop a bad case of stomach flu. Some psychologists choose to describe such cases of food-aversion studying when it comes to classical conditioning. In that description, the sensation of illness or nausea induced by the x-ray treatment or drug is the unconditioned stimulus for a response of aversion or revulsion, and the style and smell of the food turn out to be conditioned stimuli for that response. But John Garcia, the researcher who pioneered the research of foodaversion learning, argues that such learning is sort of totally different from normal instances of classical conditioning (Garcia et al. One particular attribute of food-aversion studying has to do with the optimal delay between the conditioned and unconditioned stimuli. In typical instances of classical conditioning, such because the salivary reflex studied by Pavlov, conditioning occurs only when the unconditioned stimulus follows immediately (within a quantity of seconds) after the conditioned stimulus. But food-aversion learning has been demonstrated even when x-rays were administered as much as 24 hours after the animals had eaten the meals (Etscorn & Stephens, 1973). In reality, food-aversion studying fails to occur if the hole between tasting the meals and the induction of illness is lower than a few minutes (Schafe et al. Another particular characteristic has to do with the kinds of stimuli that can serve as conditioned stimuli for such learning. In typical cases of classical conditioning, virtually any type of detectable stimulus can serve, but in food-aversion learning the stimulus must be a particular taste or scent (and taste usually works higher than smell). Also, when the x-ray�induced radiation illness was paired with flashing lights or sounds, it was very tough for the rats to relate the 2 experiences. These distinguishing traits of food-aversion studying make wonderful sense when thought of within the mild of the perform that such studying serves in the pure surroundings. For example, a food that has begun to rot and makes an animal sick could look identical to one which has not begun to rot, however its taste and odor are quite totally different. Counter to the conventional wisdom of his day, Garcia argued that the rats were prepared to make an affiliation between nausea and food consumption (especially novel food), something that would be adaptive within the wild. Unprepared behaviors are these acquired by way of the traditional processes of operant conditioning and often take repeated trials to purchase. Contraprepared behaviors, in contrast, are those which are impossible or tough to study despite in depth training, such because the association between nausea and patterns of sunshine and sounds in rats. Food-Preference Learning the opposite side of the coin of studying to keep away from harmful foods is learning to choose foods that fulfill a particular nutritional requirement. In one collection of experiments, researchers deprived rats of thiamine (one of the B nutritional vitamins, essential for health) for a time period and then offered them a alternative of meals, solely certainly one of which contained thiamine (Overmann, 1976; Rozin & Kalat, 1971). Each meals had a definite flavor, and thiamine-which itself has no flavor-was added to a special food for different rats. The end result was that, within a few days of expertise with the meals, most rats strongly most well-liked the thiamine-containing meals. Close inspection of their consuming patterns suggests a possible reply (Rozin & Kalat, 1971). When first offered with the alternatives, a rat normally ate just one or two of the foods. Then, usually after a number of hours, the rat would swap to a special meals or two.
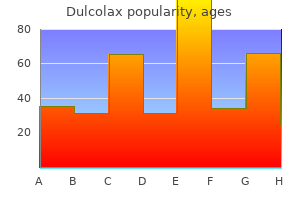
Purchase dulcolax 5 mg without prescription
The "antirepression" peptide present within the crustacean Ubx protein might intrude with the flexibility of the repression domains to recruit these complexes treatment uti infection generic dulcolax 5 mg otc. When this peptide is connected to the fly protein medications for high blood pressure 5 mg dulcolax otc, the hybrid protein behaves just like the crustacean Ubx protein and no longer represses Dll. The carboxy-terminal antirepression peptide blocks the exercise of the amino-terminal repression area. Changes in the Ubx expression pattern appear to be responsible for the transformation of swimming limbs in to maxillipeds in crustaceans. Moreover, the lack of the antirepression motif in the Ubx protein probably accounts for the suppression of abdominal limbs in insects. In this final section on that theme, we evaluate proof that modifications within the regulatory sequences in Ubx target genes might explain the different wing morphologies found in fruit flies and butterflies. In Drosophila, Ubx is expressed within the creating halteres, the place it features as a repressor of wing development. These genes encode proteins that are crucial for the growth and patterning of the wings. In Ubx mutants, these genes are now not repressed within the halteres, and in consequence, the halteres develop in to a second set of wings. Fruit flies are dipterans, and all the members of this order include a single pair of wings and a set of halteres. It is most likely going that Ubx functions as a repressor of wing improvement in all dipterans. All of the members of this order (which also contains moths) contain two pairs of wings somewhat than a single pair of wings and a set of halteres. What is the premise for these completely different wing morphologies in dipterans and lepidopterans This is about the time of divergence that separates humans and nonmamalian vertebrates such as frogs. Such a loss would permit the developing hindwings to specific the entire genes that are normally repressed by Ubx. The transformation of swimming limbs in to maxillipeds in isopods supplies a transparent precedent for such a mechanism. It seems easier to modify repression activity than to change the regulatory sequences of 5 to 10 totally different Ubx goal genes. Surprisingly, it appears that the much less doubtless explanation-changes in the regulatory sequences of a quantity of Ubx target genes-accounts for the totally different wing morphologies. The Ubx protein appears to operate in the same way in fruit flies and butterflies. For instance, in butterflies, the lack of Ubx in patches of cells within the hindwing causes them to be remodeled in to forewing constructions. This statement suggests that the butterfly Ubx protein features as a repressor that suppresses the event of forewings. Our ultimate dialogue of the comparison of the Neanderthal genome with those of chimpanzee and human offers a couple of startling insights in to human origins. Diverse Animals Contain Remarkably Similar Sets of Genes About one hundred different animal genomes have been absolutely sequenced and assembled, but the majority of those sequences correspond to only a few animal teams, centered across the human genome, as well asthose of key model organisms such because the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, and the nematode worm, Caenorhabditis elegans. Twelve different species of Drosophila have been sequenced to help perceive the diversification of distinct species of fruit flies. Currently, just one-third of all animal phyla are represented bya member species with acomplete genome sequence assembly. By far, the most startling discovery arising from comparative genome sequence analysis is the truth that wildly divergent animals, from the sea anemone to humans, possess a highly conserved set of genes. A glimpse in to the set of genes required for the distinctive attributes of all animals is offered by the genome sequence meeting of a single-cell eukaryote, a protozoan, called Monosiga. It additionally lacks important regulatory genes liable for differential gene activity in developing animal embryos, including Hox genes and Hox clusters. Thus, the evolutionary transition of simple eukaryotes in to fashionable animals required the creation of numerous novel genes not seen among the many easy organisms that lived within the ancient oceans more than 1 billion years ago. Many Animals Contain Anomalous Genes Despite a continuing set, or "toolkit," of basic genes required for the development of all animals, every genome contains its personal distinctive-and sometimes surprising-attribute. The gene finder program recognized 15 putative exons in the Ciona gene, indicated as green rectangles. The flanking genes are conserved in worms, flies, and humans, whereas the endoglucanase gene is unique to Ciona, which incorporates a cellulose sheath. Note differences in the detailed intron�exon structures of the flanking genes among the totally different animal genomes. It incorporates a rubbery protective sheath composed of tunicin, a biopolymer associated to plant cellulose. However, prior to the genome meeting, it was unclear whether the sea squirt contained its own endogenous cellulose synthase gene or employed a symbiotic organism for producing the tunicin sheath. Indeed, there are numerous examples of animals utilizing easy symbionts for unusual genetic features. For example, termites and wood-eating cockroaches contain symbiotic bacteria in their hindguts that contain the required genes required for digesting wood. One of the distinctive attributes of vertebrates is the flexibility to mount an adaptive immune response upon infection or damage. This contains the production of specific antibodies that recognize overseas antigens with great specificity and precision. Invertebrates possess a common innate immunity, however they lack the capability to produce an adaptive immune response. Synteny Is Evolutionarily Ancient One of the hanging findings of comparative genome analysis is the excessive diploma of synteny, conservation in genetic linkage, between distantly associated animals. In many circumstances, this linkage even extends to the pufferfish, which final shared a common ancestor with mammals greater than 400 million years in the past. The deuterostomes embody 4 animal phyla: Xenoturbellida, Echinodermata, Hemichordata, and Chordata. There are five courses of organisms within the echinoderms, two courses of hemichordates, and three lessons of chordates. Note that the closest residing relations of the vertebrates are the urochordates, which embody the sea squirts (see Box 19-3). Genetic linkage is essential in prokaryotes, where linked genes are coregulated inside a common operon (Chapter 18). Such linkage is generally absent in metazoan genomes, though the nematode worm C. Early comparative genome analyses appeared to affirm that genetic linkage bore no influence on gene regulation. Evidence for this view stems from the evaluation of the genome of Nematostella, a simple sea anemone. Despite their simplicity and ancient historical past, they include several genes which have been misplaced in flies and worms.
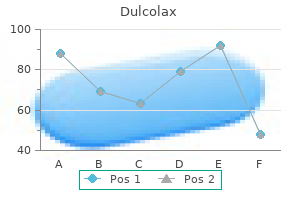
Buy dulcolax 5 mg amex
In this dialogue medicine 627 order dulcolax 5 mg line, although medications depression purchase dulcolax 5 mg without prescription, our focus is on the longer-term results of hormones on sexual drive. Hormonal Influences on Male Sex Drive Although sexual want and response are influenced by a number of totally different hormones, in male mammals, probably the most crucial hormone for the maintenance of the sexual drive is testosterone, a type of androgen, produced by the testes. Testosterone Maintains the Capacity for Male Sex Drive In male animals, castration (removal of the testes, and therefore of the principle supply of testosterone) causes a marked decline in the intercourse drive-not all of sudden, however progressively (Feder, 1984). The injection of testosterone in to the bloodstream of castrated animals progressively but ultimately absolutely restores their drive. Neurons in this space include many receptor websites for testosterone, and small lesions there abolish sexual conduct in male rats (Meisel & Sachs, 1994). Apparently, the medial preoptic area of the hypothalamus is a crucial part of the central drive system for sex in male rats and other male animals which were studied, and testosterone acts there in a quite prolonged approach to enable neural activity to happen and maintain the drive. Men castrated in an accident or for medical reasons nearly at all times experience a decline (though often not a whole loss) in intercourse drive and conduct, and testosterone injections restore their drive, normally fully (Money & Ehrhardt, 1972). In other research, testosterone injections administered to noncastrated males whose testes have been producing unusually low Posterior quantities of the hormone sharply inarea creased their reported sexual drive Hypothalamus and conduct (Davidson et al. At least for area many males, the consequences of such remedy have more to do with drive Anterior area than with sexual functionality. Lowtestosterone men are typically caMedial pable of the mechanics of sexual preoptic space habits, including erection and Hypothalamus ejaculation, but have relatively little need for it till injected with testosterone (Davidson & Myers, 1988). For instance, profitable a game, even a sedentary sport like chess, commonly results in increased blood ranges of testosterone in males, detectable inside minutes of the victory (Archer, 2006). Pleasant social encounters with girls can also increase testosterone manufacturing in men (Roney et al. Moreover, in one experiment, men who confirmed elevated levels of testosterone after losing a game have been more likely to desire a rematch than were men who showed the more typical decline in testosterone after losing (Mehta & Josephs, 2006). High status and dominance is one route by which males appeal to women, so an impact of testosterone on competitors and status seeking could possibly be an oblique means toward increased sexual behavior. In both people and nonhumans, this cycle controls ovulation (the release of one or more eggs in order that pregnancy can occur). How do female primates differ from feminine rats regarding the regulation of sexual drive Effects of the Estrous Cycle in Nonhuman Mammals In most mammals, feminine sexual drive and habits are tightly controlled by the estrous cycle. The feminine will search out opportunities for mating, and can copulate, only at that time within the cycle when she is ovulating and therefore able to turning into pregnant. Removal of the ovaries fully abolishes sexual conduct in most nonhuman female mammals, and injection of hormones can totally restore it. For some species an injection of estrogen alone is most effective, and for others (including rats) a sequence of estrogen adopted 2 or three days later by progesterone is most effective, a sequence that mimics the natural change of hormones during the estrous cycle. Insertion of small amounts of estrogen and progesterone immediately in to this area brings on sexual behavior in rats whose ovaries have been eliminated, and lesions on this space abolish sexual behavior in in any other case intact females (Blaustein, 2008; Pleim & Barfield, 1988; Schwartz-Giblin et al. Apparently the cyclic variation in ovarian hormones acts on the ventromedial space to cause the cyclic waxing and waning of sexual drive. In at least some species of primates, including rhesus monkeys, sexual drive throughout nonfertile instances depends not on ovarian hormones however on testosterone and different androgens. Effects of the Menstrual Cycle in Women Human females exhibit still greater liberation of sexual habits from cyclic hormonal management than do other primates. Apparently, in ladies, hormonal activation of the drive has been taken over largely by adrenal androgens. The studies have proven that, on average, women during the fertile part dress more provocatively, speak in additional interesting tones of voice, are comparatively more drawn to men with extremely masculine features, feel themselves to be extra sexually attractive and sexually motivated, and provoke sex extra regularly than at different instances of their menstrual cycle (Gangestad et al. A helpful distinction here is that between arousability and proceptivity (Diamond, 2006). The information recommend that arousability stays comparatively fixed for ladies over the course of the menstrual cycle, however proceptivity increases through the fertile period. The elevated proceptivity would possibly result from the rise of estrogen and/or progesterone through the fertile interval, however it may also outcome from the rise of adrenal androgens. Researchers have discovered that secretion of adrenal androgens, particularly testosterone, will increase markedly in the course of the fertile stage of the menstrual cycle (Salonia et al. What evidence suggests, however, that female sexual drive does improve through the time of ovulation Sexual Differentiation and Determinants of Sexual Orientation Sex hormones influence sexual drive and behavior by way of two completely different kinds of results on the brain: activating and differentiating. They happen across the time of puberty and after, when hormones work on already-developed brain buildings to prime, or activate, sexual drive. Differentiating results, in contrast, occur before and (in some species) instantly after birth and trigger the brain to develop in a male or female direction. They are liable for the organic differences between males and females in sexual drive and orientation. We turn now to a dialogue of the function of hormones in differentiating women and men sexually and to the overall problem of causes of human variations in sexual orientation. Brain-Differentiating Effects of the Early Presence or Absence of Testosterone As famous in Chapter 3, the only initial distinction between the two sexes, in all mammals, is that females have two X chromosomes and males have a small Y chromosome instead of the second X. A specific gene on the Y chromosome causes the growth of testes (the male gonads) from buildings that would otherwise develop in to ovaries (the feminine gonads) (Page et al. Before birth the testes start to produce testosterone, which acts on the brain and other bodily structures 23 What are some results of the presence or absence of testosterone before start on development of the genitals, the mind, and behavior What has been discovered from studies of girls and women born with congenital adrenal hyperplasia The rudimentary genitals of the fetus develop in to male buildings (including the penis and scrotum) if testosterone is present, and so they develop in to feminine structures (including the clitoris and vagina) if testosterone is absent. Early testosterone additionally promotes the event of brain pathways involved within the male sex drive and inhibits the event of brain pathways involved in the female intercourse drive (Gorski, 1996; Simerly, 2002). In rats, this era runs from a number of days earlier than start to a day or so after delivery. Because of this difference in timing of critical durations, manipulation of hormones at the appropriate time can produce animals which have the genitals of one intercourse but the mind structures and habits of the opposite intercourse (Feder, 1984; Ward, 1992). In developed nations, hormone therapies are begun at start or shortly thereafter to terminate the overproduction of androgens, and surgery is used to feminize the genitals. These women are raised by their dad and mom as normal women, but many research have proven that in numerous methods they exhibit masculine characteristics. These effects appear clearly to be attributable to the prenatal androgens and never by any distinction in how they were treated throughout their development. The answer is that the feminine hormones (progesterone and estrogen) are produced by pregnant females at high ranges and get in to the tissues of all fetuses, of both sexes. If female hormones promoted growth of feminine structures during fetal development, all mammalian infants would be feminized. Falling in Love Sex among people is commonly accompanied by romantic love, or "falling in love. This is typically accompanied by a loss of urge for food, anxiousness, or sleeplessness (Fisher, 2000, 2004). Anthropologist Helen Fisher (2000) proposed that human pair bonding advanced as females required growing protection and resources to care for his or her slow-developing offspring. The survival of their dependent offspring is tremendously benefited by paternal help (Geary, 2005b). Fisher (2000, 2004) proposed that falling in love includes three primary emotional techniques that evolved to help mating, replica, and parenting: lust, attraction, and attachment. Lust-becoming sexually excited by members of the other sex (or by the identical sex for someone with a gay orientation)-is driven in each women and men primarily by androgen hormones (testosterone being a potent example of an androgen hormone). For example, when male sparrows had been injected with testosterone, thereby rising lust, they deserted their mates to pursue different females (Wingfield, 1994).
Dulcolax 5 mg trusted
During the lytic cycle symptoms 9f anxiety dulcolax 5 mg order with amex, Mu completes roughly a hundred rounds of transposition per hour symptoms blood clot leg generic dulcolax 5 mg fast delivery, making it the most environment friendly transposon recognized. Furthermore, even when current as a quiescent lysogen, the Mu genome transposes quite frequently, compared with conventional transposons similar to Tn10. The Mu genome is 40 kb and carries more than 35 genes, however only two encode proteins with dedicated roles in transposition. This problem is solved as a outcome of Mu transposition is regulated by a course of known as transposition target immunity (see Box 12-4, Mechanism of Transposition Target Immunity). Transposition goal immunity is noticed for several completely different transposable parts and can work over very lengthy distances. For Mu, sequences within 15 kb of an present Mu insertion are resistant to new insertions. Target immunity protects a component from transposing in to itself or from having one other new copy of the same type of element insert in to its genome. Although these components are clearly related, members isolated from totally different organisms have distinguishing options and are named differently. For example, components from the worm Caenorhabditis elegans are called Tc components, whereas the original component named Mariner was isolated from a Drosophila species. This simplicity in structure and mechanism may be liable for the large success of these components in such a broad range of host organisms. The MuA-binding websites are in the terminal inverted repeats on the ends of the transposon (dark green). Perhaps because of this lack of management, many parts discovered by genome sequencing are "lifeless". For example, many components carry mutations in the transposase gene that inactivate it. Using a large quantity of sequences from both inactive and energetic components, researchers constructed a man-made hyperactive Tc1/ mariner element. This factor, named Sleeping Beauty, transposes at very high frequencies in contrast with naturally isolated parts. Furthermore, this reconstruction experiment reveals that the frequency of transposition by Tc1/mariner elements is naturally kept at bay because of the suboptimal activity of their transposase proteins. Yeast Ty Elements Transpose in to Safe Havens in the Genome the Ty components (transposons in yeast), distinguished transposons in yeast, are virus-like retrotransposons. In this case, integration is precisely targeted to the start web site of transcription (+2 bp). In contrast, Ty5 preferentially integrates in to areas of the genome that are in a silenced, transcriptionally quiescent state. Silenced regions targeted by Ty5 embrace the telomeres and the silent copies of the mating-type loci (see Chapter 11). It is proposed that this target specificity enables the transposons to persist in a number organism by focusing most of their insertions away from important areas of the genome which might be involved directly in coding for proteins. The use of this kind of focused transposition may be especially essential in organisms with small gene-rich genomes, corresponding to yeast. These Ty1 components carry a truncated Gag protein that types the spiky shells with trimeric models of the particles. Ty5 is found near the ends of chromosomes and near the mating-type loci (see Chapter 11) which are "silenced". Genome sequences reveal, as quickly as once more, the presence of giant numbers of those parts, that are usually only between a hundred and 400 bp in size. These parts are also flanked by targetsite duplications which are variable in size (blue arrows). Cells, nevertheless, have additionally harnessed this recombination mechanism for features that directly help the organism. The greatest instance is V(D)J recombination, which occurs in the cells of the vertebrate immune system. The immune system of vertebrates has the job of recognizing and heading off invading organisms, including viruses, bacteria, and pathogenic eukaryotes. Vertebrates have two specialised cell sorts dedicated to recognizing these invaders: B-cells and T-cells. B-cells produce antibodies that circulate within the bloodstream, whereas T-cells produce cell surface�bound receptor proteins (called T-cell receptors). Recognition of a "foreign" molecule by either of these lessons of proteins starts a cascade of occasions targeted on destruction of the invader. To fulfill their functions efficiently, antibodies and T-cell receptors should be ready to acknowledge an enormously numerous group of molecules. To understand how this recombination generates the needed diversity, we have to look at the structure of an antibody molecule. The a part of the protein that interacts with foreign molecules known as the antigen-binding web site. The variable and fixed areas are labeled on the left side of the molecule only. This is simply one of the many kinds of recombination occasions that may happen in different pre-B-cells. The situation for meeting of the gene segments encoding the antibody heavy chain is comparable. For instance, a selected heavy-chain locus in a mouse has more than one hundred V regions, 12 D regions, and 4 J regions. V(D)J recombination can assemble this gene to generate more than 4800 different protein sequences. Because useful antibodies could be constructed from any pair of light and heavy chains, the variety generated by recombination on the gentle and heavy loci has a multiplicative impact on protein construction. The Early Events in V(D)J Recombination Occur by a Mechanism Similar to Transposon Excision Recombination sequences, called recombination sign sequences, flank the gene segments which are assembled by V(D)J recombination. These alerts all have two highly conserved sequence motifs, one 7 bp (the 7-mer) and the second 9 bp (the 9-mer) in size. One class has the 7-mer and 9-mer motifs spaced by 12 bp of sequence, whereas the second class has these motifs spaced by 23 bp. Recombination always occurs between a pair of recombination signal sequences in which one companion has the 12-bp "spacer" and the opposite partner has the 23-bp "spacer. The hairpin buildings are subsequently hydrolyzed and then joined collectively to type a coding joint between the V and J regions. The two ends carrying the recombination sign sequences are additionally joined to type a sign joint. The former construction undergoes further recombination, whereas the latter is discarded.
Diseases
- Oculocutaneous albinism, tyrosinase negative
- Hypocalcinuric hypercalcemia, familial type 1
- Growth delay, constitutional
- Mesomelic dwarfism Langer type
- Epilepsy microcephaly skeletal dysplasia
- Actinic keratosis
- Wallerian degeneration
- Braddock Jones Superneau syndrome
Dulcolax 5 mg generic with mastercard
Mitosis Maintains the Parental Chromosome Number We now return to the overall strategy of mitosis treatment 3 antifungal best dulcolax 5 mg. At the tip of prophase symptoms 0f brain tumor buy discount dulcolax 5 mg online, in most cells the nuclear envelope breaks down and the cell enters metaphase. During metaphase, the mitotic spindle varieties and the kinetochores of sister chromatids attach to the microtubules. Proper chromatid attachment is simply achieved when the 2 kinetochores of a sister-chromatid pair are connected to microtubules emanating from reverse microtubule-organizing facilities. During prophase, chromosomes are condensed and detangled in preparation for segregation, and the nuclear membrane surrounding the chromosomes breaks down in most eukaryotes. During metaphase, every sisterchromatid pair attaches to opposite poles of the mitotic spindle. Anaphase is initiated by the loss of sister-chromatid cohesion, resulting in the separation of sister chromatids. Telophase is distinguished by the loss of chromosome condensation and the re-formation of the nuclear membrane across the two populations of segregated chromosomes. Cytokinesis is the ultimate event of the cell cycle throughout which the cellular membrane surrounding the two nuclei constricts and finally fully separates in to two daughter cells. Importantly, chromosome segregation begins only after all sister-chromatid pairs have achieved bivalent attachment. Chromosome segregation is triggered by proteolytic destruction of the cohesin molecules, resulting in the loss of sister-chromatid cohesion. This loss occurs as cells enter anaphase, throughout which the sister chromatids separate and transfer to opposite sides of the cell. Bivalent attachment ensures that the 2 members of a sisterchromatid pair are pulled towards reverse poles and each daughter cell receives one copy of every duplicated chromosome. The last step of mitosis is telophase, throughout which the nuclear envelope re-forms round each set of segregated daughter chromosomes. At this point, cell division may be accomplished by bodily separating the shared cytoplasm of the 2 presumptive cells in a process known as cytokinesis. During Gap Phases, Cells Prepare for the Next Cell Cycle Stage and Check That the Previous Stage Is Completed Correctly the remaining two phases of the mitotic cell cycle are gap phases. The hole phases of the cell cycle provide time for the cell to accomplish two targets: (1) to prepare for the next phase of the cell cycle and (2) to check that the previous section of the cell cycle has been completed appropriately. These delays enable time for the damage to be repaired earlier than the cell cycle continues. Meiosis Reduces the Parental Chromosome Number A second kind of eukaryotic cell division is specialised to produce cells which have half the number of chromosomes because the parental cell. Like the mitotic cell cycle, the meiotic cell cycle includes a G1, S, and an elongated G2 part. During the meiotic S section, every chromosome is replicated, and the daughter chromatids stay associated as in the mitotic S part. The most significant distinction between the mitotic and meiotic cell cycles occurs throughout chromosome segregation. For simplicity, solely a single chromosome is proven segregating with the blue copies being from one mother or father and the yellow copies from the other. During pairing, chromatids from the different homologs recombine to type a link between the homologous chromosomes known as a chiasma. During metaphase I, the 2 kinetochores of each sister-chromatid pair attach to one pole of the meiotic spindle. Entry in to anaphase I is pushed by the lack of sister-chromatid cohesion along the arms of the chromosomes. The loss of arm cohesion allows the recombined homologs to separate from each other. As in mitotic metaphase, the kinetochores related to each sister-chromatid pair connect to opposite poles of the meiotic spindles. The 4 separate sets of chromosomes are then packaged in to nuclei and separated in to 4 cells to create four spores or gametes. Like mitosis, every of those segregation events includes a prophase, metaphase, and anaphase stage. During the metaphase of meiosis I, additionally called metaphase I, the homologs attach to reverse poles of the microtubule-based spindle. Because each kinetochores of every sister-chromatid pair are hooked up to the identical pole of the microtubule spindle, this interaction is referred to as monovalent attachment (in contrast to the bivalent attachment seen in mitosis, during which the kinetochores of each sister-chromatid pair bind to opposite poles of the spindle). As in mitosis, the paired homologs initially resist the tension of the spindle pulling them aside. In the case of meiosis I, this resistance is mediated through the physical connections between the homologs, called chiasma or crossovers, which might be the result of recombination between the homologs. This resistance also requires sister-chromatid cohesion along the arms of the sister chromatids. When cohesion along the arms is eliminated throughout anaphase I, the recombined homologs are released from each other and segregate to opposite poles of the cell. Importantly, the cohesion between the sisters is maintained near the centromere, preserving the sister chromatids paired. Instead, a spindle is formed in affiliation with each of the 2 newly separated sister-chromatid pairs. The cohesion that continues to be at the centromeres after meiosis I is crucial to oppose the pull of the spindle. At this level, there are 4 sets of chromosomes in the cell, each of which contains a single copy of each chromosome. A nucleus forms around each set of chromosomes, after which the cytoplasm is divided to type four haploid cells. Different Levels of Chromosome Structure Can Be Observed by Microscopy Microscopy has lengthy been used to observe chromosome structure and function. Indeed, lengthy earlier than it was clear that chromosomes have been the supply of the genetic info in the cell, their movements and modifications throughout cell division had been well-understood. The compact nature of condensed mitotic or meiotic chromosomes makes them comparatively straightforward to visualize even by easy light microscopy. Microscopic analysis of condensed chromosomes is used to decide the chromosomal makeup of human cells and detect such abnormalities as chromosomal deletions or people with too few or too many copies of a chromosome. In the electron microscope, two states of chromatin are noticed: fibers with a diameter of both 30 nm or 10 nm. In contrast, the 10-nm fiber is a less compact form of chromatin that resembles an everyday series of "beads on a string. Note that the colours of the totally different histone proteins right here and in following constructions are the identical. Although not sure by nucleosomes, these websites are usually associated with nonhistone proteins that are either regulating or participating in these events. Eukaryotic cells generally include five abundant histones: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. H1 is half as ample as the opposite histones, which is in preserving with the discovering that only one molecule of H1 can affiliate with a nucleosome.

Dulcolax 5 mg buy discount online
As its name suggests symptoms 2016 flu purchase dulcolax 5 mg on line, this issue makes transcription on chromatin templates much more efficient 5ht3 medications 5 mg dulcolax purchase with mastercard. This allows polymerase to move that nucleosome (in vitro, it has been proven that eradicating H2A. In each case, the first catalytic magnesium ion is designated as Metal A (pink), and the positions of the two conserved acidic residues are indicated (green circles). Thus we see that although the 2 proteins are so completely different, they act in essentially the same means. Here we consider the opposite two processes-capping and polyadenylating the transcript. In step one, a phosphate group is faraway from the 50 finish of the transcript. This occurs when the transcription cycle has progressed only as far as the transition from the initiation to elongation phases. The polymerase can proceed transcribing for several thousand nucleotides earlier than terminating and dissociating from the template. It can be possible that other elements are needed in addition to Rat1 to dislodge polymerase as, in vitro, Rat1 is alone inadequate to perform this operate, even after it has degraded the transcript. According to this model, termination is decided by a conformational change within the elongating polymerase that reduces the processivity of the enzyme leading to spontaneous termination soon afterward. Each of these enzymes additionally works with its own distinctive set of general transcription elements. The set of proteins involved in helping Pol I transcription in yeast is somewhat completely different. Both resemble a crab claw in shape, the pincers being made up of the largest subunits, b and b0 in the case of the bacterial enzyme. The former has a so-called tail on the carboxy-terminal finish of the massive subunit, and this is absent from the bacterial enzyme. A round of transcription proceeds by way of three phases known as initiation, elongation, and termination. In bacteria, there is simply one initiation factor, s, whereas in eukaryotes there are several, collectively called the final transcription factors. There are also interactions between the elongation factors and people concerned in processing, making certain correct coordination of these events. Another difference between bacteria and eukaryotes is that the latter must deal with nucleosomes throughout elongation. This requires one more complex that may dismantle nucleosomes forward of, and reassemble them behind, the advancing polymerase. Thus, in bacteria, there are two sorts of terminators: intrinsic (Rho-independent) and Rho-dependent. In mixture with a string of U nucleotides (which bond only weakly with the template strand), this leads to launch of the transcript. Transcriptional regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Transcription issue regulation and performance, mechanisms of initiation, and roles of activators and coactivators. Choose a number of of the following phrases: template strand, non-template strand, coding strand, non-coding strand. Explain why regulation of transcription regularly includes the promoter and protein interactions with the promoter. State whether or not the next assertion is true or false, and explain your conclution. Given the three models for initial transcription in micro organism (transient tour, inchworming, and scrunching), For instructor-assigned tutorials and issues, go to MasteringBiology. Why does some extent mutation at any one of many bolded nucleotides disrupt termination of transcription Explain why the mediator and nucleosome modifiers are required for high levels of transcription in eukaryotic cells but not in vitro. Researchers studying the torpedo model of eukaryotic termination wanted to test Rtt103 and Rat1 positioning on transcribed genes. They included a reaction utilizing primers particular for amplification of a nontranscribed area on chromosome V in each lane (lower band in each reaction). In those instances, the coding sequence is periodically interrupted by stretches of non-coding sequence. Many eukaryotic genes are thus mosaics, consisting of blocks of coding sequences separated from one another by blocks of non-coding sequences. The coding sequences are known as exons and the intervening sequences are referred to as introns. The variety of introns found within a gene varies enormously-from one within the case of most intron-containing yeast genes (and a few human genes), to 50 within the case of the rooster proa2 collagen gene, to as many as 363 in the case of the Titin gene of people. Clearly, the typical number increases as one appears from simple single-celled eukaryotes, corresponding to yeast, through larger organisms corresponding to worms and flies, all the finest way as much as people. Thus, for instance, exons are sometimes on the order of one hundred fifty nucleotides, whereas introns-although they too could be short-can be so long as 800,000 nucleotides (800 kb). The average variety of introns per gene is proven for a choice of eukaryotic species. The names in pink are those of the widespread mannequin organisms (Appendix 1): the yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster), the roundworm (Caenorhabditis elegans), the plant (Arabidopsis thaliana), and the mouse (Mus musculus). The different species shown are Anopheles gambiae; Aspergillus nidulans; Bigelowiella natans nucleomorph; Caenorhabditis briggsae; Candida albicans; Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Ciona intestinalis; Cryptococcus neoformans; Cryptosporidium parvum; Cyanidioschyzon merolae; Dictyostelium discoideum; Encephalitozoon cuniculi; Giardia lamblia, Guillardia theta nucleomorph; Homo sapiens; Leishmania main; Neurospora crassa; Oryza sativa; Paramecium aurelia; Phanerochaete chrysosporium; Plasmodium falciparum; Plasmodium yoelii; Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Takifugu rubripes; Thalassiosira pseudonana; and Trichomonas vaginalis. Called different splicing, this strategy enables a gene to give rise to multiple polypeptide product. It is estimated that 90% or extra of the protein-coding genes in the human genome are spliced in alternative ways to generate multiple isoform. For instance, the Slo gene from rat, which encodes a potassium channel expressed in neurons, has the potential to encode 500 different variations of that product. And, as we shall see, one explicit Drosophila gene can encode as many as 38,000 attainable products because of various splicing. Alternative splicing is often a regulated process, with completely different isoforms being produced in response to different signals or in several cell sorts. Splicing was found in research of gene expression in the mammalian adenovirus, as described in Box 14-1, Adenovirus and the Discovery of Splicing. The intron�exon boundary at the 30 finish of the intron is marked by the 30 splice website. It is discovered entirely inside the intron, often close to its 30 finish, and is adopted by a polypyrimidine tract (Py tract). The consensus sequences for each the 50 and 30 splice sites, and in addition the conserved A on the department site. As in different instances of consensus sequences, where two alternative bases are equally favored, those bases are both indicated at that place.
5 mg dulcolax buy with mastercard
Methods for rapidly identifying proteins that work together with one another (such as two-hybrid evaluation; see Box 19-1) medicine x xtreme pastillas 5 mg dulcolax mastercard, which have had an excellent impact in yeast and different eukaryotic techniques medicine 6 year program dulcolax 5 mg purchase with mastercard, are additionally highly effective instruments for elucidating networks of interactions amongst bacterial proteins. The availability of whole-genome sequences and promiscuous conjugative plasmids has created alternatives for finishing up molecular genetic manipulations in bacterial species that otherwise lack refined, traditional tools of genetics. First, massive quantities of bacterial cells can be grown Model Organisms 807 in an outlined and homogeneous physiological state. Second, the instruments of conventional and molecular genetics make it potential to purify protein complexes harboring exactly engineered alterations or to overproduce and thereby get hold of particular person proteins in massive portions. Thus, elucidating basic mechanisms proceeds extra quickly in bacteria in which fewer proteins need to be isolated and by which mechanisms are generally extra streamlined than in larger cells. Bacteria Are Accessible to Cytological Analysis Despite their obvious simplicity and the absence of membrane-bound cellular compartments. Instead, as we now know, proteins and protein complexes have attribute places within the cell. The applications of such methods have provided invaluable insights in to a number of of the molecular processes thought-about on this textual content. For example, we now know that the replication machinery of the bacterial cell is comparatively stationary and is localized to the cell center (Chapter 9). As another instance, the appliance of cytological methods have taught us (again contrary to the traditional view) that during replication the two newly duplicated origin areas of the chromosome migrate towards reverse poles of the cell. Cytological methods are an essential a part of the arsenal for molecular studies on the bacterial cell. Phage and Bacteria Told Us Most of the Fundamental Things in regards to the Gene Molecular biology owes its origin to experiments with bacterial and phage model methods. Crick and Sydney Brenner (Chapter 16) revealed that the genetic code is constructed of triplet codons; the elegent genetic research carried out by Charles Yanofsky in E. There are numerous other examples where, by selecting these simplest of methods, fundamental processes of life have been understood. Benzer launched the term cistron to describe the gene (based on the words cis and trans). In particular, noise in the regulation of genetic circuits has been identified by looking at expression in lots of individual cells within genetically similar populations. The variations seen, and the organic consequences of these variations, have allowed people to higher perceive the advantages as nicely as the issues of noise in gene networks. These studies are aided by advances in reporter and imaging know-how, however once more depend on the basic advantages of the bacterial scale and life cycle. Many novel gene regulatory circuits have been constructed and these afford new methods of learning basic traits of such networks in addition to offering the potential to design new strains with helpful functions-such as cells that can digest oil slicks. Recently it was even demonstrated that a whole bacterial genome might be constructed artificially from numerous synthesized fragments and, as soon as constructed, might perform well enough to maintain a residing cell. They have comparatively small genomes compared to other eukaryotes (see Chapter 8) and a similarly smaller number of genes. Despite this simplicity, yeast cells have the central characteristics of all eukaryotic cells. They include a discrete nucleus with multiple linear chromosomes packaged in to chromatin, and their cytoplasm features a full spectrum of intracellular organelles. These studies finally led to the identification of the primary enzymes and the development of biochemistry as an experimental strategy. Conversion between the haploid and diploid states is mediated by mating (haploid to diploid) and sporulation (diploid to haploid). Under conditions of reduced vitamins, a/a diploids undergo meiotic division (see Chapter 8) to generate a structure known as the ascus that incorporates 4 haploid spores (two a spores and two a spores). When growth conditions enhance, these spores can germinate and develop as haploid cells or mate to re-form a/a diploids. In the laboratory, these cell types could be manipulated to perform quite lots of genetic assays. Genetic complementation could be carried out by merely mating two haploid strains, each of which contains one of the two mutations whose complementation is being tested. If the mutations complement each other, the diploid might be a wild kind for the mutant phenotype. For example, to ask if a given gene is crucial for cell progress, the gene could be deleted in a haploid. Two haploid cell types, a and a, and the diploid product of mating between these two. This method can be utilized to precisely delete the coding area of an entire gene, change a selected codon in an open studying frame, or even change a selected base pair in a promoter. The capability to make such precise modifications within the genome permits very detailed questions in regards to the perform of specific genes or their regulatory sequences to be pursued with relative ease. When the donor fragments are introduced to the cell, high ranges of homologous recombination in this organism ensure a excessive frequency of recombination with the chromosome, resulting in the genetic exchange shown. Because of its wealthy history of genetic studies and its relatively small genome, S. Other genome-wide assets include a library of 6000 strains, each deleted for just one gene. Greater than 5000 of those strains are viable as haploids, indicating that virtually all of yeast genes are nonessential beneath the ideal growth situations in the laboratory. This collection of strains has allowed the event of latest genetic screens in which each gene within the S. The use of microarrays has also allowed the genome-wide mapping of binding sites for transcriptional regulators utilizing chromatin immunoprecipitation techniques (see Chapter 7). Immediately after a new cell is launched from its mom, the daughter cell appears slightly elliptical in form. As the cell progresses through the cell cycle, it types a small "bud" that will finally become a separate cell. The bud grows till it reaches a measurement barely smaller than the "mother" cell from which it arose. At this level the bud is launched from the mom and each cells begin the process once more. The development of a daughter bud via the mitotic cycle is proven and described in the text. Similarly, a growing cell with a very massive bud is almost always within the strategy of executing chromosome segregation. Perhaps most importantly, the proteins and genes recognized as important to these basic events in S. Even more so than its animal counterparts, Arabidopsis illustrates most key features of plant biology, especially among the many angiosperms (flowering seed plants). And just as maize revolutionized plant genetics in the 20th century, Arabidopsis guarantees 812 Appendix 1 to revolutionize plant genomics and most features of plant biology in to the longer term.
Discount dulcolax 5 mg on line
Although the D- and L-amino acids have similar covalent bonds medications you can take when pregnant 5 mg dulcolax cheap visa, their binding properties to uneven molecules are often very totally different treatment leukemia dulcolax 5 mg proven. If an L-amino acid is in a position to connect to a particular enzyme, the D-amino acid is unable to bind. Most molecules in cells could make good "weak" bonds with only a small number of other molecules, partly as a end result of most molecules in biological techniques exist in an aqueous environment. The formation of a bond in a cell therefore depends not only on whether or not two molecules bind well to one another, but additionally on whether or not bond formation is general more favorable than the choice bonds that can form with solvent water molecules. The nature of the chemical bond and the construction of molecules and crystals: An introduction to modern structural chemistry, 3rd ed. Hydrophobic bonds are essential each in the stabilization of proteins and complexes of proteins with other molecules and within the partitioning of proteins in to membranes. They could account for as a lot as one-half of the whole free energy of protein folding. Consider, for example, the different quantities of vitality generated when the amino acids alanine and glycine are sure, in water, to a third molecule that has a floor complementary to alanine. The structural formulas adjacent to every spacefilling drawing point out the arrangement of the atoms. From Equation 3-4, we know that this small power distinction alone would give solely a factor of 6 between the binding of alanine and glycine. It is in all probability going that the water tends to exclude alanine, thrusting it towards a 3rd molecule, with a hydrophobic pressure of 2 � three kcal/mol larger than the forces excluding glycine. We thus arrive at the essential conclusion that the energy difference between the binding of even probably the most comparable molecules to a third molecule (when the distinction between the similar molecules includes a nonpolar group) is at least 2�3 kcal/mol larger within the aqueous interior of cells than under non-aqueous circumstances. Frequently, the power difference is 3 � 4 kcal/mol, as a outcome of the molecules involved typically contain polar teams that may form hydrogen bonds. Larger vitality differences would imply that the secondary bonds would seldom break, leading to low diffusion rates incompatible with mobile existence. Weak Bonds Attach Enzymes to Substrates Weak bonds are necessarily the basis by which enzymes and their substrates initially combine with each other. Because enzymes catalyze each directions of a chemical reaction, they should have specific affinities for both units of reacting molecules. This explains why enzymes can perform rapidly, typically as typically as 106 occasions per second. Despite the low power of every particular person bond, affinity in these interactions, and specificity as properly, outcomes from the mixed effects of many such bonds between any two interacting molecules. Each time a possible weak bond was thought of, the question was posed: Does its formation involve a gain or a lack of free energy Upon superficial examination, nevertheless, lots of the important covalent bonds in cells seem to be shaped in violation of the legal guidelines of thermodynamics, significantly those bonds joining small molecules together to form large polymeric molecules. Originally, this fact suggested to some people that cells had the unique capacity to work in violation of thermodynamics and that this property was, in reality, the true "secret of life. Below, we illustrate these concepts by concentrating on the thermodynamics of peptide (protein) and phosphodiester (nucleic acid) bonds. First, however, we should briefly look at some basic thermodynamic properties of covalent bonds. As an example, the covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is considerably stronger than the bond between hydrogen and hydrogen, or oxygen and oxygen. The formation of an O-H bond at the expense of O-O or H-H will thus release vitality. Energy considerations, subsequently, inform us that a sufficiently concentrated mixture of oxygen and hydrogen will be remodeled in to water. This idea seems nearly paradoxical at first look as a outcome of it implies that the stronger the bond, the less power it can give off. But the notion routinely makes sense when we notice that an atom that has shaped a very strong bond has already lost a appreciable quantity of free vitality on this course of. Therefore, the most effective food molecules (molecules that donate energy) are those molecules that comprise weak covalent bonds and are due to this fact thermodynamically unstable. This is as a end result of even a weak covalent bond is, in reality, very sturdy and is simply hardly ever broken by thermal motion inside a cell. For a covalent bond to be broken in the absence of a catalyst, energy must be supplied to push apart the bonded atoms. In the process of recombination, the energy released is the sum of the free vitality equipped to break the old bond plus the difference in free energy between the old and the new bond. The energy that have to be provided to break the old covalent bond in a molecular transformation known as the activation energy. Instead, a collision between the 2 reacting molecules is required, followed by the temporary formation of a molecular advanced known as the activated state. High activation energies are thus limitations preventing spontaneous rearrangements of cellular-covalent bonds. This also should happen if cell development is to happen at a price sufficiently fast in order not to be critically impeded by random harmful forces, such as ionization or ultraviolet radiation. The perform of enzymes is to velocity up the rate of the chemical reactions requisite to cellular existence by reducing the activation energies of molecular rearrangements to values that could be provided by the warmth of motion. This is clearly the case for degradative pathways, in which thermodynamically unstable meals molecules are converted to extra secure compounds, similar to carbon dioxide and water, with the evolution of warmth. All degradative pathways have two primary functions: (1) to produce the small organic fragments necessary as building blocks for bigger natural molecules and (2) to preserve a significant fraction of the free energy of the unique meals molecule in a kind that may do work. Not all of the free energy of a food molecule is transformed in to the free vitality of high-energy molecules. Instead, we find that all degradative pathways are characterised by a conversion of at least one-half of the free vitality of the meals molecule in to warmth and/or entropy. Nonetheless, the term high-energy bond is usually used, and for comfort, we will proceed this usage by designating high-energy bonds with the image. The vitality of hydrolysis of the average high-energy bond (%7 kcal/mol) may be very a lot smaller than the quantity of energy that might be released if a glucose molecule were to be completely degraded in a single step (688 kcal/ mol). This is undoubtedly the explanation why biological glucose degradation requires so many steps. In this manner, the quantity of vitality released per degradative step is of the same order of magnitude because the free energy of hydrolysis of a high-energy bond. It is now clear that high-energy bonds involving sulfur atoms play virtually as important a job in vitality metabolism as those involving phosphorus. The traditional criterion is whether its hydrolysis may be coupled with one other reaction to impact an important biosynthesis. This means that many biosynthetic pathways demand an exterior source of free power. The making of many biosynthetic bonds is coupled with the breakdown of a high-energy bond, in order that the web change of free vitality is all the time adverse.