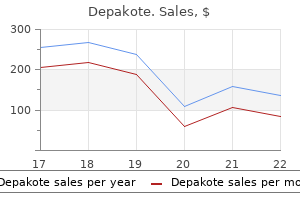
Depakote
Depakote dosages: 500 mg, 250 mg
Depakote packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

500 mg depakote order free shipping
Identify the three n Strip the peritoneum downward away from the anterior abdom4 n Commence the dissection laterally within the area of the anterior inferior epigastric vessels medications dispensed in original container buy 250 mg depakote free shipping, which are usually visible at this stage symptoms pink eye cheap 500 mg depakote fast delivery. The small balloon at the tip of the cannula can be inflated to retain the cannula throughout the pre-peritoneal space. The cell flange is handed distally along the cannula so that the abdominal wall is gripped between the distal balloon and the flange. The bladder might be seen beneath the pubic bone close to the midline and is gently stripped downwards and backwards. Look for the sac of a direct inguinal hernia, which might be seen attached to the white fold of transversalis fascia. Although transection of such a large sac with closure of the peritoneal defect may be potential, it might prove technically tough. Then insert a needle through the stomach wall and confirm this by seeing it in the extra-peritoneal house. Place the 5-mm trocar and cannula beneath laparoscopic imaginative and prescient at a point 2 cm medial to the anterior superior spine on the aspect opposite the hernia. The fringe of the peritoneum should be no much less than 3�4 cm distant from the internal ring. Do not tamper with the fatty tissue deep to these buildings as they defend you from damaging the iliac vessels three n Retract and free a direct hernia sac by stripping it away from the white fold of transversalis fascia utilizing blunt and occasional scissors dissection. Make positive the sac is totally free of its coverings and the pre-peritoneal house can be enlarged below it. As you withdraw the sac place the right-hand forceps beyond the left-hand forceps and further retract the sac with the right hand utilizing the left-hand instrument to strip tissue away from it. These buildings are applied to the deep floor of the peritoneum on the internal ring. Inferior epigastric vessels Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve Anterior femoral cutaneous nerve Pubic bone Gonadal vessels External iliac vessels. It is being held in place by two forceps as the additional peritoneal house is allowed to deflate. To orientate the mesh correctly mark the lengthy axis of the mesh by drawing a line on it. Assess 1 n If adhesions obscure your view of the inguinal area, divide 2 n Now establish the anatomy as it relates to the hernia. Starting at the midline, identify the bladder and the median them fastidiously utilizing scissors and diathermy. If you 14 Position the mesh in order that it covers the inguinal region from the midline, passing laterally for 15 cm. Ensure that it covers the area of the interior ring, the region medial to the inferior epigastric vessels and the femoral canal and that it reaches the midline. Ensure that the mesh is lying flat towards the anterior belly wall and on the psoas muscle. Omen- 2 n Prepare a pre-peritoneal pocket between the peritoneum and the abdominal muscles in which to place the artificial mesh. The pocket should prolong from the midline medially to approximately the extent of the anterior superior iliac backbone laterally. For bilateral hernias, pockets must be fashioned on either side and become continuous across the midline. Gas could now enter the pre-peritoneal area and assist to carry the peritoneum away from the underlying fascia and muscle tissue. Immediately lateral to that is the realm via which a direct inguinal hernia may cross. Lateral to this, note another ridge, the inferior epigastric vessels that form the lateral umbilical ligament. Lateral to this again is the inner ring via which an indirect inguinal hernia might move. Passing medially, particularly in thin patients, establish the vas deferens (round ligament of the uterus in females) beneath the peritoneum. Passing laterally from the internal ring is a less distinct ridge attributable to the gonadal vessels. In the separating the peritoneum from the interior ring the place the peritoneum might be at its most adherent and there shall be a danger of damage to the gonadal vessels and the vas deferens. Identify the shining white appearance of the superior ramus of the pubic bone and gently strip the tissues downwards away from the pubic ramus, extending the dissection 1�2 cm beyond the midline. Below the level of the inguinal ligament, branches of the genitofemoral nerve could also be seen lying on the psoas muscle and ought to be fastidiously preserved. However, whereas a direct hernia sac is generally simple to retract, a large oblique hernia sac could additionally be difficult to retract from the scrotum and may need to be divided at or distal to the internal ring. The sac lies anterior 17 n Orientate the mesh so that it covers the groin from the midline to the anterior superior iliac spine throughout the pocket in front of the peritoneal flap, using graspers in each hand. Retract it progressively from the inguinal canal using a grasper held within the left hand. Control scissors in the best hand for blunt and sharp dissection, to strip away the coverings of the sac. As the dissection proceeds, search for the gonadal vessels laterally and the vas deferens medially. Dissect the transected proximal sac away from the gonadal vessels and vas deferens. Take nice care pass it behind the midline peritoneum, which has been left undivided, and place it to lie flat and cover the relevant areas on either side. Place three to 5 staples spaced throughout the upper border of the mesh, attaching it to the belly muscle tissue. Divide any strands of tissue that may get in the way in which and stop the mesh from lying flat. Persistent genitofemoral neuralgia and even femoral nerve paralysis have been reported. Bilateral hernias could be repaired using two separate 15-cm � 10-cm patches or by one massive 28-cm � 10-cm mesh; this is stronger however harder to place. The latter is more difficult to orientate within the stomach however is aided by chopping off the corners alongside one of the lengthy sides 20 n Cover the mesh with the peritoneum forming the pocket. Pick up the higher border of the peritoneum with a grasper in the left hand and staple the flap of peritoneum to the abdominal wall, overlaying the mesh utterly. Alternatively, place a operating suture between the peritoneum above the mesh and the free peritoneal flap. Ensure complete coverage of the mesh to be able to avoid small-bowel adhesion and attainable small-bowel obstruction. A co-existing femoral hernia could additionally be repaired simultaneously an inguinal hernia utilizing the laparoscopic route. Control bleeding from damaged inferior epigastric and gonadal vessels utilizing haemostatic clips. Gonadal harm is unlikely unless earlier surgical procedure has been carried out, compromising alternative blood supply. If the peritoneum is thin and tending to tear, staple the margins of the defect within the peritoneum to the mesh, thereby decreasing the probability of small-bowel herniation.
Diseases
- Asbestosis
- Vitiligo psychomotor retardation cleft palate facial dysmorphism
- Syngnathia multiple anomalies
- Kathisophobia
- Leptospirosis
- Mucormycosis
- Charcot Marie Tooth disease type 4B
250 mg depakote proven
Aspirated meconium can block the massive and small airway causing areas of atelectasis and emphysema which may progress to develop air leak syndromes like pneumo thorax symptoms 0f food poisoning discount depakote 250 mg with mastercard. Presence of atelectasis and emphysema could cause air flow perfusion mismatch in these infants that may progress to respiratory failure medications given im 250 mg depakote effective. I Pneumonia Pneumonia is a standard cause of respiratory misery in each term and preterm babies and is caused by micro organism such E. Neonatal pneumonia could additionally be because of aspiration or often due to viral or fungal an infection. The neonate has options suggestive of sepsis in addition to respiratory distress. If the pneumonia is as a end result of of hospital acquired an infection, antibiotics like cephalosporins with amikacin may have to be used. Note hyperinflated lungs, distinguished bronchovascular markings and horizontal fissure (arrow) vertebrae in presence of esophageal atresia. Diaphragmatic hernia must be suspected in any neonates who has severe respiratory distress and has a scaphoid abdomen. Surgical Problems Transient tachypnea of the new child is a benign self limiting disease occurring normally in term neonates and is because of delayed clearance of lung fluid. Chest X-ray could present hyperexpanded lung fields, outstanding vascular marking and distinguished interlobar fissure. Needle aspiration or chest tube drainage is a life saving process on this situation. Apnea of prematurity occurs in preterm neonates between the second to fifth days of life and is due to the immaturity of the growing brain. Such jaundice warrants investigation for the trigger and therapeutic intervention such as phototherapy. Breastfeeding Jaundice Exclusively breastfed infants have a different sample of physiological jaundice as in comparability with artificially-fed babies. Jaundice in breastfed infants normally appears between 24-72 hr of age, peaks by 5-15 days of life and disappears by the third week of life. One-third of all breastfed infants are detected to have gentle clinical jaundice within the third week of life, which can persist in to the 2nd to third month of life in a few infants. Clinical Estimation Originally described by Kramer, dermal staining of bilirubin could also be used as a medical guide to the level of jaundice. The pores and skin of forehead, chest, abdomen, thighs, legs, palms and soles should be blanched with digital pressure and the underlying colour of skin and subcutaneous tissue should be noted. Obstructive apnea can occur due to block to the airway by secretion or improper neck positioning. High bilirubin levels may be toxic to the developing central nervous system and should trigger neurological impairment even in term newborns. Physiological Versus Pathological Jaundice Physiological jaundice represents physiological immaturity of the neonates to deal with increased bilirubin manufacturing. Yellow staining of palms and soles is a danger sign and requires pressing serum bilirubin estimation and additional administration. Total serum bilirubin may be assessed non invasively by a transcutaneous handheld gadget. If breastfeeding is inadequate with excessive weight loss Approach to a Jaundiced Neonate All the neonates should be visually inspected for jaundice every 12 hr throughout preliminary 3 to 5 days of life. Transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) can be used as an assist for preliminary screening of infants. Visual assessment (when carried out properly) and TcB have cheap sensitivity for initial assessment of jaundice. Phototherapy should be initiated if the toddler meets the criteria for serious jaundice. Total serum bilirubin should be decided subsequently in these infants to decide further plan of action. Management Investigations the aim of performing investigations is to verify the level of jaundice, determine the cause and follow response to treatment. Mother must be told to convey the child to the hospital if the baby appears deep yellow or palms and soles have yellow staining. Any newborn discharged previous to 72 hr of life must be evaluated again in the subsequent 48 hr for assessment of adequacy of breastfeeding and development of jaundice. Non-hemolytic: prematurity, extravasated blood, inadequate feeding, polycythernia, idiopathic, breast milk jaundice Risk factors for development of severe hyper biliru binernia embrace: i. Blood group incompatibility with positive direct antiglobulin check, different recognized hemolytic disease. Measure serum bilirubin and determine if child requires phototherapy or trade transfusion (refer to Table eight. Signs of acute bilirubln encephalopathy or kernicterus: hypertonia, irregular posturing corresponding to arching, retrocollis, opisthotonus or convulsion, fever, high pitched cry a. One should rule out cholestasis by noting the urine and stool shade and checking the extent of direct bilirubin. The phototherapy units out there in the market have a variety of light sources that embrace florescent lamps of various colors (cool white, blue, green, blue-green or turquoise) and shapes (straight or U-shaped generally referred as compact florescent lamps, i. The lamps should be changed if the lamps are flickering or ends are blackened, if irradiance falls under the specified level or as per the recommendation of producers. Make positive that light falls on the child perpendicularly if the infant is in incubator. Cholestasis (stool shade, urine color, direct and oblique bilirubin levels) Maximizing the efficacy of phototherapy. Urinary tract an infection Phototherapy Phototherapy remains the mainstay of treating hyperbilirubinemia in neonates. Photocopy is extremely effective and carries an excellent security observe record of over 50 yr. It acts by changing insoluble bilirubin (unconjugated) in to soluble isomers that might be excreted in urine and feces. Many evaluation articles have supplied detailed dialogue on phototherapy related points. The response is instantaneous upon publicity to mild but reversible as bilirubin reaches in to the bile duct. Keep the gap between child and light-weight 30 to 45 cm (or as per producer recommendation). Baby can be taken out for breastfeeding periods and the attention patch could be removed for better mother-infant interplay. Anti D (RhoGam) injection after first obstetrical event ensures decreased risk of sensitization in future pregnancies. Later, two longitudinal furrows develop to separate the respiratory primordium from the esophagus. Deviation or altered mobile growth on this septum leads to formation of tracheoesophageal fistulae. Clinical Features the presence of maternal polyhydramnois and single umbilical artery should alert the well being supplier to search for atresia of the upper digestive tract.
Purchase 500 mg depakote mastercard
The ideas of respiratory administration embrace airway clearance methods medicine emoji depakote 250 mg order on-line, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory brokers medicine keychain 250 mg depakote generic with visa. Mediators similar to free oxygen radicals and platelet activating components are released and injure vascular epitehlium. Microthrombi formation in vessels contributes to elevated pulmonary vascular resistance and right to left shunting. At all ages tuberculosis, rnitral stenosis, cystic fibrosis or overseas physique in the bronchus. Chronic cough, which is more widespread in sure seasons through the yr should arouse the suspicion of bronchial asthma. Chronic cough occurring only in winter months is normally indicative of viral etiology. Severe dietary disturbance in association with continual cough is discovered is circumstances of tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, pertussis, cystic fibrosis, extreme chronic bronchial asthma or immune deficiency syndromes. Investigations Chest X-ray movie, examination of the sputum, blood counts and tuberculin check may be essential for arriving at a definitive diagnosis. Treatment Patient must be managed in an intensive care unit with cardiorespiratory monitoring and artificial ventilation. Barking or brassy cough associated with modifications within the voice point out laryngotracheal illness. In case of postnasal drip, cough seems to be like an attempt to clear the throat and described as a hawking cough. Management Bronchial bronchial asthma ought to be excluded earlier than evaluating other causes of cough. These are indicated solely, if the cough is dry and exhausting or, if it disturbs sleep and prevents adequate diet. Bronchodilators are useful in the therapy of kids with cough because of occult bronchial asthma due to retained tracheobronchial secretions. Muco ciliary transport of secretions is helped by beta-adrenergic agonists and the xanthine group of medicine both in asthmatic as properly nonasthmatic kids with continual bronchitis. There is decreased movement of respiration with decreased air entry and vocal resonance. Occasionally, it might manifest as a pulsatile swelling over chest, empyema necessitans. An X-ray film of the chest reveals shift in mediastinum with obliteration of costophrenic angle and varying degree of opacification. Empyema must be differen tiated from other causes of pleural effusion including tuberculosis and neoplasia. The treatment include administration of antibiotics active in opposition to Staphylococcus. These diseases range from recurrent higher respiratory tract infections to critical bacterial infections to opportunistic infections and unique circumstances like lymphoid interstitial pneumonitis. The majority of heart ailments presenting in early childhood are congenital, occurring due to structural defects during development. Despite substantial decline in the incidence of rheumatic fever, rheumatic coronary heart illness continues to be prevalent in India. Systemic hypertension is more and more acknowledged in childhood and should predispose to cardiovascular morbidity in adulthood. The management of children with cardiovascular illnesses requires an integrated method with inputs from various specialties. Many congenital heart defects that had been thought-about universally fatal may be corrected and affected kids can count on to survive in to adulthood. These developments include an improved understanding of the pathophysiology of disease, advances in diagnostic functionality and successful surgical and medical management of varied coronary heart ailments. However, the entry to pediatric cardiology companies in developing nations is restricted. The growth of comprehensive pediatric heart packages throughout regions is essential to enhance the management of youngsters with cardiovascular illnesses. Besides hypertrophied ventricles, diastolic failure occurs in restrictive heart disease and constrictive pericarditis. Etiopathogenesis the common causes of diastolic failure are indicated in Table 15. Heart failure from congenital heart disease sometimes occurs inside the first 1-2 yr of life. Unlike left to proper shunts, congenital leakage of the mitral or the tricuspid valve can lead to coronary heart failure at an early age. Diastolic coronary heart failure is recognized by medical options of coronary heart failure with evidence of increased filling pressures with preserved systolic perform and in lots of cases, cardiac output. Any long-standing tachyarrhythmia can be associated with ventricular dysfunction which will mimic cardiomyopathy. Typical examples embody ectopic atrial tachycardia and perma nent junctional re-entrant tachycardia. Severe bradycardia, typically from full coronary heart block, can even end in coronary heart failure. Clinical Features the recognition of cardiac failure in older youngsters is predicated on the identical features as in adults. Rheumatic fever, rheumatic heart illness Congenital coronary heart disease difficult by anemia, infection or endocarditis Systemic hypertension Myocarditis, major myocardial illness Pulmonary hypertension (primary, secondary) artery pressures will increase its severity. The age of prevalence of coronary heart failure might point in path of the underlying trigger (Table 15. Heart failure at an unexpectedly early age for a patient thought to have a simple shunt lesion ought to prompt the seek for an related condition such as coarctation. Three-quarters of infants with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia are below four months old. Uncommonly, there may be an uncommon gain in weight as a end result of assortment of water, manifesting as facial puffiness or hardly ever as edema on the toes. Shortness of breath or fatigue from feeding leads to the baby accepting solely small quantities of milk at a time. Often a mother may state that the baby breathes too fast whereas feeding or that the baby is more snug and breathes better when held against the shoulder-which is the equivalent of orthopnea in older children. Not occasionally, the child is brought with persistent hoarse crying, wheezing, excessive perspiration and fewer commonly, because of facial puffiness (Table 15. Common to both left and right sided failure is the presence of cardiac enlargement, third sound gallop and poor peripheral pulses with or without cyanosis (Table 15. The 4 prongs are: (i) decreasing cardiac work, (ii) augmenting myocardial contractility, (iii) bettering cardiac perfor mance, (iv) correcting the underlying cause. If a newborn has coronary heart failure because of duct dependent systemic circulation (critical coarctation, aortic stenosis, interrupted aortic arch), administration of prostaglandin to open the closing duct improves survival. The work of the center is decreased by restricting patient activities, sedatives, remedy of fever, anemia, weight problems, and by vasodilators. Mechanical ventilation helps when coronary heart failure is severe by eliminating the work of respiration.
Trusted depakote 500 mg
Usually symptoms electrolyte imbalance buy depakote 500 mg fast delivery, the marrow accommodates very few hema topoietic cells and is changed with fats cells and lympho cytes symptoms 4 days after conception buy 500 mg depakote. Chromosomal fragility is noted even in patients who lack the attribute physical stigmata of Fanconi anemia. Supportive care ought to be instituted with packed pink cells for severe anemia, platelets transfusions for extreme thrombocytopenia and antibiotics for management of infections. The commonly used sources of hematopoietic stem cells are cytokine-mobilized peripheral blood, bone marrow and umbilical wire blood. Indications the indications for hematopoietic stem cell transplan tation are listed in Table 12. In malignant problems, the transplant serves to rescue the bone marrow from the myelotoxic effects of the excessive doses of chemotherapy or radiation used to cure the malignancy. In non-malignant diseases, the irregular marrow is destro yed and replaced by the healthy unaffected donor marrow that corrects genetic or acquired illnesses of blood cells. Patients with severe aplasia are at danger of high output cardiac failure as a result of anemia, bacterial and fungal infections due to neutropenia and severe bleeding as a outcome of thrombocytopenia. Successful hematopoietic trans plantation causes the blood group of the recipient to change to that of the donor. It classically impacts three tissues, specifically the pores and skin, gut and liver, and could additionally be accompanied by fever. The severity could be graded based on the extent of pores and skin involvement, degree of hyperbilirubinemia and severity of diarrhea. Clinically, it resembles autoimmune issues (like scleroderma) with pores and skin rash, sicca complicated, sclerosing bronchioloitis and hepatic dysfunction. The procedure is helpful only for malignancies that are sensitive to chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Virtually all autologous stem cell transplantations are performed using peripheral blood stem cell transplantations instead of the bone marrow since the engraftrnent is extra rapid. The process for peripheral blood stem cell trans plantation is much like bone marrow transplant except for variations within the technique of assortment of the stem cells and slight modifications in the engraftment potential. This course of avoids hospital admission, anesthesia and ache related to marrow aspiration. Autologous transplantation requires the stem cells to be collected similarly, but chemotherapy is required previous to the harvest to reduce tumor contamination and to yield a high proportion of stem cells. When transfused via peripheral veins, the donor marrow cells house in to the host marrow space and begin engrafting. After transplantation of the marrow, it takes about 2-3 weeks before engraftment occurs. Until engraftment happens, sufferers require a number of pink cell and platelet transfusions through the 2-4 week interval of pancytopenia. All cellular blood products ought to be irradiated previous to transfusion to inactivate the donor lymphocytes. This distinctive complication may happen in allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients in one two varieties, acute and continual. The primary limitation of cord blood is the limited variety of nucleated cells per unit, these being 1 log lower than in a bone marrow transplant. As in comparability with bone marrow transplantation wire blood transplantation is related to prolonged time to engraftment with the length to neutrophilic engraftment being about 30 and 50 days, respectively. This, along with higher incidence of non-engraftment, results in high transplant-related mortality. Clinical assessment, of kind of bleeding, history of antecedent occasions and screening exams might help identify the cause, so that specific management may be initiated. Pathogenesis the process of hemostasis involves platelets, vessel wall and plasma proteins in a fantastic stability between blood flow and local responses to vascular injury (clotting). The results of these processes is the technology of insoluble fibrin and activation of platelets to type a hemostatic plug. The coagulation cascade is commonly depicted as involving two pathways, intrinsic and extrinsic. The extrinsic pathway is the primary initiating pathway for coagulation and is measured by prothrombin time, whereas the intrinsic system works as a regulatory amplification loop, measured by activated partial thromboplastin time. Clinical Evaluation the age of onset of bleeding, sort of bleeding, precipitating factors (spontaneous or following dental extraction, surgical procedure or circumcision) help in defining the trigger (Table 12. Medications related to bleeding include anticonvulsants, penicillins, warfarin, aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines and heparin. Bleeding time is now not often used because of problems in its reproducibility and reliability. Bleeding time has been largely changed by platelet aggregation studies for inherited and purchased platelet dysfunctions. The presence of splenomegaly suggests the presence of infections, malignancy, collagen vascular issues or hypersplenism somewhat than a main bleeding defect. Rashes could also be seen following drug publicity, as a outcome of infections, collagen vascular disorders, Langerhans cell histiocytosis and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Laboratory Investigations A full hemogram is completed for platelet rely, mor phology of platelets and red cells and evidence of rnicro angiopathic hemolysis. Initial screening checks are prothrombin and activated partial thromboplastin time. Recent data describes a Thl dominant pro-inflammatory cytokine state in these people. Increased megakary ocyte quantity in the bone marrow is the hallmark of immune-mediated platelet destruction. However, a relative lower in megakaryocyte manufacturing due to specific anti-platelet autoantibodies can be described. Clinical Evaluation There is commonly an antecedent history of febrile illness, however the affected person is usually afebrile at presentation. There is a seasonal clustering of circumstances, the illness being more frequent throughout change of seasons. The child presents with sudden appearance of bruises and mucosal bleeding, epistaxis, oral oozing and prolonged bleeds with superficial trauma. It is necessary to appropriately diagnose this entity and differen tiate it from critical conditions like leukemia. Liver and renal perform checks and lactate dehydrogenase ranges are accomplished to rule out hepatitis, occult malignancy, hemolysis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Screening tests for disseminated intravascular coagulopathy are accomplished if sepsis is suspected. Bone marrow examination shows elevated megakaryocytes and excludes marrow infiltration, leukemia or bone marrow failure. Postnatal administration requires transfusion of washed maternal platelets (preferably irradiated) and close monitoring until the platelet counts normalize. The risk for neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia will increase in subsequent pregnancies.
Mary Jane (Marijuana). Depakote.
- Treating increased pressure in the eyes (glaucoma).
- What is Marijuana?
- Dosing considerations for Marijuana.
- Treating multiple sclerosis (MS).
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dandruff, hemorrhoids, obesity, asthma, urinary infections, leprosy, preventing rejection after kidney transplants, and other conditions.
- Stimulating appetite in people with AIDS.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96910

Generic 500 mg depakote with amex
Advances in vaccine expertise have led to the introduction of potent vaccines towards a wide spectrum of infections medications derived from plants order depakote 250 mg mastercard. Terminology Active immunity is the protective response mounted by the immune system following publicity to an infectious organism (as clinical or subclinical infection) or after vacci nation with stay or killed organism treatment hepatitis b depakote 500 mg buy generic online, a toxoid or subunit. Following first publicity, the primary immune response is slow to develop (over 3-14 days or longer) and should or may not be adequate to counteract the infection. Host response to re-exposure to the infectious agent (or its component), termed secondary response, is fairly fast, includes induction of high titers of IgG anti our bodies, is normally sufficient to stop disease and supplies protection for a quantity of years. Passive immunity refers to protection from disease provided by introduction of preformed animal or human antibodies in to the body. A v accine is composed of one or more antigens of a pathogenic agent which, when administered to a beforehand unexposed individual, will elicit an immune response however not trigger disease. The secondary immune response, elicited when the host encounters the pathogen itself, is fast and protects from illness. Seroconversion refers to the change from antibody adverse to antibody optimistic state, because of induction of antibodies in response to infection or vaccination. Seroprotection refers to the state of protection from illness, due to the presence of detectable serum levels of antibody. Immunogenicity is the ability of a vaccine to elicit an immune response, whether cellular, humoral or each. Adjuvants are substances unrelated to the organism that, when added to a vaccine, enhance its immunogenicity. The action outcomes from nonspecific stimulation of lymphocytes or by enabling slow release of the antigen. Vaccine effectiveness is dependent upon vaccine efficacy, program implementation and herd effect (see below). Vaccine failure is the prevalence of disease in an individual regardless of vaccination. Primary vaccine failure is the lack of the recommended vaccine dose(s) to induce an immune response, whereas secondary failure refers to the prevalence of illness despite an immune response. If a large proportion of prone people are protected from an infection with an organism by simul taneous vaccination, the transmission chain of the infectious agent may be damaged by lowering carriage of the causative microorganism by vaccinated individuals, thus reducing the risk of disease even among the many unimmu nized people. This phenomenon, termed the herd impact, is much less pronounced for vaccines that protect solely against disease. Herd impact is utilized as one of many strategies for eradication of poliovirus, and potentially, throughout measles epidemics. The timing of administration is dependent upon the age at which the disease is anticipated, the flexibility to mount immune response to administered antigen(s) and feasi bility. Vaccines could encompass reside attenuated, killed or inactivated organisms, modified toxins (toxoids), or subunits. Live Vaccines Live vaccines replicate within the host to produce an immune response mimicking natural an infection. Rarely, an attenuated viral vaccine may revert to its virulent form causing illness. Killed Vaccines Killed vaccines, ready by growing micro organism or viruses in media followed by heat or chemical. Primary immunization is in type of multiple divided doses so as to decrease the adverse results at each administration and to elicit excessive antibody titres with repeated exposure to the same antigen. Subunit Vaccines Other nonreplicating antigens embody capsular poly saccharide and viral or bacterial subunits. Capsular poly saccharides are carbohydrate antigens that elicit humoral response by stimulating B cells immediately, without modulation by helper T cells. Principles of Immunization While immunizing youngsters, certain pointers are useful to find a way to maximize the profit from vaccination. Compliance with the beneficial dose and route of vaccination limits adverse occasions and lack of efficacy. A minimal interval of 4 weeks is recommended between the administrations of two reside vaccines, if not administered concurrently. Killed antigens could additionally be administered concurrently or at any interval between the doses. A gap of 3-4 weeks is really helpful between two doses of cholera or yel low fever vaccine. A reside and an inacti vated viral vaccine could be administered simulta neously at two totally different websites. Live vaccines are contraindicated in children with inherited or acquired immunodeficiency and during therapy with immunosuppressive medication. Live viral vaccines could additionally be given after brief programs (less than 2 weeks) of low dose steroids. If immunoglobulins are administered within 14 days of the vaccine, vaccination ought to be repeated after 3-6 months. Hepatitis B, tetanus and rabies vaccine or toxoid may be administered concurrently with their corresponding immunoglobulin. Active immunization is really helpful following exposure to rabies, measles, varicella, tetanus and hepatitis B. Some vaccines are beneficial to be used solely in sure high-risk categories of sufferers. Since the vaccine is extre mely delicate to warmth, the cold chain should be maintained during transit. Due to lack of interference in mobile immune response by maternal antibody, administration at start supplies early safety, ensures compliance and is convenient to implement. Bacilli multiply to kind a small papule by 2-3 weeks that enlarges to 4-8 mm in size at 5-6 weeks. Most youngsters show a positive tuberculin test if examined 4-12 weeks after immunization. Adverse results including persistent ulce ration and ipsilateral axillary or cervical lymphadenopathy are extra doubtless with subcutaneous injection. Each dose (two drops) accommodates a hundred and five -106 median cell tradition infectious doses of each serotype 1, 2 and three. When administered orally, the vaccine viruses infect the intes tinal mucosa and multiply in the mucosa! For these causes, vaccine take and seroconversion charges are decrease in growing international locations as compared to developed nations. To decrease the possibilities of vaccine failure, no much less than 3 doses ought to be administered 4-8 weeks apart. The vaccine primarily induces humoral immune response, however pharyngeal and presumably, intestinal mucosal antibodies are also induced.
Depakote 500 mg buy otc
It is the cellular and variable-length sigmoid and transverse colon that trigger probably the most difficulty through looping of the instrument treatment effect 500 mg depakote order with visa. Characteristically medications like abilify cheap depakote 500 mg with mastercard, the colonoscope, when straight and without loop formation, should be in a roughly U-shaped configuration with 70�80 cm of instrument inserted to the caecal pole. Ensure that every one equipment, corresponding to biopsy forceps polypectomy snares and injection needles, are available within the room. Access 1 n Modern colonoscopes are refined precision instruments designed to enhance intubation of the colon in essentially the most environment friendly method. As nicely as a wide-angled lens to permit a higher visual field and excessive definition video chip camera, graduated torque traits help variability in the stiffness of the instrument. In addition, some colonoscopes have an ability to vary the stiffness of the insertion shaft. Change of path may be achieved by angulation of the distal end, up/down or left/right. Change of course can also be achieved by up/down deflection, combined with rotation or torque. Keeping the distal section of the instrument as straight as possible and restoring this to a neutral place as soon as potential after angulation round an acute bend helps to forestall loop formation. Avoid most up/down and left/right angulation, as this ends in a J-shape and rotation of the top of the instrument quite than change of course. Otherwise reduce the loop, using a logical approach of first pulling back with clockwise torque. If nonetheless not resolved then change patient place and repeat the above steps if essential. Luminal view ought to be maintained by 2 n During intubation, the instrument may be pushed forward or 206. Continue pulling again till one-to-one withdrawal happens and then reinsert whilst maintaining the torque and steering with the angulation controls, to avoid re-looping. Repeated lubrication is required to prevent friction at the anus, one of the commonest causes of failure to advance the endoscope. Control of the instrument is finest achieved by rotation of the up/down and left/right angulation control wheels, using your left thumb. During intubation, insufflate only the minimal quantity of air to enable enough visualization of the lumen. Intubation at this level can be achieved by upward deflection of the tip and clockwise rotation of the shaft. In patients with a relatively quick sigmoid colon, continuation of the clockwise rotation with development typically leads to passage so far as the descending sigmoid junction. Intubation of the rectosigmoid can typically be essentially the most uncomfortable part of the procedure for the affected person; if excess angulation is required to view the lumen then change the affected person position to supine or proper lateral to decrease the rectosigmoid angle and permit intubation with minimal tip angulation. In many patients, particularly these with diverticular illness or those who have undergone pelvic surgery, the configuration is variable and there could additionally be a selection of acute angles. In these circumstances, achieve advancement by a combination of, place change, torque and adjustments to the left/right wheel. Aim to take the shortest attainable route through the bowel, keeping the instrument tip in the centre of the lumen and preserving to the inside of every bend. Clues as to the position of the lumen may be obtained from the arcuate folds and the light reflex attributable to the instrument. As a common rule, steer in the course of the concavity of the folds and away from the intense light reflex. Position change will typically enable a greater luminal view and advancement with minimal angulation. If at any time the luminal view is lost, withdraw the instrument till the view is regained. Pushing towards the colon wall tends to create loops and can also lead to perforation. This is particularly essential dicated by a lack of one-to-one development of the instrument tip in contrast with the shaft, which can also trigger the patient some discomfort. Straighten the loop by making use of rotational torque to the shaft, within the direction that produces the least resistance, whereas on the same time withdrawing the instrument. Once one-toone withdrawal has been achieved, re-advance the instrument while sustaining the identical torque, preventing reformation of the loop. In the sigmoid colon, the torque often needs to be applied in a clockwise direction. The effect of that is to fold the sigmoid loop over and obtain a relatively straight sigmoid colon. Once the attribute triangular lumen of the transverse colon is acknowledged, straighten the tip and advance the instrument with a mix of intermittent suction and insertion. This has the impact of creating the bowel concertina over the colonoscope and shortening the effective length. The transverse colon usually has at least one acute angle at its centre level, however could have more, notably if postoperative adhesions are present. On reaching such an angle, angle the tip across the bend and, whereas sustaining a luminal view, apply torque and withdrawal as for the sigmoid loop, once more in the course of least resistance. As soon as one-to-one advancement is achieved, straighten the tip and advance the instrument, once more utilizing intermittent suction. The tip of the instrument should then move quickly to the hepatic flexure, which can be recognizable by a bluish hue of the best lobe of the liver visible by way of the colonic wall. However, this is an unreliable landmark as the left lobe of the liver may give the same appearance within the mid-transverse colon. Occasionally, through the process of straightening the transverse colon, the sigmoid loop could re-form. It is beneficial at this stage, having restraightened the sigmoid loop, both to make use of an assistant to hold the sigmoid or transverse loop in its straightened configuration or increase the stiffness of the insertion shaft if using a variable stiffness colonoscope. In the case of the sigmoid colon, belly compression is carried out utilizing the flat of the hand to exert stress downwards and towards the left iliac crest. The caecum often has a pool of fluid at its pole and the ileocaecal valve is visible as a shelf-like protrusion, with a lip-like centre. Advancement to the caecal pole can usually be achieved by a mix of suction and delicate advancement. The splenic flexure could also be recognized by a bluish discoloration produced by the spleen adjoining to the colon wall, or a gate-like look on the entrance to the transverse colon. In many patients, the splenic flexure is acutely angled, resulting in sigmoid looping as advancement is attempted. Changing the position of the patient to the right lateral permits the transverse A B 208.
Safe depakote 500 mg
Laparoscopic vascular surgery requires a excessive degree of laparoscopic talent and will solely be undertaken by skilled and competent fanatics medications recalled by the fda depakote 250 mg buy discount on line. Closure 1 n Close each muscle layer separately asthma medications 7 letters depakote 500 mg order with visa, with interrupted sutures for the transverses and inner oblique and a steady suture for the exterior oblique aponeurosis. Femoro-femoral bypass is nearly a subcutaneous process and if needed it could be carried out under local anaesthetic in very unfit patients. Iliofemoral crossover bypass has the important benefit of leaving the groin and femoral artery on the donor side undisturbed for possible future procedures. The angle between the graft and the donor artery can also be consistent with the course of blood flow and this will likely have haemodynamic advantages. It is a extra invasive operation than femoro-femoral bypass and requires a regional or general anaesthetic. Complications 1 n In addition to those described for aortobifemoral bypass, beware 2 n Application of clamps at or close to the aortic bifurcation is assoof acute arterial occlusion within the reverse limb. Occasionally, a radiological strategy with iliac angioplasty and stent insertion is feasible. Special instrumentation including aortic clamps has been designed for the purpose. The technical aspects of the operation are primarily based upon the ideas of different established laparoscopic procedures. Otherwise, the factors to be thought-about failure of these operations in addition to their effect on the perfusion of the donor limb. Reliance on subjective assessment of angiograms is unsafe and some objective check is therefore helpful. Intra-arterial cannulae are connected to stress transducers in order to report strain waves from radial and femoral arteries. If the prognosis is in dispute, a bolus of papaverine 20 mg is then injected in to the femoral artery via a three-way faucet connected to the pressure line. There are three choices possible following a optimistic strain test: n Abandon the operation completely n Treat the inflow stenosis by balloon angioplasty dilatation both earlier than or through the operation (see below) and then proceed with the femoro-femoral bypass n Convert to an axillofemoral bypass. Although occlusive disease is uncommon within the upper limb Action 1 n For 2 n For crossover iliofemoral bypass expose the frequent femoral artery in the recipient limb. On the donor aspect expose the external iliac artery by making a transverse incision 3�5 cm above the inguinal ligament and entering the retroperitoneum as previously described. Therefore, different issues being equal, use the right axillary artery because the donor vessel. If important ischaemia is confined to one leg and brachial artery pressures are equal, then use the axillary artery on the identical aspect for the donor vessel. In the case of a crossover iliofemoral bypass make an extraperitoneal tunnel passing deep to the rectus muscular tissues. Draw the graft in to the tunnel using either a tunnelling instrument or a big aortic clamp. When utilizing a preformed graft, trim it in such a way as to make certain that its size from the junction of the side-arm to the distal anastomosis is as quick as potential. The purpose for that is that the velocity of move within the graft is potentially halved beyond this point, with a greater threat of thrombosis on this section. When constructing the bypass from separate axillofemoral and femoro-femoral elements, use a 10-mm diameter graft for the former and an 8-mm graft for the crossover. Construct the crossover bypass first (see above, Femoro-femoral bypass) and anastomose the distal finish of the axillofemoral element to it in end-to-side style. When infection of a pre-existing aortobifemoral graft is the indication for operation consider impregnating the graft with antibiotic. This is ready by soaking the graft in a solution of rifampicin before implantation. A Dacron graft impregnated with silver, which is meant to resist infection, can additionally be available commercially. Prepare 1 n General anaesthesia is required, with the affected person supine on the two n It is critical to put together the pores and skin and arrange the drapes in such a means as to make out there the entire of the trunk and each legs to mid-thigh stage. The process may be performed beneath native anaesthetic with sedation being used for graft tunnelling. Closure Close both wounds rigorously in layers, ensuring haemostasis and thus avoiding the necessity for drains. Complications 1 n In addition to the risks of haemorrhage, occlusion and infection (see Aortobifemoral bypass) the principle concern is the potential of ischaemia within the donor limb. Less severe ischaemia warrants angiography with a view to further elective surgical procedure. Action 1 n Expose the axillary artery and both widespread femoral arteries 2 n Select 10-mm and 8-mm Dacron grafts of applicable size or a preformed axillofemoral graft. An necessary reason for occlusion is angulation as a end result of pressure on the axillary artery and this should be corrected during secondary intervention. The addition of an intraluminal stent is indicated when: n the stenosis is resistant to angioplasty or recurs immediately due to elastic recoil n Treatment is being undertaken for a recurrent lesion. Increasingly, angioplasty is being utilized in tandem with surgery to safe an enough inflow in anticipation of an infrainguinal arterial reconstruction, during which case it might be undertaken percutaneously or intra-operatively through the uncovered widespread femoral artery. Pass it deep to the pectoralis main muscle after which subcutaneously in the anterior axillary line, lastly curving forwards above the anterior superior iliac backbone to the ipsilateral groin incision. Attach the top of the main stem of the graft to the tunneller and then draw it via to the higher incision. When utilizing a preformed graft continue to pull it through till the junction with the side-arm lies at the upper finish to the groin incision. Prepare 1 n When undertaken percutaneously, put together the pores and skin and drape the two n When undertaken intra-operatively, put together the patient as for a femorodistal bypass (see below). Trim the ends of the graft obliquely to match the length of the arteriotomies and complete the anastomoses in end-to-side fashion with 5/0 polypropylene suture. Open the circulation in to one leg at a time so as to scale back the risk of reperfusion damage. Insert a 5/0 polypropylene purse-string suture in to the entrance of the artery to help post-procedure haemostasis. Having crossed the lesion with a straight 4F angiography catheter over the guide-wire, connect it to a strain transducer to record intraluminal stress. Withdraw the catheter slowly by way of the stenosis and report the strain gradient throughout it. For extra accurate assessment repeat the method following injection of a vasodilator. There can be a risk that the patency of the contralateral common iliac artery could additionally be compromised. Insert balloon catheters in to both widespread iliac arteries and inflate them concurrently. Complications Rupture of the iliac artery wants both the immediate deployment of a lined stent or surgical repair.

Purchase 500 mg depakote
Balloon (inflated) 5 In order to trend a pre-peritoneal house symptoms neck pain depakote 250 mg purchase line, move a 10-mm trocar and cannula with a balloon at its tip in to the rectus sheath and guide it downwards until it reaches the pubic symphysis and then angle the tip to a place just behind the symphysis treatment 002 depakote 250 mg purchase visa. Prior to inflation, the balloon is placed via the subumbilical incision and used to provoke the dissection of the pre-peritoneal house. Gently inflate the balloon across the end of the cannula till the pubic bone is visible, thereby creating an area between the peritoneum posteriorly and the rectus muscle anteriorly. Inflate the balloon underneath direct vision and resist the urge to pump the balloon up quickly as this can cut back the likelihood of bleeding. Assess 1 n Place a blunt-ended 5-mm dissector within the second (subumbilical) cannula and enlarge the pre-peritoneal space by blunt dissection. Replace the 10-mm cannula with one other that has a small retaining balloon at its tip and inflate this in order that the balloon sits just inside the rectus sheath. If gas escapes in to the peritoneal cavity via a small hole in the peritoneum, place a Veress needle within the left higher quadrant of the peritoneal cavity. Avoid taking too deep a chew or the needle level will break as it strikes the pubic crest. One, two or three stitches could additionally be used but, for ease of entry, insert all of the stitches earlier than tying any. This technique is easier to carry out, less prone to lead to compression of the femoral vein and less susceptible to recurrence. Access 1 n Make an incision 4�5 cm lengthy in the crease of the groin, below 2 n Cut the superficial tissues over the hernia within the line of the pores and skin incision. Look out for the small veins working in to the lengthy saphenous vein; ligate and divide them as needed. Often, what appears to be a large swelling is generally extra-peritoneal fats, in which lies a small sac. Recognize the inside of the sac by seeing free fluid, a glistening floor and contents which may be decreased in to the principle peritoneal cavity. Repair 1 n the inguinal and pectineal ligaments meet medially by way of the arched lacunar ligament. The object of the repair is to unite the ligaments for about 1 cm laterally, without producing constriction of the femoral vein. If the sac incorporates free fluid it seems bluish and could also be confused with the appearance of congested bowel. If you inadvertently tear the neck of the sac, gently free peritoneum from the peritoneal cavity in order that it can be drawn all the means down to form a new neck. If the femoral vein is torn, control the bleeding with stress from gauze packs for 5 minutes. Meanwhile, order blood, arterial sutures, tapes, bulldog clamps and heparin answer, and summon assistance. Insert nice 5/0 sutures set 1 mm aside, 1 mm from the torn edges, to evert them and close the opening. Femoral vein Pectineal ligament Access 1 n Expose the inguinal canal and dislocate the wire, as for operation 2 n Incise the transversalis fascia. Open and 3 n For a strangulated hernia (which is the explanation for using this ap4 n Repair the canal from above. In front is the inguinal ligament, medially the lacunar ligament, posteriorly the pectineal ligament and laterally the femoral vein. Appraise 1 n Most hernias in adults are para-umbilical, protruding adjoining to 2 n Some adults, particularly of African origin, have true umbilical her3 n Repair umbilical hernia by early operation for worry of strangulanias that have been present all through life. The contents are most frequently omentum, which is commonly adherent to the interior of the sac. Closure Close the inguinal canal, subcutaneous tissue and skin as for an inguinal hernia. In particular operate on strangulated, painful (reducible or not) hernias, particularly these with small, exhausting margins. However: n Small para-umbilical hernias (less than 1 cm) could be left untreated if asymptomatic. With a laparoscopic approach the mesh is secured intra-peritoneally against the defect with staples or sutures. For recurrent or periumbilical incisional hernias a laparoscopic strategy could also be thought-about. Access 1 n Make an incision from three cm above the pubic tubercle operating obliquely upwards and laterally for 7�8 cm, crossing the lateral border of the rectus muscle, which lies more vertically. If the hernia is giant, make a spindle-shaped incision to include the umbilicus, excising the stretched skin. Rectus muscle Rectus sheath Action 1 n Cut through the thinned-out fringe of aponeurosis to expose the 2 n Clear the sac of fatty tissue and minimize it right round, no much less than 2 cm distal to the neck if attainable. The contents of the sac are much less prone to be adherent right here than within the fundus, however free them if essential. Secure the mesh in to good tissue with 2/0 polypropylene sutures allowing a 2-cm margin. Onlay mesh repair Repair 1 n For the underlay repair of a small, well-defined direct defect, take mining of the skin and placement of a foreign physique is susceptible to seroma formation. At every quadrant insert a 2/0 polypropylene suture through the intact tissue about 8 mm from the sting of the defect, pick up a small chunk of the mesh and pass the needle back out via the intact tissue of the posterior wall, near the purpose of entry. Hold the suture with an artery forceps and repeat the manoeuvre at each quadrant of the defect. Then parachute the mesh via the defect in to the extra-peritoneal house and tie the 4 sutures. Additionally, suture the edge of the defect to the surface of the mesh with steady polypropylene. Closure 1 n If the pores and skin over the fundus was preserved, decide up the undersurface of the navel with a synthetic absorbable stitch and stitch it to the rectus sheath to produce a dimple. Each stitch penetrates the upper leaf of the rectus sheath 3 cm from the sting, passes beneath it to catch the decrease leaf 1 cm from the sting and passes again three cm from the sting. Polytetrafluoroethylene, as a composite with polypropylene with the polytetrafluoroethylene facet in contact with the viscera, considerably lowers the incidence of adhesions. Preparation 1 n Place the anaesthetized affected person supine on the operating desk 2 n Clean the stomach with povidone-iodine 10% alcoholic soluwith their arms by their aspect. Access 1 n Obtain access in an area away from any previous incision and away from the hernia, both of which are often in the midline. Previous incisions might have adhesions or bowel adherent to them, presenting an inherent risk of injury, so acquire entry to the stomach cavity as far back laterally as is safe on the insufflated stomach. Use either an open (Hasson) technique or a closed method using a Veress needle. The left subcostal area is often suitable for initial insufflation with a Veress needle. Continue to divide any adhesions to allow visualization of the anterior abdominal wall for an space giant enough to allow placement of a flat mesh of enough size.

Cheap 500 mg depakote amex
Appraise Before you embark on adrenalectomy medicine keflex purchase depakote 500 mg on-line, consider: 1 n the useful status of the adrenal nodule treatment jiggers depakote 250 mg generic overnight delivery, as this determines pa- n tient preparation earlier than surgery and perioperative management. They obtain arterial blood provide from a number of small branches of the inferior phrenic artery, aorta and renal artery. Each adrenal gland consists of medulla, secreting catecholamines (adrenaline (epinephrine), noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and dopamine), and cortex, secreting cortisol, aldosterone and adrenal sex hormones. Lymphatic capillaries draining the cortex observe arteries while the medulla lymphatics observe veins. It is difficult to predict their biological behaviour but 10% of them are malignant and 10% come up from chromaffin cells exterior the adrenals (paragangliomas). Establish the biochemical prognosis by measuring catecholamine and metanephrine levels in urine and plasma. Carefully put together all sufferers with phaeochromocytomas with a blockade and typically b blockade to minimize the risk of hypertensive disaster. Most of those tumours are massive at diagnosis and an open method must be used to resect them. Surgery usually needs to be extensive with en bloc elimination of adrenal and surrounding organs combined with lymphadenopathy. Hyperfunctioning and huge incidentalomas suspicious of being malignant must be resected. Right inferior pole adrenal artery Prepare 1 n With the proper analysis established and the perioperative plan discussed with an endocrinologist and implemented, you can now plan your surgical procedure. Depending on pathology you must decide: n Whether to carry out unilateral or bilateral adrenalectomy n Which access is finest (anterior, lateral, posterior) n Whether to carry out an open or laparoscopic adrenalectomy. You should work with an experienced anaesthetist who is prepared to control surges of blood strain during dissection and hypotension after the elimination of the tumour. Patients current with central weight problems, hypertension, diabetes and muscle weakness. Before surgical procedure hypercorticolism may be controlled with ketaconazole or metyrapone. After bilateral adrenalectomy sufferers need lifelong therapy with hydrocortisone and mineralocorticoids. The contralateral gland is usually suppressed after unilateral adrenalectomy and these patients also want treatment with hydrocortisone for so much of months. Biochemical analysis is confirmed by an elevated plasma aldosterone focus and suppressed plasma renin exercise. Adrenal venous sampling is sometimes necessary to differentiate unilateral from bilateral illness. The purpose of the therapy is to normalize aldosterone levels and stop mortality and morbidity caused by hypertension, low potassium, cardiovascular and renal harm. Unilateral adenomas should be handled with adrenalectomy, which corrects hypokalaemia in 98% and improves hypertension in 90% of patients. Patients with bilateral hyperplasia must be treated with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. Its primary benefit is good entry and publicity of the adrenal gland, which permits removal of large and malignant tumours. Potential disadvantages are important trauma from the incision, together with rib excision within the open posterolateral strategy, and the necessity to reposition the affected person if you plan bilateral adrenalectomy. Place the affected person in the lateral decubitus position with the affected side uppermost. Prepare the pores and skin of the chest and abdomen to allow for either extension of the incision or conversion to an open process. Insert two or three additional ports in the posterior, center and anterior axillary lines. Be aware of the spleen, colon, pancreas and splenic vein to find a way to keep away from damaging them. Make sure that complete gland is mobilized � the lower limb incessantly descends as far as the renal hilum. Be careful not to damage the renal vessels, which can contribute an accessory renal artery to the superior pole. Mobilize the remaining gland from the kidney, liver and posterior muscular tissues by dividing small arteries with a harmonic scalpel. Incise the deep fascia, allowSweep the pleura superiorly and posteriorly and similarly sweep the peritoneum anteriorly, utilizing gauze swabs. Divide latissimus dorsi and serratus posterior muscular tissues with chopping diathermy and incise the periosteum of the eleventh rib using a diathermy level. Strip the periosteum from the rib all through its length, liberating the deep attachments to the rib with a gauze swab. Have your assistant retract the kidney inferiorly when you proceed fastidiously to bluntly dissect the fat above and medial to the kidney. Handle the gland gently to avoid disruption and keep away from damaging surrounding organs. As a rule, order a chest X-ray within the restoration ward to exclude a significant pneumothorax. Endoscopic posterior (retroperitoneal) approach 1 n the technique for left and proper adrenalectomy is similar. Take care to shut the pleura if it was three n Introduce two additional ports (5 mm) close to the costal margins on either facet of the port used for the zero or 30 digital camera. Identify the kidney, retract it downwards and dissect perirenal fat till you see the sting of the adrenal. Division of the adrenal vein between clips or utilizing a vascular stapler tremendously will increase mobility of the gland. Its primary disadvantage is limited working house, which solely permits resection of adrenals smaller than 6 cm. Excise the rib, rigorously avoiding damage to the neurovascular bundle at the inferior margin of the rib. This strategy supplies access to both adrenals, allows extension of the incision in to the chest and protected control of major blood vessels if essential, resection of involved organs and extended lymphadenectomy. The commonest causes for conversion are extreme bleeding, issue in mobilizing the mass because of its massive dimension, injury to surrounding organs or, especially early on the training course, the size of operation. Complications after adrenalectomy (10�15%) could additionally be the results of both suboptimal perioperative management of metabolic and cardiovascular abnormalities caused by functioning adrenal plenty or associated to the surgical procedure itself. This provides good access to the adrenal and renal hilum and allows protected dissection of large tumours. Open anterior method 1 n Electrolyte 2 n Failure to stop medications no longer required after surgical procedure. For giant and infiltrating tumours encircle the inferior vena cava with tapes placed below and above the liver to provide secure management in case of main haemorrhage or if its resection and graft replacement are indicated. Carefully dissect and retract and sensibly make use of the harmonic scalpel, diathermy, clips or vascular stapler to prevent this complication. Repair injuries detected during operation instantly � but the presentation of thermal damage to the bowel may be delayed by 24�48 hours. Remember to examine publish operatively potassium and cortisol levels as some sufferers can suppress cortisol production in contralateral gland.