Brahmi
Brahmi dosages: 60 caps
Brahmi packs: 1 packs, 2 packs, 3 packs, 4 packs, 5 packs, 6 packs, 7 packs, 8 packs, 9 packs, 10 packs

Brahmi 60 caps generic visa
Water consumption consists of ingested liquids plus a median of 750 mL ingested in solid food and 350 mL generated metabolically medicine 2015 discount brahmi 60 caps on line. Renal water dealing with has three necessary parts: (1) delivery of tubular fluid to the diluting segments of the nephron medications memory loss brahmi 60 caps buy generic on-line, (2) separation of solute and water in the diluting section, and (3) variable reabsorption of water in the accumulating ducts. This concentrated fluid is then diluted by energetic reabsorption of electrolytes within the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and distal tubule, both of which are relatively impermeable to water. As fluid exits the distal tubule and enters the amassing duct, osmolality is ~50 mOsm/ kg. Vasopressin binds to V2 receptors alongside the basolateral membrane of the accumulating duct cells and stimulates synthesis and insertion of aquaporin-2 water channels into the luminal membrane of collecting duct cells to facilitate water permeability. Daily necessities for Na+ and K+ are approximately 75 mEq/ day and forty mEq/day, respectively, though wider ranges of Na+ intake than K+ intake are physiologically tolerated because conservation and excretion of Na+ are extra environment friendly than of K+. Therefore wholesome 70-kg adults require 2500 mL/day of water containing a Na+ of 30 mM and a K+ of 15 to 20 mM. The major nonfluid parts are fibrils and the interstitial ground substance that could be subdivided into a colloid-rich and a water-rich phase. The amorphous ground substance or gel-like matrix is produced by the same cell sorts as the fibrillar parts. Plasma proteins passing the capillary wall are primarily restricted to a random community of interstitial channels corresponding to colloid-poor, water-rich areas. The physiologic distribution is maintained by biologic barriers and adenosine triphosphate�requiring pumps. The vascular wall is impermeable to larger molecules or proteins, with regular fluid distribution subject to an intact internal lining of the endothelial wall (glycocalyx). However, deterioration of the glycocalyx, as seen in systemic inflammatory situations, is of higher importance than interstitial protein concentration for fluid escape via the endothelial barrier. These are primarily syndecans and membrane-bound glypicans that include heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate chains. Together with some plasma proteins which are membrane sure, hyaluronan, and dissolved glycosaminoglycans, the inside endothelial floor layer is tens of nanometers thick. Water intake is required to offset gastrointestinal, urinary and insensible losses. In this pathway, decreased stretch in the baroreceptors of the aortic arch and carotid body and stretch receptors in the nice veins, pulmonary vasculature, and atria lead to elevated sympathetic tone. Increased sympathetic tone, in combination with decreased renal perfusion, leads to renin release and formation of angiotensin I from angiotensinogen. Abbreviations refer to the Starling formulation, which is modified by the existence of the glycocalyx. There is also normal transcapillary escape of albumin of about 5% of the intravascular albumin per hour, which is increased in a variety of ailments. The concept of the third space has been a subject of debate and controversy for many years. Fluid throughout the hypothetical third space is assumed to be a "nonfunctional" body fluid separated from the interstitial house. The tracer is assumed to equilibrate throughout the desired space, and the dye or isotope allows identification of the distribution quantity. Furthermore, tracers are topic to variations in perfusion and equilibration time. The Shires group had considerable influence on researchers and clinicians within the Sixties, but few different researchers have managed to replicate their findings. Although these fluids present different properties, it has not been possible to show any differences in mortality in giant randomized studies. Fluid was given over 10 minutes, reflecting the time course of preload augmentation. Hemoglobin is used as an endogenous tracer to calculate plasma dilution and the information fitted to nonlinear equations. The effect is transitory and the fluid is almost eradicated from the central area within 3 hours. Surgical manipulation per se can enhance interstitial water quantity, and crystalloid infusion can affect its extent. Urinary output and evaporation ought to affect the extracellular space (vascular system and interstitium) and may cause no internet change in colloid osmotic pressure in the vascular system. On the contrary, intravascular loss (bleeding) accommodates blood elements and thereby causes a change in colloid osmotic stress with crystalloid substitute. The standard perception of the distribution of crystalloids is that as much as 80% are distributed to the interstitial space. Advanced kinetic analysis (see later "Body Fluid Dynamics" section) demonstrates a central accumulation of fluid that finally distributes to the periphery or is eliminated as urine. This, nevertheless, has been challenged by those that advocate direct evaluation of plasma and blood quantity. Only trials using the sulphate tracer and brief equilibration times have reported a "third house contraction. The idea of a loss to third area needing substitute was introduced concurrently with the conflict in Vietnam. On the other hand, "the wet lung syndrome" (later identified as acute respiratory distress syndrome) was reported in otherwise healthy troopers resuscitated with giant amounts of fluids after traumatic harm. Less than 50% of important care patients given fluid boluses are volume responsive. Eventually a deflection point is reached (between C and D), after which the heart will now not carry out elevated work with increasing preload (Nonresponder). Transesophageal Echocardiography Widely utilized in cardiothoracic surgical procedure, transesophageal echocardiography has not proved a dependable predictor of fluid responsiveness in critically unwell sufferers. All these signs are nonspecific and unreliable indicators of enough resuscitation. Intrathoracic Blood Volume Index and Global End-Diastolic Volume Index Transpulmonary thermodilution is a technique that uses a cold bolus as a single indicator for determination of the evaluation of the most important quantity of blood contained within the four coronary heart chambers, referred to as the worldwide end-diastolic quantity. It requires using a specific thermodilution arterial catheter (pulse contour cardiac output monitoring) that measures temperature adjustments after the injection of the bolus by way of a central vein catheter (normally the central vein catheter is positioned in the neck, the arterial line in the femoral artery). In most medical circumstances, a basic assumption is that the patient is on the ascending part of the Starling curve and has a submaximal cardiac output. When the topic reaches the flat a part of the curve, more fluid administration has little effect on cardiac output/stroke volume and can solely enhance tissue edema. Although this concept applies to wholesome volume-depleted sufferers, lower than half of critically ill patients may respond to a fluid problem. Patients must be anesthetized or at least sedated to tolerate the probe; as soon as in the esophagus, the catheter is rotated so that the transducer faces the aorta. The circulate time corrected for heartbeats is taken into account an indicator for volume and afterload status. It seems to be a reliable predictor of fluid responsiveness, and has advantages for specific affected person groups in reducing morbidity and hospital stay. This procedure quickly returns one hundred fifty to 200 mL of blood from peripheral veins within the decrease extremities to the central circulation.
Effective 60 caps brahmi
Prostatism: A syndrome associated with outlet obstruction at the bladder neck symptoms thyroid purchase 60 caps brahmi visa, and mostly attributable to benign prostatic hypertrophy medicine 8 - love shadow best 60 caps brahmi. Protectant: An agent that types an occlusive barrier between the skin and surrounding moisture. Proteinuria: the presence of measurable amounts of protein in the urine, which is commonly indicative of glomerular or tubular harm within the kidney. Proteoglycan: Any certainly one of a category of glycoproteins of high molecular weight which are found in the extracellular matrix of connective tissue. They are made up largely of carbohydrate consisting of various polysaccharide side chains linked to a protein and resemble polysaccharides rather than proteins with regard to their properties. Photochemotherapy: using psoralens in addition to ultraviolet rays for patients with a big quantity of body surface area affected (> 10%). Photodynamic remedy: Treatment with medicine that turn out to be energetic when exposed to mild. Phototherapy: using ultraviolet rays for sufferers with a major quantity of body floor space affected (> 10%). Plaque psoriasis: the commonest type of psoriasis and manifests as well-defined, sharply demarcated, erythematous plaques sometimes coated with silvery scales. These plaques are irregular, round to oval in shape, and are virtually always found on the scalp, trunk, buttocks, and limbs. Pleocytosis: Increased cell depend, notably a rise in white blood cells count in a bodily fluid, such as cerebral spinal fluid. Pneumatic otoscopy: A diagnostic technique involving visualization of the tympanic membrane for transparency, place, and color, and its response to optimistic and adverse air stress to assess mobility. Pneumothorax: A condition that occurs when air leaks into the area between chest wall and lung. The air pocket exerts pressure in opposition to the lung causing it, or a portion of it, to "collapse. Polycystic ovary syndrome: Condition during which ladies have many small cysts on their ovaries that can lead to hormone imbalances and irregular durations. Posterior circulation: Blood provide to the posterior part of the mind through the vertebral, basilar, and posterior cerebral arteries (ie, brainstem, cerebellum, occipital lobe). Prader�Willi syndrome: A genetic dysfunction characterised by quick stature, psychological retardation, low muscle tone, abnormally small palms and ft, hypogonadism, and extreme eating leading to excessive weight problems. Prediabetes: An asymptomatic but abnormal state that precedes the development of clinically evident diabetes. Preemptive: Therapy administered prior to proof of lively illness (fever, radiological findings) but based mostly on a constructive biomarker or microbiological take a look at. Protooncogenes: Normal genes which may be current in all normal cells and regulate cell perform and replication, and through some genetic alteration brought on by carcinogens, become oncogenes. Pruritus: Localized or generalized itching as a outcome of irritation of sensory nerve endings. Pseudopolyp: An area of hypertrophied gastrointestinal mucosa that resembles a polyp and incorporates non-malignant cells. This situation is characterised by stiffness, pain, swelling, and tenderness across the joints and ligaments. Pulmonary artery catheter: An invasive gadget used to measure hemodynamic parameters immediately, together with cardiac output and pulmonary artery occlusion stress; calculated parameters embody stroke volume and systemic vascular resistance. Pulmonary artery occlusion pressure: A hemodynamic measurement obtained via catheter positioned into the pulmonary artery used to evaluate affected person quantity status throughout the left ventricle. Pulmonary embolus: An obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by material that originated elsewhere within the physique. Pulmonary hypertension: An elevation within the pulmonary arterial strain that can result in right ventricular failure and heart failure signs. A pulse oximeter is a small gadget positioned on a finger or earlobe that reads reflected gentle from capillary blood and estimates oxygen saturation. Pulsus paradoxus: A massive fall in systolic blood stress and pulse volume throughout inspiration or an irregular variation in pulse quantity throughout respiration during which the heartbeat becomes weaker with inspiration and stronger with expiration. Purified protein derivative: An extract of Mycobacterium tuberculosis used for intradermal injection to determine if a affected person has been beforehand exposed based mostly on immune response. Purkinje fibers: Specialized myocardial fibers that conduct impulses from the atrioventricular node to the ventricles. Pustular psoriasis: Collection of neutrophils is great enough to be seen clinically. Quality indicators: A listing of indicators utilized by long-term care facility directors and authorities overseers to establish potential problems in patient care. Radon: A chemically inert, radioactive gaseous component produced by the decay of radium. Rapid biking: Four or more mood episodes (major depressive, manic, or hypomanic) inside 1 12 months. Receptor enhancing: A process that occurs in the course of the maturation of B cells, that are part of the adaptive immune system. This process types a part of central tolerance to try to change the specificity of the antigen receptor of self-reactive immature B-cells, to rescue them from programmed cell demise, referred to as apoptosis. Rectal prolapse: Externally visible sinking of the rectum via the anal sphincter. Regurgitation: the easy and nonprojectile passage of refluxed gastric contents into the pharynx or mouth. Relapse: the return of symptoms, satisfying the full syndrome standards, after a affected person has responded, but previous to restoration. In the case of cancer, in partial remission, some however not all indicators and signs of cancer have disappeared. In full remission, all signs and signs of cancer have disappeared, though most cancers nonetheless may be within the physique. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: the hormonal system managed primarily by the kidneys and adrenal glands that regulates blood strain, blood volume, and electrolyte steadiness. Resistance-associated substitution: Resistance to a drug leading to decrease antiviral activity attributable to an amino acid change within the viral protein. Respiratory disturbance index: A summary measure that quantifies the number of apneas, hypopneas, and respiratory effort-related arousals per hour of sleep. Response: A predefined reduction of symptoms from baseline that typically leads to significant useful improvement. Response inhibition: Ability to keep on task or the flexibility to assume earlier than performing. Retinopathy: Occurs when the microvasculature nerve layer that provides blood and vitamins to the retina is damaged, and may trigger blindness. Retrograde pyelography: Injection of a radiocontrast agent into the ureters to visualize the ureter and kidney with fluoroscopy or radiography.
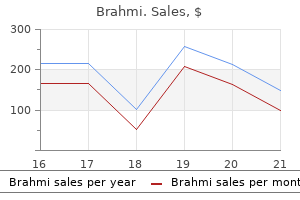
Brahmi 60 caps discount mastercard
Instead symptoms synonym 60 caps brahmi discount fast delivery, Melzack and Wall proposed that nociceptive signals had been modulated on the degree of the spinal wire medicine 2 times a day brahmi 60 caps. Melzack systematically analyzed the language used by sufferers to describe their ache, established the multidimensional character of ache, and constructed the basis for the definition of ache along the three experiential axes of sensation, have an result on, and cognition. An necessary consequence of this work was the perception that the multifaceted nature of ache requires a multidimensional strategy for remedy together with pharmacologic, behavioral, and cognitive strategies. This article provided early proof for the existence of a strong endogenous analgesic system. Electrical stimulation of midbrain buildings in nonanesthetized rats allowed for surgical interventions without frightening nociceptive behaviors. Today the critical function of the periaqueductal gray, the area stimulated by Reynolds, for controlling nociceptive signaling is nicely established. This article offered direct evidence for the expression of opioid receptors within the central nervous system and demonstrated their functional relevance in mitigating analgesia upon stimulation. This work clearly documented that opioids exert their analgesic actions through central mechanisms. Woolf demonstrated that hyperalgesia associated with tissue harm (increased sensitivity to pain) was partly as a outcome of the amplified processing of nociceptive indicators on the degree of the spinal twine. This early work documented that structures within the central nervous system can undergo plastic modifications and turn out to be sensitized (central sensitization) in response to tissue damage. Consequences of insufficient postoperative pain reduction and chronic persistent postoperative ache. The short-lasting analgesia and long-term antihyperalgesic impact of intrathecal clonidine in sufferers undergoing colonic surgical procedure. Perioperative oral pregabalin reduces chronic ache after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Distinct subsets of unmyelinated major sensory fibers mediate behavioral responses to noxious. Pungent agents from Szechuan peppers excite sensory neurons by inhibiting two-pore potassium channels. Role of presynaptic glutamate receptors in pain transmission on the spinal wire degree. Functional differences between neurochemically outlined populations of inhibitory interneurons in the rat spinal dorsal horn. Inflammatory ache hypersensitivity mediated by phenotypic swap in myelinated primary sensory neurons. Review transmitting pain and itch messages: a up to date view of the spinal cord circuits that generate gate control. A key position of the basal ganglia in pain and analgesia - insights gained via human useful imaging Review. Cognitive impairment in ache via amygdala-driven prefrontal cortical deactivation. Electrical inhibition of pain by stimulation of the dorsal columns: preliminary clinical report. Spinal cord stimulation versus typical medical management for neuropathic ache: a multicentre randomised managed trial in sufferers with failed again surgery syndrome. Parameters of spinal cord stimulation and their position in electrical charge delivery: a evaluation. Opiate is the older time period classically utilized in pharmacology to mean a drug derived from opium. Opioid, a extra trendy term, is used to designate all substances, each pure and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors (including antagonists). Laudanum, or tincture of opium (a mixture of opium and alcohol), was used as early because the 1600s as an analgesic. Sir Christopher Wren, the acclaimed Englishman of arts and letters, was the first to inject opium right into a dwelling organism utilizing a hollow feather quill because the delivery system in 1659. Having initially referred to as morphine "somniferum" (after the Latin botanical name Papaver somniferum- the poppy that brings sleep), the name was later changed to morphine, alluding to Morpheus, the Greek god of goals. Opium and its derivatives have generally been the basis of worldwide battle. The Opium Wars of the 1800s were fought between China and the Western powers in large part in response to Western importation of opium into China. The opium houses of 19th century China, the place opium was freely obtainable on the market and consumption, illustrated the scary societal consequences of large-scale drug abuse. Recognition of those problems within the United States ultimately culminated within the Harrison Narcotics Tax Act of 1914 that criminalized narcotic possession. The prevalence of addiction clinics and drug-related violence and crime in trendy society emphasizes the chronicity of the societal difficulties that stem from this drug class and others. The ongoing opioid abuse epidemic in the United States is a latest reflection of the complexity and recalcitrance of the problems related to opioid habit regardless of practically a century of analysis dedicated to the conundrum. Despite their abuse potential, opioids play an indispensable role within the practice of medicine, particularly anesthesiology, important care, and ache management. A sound understanding of opioid pharmacology, including both basic science and clinical features, is important for the secure and effective use of these important medicine. This article focuses almost solely on intravenous opioids used perioperatively. Unique options of commonly used opioids are mentioned and the ideas underlying rational drug selection and administration are outlined. Note that codeine is an easy modification of morphine (as are many other opiates); fentanyl and its congeners are more complicated modifications of meperidine, a phenylpeperidine derivative. Basic Pharmacology Structure-Activity the opioids of medical curiosity in anesthesiology share many structural options. Morphine, the principal energetic compound derived from opium, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid; the benzylisoquinoline structural backbone is current in many important naturally occurring drugs together with papaverine, tubocurarine, and morphine. Many generally used semisynthetic opioids are created by simple modification of the morphine molecule. Similarly, hydromorphone, hydrocodone, and oxycodone are also synthesized by comparatively simple modifications of morphine. More complicated alteration of the morphine molecular skeleton leads to combined agonist-antagonists similar to nalbuphine and even pure aggressive antagonists similar to naloxone. Some of the morphine derivatives have chiral facilities and thus are sometimes synthesized as racemic mixtures of two enantiomers; only the levorotatory enantiomer is significantly energetic at the opioid receptor. The naturally occurring, stereospecific enzymatic equipment in the poppy plant produces morphine solely within the levorotatory form. Meperidine is the primary utterly synthetic opioid and may be regarded as the prototype clinical phenylpiperidine.
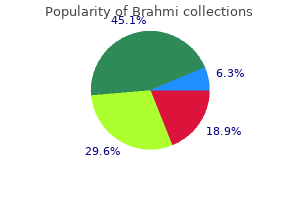
60 caps brahmi cheap with mastercard
Sudden withdrawal of -receptor blockers can result in medications used to treat ptsd 60 caps brahmi with amex rebound adrenergic effects medicine vs dentistry purchase 60 caps brahmi overnight delivery, together with tachycardia, hypertension, arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and infarction. Owing to fast hydrolysis by pink blood cell esterase, it has a brief length of motion with a half-life of solely 9 to 10 minutes (see Table 14. The brevity of esmolol makes it helpful as a bolus of 1 to 2 mg/kg to scale back cardiac results from transient -adrenergic stimulation in the perioperative period and as an infusion in critically unwell patients in whom it could be withdrawn quickly if antagonistic cardiac effects (congestive coronary heart failure, bradycardia, hypotension) occur. As an infusion for supraventricular tachycardia or hypertensive crisis, a loading dose of 500 �g/kg over 4 minutes followed by a 50- to 300-�g/kg per minute infusion ends in steady-state concentrations in 5 minutes. The peak hypotensive effect from intravenous labetalol happens inside 5 to quarter-hour and the period of action is 4 to 6 hours. It could additionally be given in 5- to 10-mg bolus doses at 5-minute intervals to management a hypertensive crisis. Metoprolol and Atenolol Metoprolol is cardioselective with a ratio of 30: 1 in affinity for 1 and 2-receptors (see Table 14. It is lipid soluble and has a high first-pass hepatic metabolism ensuing within the want for top oral doses (100�200 mg/day) compared with intravenous doses of two. It is roughly half as potent as propranolol, and most 1-blockade impact is achieved at 0. Atenolol is also 1 selective, is lipophilic and has an elimination half-life of 6 hours. In a current examine, perioperative blockade with atenolol resulted in a lowered short- and long-term mortality in high-risk sufferers present process noncardiac surgical procedure in contrast with metoprolol. Guanethidine acts by reducing norepinephrine launch from sympathetic terminals and by depleting norepinephrine storage. Side effects from the false transmitters embody orthostatic hypotension, drowsiness, diarrhea, bradycardia, hepatitis, and autoimmune hemolytic anemia. The naturally occurring substances, muscarine and nicotine, were originally used to define and name the two receptor families. The odd-numbered subtypes are defined by Pertussis toxin insensitivity, coupling to Gq/G11 protein and stimulating phospholipase C to alter a quantity of ion channels. Muscarinic subtypes M1 and M4 are discovered primarily in mind; M3 and M4 are found in lung, gastrointestinal tract, and glandular tissue; and M2 receptors are positioned in cardiac tissue. In addition, "adrenergic" muscarinic receptors are located on presynaptic sympathetic terminals within the cardiovascular and coronary systems, and their activation reduces norepinephrine release. Nicotinic receptors activate postganglionic junctions of each the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous methods (see Chapter 13). Nicotinic receptors are additionally located at the neuromuscular junction (see Chapter 21). Nicotinic cholinergic receptors are heteropentameric ligand-gated ion channels that enable depolarizing inward flow of monovalent cations. It is metabolized to -methyldopamine after which to -methylnorepinephrine, which are less potent at adrenergic receptors than dopamine and norepinephrine, thus accounting for some of their antihypertensive results. Central effects of the metabolites outcome from action on 2 receptors to decrease sympathetic outflow and to cut back anesthetic requirements by 20% to 40%. Muscarinic Receptor Agonists Muscarinic agonists are divided into two common teams: 1. Newer drugs have been designed to enhance cognitive perform in Alzheimer disease. Longer activity of the direct-acting agonists may be achieved by methylation of the choline moiety as famous with the artificial drug methacholine. This modification prevents important nicotinic receptor results and slows acetylcholinesterase metabolism (Table 14. Carbachol and bethanechol are long-acting artificial parasympathetic agonists; the carbamic-linked ester moiety considerably reduces metabolism. Bethanechol is just like methacholine and is extremely specific for muscarinic receptors. It is used orally or parenterally, has only minimal cardiac adverse chronotropic and inotropic effects, and is useful therapy for postoperative urinary retention and neurogenic bladder from spinal cord injury. Pilocarpine is a tertiary amine alkaloid with actions similar to methacholine (see Table 14. Pilocarpine has minimal nicotinic effects unless given systemically, by which case hypertension and tachycardia may result. Echothiophate, a long-acting irreversible anticholinesterase, is instilled into the attention to cut back resistance to aqueous humor outflow and decrease intraocular stress. Echothiophate is absorbed into the circulation and due to this fact can prolong the period of succinylcholine due to a discount in cholinesterase levels. The motion of ester-based native anesthetics may also be lengthened in sufferers receiving echothiophate by way of slower metabolism of the native anesthetic. The naturally occurring anticholinergic medicine atropine and scopolamine are tertiary amines derived from the belladonna plant. It reduces gastric secretion of acid, mucin, and proteolytic enzymes, slows gastric emptying, reduces decrease esophageal tone, and slows gastric motility. Atropine reduces the exercise of sweat glands and thus evaporative warmth loss, even in small doses. It relaxes bronchial smooth muscle, reduces airway resistance, inhibits mucociliary clearance within the airways, and thickens bronchial secretions. Their central effects may account for his or her antiemetic properties and control of nausea triggered by the vestibular apparatus. Atropine can block presynaptic muscarinic receptors on adrenergic terminals, leading to a sympathomimetic impact. They are thought-about secure when given parenterally to patients with the more widespread openangle glaucoma. One limitation imposed by the central actions of higher doses of scopolamine (and atropine) is an infrequent facet impact termed the central anticholinergic syndrome. It can manifest as somnolence and should be thought of within the differential prognosis of delayed awakening from anesthesia. It is more potent and longer-acting at peripheral muscarinic receptors than atropine. It is used clinically as an antisialagogue to treat bradycardia and to inhibit cardiac muscarinic receptor side effects when anticholinesterase brokers are used to reverse the effects of muscle relaxants. Inhalation of anticholinergics is the most effective route of administration when bronchodilation with out systemic unwanted side effects is desired. Ipratropium, a derivative of methylatropine, is an inhaled anticholinergic that inhibits muscarinic receptor subtypes with a peak impact of 30 to 60 minutes and a length of action of three to 6 hours. However, following large ipratropium doses, bronchodilation outcomes from blockade of M3-muscarinic receptors on airway easy muscle. In continual obstructive pulmonary disease, ipratropium is beneficial in improving pulmonary operate, and tachyphylaxis with long-term use has not been demonstrated.
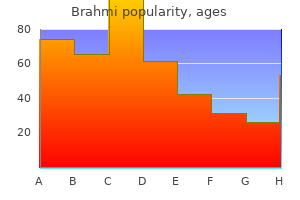
Discount brahmi 60 caps on-line
The combination of antacids and H2-histamine receptor antagonists is more effective in decreasing gastric pH than antacids alone or no pharmacologic intervention medicine 750 dollars brahmi 60 caps discount on-line. Current American Society of Anesthesiologists guidelines for obstetric anesthesia state " medications known to cause hair loss brahmi 60 caps buy generic on line. Urine protein and urine glucose levels are often elevated from decreased renal tubular resorption capability, and 300 mg protein or 10 g glucose in a 24-hour urine assortment is taken into account the higher limits of normal during being pregnant. In contrast to these findings, an electroencephalographic study suggests that anesthetic results of sevoflurane on the brain are related between pregnant and nonpregnant sufferers. Anatomic adjustments to the nervous system during pregnancy embody engorgement of the epidural veins, decreased size of the epidural area, and decreased volume of cerebrospinal fluid. The lower volume of those areas might result in larger spread of local anesthetics. However, research suggests that the decreased local anesthetic requirements observed throughout pregnancy happen in the first trimester, before vital anatomic adjustments within the neuraxial system are seen, suggesting a biochemical role for the increased nerve sensitivity. Hepatic and Gallbladder Changes During being pregnant, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and bilirubin levels rise to the upper limits of regular, while plasma protein concentrations are lowered. The decreased protein concentrations can cause elevated free serum levels of extremely protein-bound medication. Alkaline phosphatase ranges will double in pregnancy secondary to placental production. Of note, incomplete gallbladder emptying and modifications in bile composition increase the risk of gallbladder disease throughout pregnancy. Uteroplacental Physiology the placenta, composed of each maternal and fetal tissues, is the means by which physiologic exchange between mom and fetus happens. Two umbilical arteries return fetal blood to the placenta and then turn into umbilical capillaries that cross the chorionic villi. After placental trade happens at the chorionic villi, nutrient-rich and waste-free blood is returned from the placenta to the fetus through an umbilical vein. Renal Changes By the tip of the primary trimester, renal blood circulate and glomerular filtration price are elevated by 50% to 60% and remain elevated for 3 months postpartum. The higher limits of blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine values are about 50% lower during being pregnant, Uterine Blood Flow In the nonpregnant state, uterine blood flow is roughly one hundred mL/min. At time period, uterine blood circulate reaches seven-hundred mL/min, or about 10% of the cardiac output. At term, about 80% of uterine blood move perfuses the intervillous areas within the placenta, whereas the other 20% supports the myometrium. Autoregulation of uterine blood flow is minimal, because the uterine vessels are fully dilated throughout pregnancy. Therefore maternal cardiac output, uterine vascular resistance, and uterine perfusion pressure dictate uterine and placental blood circulate. A decrease in systemic vascular resistance, from both general or neuraxial anesthesia, or maternal hypotension from aortocaval compression or hypovolemia, could end in a decreased placental perfusion pressure. Illustration of the placenta exhibiting its structure and parts of both fetal and maternal circulation. Maternal arterial blood flows to the uterine spiral arteries, fills the intervillous house, and contacts the fetal chorionic villi. Deoxygenated blood from the fetus flows through the umbilical arteries and branches into chorionic arteries (within the chorionic villi), where oxygen is transferred from the mother and the oxygenated blood returns to the fetus by way of the umbilical vein. Throughout this course of, a placental barrier separates the maternal and fetal circulatory methods. Decreases in uterine perfusion could result in placental hypoperfusion and cause fetal hypoxemia and acidosis. Placental Exchange In addition to uterine and fetal blood move, oxygen delivery from mom to fetus is affected by the oxygen partial pressure gradient, diffusion capability of the placenta, acid-base standing of maternal and fetal blood (Bohr effect), and maternal and fetal Hb concentrations and oxygen affinities. The oxygen supply to the fetus is primarily dependent on the speed of blood circulate on all sides of the placenta rather than limitations to diffusion. Fetal PaO2 is typically 20 to 40 mm Hg15 however can attain as a lot as 60 mm Hg if the mom is respiration one hundred pc oxygen,16 although typical fetal tissue arterial Hb saturation remains beneath 65% even with maternal impressed oxygen near 100 percent. Concern has been expressed for potential fetal hurt from generation of free radicals based on chemical markers in the fetal umbilical circulation with maternal hyperoxia. The fee of transfer is dependent upon maternal-to-fetal concentration gradients, maternal protein binding, molecular weight, lipid solubility, and ionization. The diploma of fetal transfer for a specific drug is typically presented as a ratio of focus in the umbilical vein to the maternal artery. Although all medicine transfer throughout the placenta to some degree, a few are considerably restricted. Nondeloparizing neuromuscular blockers have high molecular weights and are poorly lipid-soluble, thus limiting their capacity for crossing the placenta and reaching the fetus. Succinylcholine has a low molecular weight however can also be extremely ionized and poorly lipid-soluble, which limits its capability to cross the placenta until given in massive doses. In contrast, risky anesthetic brokers, benzodiazepines, local anesthetics, and opioids all have comparatively low molecular weights and readily cross the placenta. These newly ionized molecules are unable to readily diffuse again to the maternal circulation through the placenta, thus accumulating within the fetal circulation and probably reaching ranges higher than the maternal focus. This is called "ion trapping" and can be more extreme during fetal distress, when the fetal pH is decrease than normal. Unintended intravascular injection of native anesthetics could cause extraordinarily excessive fetal concentrations of those medicine, which may end in bradycardia, ventricular arrhythmias, acidosis, and extreme cardiac melancholy. The upcoming sections "Labor Analgesia" and "Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery" additional focus on placental switch and fetal uptake issues of particular brokers. The majority of this blood flows by way of the foramen ovale, into the left atrium, then the left ventricle, and empties into the aorta (a small portion travels through the pulmonary arteries to perfuse lung tissue). This shunted portion traveling via the foramen ovale has the highest oxygen ranges and directly perfuses the mind (carotid arteries) and coronary heart (coronary arteries). Fetal deoxygenated blood coming back from the superior vena cava and decrease extremities is directed toward the proper ventricle and pulmonary trunk. The majority of this blood flow passes by way of the ductus arteriosus, into the descending aorta, and perfuses the decrease extremities and hypogastric arteries. The bulk of this blood passes by way of the foramen ovale, into the left atrium, then the left ventricle, and empties into the aorta (directly perfusing the brain and heart). Although this majority of flow bypasses the fetal lungs, a small portion does perfuse the lung tissue through the pulmonary arteries. Deoxygenated blood from the superior vena cava and lower extremities is directed toward the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk. The majority of this blood move passes via the ductus arteriosus, into the descending aorta, and perfuses the lower circulation.
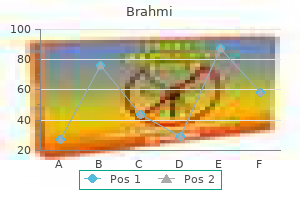
Discount brahmi 60 caps on-line
The impression of ancillary subunits on small-molecule interactions with voltage-gated potassium channels symptoms 5 days before your missed period 60 caps brahmi generic with visa. Electrophysiologic results of chronic amiodarone remedy and hypothyroidism medicine 014 brahmi 60 caps buy generic on line, alone and in combination, on guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Mapping the block of a cloned human inward rectifier potassium channel by dofetilide. Identification of a area of RyR1 that participates in allosteric coupling with the alpha(1S) (Ca(V)1. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated calcium channels. Molecular determinants of high affinity phenylalkylamine block of L-type calcium channels. Identification of benz(othi) azepine-binding areas within L-type calcium channel alpha1 subunits. Atrial induction of ventricular tachycardia: reentry versus triggered automaticity. Clinical implications of new research in the remedy of benign, probably malignant and malignant ventricular arrhythmias. Flecainide prevents catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in mice and humans. Pharmacological cardioversion of atrial fibrillation: current administration and remedy options. Tedisamil and dofetilide-induced torsades de pointes, price and potassium dependence. Executive summary: American College of Chest Physicians guidelines for the prevention and administration of postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgical procedure. Interventions for stopping post-operative atrial fibrillation in patients present process heart surgical procedure. Prophylactic amiodarone for prevention of atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgical procedure: a meta-analysis. Augmented potassium present is a shared phenotype for 2 genetic defects related to familial atrial fibrillation. Ultra-rapid delayed rectifier channels: molecular foundation and therapeutic implications. The position of diltiazem in treating hypertension and coronary artery illness: new approaches to preventing first occasions. Does a rise in repolarization capability constitute a model new antiarrhythmic precept Phenotypic manifestations of mutations in genes encoding subunits of cardiac potassium channels. When should we recommend catheter ablation for sufferers with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome Mechanism of spontaneous excitability in human embryonic stem cell derived cardiomyocytes. The content material of CaO2 depends on the volume of oxygen sure to hemoglobin (Hbg) and of free oxygen dissolved in blood (CaO2 = 1. SaO2 represents the oxygen saturation, PaO2 the arterial oxygen tension (in millimeters of mercury), and zero. The overwhelming majority of oxygen is sure to hemoglobin such that even at very high oxygen tensions the extra dissolved oxygen contributes little to total CaO2. The Fick precept derives oxygen consumption from the difference in oxygen content between arterial and venous blood, V O2 = Q * (CaO2 - CvO2). Normal oxygen consumption in a resting adult is a hundred and ten to a hundred and sixty mL/min per meter squared; V O2 lower than 100 mL/min meter squared indicates impaired tissue oxygenation. Resuscitation maneuvers improve Do2, optimize tissue uptake of oxygen, and preserve metabolic price of oxygen. T Historical Perspective Peter Safar is credited with the primary printed account of expired gasoline air flow via mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-airway strategies using a novel system of two fused oral airways in 1957. Advances and experience with new technology, including automated units and extracorporeal life assist, are actively being pursued. Assuming an SaO2 of 100%, normal combined venous saturation (ScvO2) of 70% implies 30% extraction of the oxygen delivered. Normal ScvO2 sampled from the pulmonary artery is 65% to 75%, implying an oxygen extraction of ~25% to 35%. ScvO2 is inversely proportional to oxygen consumption and directly proportional to arterial saturation, hemoglobin concentration, and cardiac output. Therefore maneuvers to improve ScvO2 aim to improve arterial oxygen content and supply. Epinephrine infusion Lidocaine Magnesium sulfate Metoprolol Procainamide infusion Sotalol Verapamil Compensated Hypovolemia and Supply-Dependent Oxygen Consumption In shock, Do2 is decreased and in response very important organ beds turn out to be extra oxygen avid. This supply dependence underscores the importance of Do2 during shock and demonstrates the physiologic foundation of goal-directed remedy. The dynamic nature of septic shock is described as an ebb and circulate, shifting from hyperdynamic physiology to an end-stage hypodynamic state. The mortality profit from these early research is attributed to the perpetuation of a hyperdynamic state. The basis of goal-directed remedy is the profit of maximizing parameters of Do2. The natural history of septic shock entails an imbalance of Do2 and oxygen demand, main eventually to global dysoxia and demise. This progression hinges on the crucial "golden hour" during which the pathophysiology transitions to multiorgan failure. In a seminal 2000 trial, Rivers and colleagues really helpful expeditious, protocolized intervention throughout this golden hour. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign, a world consortium tasked to recommend finest practices for sepsis administration, endorsed early goal-directed remedy as first-line treatment. This "6-hour bundle" was disseminated internationally as the standard of take care of sepsis management14 by the Surviving Sepsis Campaign in addition to the U. The thoracic pump mechanism proposes that the heart, with an open mitral valve, acts as an open conduit during compression. With every cycle, a strain gradient is formed between intrathoracic and extrathoracic arteries, and this drives blood out of the center; the valves within the venous system prevent reflux of blood. In zone 2, arteriolar pressure is greater than alveolar pressure and venous capillary pressure (Parteriolar > Palveolar > Pvenous),22 and lifeless area ventilation persists. Gas exchange happens primarily in zone 3, the place arteriolar stress is larger than each venous capillary strain and alveolar strain (Parteriolar > Pvenous > Palveolar). A balance between the ventilation rate and tidal volume can be necessary to maximize both air flow and perfusion. Positive-pressure air flow is deleterious as a outcome of increased intrathoracic strain impedes venous return and compresses the pulmonary vasculature. This vascular compression recruits a bigger portion of the lung into West zone 1, with substantial growth of lifeless area. The balance between compression and air flow is essential; hypoventilation results in hypercarbia, Compression and Decompression Closed chest cardiac resuscitation entails the bodily compression and decompression of the chest in a cyclic trend to promote organ perfusion.
Diseases
- Short stature webbed neck heart disease
- Bruyn Scheltens syndrome
- Cutaneous anthrax
- Tracheoesophageal fistula symphalangism
- Urioste Martinez Frias syndrome
- Female sexual arousal disorder
- Kurczynski Casperson syndrome
- Multiple vertebral anomalies unusual facies
- Aplasia/hypoplasia of pelvis, femur, fibula, and ulna with abnormal digits and nails
60 caps brahmi purchase with amex
Patients can have preexisting muscle weak spot and be delicate to the results of neuromuscular blocking brokers treatment zone guiseley discount 60 caps brahmi with amex. Patients with Cushing syndrome are likely to medicine articles cheap 60 caps brahmi with amex be hypervolemic with hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis. Clinical manifestations embody weakness, fatigue, hypoglycemia, hypotension, and weight loss. Thus, sudden withdrawal of exogenous glucocorticoids throughout a stressful interval or critical sickness can precipitate an Addisonian crisis (acute adrenal failure), which is a medical emergency. Patients can experience circulatory collapse, fever, hypoglycemia, and mental obtundation on account of the acute decrease in cortisol and the shortcoming to secrete cortisol in response to stress. Anesthetic concerns for sufferers with glucocorticoid deficiency (whether chronic or acute) mainly give consideration to steroid substitute therapy through the perioperative period-a time of acute physiologic stress. Historically, stressdose steroid therapy consisted of hydrocortisone a hundred mg each 8 hours. However, this dose can precipitate hyperglycemia and decreased wound healing in some patients. Thus, a lower-dose regimen could be thought-about: hydrocortisone 25 mg at induction of anesthesia, followed by a total of 100 mg of hydrocortisone over the subsequent 24 hours. The initial bolus dose of hydrocortisone may be increased primarily based on the urgency and complexity of the surgical process. Primary hyperaldosteronism, or Conn syndrome, is as a result of of adrenal oversecretion of aldosterone by benign adrenal tumors. Patients exhibit hypertension owing to Na+ and water retention, and exhibit hypokalemia owing to K+ excretion, muscle weakness, and metabolic alkalosis. Secondary hyperaldosteronism often results from one other pathologic state that reduces the effective circulating blood volume, similar to cirrhosis with ascites or congestive coronary heart failure. This decrease in the efficient circulating quantity causes steady stimulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system with overproduction of aldosterone. Anesthetic considerations embody correction of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities preoperatively. Potassium-sparing diuretics, corresponding to spironolactone, are sometimes prescribed to help handle the hypokalemia and hypervolemia and to control hypertension. Primary hypoaldosteronism, or Addison illness, happens as a end result of destruction of the adrenal gland because of infection, damage, autoimmune problems, or genetic disorders. In Addison disease, renin activity is increased, which helps differentiate main hypoaldosteronism from the other types of deficiency. Clinical manifestations include hyponatremia, hypovolemia, hypotension, hyperkalemia, and metabolic acidosis. Anesthetic considerations embody preoperative mineralocorticoid therapy, corresponding to fludrocortisone, which helps correct the hypovolemia and hyperkalemia. Adrenal Medulla Physiology the adrenal medulla is the inner part of the adrenal gland and is extremely vascular, made up of 2 kinds of chromaffin cells: those that produce epinephrine and those who produce norepinephrine. Catecholamines are launched in direct response to sympathetic nervous stimulation of the adrenal medulla. Acetylcholine released from the preganglionic sympathetic nerve terminals binds to nicotinic receptors within the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. The physiologic results of the catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine are mediated by G protein�coupled receptors discovered in many tissues (Table 35. This causes a rise in intracellular Ca2+ and corresponding improve in smooth muscle contraction. Sympathetic stimulation results in secretion of catecholamines, which play a chief position in the stress response to perceived or real bodily or psychological injury, together with hemorrhage, severe hypoglycemia, trauma, surgical trauma, and worry. The fundamental physiologic results attributed to catecholamine secretion are mental arousal and alertness, pupillary dilation, diaphoresis, bronchial smooth muscle dilation, tachycardia, reduced activity of gastrointestinal tract, sphincter constriction, and uterine muscle leisure. Catecholamines activate catabolism for the expenditure of vitality in order to present substrate for the stress response. As such, glucose is mobilized from the liver through glycogen breakdown and fats breakdown. Pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma represents the most significant illness related to adrenal medullary tissue. As a end result, patients with pheochromocytoma present with extreme (sustained or paroxysmal) hypertension, headaches, sweating, and palpitations. Most pheochromocytomas are benign and located unilaterally in an adrenal gland, but roughly 10% may be malignant and 10% may be bilateral/ extra-adrenal in origin. Under common anesthesia, the indicators of undiagnosed pheochromocytoma embody tachycardia and hypertension. Preoperative analysis and evaluation should concentrate on treatment with -adrenergic blockers and volume substitute. At the time of diagnosis, patients with pheochromocytoma are often hypovolemic with a standard to elevated hematocrit. Preoperative -adrenergic blocker remedy with phenoxybenzamine or phentolamine helps right the hypertension and vasoconstriction as nicely as cut back the intravascular quantity deficit. Beta-blocker remedy is typically began after initiation of -adrenergic blocker remedy to assist control coronary heart price and blood pressure. Management of pheochromocytoma resection mandates intraarterial blood pressure monitoring for immediate analysis of rapid adjustments in blood stress, which can aid in titration of any necessary vasopressor or vasodilator remedy, and frequent laboratory analysis to assess acid�base standing, hematocrit, and electrolyte values. Central venous access may be useful to enable infusion of vasoactive substances and enormous volumes of fluid and blood merchandise if required. Intraoperative hypertension can be handled with phentolamine, nitroprusside, or nicardipine. Phentolamine blocks -adrenergic receptors, is relatively short acting, and prevents results of catecholamines. Nitroprusside is well titratable, with fast onset and offset, however can end result in cyanide accumulation with high doses. Potential anesthetic medicine to avoid include people who stimulate sympathetic nervous system activity or block parasympathetic exercise, similar to ketamine, ephedrine, and pancuronium. After the tumor is resected, hypotension can complicate the intraoperative and postoperative course owing to a decrease in circulating catecholamines and residual antihypertensive therapies. However, in some sufferers, hypertension continues to be problematic and requires therapy. Persistent hypertension is treated with antihypertensive medications as well as serial surveillance for recurrence of the pheochromocytoma. Most of the mass of the pancreas is made up of exocrine cells, which secrete an alkaline digestive fluid into the pancreatic duct and duodenum. Comprising 1% to 2% of the mass of the pancreas, throughout the pancreatic lobules, are small clusters of endocrine cells-the islets of Langerhans-which embody, and cells. Of endocrine cells, 18% to 20% are cells, which secrete glucagon, and the remaining 5% are cells, which secrete somatostatin. The arterial blood supply to the pancreas consists of branches from the splenic artery and the superior and inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries. The islets obtain 10% to 15% of the pancreatic blood flow; thus, their wealthy vascularization allows easy access for the hormones to be secreted by the islet cells into the bloodstream.
Brahmi 60 caps discount amex
In 1772 nitrous oxide (N2O) was found by the English philosopher and chemist Joseph Priestley (1733�1804) symptoms vaginal yeast infection 60 caps brahmi purchase amex. He and different scientists such as Joseph Black (1728�1799) and Antoine Lavoisier (1743�1794) identified many other atmospheric gases symptoms after embryo transfer buy discount brahmi 60 caps online, together with oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide, pioneering the sector of "pneumatic medication" and elucidating the fundamental properties of gases. In 1799 Thomas Beddoes (1760�1808) established the Pneumatic Institution for Relieving Diseases by Medical Airs in England. Together with younger assistant Humphry Davy (1778�1829), who in the end became extra successful than him, Beddoes experimented with N2O. Davy carried out numerous experiments on himself and discovered both the mood-enhancing results, leading to the name laughing gas, and the analgesic effect of N2O. Decades later Gardner Quincy Colton (1814�1898), a selfproclaimed professor of chemistry, went on tour along with his (lucrative) "scientific reveals" and public demonstrations of N2O. During the demonstration the affected person cried out and moaned, probably owing to failure of steady delivery of the gas, an incident that discredited N2O as an anesthetic. Morton was searching for one other appropriate substance to relieve pain throughout tooth extractions. Jackson (1805�1880), a Harvard professor in chemistry who launched him to ether. Bigelow (1818�1890), who helped schedule a successful public demonstration at Massachusetts General Hospital on October sixteen, 1846, which is taken into account by many the beginning of the era of anesthesia. Most likely he saw a possible for profit and unsuccessfully attempted to patent Letheon. Under stress from the hospital, Morton revealed the id of the primary ingredient ether, and after further procedures with ether followed, Bigelow revealed the results of ether as an appropriate agent to be used in surgical procedures. The use of each ether and N2O was rapidly adopted by many establishments, revolutionizing surgery and defining the sector of anesthesia. The science of anesthesia started with the introduction and development of chloroform as an anesthetic by John Snow (1813�1858) in England. His work established the scientific basis of anesthesia by determining the relationships between anesthetic solubility, vapor stress, and potency. This allowed the synthesis and testing of many fluorinated alkane and ether compounds that have been safer and less flamable than ether or cyclopropane. Robbins demonstrated the potential of fluorinated hydrocarbons as nonflammable inhaled anesthetics with higher therapeutic ratios than ether or chloroform. Subsequent investigations confirmed that for a majority of anesthetic agents efficiency is proportional to lipid solubility as measured by the oil-gas partition coefficient. Remarkably, this correlation holds across multiple animal phyla from invertebrates to people and spans over 5 orders of magnitude in efficiency. This remark fashioned the basis for a unitary speculation that argued that the mechanism of action of inhaled anesthetics was derived from their effects on bulk lipid membrane properties. A extra trendy, mechanistic form of the lipid-based speculation suggests that anesthetic-induced adjustments in the bilayer lateral strain profile of lipids within the neighborhood of membrane proteins alter their functional properties. Note the similarities among the many trendy methyl ethyl ethers, specifically desflurane and isoflurane, which differ by a single substitution. The amphipathic (having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic qualities) solvents methanol, octanol, and lecithin produce even better correlations than olive oil, accurately predicting that enflurane is much less potent than isoflurane. These so-called nonimmobilizers have been useful experimentally as a adverse take a look at in evaluating potential anesthetic targets. B, General anesthetic potencies correlate equally well with their potency for inhibition of the soluble enzyme firefly luciferase. The activities of consultant inhaled anesthetics on these targets in vitro are summarized. A dark green or pink spot signifies significant potentiation or inhibition, respectively, by the anesthetic at clinically relevant concentrations; a light-weight pink spot indicates some inhibition, and an empty spot indicates no effect at clinically related concentrations. This abstract represents a synthesis of major effects, but important variations exist between numerous receptor and channel isoforms (not indicated here). The prevailing view is that inhaled anesthetics have multiple, agent-specific results on a quantity of molecular targets critical to neuronal communication and excitability, as summarized in Table 11. Specific receptor isoforms appear to mediate numerous anesthetic endpoints, as proven for certain intravenous anesthetics (see Chapter 9). Mechanisms of Action From Lipid-Based to Protein-Based Mechanisms the chemical range of the agents that can be used as basic anesthetics historically favored a unitary mechanism to clarify anesthesia. The Meyer-Overton correlation suggested that the impact websites of anesthetics were lipophilic or amphipathic. As a result, preliminary concepts of basic anesthetic mechanisms favored effects on the bulk properties of lipid membranes, which allowed for the huge chemical range of brokers found to produce an anesthetic state (see earlier text). However, no verifiable hypothesis of a lipid-based mechanism, which usually invoked effects on lipid membrane properties. Subsequently, the nonimmobilizers had been discovered to violate the essential Meyer-Overton correlation between efficiency and lipophilicity. The goal is expressed in applicable anatomic areas to mediate the specific behavioral results of the anesthetic (plausibility). Stereoselective results of the anesthetic or nonimmobilizer in vivo parallel results on the target in vitro. Pharmacologic or genetic disruption of the anesthetic sensitivity of the target abolishes the impact of the anesthetic on the relevant endpoint. Unconsciousness is most likely going due to enhanced inhibition at a quantity of websites within the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem concerned in arousal. Although the neuronal correlates of consciousness stay unclear, it has been proposed that anything that sufficiently perturbs activity in thalamocortical loops, and therefore long-range cortical connectivity, might dysfunction consciousness. Immobility is as a outcome of of results on spinal wire networks, probably through suppression of central pattern turbines critical to coordinated motion. A shortcoming of the risky anesthetics is their poor management of the autonomic nervous system response to painful stimuli. In the fashionable period, inhalation anesthesia is routinely supplemented with opioids to obtain optimum anesthetic circumstances. B, Amnesia, probably the most sensitive anesthetic endpoint, probably involves the hippocampus, amygdala, mediotemporal lobe, and presumably different cortical structures involved in studying and memory. Unconsciousness likely entails the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem reticular formation essential to consciousness and arousal. Immobility happens by anesthetic motion on the spinal cord central pattern turbines. Anesthetic results on the spinal wire blunts ascending impulses arising from noxious stimulation, leading to analgesia, and may not directly contribute to anesthetic-induced unconsciousness. Inhaled anesthetics produce immobilization at growing doses primarily via results on the spinal cord. A sequence of elegant experiments in vivo confirmed that the efficiency of risky anesthetics for immobilization was decided by effects on the spinal twine.
Brahmi 60 caps buy cheap on line
A theoretical analysis of the relationship between venous blood and mean tissue oxygen pressures treatment 3rd metatarsal stress fracture brahmi 60 caps buy cheap line. Comparison of oxygen consumption measurements: indirect calorimetry versus the reversed Fick technique symptoms tuberculosis generic brahmi 60 caps mastercard. Molecular construction of free radicals and their significance in organic reactions. Relationship of oxygen delivery and blended venous oxygenation to lactic acidosis in patients with sepsis and acute myocardial infarction. Oxygen extraction ratio: a sound indicator of transfusion want in restricted coronary vascular reserve The dependence of oxygen uptake on oxygen delivery in the grownup respiratory misery syndrome. Relationship between O2 delivery and O2 consumption within the grownup respiratory distress syndrome. Right and left ventricular O2 uptake during hemodilution and beta-adrenergic stimulation. Nimmagadda U, Salem M, Crystal G: Preoxygenation: physiological foundation, benefits, and potential dangers. Lack of role for nitric oxide in cholinergic modulation of myocardial contractility in vivo. Control of myocardial oxygen consumption: physiologic and medical considerations. Myocardial necrosis induced by momentary occlusion of a coronary artery in the canine. Physiological affect of basic perturbations assessed by non-invasive optical techniques in people. Swenson this particular section on Anatomy and Imaging outlines essential anatomic constructions and imaging strategies for the cardiovascular system, including the guts and main vessels in the neck and groin. The right panel exhibits the transducer positioned with the indicator toward the right shoulder at the third to fourth intercostal interspace. The proper panel shows probe placement below the xiphoid, with the indicator to the left. Coronary angiography is an invasive process that allows visualization of coronary artery anatomy and is taken into account the gold normal for prognosis of coronary artery stenosis. Common pictures are named based on the relation of the image intensifier (located above the patient) to the affected person. These photographs correspond to the echocardiogram apical 2-chamber, apical 4-chamber and parasternal short-axis views. Three-dimensional renderings of cardiac anatomy are illustrated in the center panel and in the proper panel. The proper upper and lower panels are corresponding ultrasound pictures; the underside left panel exhibits the position of the transducer used to visualize these buildings. The lower right panel illustrates how simply the femoral vein is compressed utilizing mild stress with the transducer. Images such as these are necessary in vascular entry and nerve block strategies in the groin, such as femoral artery cannulation and fascia iliaca nerve block catheters. Although not typically visualized in ultrasound pictures, the thoracic duct drains lymph into the circulatory system through the left brachiocephalic vein between the left subclavian and left inner jugular veins. Thus, injury to the thoracic duct that may end up in chylothorax is a possible complication of central venous access procedures on the left aspect of the physique however not on the proper. The anterior and posterior circumflex arteries type an anastomosing circle around the surgical neck of the humerus. The profunda artery arises from the brachial artery at the level of the proximal humerus and follows the radial nerve. The superior and inferior ulnar collateral arteries arise from the brachial artery proximally and anastomose distally with the ulnar artery. The superior ulnar collateral artery could be visualized adjoining to the ulnar nerve within the higher arm. The brachial artery terminates on the neck of the radius by dividing into the radial and ulnar arteries. The superficial and deep palmar arches are direct continuations of the ulnar and radial arteries, respectively. There is asymmetry of those vessels in that right subclavian and proper widespread carotid arteries come up from the brachiocephalic artery. By distinction, the left subclavian and common carotid arteries come up immediately from the arch. It can additionally be important to notice that the vertebral arteries come up from the subclavian arteries. Occasional anatomic variations can produce surprising findings on ultrasound and radiographic examinations. These features are illustrated in the diagram and by an ultrasound picture at the level of the first rib. This image features a recent cadaver dissection displaying the proximity of the radial nerve and profunda artery inside the lateral intermuscular septum. Note that the brachial artery is in close proximity to the median nerve alongside its course. The cadaver dissection shows the gradual transition of the nerve from a position superficial to the brachial artery to a more medial place on the degree of the elbow. By contrast, the radial artery travels in proximity to the superficial department of the radial nerve within the middle third of the forearm however this department passes deep to the tendon of the brachioradialis muscle at the distal forearm. Thus, no neural constructions are visible on ultrasound in proximity to the radial artery at the degree of the wrist. Focused cardiac ultrasound: recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography. Mass flow and volumetric flow are related to one another by the density of the fluid, during which density is the mass of a fluid per unit volume as measured in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3): mass fluid circulate fee = density � volumetric fluid circulate price In anesthesia, mass circulate is used, for example, when describing intravenous delivery of medication, although in this case the mass refers to just 1 component of the fluid. Gases change quantity with changes in pressure and temperature, resulting in adjustments in their density. Differences in gas properties can have a significant impact on the dynamics of these flows, influencing how anesthetic and ventilation gear performs. Fluid Flow A fluid is a substance that flows freely and takes the shape of its container. The fee at which fluids move can be described in 2 ways: volumetric circulate and mass circulate. From empirical testing in cylindrical tubes, flows with a Reynolds quantity below 2000 are prone to be laminar, whereas those above 2000 are inclined to be turbulent.
Buy generic brahmi 60 caps on-line
Tachycardia and peripheral vasoconstriction heralding a "fight-or-flight" response or a vasovagal response (fainting) are well-known examples of this greater cortical sensory processing medical treatment 80ddb 60 caps brahmi cheap amex. These indicators are despatched to the brainstem administering medications 7th edition ebook buy 60 caps brahmi with amex, the place reflex responses are processed in the hypothalamus and the limbic forebrain. Higher cortical centers present descending enter to the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, which has projections to sympathetic and parasympathetic nuclei. Chronic stress alters these constructions and their operate, leading to both sensitization and habituation of the stress response. Hunger, sleep, and sexual operate are additionally regulated by the hypothalamus, dependent on both cortical enter and sophisticated feedback control. The anterior hypothalamus controls temperature, while the posterior hypothalamus is involved in water regulation. Immediate management of blood strain, coronary heart fee, cardiac output, and air flow is organized and integrated in specific nuclei. The 22 paired sympathetic ganglia are situated near the vertebral column within the sympathetic chain. The exception is the adrenal gland, the place the sympathetic preganglionic nerve fibers travel on to the adrenal medulla. The parasympathetic preganglionic fibers travel directly to the organ of innervation to synapse with postganglionic neuronal cell our bodies. These myelinated fibers enter the paravertebral ganglia and travel a variable distance up or down the sympathetic chain to synapse with the neuronal cell our bodies of postganglionic sympathetic neurons. The chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla are derived from neuronal tissue and basically perform as the postganglionic cells. The stellate ganglion consists of postganglionic neurons that provide sympathetic innervation to the head and neck. Preganglionic fibers from the primary 4 or five thoracic segments kind this ganglion in addition to the superior and center cervical ganglia. This neurotransmitter is stored in vesicles located in the presynaptic terminal and launched upon nerve stimulation. These preganglionic fibers have an result on the center, lungs, and belly organs aside from the distal portion of the colon. A combination of the distal location of the ganglion and the smaller two- to threefold amplification issue between preganglionic and postganglionic fibers causes parasympathetic results to be particular to every organ. Recent advances in the pharmacology of these drugs have been directed at lowering these ganglionic actions (see Chapter 22). Thus the ganglionic synapse serves complicated integrative and processing features during regular physiology and while underneath the influence of anesthetic agents. Receptor classification is pharmacologic or primarily based on second messenger sign transduction. Building on the unique observation by Ahlquist, adrenergic "receptors" are of two differing types (and) categorised when it comes to the overall physiologic response they elicit (the "basic pharmacology" approach). From a mechanistic perspective, these receptors can also be categorised by method of how their indicators are transduced. For example, norepinephrine released from sympathetic postganglionic neurons stimulates both - and -adrenergic receptors, eliciting traditional adrenergic responses. The postsynaptic receptors regulate effector cells via second-messenger signaling. The various and widespread physiologic actions of adrenergic and dopaminergic receptors are summarized in Table 13. Synthesis of the adrenergic neurotransmitters takes place in the presynaptic varicosities of postganglionic sympathetic neurons. The neurotransmitters are saved and released from synaptic vesicles, and reuptake into presynaptic nerve endings assists in the termination of transmitter motion. In addition, diffusion of transmitters away from the synaptic cleft and metabolism by monoamine oxidase and catechol-O-methyl transferase quickly terminate the motion of norepinephrine. Receptor classification is pharmacologic or primarily based on second-messenger signal transduction. Nicotinic receptors, which operate at the neuromuscular junction, are also current in autonomic ganglia (see earlier text). Choline is taken up by the presynaptic nerve endings to be reused, while acetate diffuses away from the synaptic cleft. M1, M2, and M3 receptors have effects on the airway clean muscle with the vast majority of receptors being M2 and M3. The relative tone of every of the two subsystems varies with age, sex, organ system, and environmental results such as stress. Enteric Nervous System the gastrointestinal tract is innervated by sympathetic and parasympathetic efferents arising from preganglionic and postganglionic websites. These neural inputs, along with visceral afferents, work together with intrinsic neural components (often referred to because the enteric nervous system) to control gut perform. The vagal efferents end on smooth muscle within the walls of the gut, interacting with the intrinsic myenteric ganglion to control motility (see Chapter 31). Efferent outflow from the sympathetic and the parasympathetic systems modulate blood flow, secretory exercise, and motility. Anesthetic results on the enteric nervous system may be divided into direct pharmacologic effects on the intestinal easy muscle and effects ensuing from spinal or epidural anesthesia. This inhibitory sympathetic reflex could be interrupted by division of the splanchnic nerves, destruction of afferent sensory nerves, or chemical sympathectomy by way of thoracic epidural anesthesia. The clinical result of thoracic epidural anesthesia has been proven to be a shortened time to decision of postoperative ileus. Autonomic Dysreflexia Historically termed autonomic hyperreflexia, this situation outcomes from persistent disruption of efferent impulses down the spinal cord, as seen in spinal twine trauma or tumor impingement. Inciting stimuli corresponding to bladder distention, bowel distention, or surgical stimulation can produce an exaggerated sympathetic response. A portion of the exaggeration in the response is as a outcome of of adrenergic receptor supersensitivity secondary to denervation. Management of the quadriplegic or high paraplegic patient consists of both spinal or basic anesthesia mixed with cautious manipulation of blood pressure. These signals are processed by the hypothalamus, which maintains physique temperature within a slender range of some tenths of a level around 37�C. The output of the hypothalamus controls effector responses, including peripheral vasculature action (vasodilation or vasoconstriction), sweating, and shivering. Efferent visitors goes to the principal thermoregulatory effectors: (1) cutaneous blood vessels, which vasoconstrict to reduce warmth loss and vasodilate to facilitate heat loss; (2) brown fat and skeletal muscle for thermogenesis and shivering; and (3) sweat glands to provide for evaporative warmth loss. Second Messengers within the Autonomic Nervous System the interplay of neurotransmitters with their postsynaptic receptors leads to sign transduction, which interprets receptor binding into an effector cell response. In the adrenergic system, transduction is mediated by G proteins, which then regulate adenylyl cyclase and phospholipase C to generate second messengers and/or instantly modulate numerous ion channels (see Chapter 1). Second-messenger responses to muscarinic receptor stimulation depend upon the effector web site and the muscarinic receptor subtypes expressed (see Table thirteen. Chromaffin cells are homologous to the sympathetic ganglion neurons and are similarly derived from the neural crest.

