Avodart
Avodart dosages: 0.5 mg
Avodart packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Avodart 0.5 mg without prescription
Most sufferers can obtain an appropriate stage of continence via an individualized bowel regimen treatment xanax overdose buy avodart 0.5 mg with visa. Dietary fiber symptoms lymphoma buy 0.5 mg avodart with mastercard, stool softeners, suppositories, and enema continence catheters are therapy options. Treatment of sufferers with spinal or nerve harm or dysfunction from other causes is similar. Therapy for these complications includes correcting electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia), broad-spectrum parenteral antibiotics, bowel rest, rectal tube placement, and if wanted, emergency cecostomy or colectomy. Treatment for Hirschsprung illness is surgical resection of the affected section of bowel and varied strategies for an ileal or colonic rectal pullthrough process. Chronic Intestinal Pseudoobstruction this disorder is characterized by manifestations of intestinal obstruction without an identifiable anatomic lesion and could additionally be secondary to an intestinal neuropathy or myopathy. Congenital cases may be sporadic or inherited, in both autosomal dominant or recessive patterns. Manifestations include belly distention, emesis, constipation, development Metabolic Diseases the appropriate laboratory exams must be carried out to rule out the assorted metabolic and endocrinologic situations which will manifest with constipation (see Table sixteen. As the fecal mass accumulates, it causes rectal distention, will increase rectal compliance, and ultimately results in blunted or absent sensitivity of the rectum to the presence of liquid stool passing round a firm fecal mass. It is important to specifically query the affected person or parents relating to these large stools as a end result of this information is incessantly not volunteered. Encopresis has been incorrectly thought-about a symptom or manifestation of psychiatric illness. It was thought that the affected person retained stools either consciously or subconsciously as a method to rebel in opposition to, please, or anger caretakers. Idiopathic constipation with or without encopresis may compress the bladder by a dilated rectum, thus inflicting stasis and urinary tract infections. It should be suspected in any toddler presenting with constipation and a historical past of extended neonatal jaundice. Neurologic Disease Children with neurologic illness may have constipation for lots of causes, including poor intestinal motility, lack of dietary fiber, and poor awareness of rectal vault distention with stool retention. Any illness affecting the spinal wire or sacral nerves, degenerative muscle illnesses, cerebral palsy, and demyelinating diseases can end result in constipation. Medication-Related Constipation A complete medication historical past may reveal substances that can trigger constipation (see Table 16. A detailed historical past of bowel patterns identifies many children with regular bowel movements whose mother and father want reassurance. The historical past should embrace a evaluate of all medicines and a seek for an associated persistent illness, such as a metabolic or neurologic illness. This complete historical past, mixed with a careful physical examination, together with the spine and sacral area, the placement of the anus, and a digital rectal examination, ought to alert the doctor to the necessity for additional evaluation. Red flags embody onset within the neonatal interval, progress failure, and extended jaundice within the neonatal interval. Distinguishing options related to Hirschsprung illness are listed in Table 16. At what age is a suction rectal biopsy less more likely to provide sufficient tissue for identification of ganglion cells The anal position index: a easy methodology to define the traditional position of the anus within the neonate. Urological manifestations related to chronic intestinal pseudo-obstructions in youngsters. Comparison of breast- and formulafed normal newborns in time to first stool and urine. Densmore An stomach mass or abdominal fullness in a toddler normally becomes apparent when it enlarges sufficient to be visualized during bathing or palpable on physical examination. Hepatomegaly and splenomegaly typically characterize systemic diseases corresponding to infection, hemolysis, storage disease, or malignancy. A baby with an abdominal mass requires a prompt and thorough work-up with testing guided by historical past, bodily examination findings, age, and gender. Early surgical referral might assist on this work-up following a directed screening method. The period and character of related signs are necessary for narrowing the differential analysis. A history of abdominal trauma should be elicited, as stable organ injuries may end in hematoma, seroma, persistent pseudocyst, or arteriovenous malformation. Infectious illness could have sequelae of cyst, lymphadenopathy, or intraabdominal abscess. A family and sexual historical past are additionally pertinent, notably in adolescent females. Modern prenatal imaging regularly identifies congenital malformations and neoplasms, requiring postnatal imaging and surgical assessment. Physical Examination A complete physical exam should be performed in children with abdominal masses. Attention must be paid to the overall situation of the child and to indicators of metastatic disease. Enlarged lymph nodes and their areas must be famous, the pores and skin inspected, and the lungs and heart auscultated. Extremities must be evaluated for proof of swelling, venous phlegmasia, or evidence of embolic disease. Genitourinary exam ought to make observe of any inappropriate virilization, testicular changes, and hymenal patency within the case of a feminine with a low pelvic mass. In addition, a neurologic examination could reveal indicators of nervous system involvement. The eyes must be carefully inspected for periorbital ecchymosis, proptosis, squint, opsoclonusmyoclonus syndrome, heterochromia of the iris, Horner syndrome, and scleral icterus. To efficiently carry out belly palpation in a baby, the doctor must approach the patient calmly and gently, as essentially the most dependable exams are accomplished in cooperative and relaxed kids. Creative play is typically necessary, with using pacifiers or bottles to distract the child from the examination. With the affected person within the supine place, the symmetry of the stomach must be inspected, and any visible lots or the presence of ascites must be famous. A very enlarged spleen is incessantly visible, with fullness of the left facet of the stomach. The presence of tense fluid-filled hernias or prominent periumbilical veins as sequelae of portal hypertension should be famous. The mass must be localized, and its measurement, form, texture, mobility, tenderness, and relation to midline famous. Dull visceral ache performed by gradual C nerve fibers may be reported for inflammatory processes in the vascular distributions of the celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric arteries and referred to the epigastrium, umbilical area, or hypogastrium, respectively.
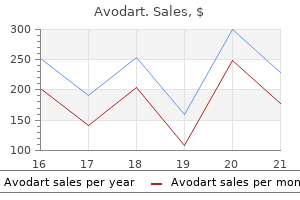
Avodart 0.5 mg cheap on line
Boys are more probably to medicine 5325 order avodart 0.5 mg on line exhibit acts of violence medicine expiration dates avodart 0.5 mg buy fast delivery, similar to combating and stealing, than are women, who are extra probably to exhibit truancy, runaway habits, and high-risk sexual exercise. The earlier the onset of conduct dysfunction, the greater the chance of creating antisocial character disorder as an grownup. Although the trigger of conduct disorder is unknown, each genetic and psychosocial factors play a job. A historical past of parental rejection, tough toddler temperament, bodily or sexual abuse, early institutional dwelling, and lack of applicable discipline are associated with the development of conduct disorder. A biochemical or genetic trigger for this condition has been postulated because of the high prevalence of this condition in households with psychiatric disorders. The analysis of any affected person with a disruption in mood should embrace an evaluation of the risk of suicide. Major depressive disorder is related to critical dangers of both suicide and significant social and educational impairment (see Table 27. Even although a baby may be pervasively sad, he or she can also present with habits issues and irritability. The psychotic signs are typically mood-congruent auditory hallucinations and delusions of guilt, medical illnesses, or deserving punishment. During this era, the affected person has to have no much less than 5 of the next signs: 1. Feelings of worthlessness or guilt Are there signs of mania or hypomania (abnormally elevated mood) The clinician should determine whether the response to the stressor is regular, an adjustment dysfunction, or main depression. The differential diagnosis of major despair encompasses various medical disorders, together with neurologic disorders, endocrine disorders similar to hypothyroidism or hyperparathyroidism, unwanted aspect effects from medicines such as H2-blockers or isotretinoin, and substance abuse or use (see Table 27. Major depressive dysfunction can manifest at any age; however, most patients current in early maturity. Children usually present with somatic complaints, social withdrawal, and irritability, whereas adolescents often present with psychomotor retardation, ideas of guilt and worthlessness, and excessive sleep. Approximately 15% of kids with major depression finally develop bipolar problems. Fifty % of youngsters with major depression have multiple episodes, regularly related to important stressors. Approximately 25% of patients with sure continual medical circumstances corresponding to cancer or diabetes develop main depressive dysfunction through the course of the illness. The primary problem in diagnosing major depression is that the gravity of the depressive temper is usually not always obvious to the mother or father and the clinician. Given that youngsters and adolescents usually current with irritability, sullenness, or mean-spiritedness, the dad and mom and/or clinician could attribute this habits to typical adolescent habits. Obtain a radical family history for signs and formal diagnoses of mood issues. In the overwhelming majority of cycles, a minimum of four of the next symptoms: marked affective lability (mood swings, elevated sensitivity to rejection), irritability or anger, increased interpersonal conflicts, 427 depressed mood, emotions of hopelessness or self-deprecating thoughts, anxiousness, tension 2. At least 1 of the following: decreased interest in activities, problem concentrating, lack of energy, change in appetite, change in sleep, sense of being out of control, bodily symptoms of breast tenderness, joint pain, bloating, or weight gain three. Symptoms present throughout nearly all of cycles over the yr prior the severity of symptoms is much like that in other psychiatric issues, corresponding to major depression or generalized nervousness dysfunction, although the length of symptoms is shorter. Nonetheless, signs do have to be severe and cause marked impairment in functioning in order to fulfill diagnostic criteria. To affirm the prognosis, daily prospective symptom rankings are required for at least 2 cycles. Whereas the latter check with the negative consequences of substance use over time, the substanceinduced problems check with the quick effects of substance use- intoxication and withdrawal-and to the substance-induced psychological problems, which embody psychotic problems, anxiousness disorders, depressive disorders, bipolar and related issues, obsessivecompulsive and related problems, sleep disorders, sexual dysfunction, delirium, and neurocognitive problems. While symptoms might abate as the pharmacologic exercise of the substance abates, repeated use might result in continual adjustments in neurophysiology, and as such, behavioral effects might persist even when the substance is not used. The patient interview ought to include time to speak with the patient individually, and not using a mother or father or other caregiver current, in order to establish rapport, to incorporate the methods of normalizing and remaining non-judgmental, and to encourage a patient to discuss their substance use. Adjustment dysfunction is an extreme or maladaptive response to a stressor, and analysis is contingent upon the popularity of a particular stressor. Typical stressors for kids and adolescents include separations, painful accidents, illness, hospitalization or surgery, parental divorce, change of residency, educational failure, and conflict with peers. Affected patients could also be at elevated threat for suicide, significantly if social and/ or academic impairment are severe. If the stressor is an sickness or its remedy, the morbidity of the medical situation could improve as a consequence of noncompliance. Unstable and intense relationships with extremes of idolization and devaluation three. Significant impulsivity in at least 2 areas that are doubtlessly selfdamaging: spending, sexual exercise, substance abuse, reckless driving, or binge consuming 5. Transient, stress-related paranoia or dissociation Both genetic and psychosocial factors are believed to be causative. Risk elements for borderline persona dysfunction embrace a history of abuse, neglect, or early parental loss. The median inhabitants prevalence is approximately 6% in main care settings and is as excessive as 10% in outpatient psychological well being clinics. Mania manifests acutely, results in important practical impairments, and is characterised by racing ideas, distractibility, delusions of grandeur, and different disturbances in considering. A manic episode is outlined as an abnormally elevated, euphoric, expansive, or irritable mood for at least 1 week except treated. This temper disturbance is associated with no less than 3 of the next signs or four if the temper is irritable: 1. Reckless pursuit of pleasure the signs of a hypomanic episode are the identical, although are current for a shorter duration. Cyclothymic disorder is a persistent, cyclic sickness of hypomania and depressive signs without episodes of main depression. Approximately 15% of adolescents with recurrent major depression eventually develop bipolar sicknesses. The differential diagnosis of the bipolar problems consists of schizophrenia and medical situations that cause changes in psychological standing, particularly thyroid problems, Cushing disease, and multiple sclerosis (see Table 27. Substance-induced mood disorders must also be thought-about, particularly those associated with cocaine, tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. The clinician should get hold of an in depth family historical past as bipolar disorder incessantly runs in households. Because the condition is often undiagnosed in mother and father, the questions must be directed toward the presence of the symptoms for bipolar disorders. The following principles should guide the analysis of patients with signs of depression or mania: 1. Assess for drug and/or alcohol use as substances could induce bipolar disorder, and substance use is incessantly a comorbid situation.
0.5 mg avodart cheap with amex
Scleral icterus could additionally be delicate however can be the primary sign of liver illness and could additionally be more simply appreciated than jaundice in darker-skinned people symptoms you are pregnant cheap 0.5 mg avodart fast delivery. Mallory-Weiss tears are associated with repeated forceful vomiting from a variety of causes medications memory loss 0.5 mg avodart order fast delivery. The forcefulness of the vomiting causes a tear in the distal esophagus on the degree of the decrease esophageal sphincter. The historical past is usually considered one of frequent nonbloody vomiting that then turns into hematemesis. Children with identified or unknown liver illness can develop esophageal varices that will result in large-volume hematemesis and melena (or hematochezia if bleeding is brisk). Ulcers, although uncommon, can also result in significant blood loss and may be associated to H. Physical Examination Physical examination in any affected person with gastrointestinal bleeding must begin with assessment of hemodynamic standing. Local intense tenderness, fever, and erythema of the perianal area might counsel group A -hemolytic streptococcus an infection. Infants and toddlers might have a palpable right decrease quadrant stomach mass, which suggests intussusception. Skin examination could present purpura which, although not at all times current initially, is seen in Henoch-Sch�nlein purpura; it might also be seen in hemolytic uremic syndrome. Erythema nodosum or pyoderma gangrenosum is present in approximately 3% of youngsters with inflammatory bowel illness and may correlate with illness severity. Severe, acute stomach pain is usually present in sufferers with vascular compromise, similar to in intussusception, midgut volvulus, and bowel ischemia. Growth failure is suggestive of inflammatory bowel disease, particularly Crohn disease; constipation points to the potential of an anal fissure (see Chapter 16) or Hirschsprung illness with enterocolitis. Information relating to journey (either by the affected person or by visitors), sick contacts, daycare exposure, camping, and antibiotic exposure might reveal potential infectious causes. Family historical past of polyps or colon most cancers is necessary given the inherited polyposis syndromes, as is a household history of inflammatory bowel disease. Differential Diagnosis Anal fissures are in all probability the most frequent cause of streaks of shiny red blood blended with stool. The bleeding could additionally be related to hard bowel movements however could occur from straining with regular bowel actions. There can be an association with group A streptococcal perianal cellulitis and bleeding. Anal fissure may be a manifestation of milk protein allergy with resultant perianal irritation and subsequent constipation to keep away from painful defecation. More usually, a milk protein allergy will present with specks of blood within the stool. There may be a history of increasing frequency and quantity of blood and mucus within the stool. The toddler may exhibit cramping with bowel actions and vomiting may be a part of the presentation. Ischemic bowel illness, together with necrotizing enterocolitis and volvulus, might lead to rectal bleeding and an acutely ill, sick-appearing neonate or infant. Risk factors for necrotizing enterocolitis include prematurity, cardiac surgical procedure, polycythemia, continual diarrhea, and gastrointestinal malformations. There may be cramping ache earlier than and in the course of the bowel motion on account of the colitis. Common pathogens embody Salmonella and Shigella organisms, especially with dysentery type stools, however E. Clostridium difficile is a standard explanation for hematochezia in older children however can also be found in wholesome infants without inflicting illness due to lack of toxin receptors within the immature colon. For young kids, intussusception and Meckel diverticulum are common causes of hematochezia. The hallmark of intussusception is the presence of "currant jelly" stools related to colicky belly pain, lethargy, or irritability. Meckel diverticulum happens in 1-3% of the inhabitants and manifests by the age of two years in about 50% of patients. Bleeding results from mucosal ulceration secondary to secretion of gastric acid or pepsin from ectopic gastric or pancreatic tissue, respectively, within the tip of the diverticulum. Juvenile polyps additionally present with painless rectal bleeding but are unusual in children beneath 1 year of age with peak incidence between ages 5 and seven years. Most juvenile polyps occur in the distal colon and should trigger bleeding from autoamputation as they outgrow their blood provide. In older youngsters, inflammatory bowel illness turns into a extra widespread cause of hematochezia. Blood is present in 100 percent of 239 circumstances of ulcerative colitis however in solely 30-50% of circumstances of Crohn disease. Inflammatory bowel disease is generally accompanied by fever, weight loss, and rectal bleeding (see Chapter 11). It is commonly accompanied by cramping abdominal pain, purpuric rash (palpable purpura), joint swelling, scalp edema (infants and toddlers), and sometimes, nephritis (see Chapter 20). Laboratory Evaluation Initial laboratory evaluation should include an entire blood rely with differential and platelet depend, coagulation profile, and a complete metabolic profile with complete and direct bilirubin (Table 13. Patients with medical signs of great blood loss should have a blood typing with cross match despatched. In sufferers with decrease gastrointestinal bleeding, stool ought to be sent for evaluation of infectious causes. Urinalysis could additionally be useful in sufferers with hematochezia with suspicion for hemolytic uremic syndrome. Radiographs Abdominal radiographs ought to be obtained in all infants with acute hematochezia to search for pneumoperitoneum, pneumatosis intestinalis, or hepatic portal vein gas suggesting necrotizing enterocolitis. B, Longitudinal aircraft exhibits inner bowel loops (white arrows) telescoping by way of outer bowel loops (black arrows). Small bowel follow-through examination permits analysis of the small bowel from the ligament of Treitz to the ileocecal valve. In instances of intussusception, the enema not only aids in diagnosis but may be therapeutic. Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis could also be suggested by results of this check, however endoscopy is critical for histologic affirmation of these diagnoses. Abdominal Ultrasound An ultrasound could additionally be helpful in sufferers with suspected liver disease to evaluate for portal hypertension. Patients have to be awake and in a place to stay nonetheless through the prolonged study, which limits its utility in younger sufferers. Arrow signifies irregular area of elevated uptake in decrease stomach above bladder, in maintaining with gastric mucosa containing Meckel diverticulum.
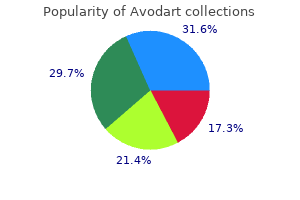
Purchase avodart 0.5 mg otc
Neuroimaging ought to be considered prior to medicine woman cast discount 0.5 mg avodart mastercard lumbar puncture medications keppra purchase avodart 0.5 mg otc, because of risk of herniation with space-occupying lesions. The indicators and symptoms of periorbital cellulitis are periorbital redness and tenderness, whereas in orbital cellulitis, the affected person can also have chemosis, proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, and visual loss. Children affected by Lyme illness commonly have headache in conjunction with different systemic symptoms. Lyme disease may cause an indolent lymphocytic meningitis, or might cause an isolated elevated intracranial pressure in the absence of different findings that, if left untreated, might lead to everlasting imaginative and prescient loss. Headaches and/or Facial Pain Related to Dysfunction of Head and Neck Structures (Table 28. Abnormal extraocular actions ought to prompt neuroimaging to consider for possible intracranial lesions. A corneal abrasion must be suspected in the irritable toddler and in the patient with excruciating eye pain. Corneal irritation, keratoconjunctivitis sicca, and recurrent erosion syndrome could current with recurrent eye ache that must be differentiated from cluster headaches. Optic neuritis (inflammation of the optic nerve) often causes ipsilateral retro-orbital pain. Optic neuritis might happen as a single entity, or it might be a part of the manifestation of a number of sclerosis. The ophthalmologic examination reveals papillitis, an afferent pupillary defect, and decreased visual acuity. A neuroimaging research must be performed to absolutely evaluate the orbit and optic nerve and to rule out multiple sclerosis. When the frontal or maxillary sinuses are involved, pain is frontal or orbital in location. When the ethmoid or sphenoid sinuses are contaminated, the headache may be frontal or occipital. Signs and signs of sinusitis embody purulent rhinorrhea, halitosis, cough, tenderness to palpation over the sinuses or enamel, and fever. Dental abscesses could produce complications which might be aching or stabbing, and may happen as a complication of dental caries, tooth extractions, or root canal procedures. Physical examination may be regular or might reveal gingival swelling, redness, or pain. Palpating each tooth individually with a tongue blade may reveal the supply of ache. Some patients report fixed pain, whereas others have pain only with jaw movement. Psychologic Factors There is a high fee of comorbid psychiatric diagnoses in kids with headaches, of which anxiety and melancholy are the most typical. Primary headaches are more generally seen in kids with a historical past of psychiatric issues. Consequently, screening for mental health symptoms should happen at the facet of the medical historical past. History should also goal to decide child coping abilities, household relationships, and parental reactions to pain. Headaches associated with conversion disorder are very tough to diagnose and treat appropriately. The frequency and severity of these complications enhance with out lasting relief from any pharmacologic or physical remedy. Secondary tension-type headache ache could occur, which additional complicates the analysis. The physician with a pre-established rapport with the household is clearly better off in convincing the family that no physical cause exists for the complications. The origins of a conversion disorder are tough to uncover and require the finesse of an skilled therapist. Psychologic intervention is necessary, not solely to determine the source of the issue but also to offer applicable counseling. Most youngsters who present with headaches may have a benign secondary headache or the first headache issues of tension-type headache or migraine. However, the clinician should at all times contemplate circumstances related to significant morbidity or mortality within the evaluation of each affected person with a headache. A thorough history and physical examination are one of the best tools to help the clinician in determining which sufferers have a severe and lifethreatening trigger for their headaches. Certain symptoms ought to be thought of red flags and immediate additional analysis (see Tables 28. If headache persists, children require continued follow-up and ongoing bodily examination assessments. Maintenance of a headache diary for sufferers with frequent or chronic complications may be invaluable in figuring out the diagnosis and assessing the response to therapy. Assessment of complications requires a strong patient-physician relationship so as to present continued review of related symptoms, ongoing assessments, appropriate evaluation, consideration of psychosocial factors, and reassurance when indicated. Prediction of Lyme meningitis in kids from a Lyme disease-endemic region: A logistic-regression model utilizing historical past, physical, and laboratory findings. Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Practice parameter: Evaluation of kids and adolescents with recurrent headaches: report of the quality requirements subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the apply committee of the Child Neurology Society. Practice parameter: the utility of neuroimaging in the analysis of headache in patients with normal neurologic examinations (summary statement). Primary versus secondary headache in children: a frequent diagnostic challenge in medical routine. Headache and neck pain in spontaneous internal carotid and vertebral artery dissections. Hypotonia affects children of all ages and may be acute or persistent, progressive or static, isolated or part of a posh scientific state of affairs, and should or will not be related to weak point. The analysis of kids with hypotonia could be simplified by a thoughtful, analytic strategy to the differential clues which would possibly be helpful in figuring out an underlying cause starting with detailed common and neurologic examinations (Table 29. Localizing the lesion primarily based on examination at the aspect of laboratory, genetic, and imaging research is key to arriving at a diagnosis (Table 29. The evaluation of muscle tone can be made by a number of observations, including: � Evaluation of spontaneous posture � Extent of mobility of joints � Response to flapping of distal extremities � Response to postural adjustments the method of evaluating muscle tone and energy is determined by the age of the patient. Muscle tone is defined as the resistance experienced by the examiner to movement of limbs about joints. Postural tone is that skilled by the regular flexion or extension of a joint and is attributable to the resultant uniform resistance of muscle to passive movement. Phasic tone is the catch experienced when an extremity is rapidly flexed or extended. The anatomic structures answerable for muscle tone are contained in a closed circuit shaped by the muscle spindle, which is linked to the spinal wire by sensory afferent pathways. The sensory afferent fibers synapse instantly or indirectly with anterior horn and motor neurons.
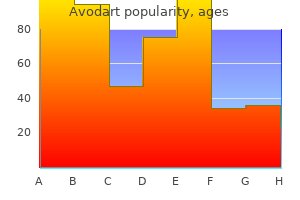
Discount avodart 0.5 mg
Regional lymphadenopathy normally reflects pathologic processes throughout the lymphatic drainage distribution of that particular nodal chain (see Table 36 medicine shoppe discount avodart 0.5 mg free shipping. The presence of palpable supraclavicular nodes is commonly a purple flag for a serious illness corresponding to malignancy medicine reaction buy avodart 0.5 mg with visa. Supraclavicular nodes which may be palpated on the proper side often mirror a mediastinal tumor or invasive mediastinal an infection, such as histoplasmosis. Supraclavicular nodes on the left aspect are sometimes the outcomes of metastatic unfold of an stomach tumor. Epitrochlear nodes, if unilateral, generally indicate the hand or arm as a supply of distal an infection; nevertheless, palpable bilateral epitrochlear lymph nodes usually mirror systemic sickness, similar to syphilis, sarcoidosis, or lymphoma. Significantly enlarged inguinal nodes can also be present with sexually transmitted infections, corresponding to syphilis, chlamydial urethritis, lymphogranuloma venereum, or with urinary tract infection, lymphoma, or stomach tumors. Mediastinal adenopathy (or mass) could additionally be detected by the way, or secondary to chest symptoms, or in the course of the analysis of peripheral however generalized lymphadenopathy. Physical Examination Physical examination ought to assess general appearance and look for signs or symptoms that may reveal the underlying cause of lymphadenopathy. Examination of the lymphatic system ought to establish the dimensions, quality, and distribution of any abnormal lymph nodes and should assess for the presence of tenderness or modifications within the overlying pores and skin or surrounding tissues. Differential Diagnosis the differential analysis of lymphadenopathy is developed in a stepwise trend, first by determining whether or not the lymphadenopathy is regional or generalized. Next, the time course of the lymphadenopathy should be defined as acute or as continual, defined as being current for a interval of greater than four weeks. Children presenting with prolonged diffuse lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly or splenomegaly, weight loss, night time sweats, fevers, recurrent infections, or failure to thrive must be more completely studied. Only after the entire blood cell count and differential and chest radiograph are analyzed should different diagnostic studies be thought of. Regional Lymphadenopathy the standard baby with acute regional lymphadenopathy presents with enlarged nodes, commonly in the cervical area. A thorough historical past and cautious bodily examination ought to reveal whether nodes are definitively concerned, versus different nonnodal buildings, such because the parotid gland. In many instances, no different abnormalities are discovered on examination, and systemic signs are minimal. Laboratory checks should embody a complete blood cell rely and differential as nicely as measurement of the erythrocyte sedimentation price and the C-reactive protein. In the kid with fever and a tender cervical lymph node, oral antibiotics (with activity against mouth flora, streptococci, and staphylococci) must be started; if the lymphadenopathy persists or worsens, intravenous antibiotics are indicated. In distinction, if the lymphadenopathy continues or becomes frank lymphadenitis with erythema and tenderness regardless of antimicrobial remedy, additional work-up is indicated. If an abscess is discovered, incision and drainage, adopted by appropriate bacterial and mycobacterial cultures and stains, are acceptable. Differential Diagnosis of Head and Neck Lymphadenopathy: Head and Neck Masses Several congenital and bought lesions of other head and neck buildings, many of which are benign, could mimic lymphadenopathy and deserve consideration. History and physical examination ought to present adequate info to arrive at an acceptable differential analysis and evaluation strategy of these mimics. Evaluation and Management Strategies Many beforehand wholesome youngsters with acute lymphadenopathy require few, if any, laboratory or imaging research. No laboratory testing could also be required for well-appearing kids whose acute, localized adenopathy can be attributed to an an infection within the neighborhood of the node. Acute cervical adenopathy accompanying pharyngitis in children older than 18 months could necessitate a throat culture for group A Streptococcus. Generalized Lymphadenopathy In the kid with generalized lymphadenopathy, the trigger could also be infectious, immunologic, or malignant. Drugs might trigger serum illness but may also produce hypersensitivity reactions with ensuing generalized lymphadenopathy. Medications associated with drug-induced lymphadenopathy embrace allopurinol, atenolol, captopril, carbamazepine, gold, hydralazine, penicillins, phenytoin, primidone, procainamide, pyrimethamine, quinidine, sulfonamides, sulindac, and tetracyclines. An abnormal complete blood cell count demonstrating anemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia, or radiologic evidence of mediastinal adenopathy or pleural illness is highly suggestive of malignancy. Excision of a node is preferred in some instances so as to get hold of adequate tissue for pathologic examine, stains, or cultures. Pharyngeal infection is the commonest reason for regional lymphadenopathy in children (see Chapter 1). Many of those pharyngeal infections are related to cervical lymphadenopathy and are viral in origin. Frequent viral causes include adenovirus, parainfluenza, influenza, rhinovirus, and enterovirus. The chief grievance normally contains ache with swallowing and with speaking, as well as tender, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck. Systemic manifestations, corresponding to fever, myalgia, chills, and rhinorrhea may also be present. An examination of the throat typically reveals a symmetrically erythematous posterior oropharynx with enlarged tonsils that often contain exudates. Herpes stomatitis with mucocutaneous involvement and herpes pharyngitis with oropharyngeal vesicles are also related to bilaterally enlarged, tender, non-erythematous cervical nodes. Bacterial an infection of the pharynx can be commonly associated with enlarged, tender cervical lymph nodes. Other bacteria could cause pharyngitis and cervical adenopathy, including non�group A streptococci and anaerobic organisms, corresponding to Fusobacterium species. Anaerobic organisms can lead to painful oral gingivitis or stomatitis and pharyngitis (Vincent angina) that may progress to peritonsillar abscess. Asymmetry in the tonsils and surrounding tissues, as nicely as deviation of the uvula away from the affected facet could additionally be seen with peritonsillar abscesses, along with unilateral tender, enlarged cervical lymph nodes ipsilateral to the abscess. Complications of acute bacterial pharyngitis may embrace Lemierre syndrome, the findings of which include high fever and unilateral, lateral neck swelling which may be confused with adenopathy. Lemierre syndrome is due to septic thrombosis of the interior jugular vein (and pulmonary septic emboli), often brought on by invasion of the bloodstream by Fusobacterium organisms, and will result in immediate hospitalization, blood cultures, therapy with intravenous antibiotics, and imaging of the interior jugular vein via Doppler move ultrasonography or contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Acute cervical lymphadenitis-inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes with tender enlargement-is most likely to happen with group A streptococcal or Staphylococcus aureus infection. There could or will not be a historical past of sore throat or pharyngeal irritation on examination. Infection with different oral bacteria, together with non�group A streptococci and anaerobes corresponding to Fusobacterium or Arcanobacterium species may occur, presumably with the pharynx because the portal of entry. Usually, these nodes quickly diminish in size after institution of acceptable antibiotic therapy, providing a point of retrospective analysis whereas concurrently being therapeutic. Acute suppurative cervical adenitis could be seen in infections of the face and scalp and is usually caused by an infection with group A streptococci or S. Management of suppuration includes incision and drainage or excision of the suppurative node. Gram stain and bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial cultures of the drainage ought to be obtained. Total excision ought to be carried out if atypical mycobacterial an infection is suspected, as a result of draining fistulas could type if a needle biopsy or partial resection is performed.
Syndromes
- Limit cholesterol intake to less than 300 mg/day.
- Biopsy of the biliary tract
- Two weeks before surgery you may be asked to stop taking drugs that make it harder for your blood to clot. These include aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve), blood thinners such as warfarin (Coumadin), and other drugs.
- Joint or muscle aches
- Hypothermia
- Adrenal insufficiency is not properly treated
- Type 1 (also called erythrocyte reductase deficiency) occurs when red blood cells lack the enzyme.
- MRI of the kidney arteries, which can show a lack of blood flow to the affected kidney
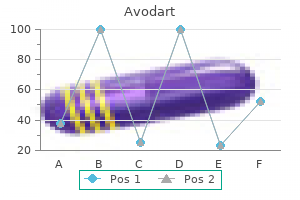
Avodart 0.5 mg buy cheap
The essential options that distinguish such behavior from epileptic exercise are the setting during which it occurs medicine vs surgery buy avodart 0.5 mg with visa, the variable content material and length of the "assaults symptoms zithromax 0.5 mg avodart effective," and the entire failure of the episodes to interrupt more stimulating actions. Acute Symptomatic Seizures and Occasional Seizures Febrile convulsions stay one of the widespread causes of occasional seizures in early childhood. Head injury is extra frequent in childhood than in infancy, however the record of different potential causes of seizures, together with mind tumor, intracranial an infection, and poisoning, could be very comparable. In addition, some metabolic and neurodegenerative problems manifest in childhood, not in infancy (Table 30. There is a bunch of idiopathic partial epilepsies beginning in children with out abnormalities on neurologic examination or neuroimaging studies, and incessantly, with a family history of epilepsy. The seizures are brief and stereotyped in a person, though they vary among sufferers. The sharp waves or spikes have a characteristic construction and are sometimes very frequent, increasing throughout sleep. Brief hemifacial motor seizures with anarthria and drooling are typical, incessantly when popping out of sleep. Consciousness is often preserved, although this is in all probability not true with longer seizures. A somatosensory aura involving the tongue, cheek, or gums might precede the motor seizure. Many seizures happen at evening as tonic-clonic seizures, presumably secondary generalized with unwitnessed partial onset. If seizures are rare and nocturnal, the option of no treatment must be mentioned. Benign childhood epilepsy with occipital paroxysms varieties a subset of idiopathic partial epilepsies of childhood. There are 2 kinds of this subset: 1 with early onset (peak onset at 3-5 years), nocturnal seizures with tonic eye deviation, and vomiting; and one other with later onset (peak onset at 7-9 years) characterised by seizures starting with visible symptoms, which is according to an occipital origin. These are also referred to as Panayiotopoulos syndrome and the benign occipital epilepsy of Gastaut, respectively. Hemiclonic seizures or the automatisms of temporal lobe advanced seizures typically follow according to whether or not the seizure spreads to suprasylvian or infrasylvian regions. A extreme headache could follow the visual auras and a diagnosis of childhood migraine is commonly considered. The discharges are current when the eyes are closed and will disappear with eye opening. There is some controversy in regards to the specificity of the electroclinical options and whether these instances are true variants of benign childhood epilepsy. The absence seizures are easy, or more often, sophisticated with delicate automatisms or different motor features. Absence seizures are very frequent, occurring every day, however they generally respond well to antiepileptic therapy. Prognosis is usually favorable, with remission in approximately 80% of instances by late adolescence. They typically develop years after the onset of absences and should seem after remission from the absence seizures. Treatment with ethosuximide or valproate controls absence seizures in most patients. However, ethosuximide presents no safety towards tonic-clonic seizures, whereas valproate can be effective towards tonic-clonic seizures. If either ethosuximide or valproate proves ineffective after an adequate trial at most tolerated doses, a trial of the opposite should be commenced. Combination ethosuximide and valproate therapy has been effective in some patients with absence seizures not controlled by both drug alone. Alternatives may include lamotrigine, topiramate, or zonisamide; medicines corresponding to carbamazepine or phenytoin which may be specific for focalonset seizures will in fact exacerbate absence seizures. Epilepsia partialis continua describes steady focal motor seizures often manifesting as repetitive clonic jerks of the face, upper limb, decrease limb, or larger portion of one-half of the body that proceed in this localized manner for hours to days or months. These seizures are attributable to cortical processes that immediately overlie the motor cortex that include vascular lesions, focal cortical dysplasia, neoplasms, and unidentified focal areas of atrophy. The danger of motor and sensory deficits limits attainable resections, and cautious mapping of the positioning of seizure onset and its relationship to functional cortex is required. Rasmussen encephalitis is a clinically outlined syndrome of predominantly hemispheric cerebral dysfunction, with onset of seizures between 2 and 10 years of age. The disorder is characterized by a progressive hemiparesis, language disturbances if the dominant hemisphere is affected, and mental decline. Progressive hemispheric atrophy, maximal within the central, temporal, and frontal areas, may be documented with neuroimaging research. Pathologic specimens show nonspecific changes suggestive of encephalitis, though no etiologic agent has been recognized. Worsening of the neurologic deficits could be anticipated over time, though the seizures might lessen and even "burn out. However, important morbidity and mortality charges are associated with the surgery, and lesion. In every, the epileptiform exercise is believed to disturb synaptogenesis and connectivity in the maturing mind. Epileptic aphasia, or Landau-Kleffner syndrome, begins in a previously normal youngster (peak age at onset, 5-7 years) with the regression of language. There is extreme auditory agnosia, speech may disappear, and the kid often appears to be deaf as a end result of impairment of cortical processing of sound and language. There is usually a marked deterioration in conduct as properly, and social interactions turn into altered. Childhood psychosis and the autistic spectrum issues are often considered within the differential prognosis, although the age of behavioral regression is atypical for these problems and should be a red flag when this scientific historical past presents. The most typical seizure sort in children with focal epilepsy with an recognized trigger is the focal dyscognitive seizure. Focal dyscognitive seizures might arise from temporal, frontal, parietal, or occipital lobes, but most frequently from the temporal lobe. The causes of focal epilepsy in childhood are various and embrace start asphyxia, later anoxic episodes, head damage, neoplasms, an infection, malformations of cortical growth, the cerebral lesions of neurocutaneous syndromes, vascular malformations, and cerebral infarction. Focal epilepsy generally evolves as a medically refractory disorder; in some sufferers, it can be amenable to surgical resection. The investigation of children for epilepsy surgery is a extremely specialized course of that follows documentation of medical intractability, which is outlined as failure of a minimum of 2 appropriately chosen and optimized antiepileptic medications. Childhood absence epilepsy is an idiopathic generalized epilepsy starting in beforehand normal kids between 4 and 12 years of age, with peak incidence at 6-7 years of age; women are extra incessantly affected. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome is characterised by generalized seizures and epileptiform discharges with delayed psychological improvement and behavioral issues beginning between the ages of 1 and 8 years.
Generic 0.5 mg avodart
Approximately 95% of youngsters with an recognized trigger (structural symptoms of anemia trusted 0.5 mg avodart, genetic medicine cat herbs buy avodart 0.5 mg otc, or metabolic) have a prognosis of moderate-to-severe neurologic damage, together with refractory epilepsy, cognitive impairment, or everlasting developmental sequelae. This subset of sufferers is prone to have a much better longterm outcome: 38% of those patients are regular or mildly impaired, as compared with only 5% of symptomatic sufferers. A distinctive subset of patients who could develop infantile spasms is children with trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). Persistence of the epilepsy in a lot of the patients is associated with loss of the spasms and development of different seizure sorts, corresponding to tonic seizures, focal seizures, and tonic-clonic seizures. Seizures very comparable in appearance to childish spasms (brief myoclonic or tonic seizures occurring in clusters) may recur later in childhood, and these are referred to as epileptic spasms. Both remedy regimens generally last 8-12 weeks, and both require frequent monitoring for side effects. The pediatrician may be known as upon to monitor electrolytes, blood pressures, or signs of sickness whereas the kid is underneath therapy. Live vaccinations are typically held for 6-12 months after a course of immunomodulatory therapy. However, this medication is at present strictly regulated in its prescription, and sufferers on vigabatrin require examinations by an ophthalmologist each three months as a result of the small risk of everlasting peripheral vision loss with prolonged use of the treatment. Many different antiepileptic medications, together with topiramate, lamotrigine, valproic acid, and benzodiazepines, have had some efficacy in isolated circumstances, however this response is unpredictable. The youngster could current with febrile or afebrile seizures, usually with normal psychomotor improvement preceding the onset of seizures, and sometimes with a family history of epilepsy. The seizures are generalized or unilateral clonic seizures; myoclonic seizures seem later (and will not be a major feature of the disorder, despite the name), between 8 months and four years of age; and focal seizures and atypical absences could occur. Antiepileptic medicines that may worsen seizures or be ineffective in Dravet syndrome embrace phenytoin, lamotrigine, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, and vigabatrin. Childhood the paroxysmal issues of childhood (2-12 years) are given in Table 30. Typically, there are symptom-free intervals lasting weeks to months, and recurrence is unpredictable. There may be a powerful family historical past of migraine, and there seems to be some overlap of the cyclic vomiting with migraine. Children could have phonic tics (such as tongue clicking or throat clearing), motor tics (such as blinking, sniffing, or shrugging), or any mixture of both. The presentation of migraines in children can also be markedly different than that in adolescents and adults; "migraine equivalents" are paroxysmal disorders which would possibly be strongly associated with the later improvement of migraines and will share related underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms. This temporal association has led to the misunderstanding that the stimulant drugs have caused the tics. Tourette syndrome is recognized when a toddler has had multiple motor tics and at least 1 phonic tic current for longer than 1 year. Other tic disorders can be purely motor or purely phonic, and are categorised based on their symptoms and length (transient vs. Sleepdisorders � Peak presentation: age 2-7 years � Classical features: occurring a number of hours after falling asleep ("round midnight"), nonstereotyped behaviors, screaming, agitation, and inconsolability regardless of being apparently awake, no reminiscence of frightening imagery � Acuity: low � Prognosis: excellent, although kids with frequent episodes may need to be monitored by their mother and father to prevent harm during a panicked state Night terrors and confusional arousals. Night terrors are a standard phenomenon in youngsters and are most frequent in boys aged 5-7 years. Up to 15% of kids younger than 7 years have experienced some type of these episodes. The assaults are characterised by sudden arousal from sleep, typically screaming in terror, and then crying with agitation and tachycardia. There could additionally be vigorous and probably injurious motor activity in older children, such as operating or hitting the bed or wall. The striking characteristic of those episodes is that the child is inconsolable but seemingly awake. Prior sleep deprivation, febrile illness, emotional stress, and some drugs (sedatives/hypnotics, neuroleptics, stimulants, antihistamines) may be precipitants. In distinction to the experience of nightmares, kids are amnestic for the occasions and their misery in night time terrors. Confusional arousals are much less dramatic assaults with related origin from slow-wave sleep and are extra typical in younger kids. Nocturnal frontal lobe seizures occur throughout sleep and can have bizarre hypermotor behaviors similar to rolling, turning, picking, yelling, and fumbling. In school-aged youngsters, benign rolandic epilepsy manifests itself as seizures when popping out of sleep with gurgling, salivation, hemifacial and hemibody twitching, and infrequently partially preserved consciousness of the occasion. Important distinguishing historic components between seizures and parasomnias are the time of onset (seizures: shortly after falling asleep or early in the morning), length (most seizures final 1-2 minutes, and parasomnias can have a significantly longer duration), and any associated tongue bite, urinary incontinence, or insidious behavioral or developmental regression. Approximately 15% of kids have walked in their sleep, especially within the 2-3 years old age group, and a pair of. There is a household history of sleepwalking and other parasomnias in 60-80% of sufferers. These episodes of apparent unresponsiveness and "automatisms" could be mistaken for focal dyscognitive seizures or a postictal state. Repetitive purposeless actions may be carried out by kids on the autism spectrum or with cognitive disabilities. Combined with unresponsiveness, these behaviors could additionally be mistaken for automatisms in focal dyscognitive seizures. The sufferers have a blended seizure dysfunction with multiple seizure sorts; the typical seizures are tonic seizures, atypical absences, and atonic seizures, though sufferers can also have tonic-clonic, myoclonic, and focal dyscognitive seizures. Episodes of status epilepticus are common, and nonconvulsive stupor with steady spike-and-wave discharges or a stuporous state with repeated tonic seizures is typical. The epileptiform abnormalities consist of slow (<3 Hz) spike-and-wave discharges, multifocal spikes, or sharp waves and paroxysmal quick exercise (>10 Hz) in sleep. Valproate ought to be used as a first-line agent for patients with atonic, tonic, and myoclonic seizures and may be helpful with tonic-clonic seizures. Patients with refractory tonic-clonic seizures or focal seizures as properly as generalized seizures may profit from the addition of lamotrigine. Carbamazepine has been reported to exacerbate atypical absence seizures in some sufferers. Felbamate has been reported to improve control of the debilitating tonic or atonic "drop attacks" in sufferers with this syndrome. A main source of morbidity and an important management problem are repeated falls associated with tonic and atonic seizures. Appropriate restriction in day by day actions and the sporting of helmets with face protection are sometimes required. Loss of consciousness with falling is the salient characteristic of syncope (see Chapter 6 and Table 30.
Avodart 0.5 mg generic online
Sufficient blood should be inoculated into the media to detect the low-grade bacteremia of infective endocarditis; extreme blood inoculation could inhibit bacterial progress by continued exercise of leukocytes except the approach entails centrifugation lysis treatment for hemorrhoids generic 0.5 mg avodart overnight delivery. The cultures should be incubated for more than the routine seventy two hours (often 1-2 weeks) medicine and health avodart 0.5 mg best, and the laboratory ought to be notified of the attainable diagnosis in order that laboratory personnel can enrich the media to encourage the growth of fastidious nutrient-dependent organisms. To prevent infective endocarditis, high-risk sufferers, procedures, and components that predispose to bacteremia need to be identified (Table 8. Prophylaxis is reasonable as a outcome of endothelialization of prosthetic material happens within 6 mo after the procedure. Red flags in the neonatal interval include cyanosis or coronary heart failure with or without the presence of other congenital anomalies or syndromes, such as trisomy 21. Such syndromes typically manifest with multiple congenital anomalies, including those involving the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and central nervous methods. Sudden deterioration, cyanosis, or coronary heart failure with rising metabolic acidosis and a reduction in the murmur suggests closure of the ductus arteriosus. Another thing not to miss is the murmur associated with an arteriovenous malformation, such because the cerebral vein of Galen malformation, which manifests with coronary heart failure and a cranial bruit. Finally, obstructed complete anomalous venous return could also be confused with persistent fetal circulation, and it may be tough to establish the diagnosis. Total anomalous venous return is related to fixed, profound cyanosis (PaO2 <35 mm Hg), severe pulmonary venous congestion, and a small coronary heart. Acquired murmurs or symptomatic murmurs that change in high quality ought to counsel acute or recurrent rheumatic fever, or infective endocarditis. Systemic signs and peripheral indicators associated with these problems are suggestive of the analysis. Arthritis (associated with rheumatic fever or endocarditis-induced immune complexes), fever, anemia, leukocytosis, cutaneous manifestations (erythema marginatum and subcutaneous nodules in rheumatic fever; Osler nodes, Janeway lesions, petechiae, and splinter hemorrhages in infective endocarditis), and proof of prior an infection (streptococcal antibodies) or current an infection (positive blood cultures) assist determine the character of the acquired heart disease. Finally, coronary heart murmurs in a standard coronary heart could additionally be caused by hemodynamic elements, corresponding to extreme anemia or thyrotoxicosis. Mortality related to congenital heart defects in the United States: Trends and racial disparities, 19791997. The harmless supraclavicular arterial bruit-utility of shoulder maneuvers in its recognition. The second coronary heart sound: Newer concepts, part I: Normal and broad physiological splitting. Balloon angioplasty of native coarctation: Clinical outcomes and predictors of success. Pulse oximetry screening for important congenital heart defects in asymptomatic newborn babies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cyanotic congenital heart illness with decreased pulmonary blood move in children. Value and limitations of auscultation within the administration of congenital coronary heart disease. Assessment and administration of congenital coronary heart disease in the newborn by the district paediatrician. Prospective comparison of clinical and echocardiographic analysis of rheumatic carditis: Long term follow up of patients with subclinical illness. Correlations amongst clinical presentation, surgical pathologic findings, and hemodynamic sequelae. Variation in group A streptococci and the prevalence of rheumatic fever: A half-century vigil. Morphology, prevalence and medical significance of left ventricular false tendons in adults. Left ventricular false tendons in kids: Prevalence as detected by 2-dimensional echocardiography and scientific significance. Musical murmurs: Clinical implications, long run prognosis, and echo-phonocardiographic options. Physiologic strain differences between the main and branch pulmonary arteries in infants. Bacterial endocarditis in youngsters: Trends in its prognosis, course, and prognosis. Operative intervention in lively endocarditis in children: Report of a series of circumstances and review. Prevention of infective endocarditis: tips from the American Heart Association. A guideline from the American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease Committee, Council on Cardiovascular Disease within the Young, and the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group. Prevention of bacterial endocarditis: Recommendations by the American Heart Association. It is important to have a scientific, stepwise method to the analysis and management of poor growth in younger children and to comply with growth over time. The time period failure to thrive is used to describe development failure that accompanies many pathologic situations as well as psychosocial causes. Children with medical circumstances will usually have psychosocial points related to eating and dysfunctional feeding patterns with caregivers. Children with primarily social or emotional issues around consuming could develop medical consequences of undernutrition. The greatest diagnostic software obtainable to the clinician is a complete history, including food regimen, family, progress (over time) and social histories, and a whole review of systems; and an entire physical examination. Ultimate peak is set by additional components, amongst them charges of bone maturity and pubertal improvement (see Chapter 43). Any imbalance on this energy equation (losing or using more energy than are ingested) results in abnormal growth patterns. Weight is usually affected first, adopted by top and finally head circumference if the power imbalance is extreme and extended in younger children. Growth patterns which have crossed two main percentiles downward on the weight for age charts inside 6 months four. Growth velocity lower than normal for age There are inherent issues with these definitions. Three percent of the population is at or beneath the 3rd percentile, and so those who are rising appropriately per their genetic potential should be differentiated from these with progress problems. The clinician must train appreciable judgment before raising the priority of poor development. Subsequently, they achieve weight at a steady pace of about 1 oz per day for the first three months; gain at half to two thirds that price for the following three months and half to two thirds once more for the subsequent 6 months. This results in a doubling of birthweight by the age of 4-6 months and a tripling earlier than 1 12 months. These three development parameters ought to be plotted on acceptable development charts and monitored for adherence to standard growth rates. Children develop in a stepwise method, but on common their growth pattern follows the accepted curves (see Chapter 43). Stunting is outlined as a baby whose height or size is lower than -2 z-scores because of persistent undernutrition.
Discount 0.5 mg avodart free shipping
Functional constipation tends to produce massive symptoms strep throat avodart 0.5 mg generic free shipping, bulky stools medicine knowledge 0.5 mg avodart cheap mastercard, whereas constipation secondary to Hirschsprung disease or other organic etiologies tends to produce harder, pebble-like, or ribbon-like stools. The evaluation of associated signs and symptoms ought to embrace evaluating for a history of blood within the stool, in addition to for the presence of urinary signs. Bright pink blood on the surface of the stool suggests an anal fissure indicative of straining, which is seen in roughly 25% of patients with constipation. Blood on the periphery of the stool could suggest pathology in the distal colon or anorectal vault. Retention may be secondary to congenital or acquired abnormalities in the neurologic regulation of bladder voiding and could additionally be related to related abnormalities in the regulation of defecation. Alternately, retention may be secondary to urinary tract outflow obstruction, which is secondary to a large stool burden. Incontinence could additionally be as a outcome of a big stool mass distending the rectum and putting stress on the posterior bladder wall, or could indicate overflow incontinence within the setting of a neurogenic bladder. Urinary retention can also be seen in patients with persistent intestinal pseudoobstruction and is assumed to be secondary to autonomic dysregulation. Voluntary relaxation of the puborectalis muscle and the exterior anal sphincter straightens the anorectal angle and permits the child to stool. At least one episode/week of incontinence after the acquisition of toileting abilities three. History of large-diameter stools, which may obstruct the toilet Accompanying symptoms could embody irritability, decreased appetite, and/or early satiety. The accompanying symptoms disappear immediately following passage of a big stool. History of huge diameter stools, which may obstruct the toilet *Criteria fulfilled no much less than as soon as per week for at least 2 mo previous to analysis. Older youngsters might describe discomfort in the decrease stomach and a history of reduction of pain after a stool is handed. A diary recording the passage of stools, the timing of meals, and the onset of abdominal pain over a interval of several days to a couple of weeks can assist in the analysis of constipation and in monitoring of remedy. The personal medical history and the household history might reveal illnesses and situations associated with constipation (Table 16. Parents usually describe a toddler who hides in a nook, with stiffened straight legs, or who may lean into the wall or hold onto a desk whereas "straining. If a fissure is present, a small amount of blood is normally passed with the stool. The baby associates the passage of stools with pain and tries to forestall additional painful episodes by withholding fecal matter. This habits leads to the formation of even larger, tougher stools, that are painful to cross, thus establishing a link between pain and defecation that perpetuates the cycle. Physical Examination Abnormal progress patterns ought to alert the doctor to the potential for underlying natural disease, such as hypothyroidism or celiac disease (see Table 16. Abdominal examination is usually benign; there could additionally be some gentle tenderness within the left decrease quadrant on palpation of a segment of bowel that is full of stool. Stool could additionally be palpable through the belly wall within the sigmoid and descending colon. On occasion, a big, agency fecal mass extends from the symphysis pubis to the umbilicus, which may mimic findings of an abdominal malignancy. A tuft of hair, a dimple, or a palpable defect or mass in this area should immediate consideration of spina bifida occulta or a tethered spinal twine. The presence of a normal anal wink, as elicited by light stroking of the perianal pores and skin with a pointy object, such as a wood tongue blade or the corner of a small bundle of lubricant, gives proof of intact lumbosacral innervation. Presence of a standard cremasteric reflex in males additionally offers proof of intact lumbosacral innervation. The cremaster muscle, innervated by the genitofemoral nerve of the lumbar plexus, sometimes contracts when the observer brushes a finger along the higher floor of the inner thigh, leading to withdrawal superiorly of the ipsilateral testis. The perianal area ought to be examined for proof of fissures suggestive of the passage of enormous, onerous stools. Soiling in the undergarments might point out fecal impaction with overflow incontinence. Measurements could additionally be obtained utilizing calipers or by placing clear plastic tape adjoining to the landmarks and marking with a pen, after which subsequently measuring the gap on the tape. Digital examination is indicated in the analysis of childish constipation, if the cause or diploma of constipation is unclear, or if there are signs of organic illness. If the aganglionic section is brief sufficient, withdrawal of the finger might lead to an explosive launch of stool because the finger acts as a dilator to reach the dilated, ganglion-containing section. Conversely, a dilated rectal vault with a big stool impaction is more suggestive of useful constipation with withholding habits. In a cooperative patient, the examiner can ask the affected person to bear down towards their finger as if making an attempt to push out stool, which should result in relaxation of the anal canal. Endocrinologic disturbances, similar to hypothyroidism, can be related to constipation. If celiac illness (see Chapter 11) is a consideration, serum anti�tissue transglutaminase immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibody ranges should be assessed. A complete IgA level should be carried out concomitantly to exclude IgA deficiency confounding interpretation. If the affected person does have IgA deficiency, anti�tissue transglutaminase IgG levels or esophagogastroduodenoscopy with duodenal biopsies can be carried out. Plain films of the abdomen are not often necessary, although if obtained might demonstrate stool within the giant bowel. This data is occasionally useful in the case of a child with complaints of diarrhea whose symptoms are because of fecal impaction and overflow of liquid stools. Suspected Hirschsprung illness is evaluated radiographically by way of a liquid distinction enema. Neurologic signs are evaluated with magnetic resonance imaging of the backbone and/or mind, notably to assess for proof of spinal dysraphism or a tethered twine. Concerns for intestinal dysmotility may be evaluated with a Sitz marker examine, in which the patient swallows a capsule of radiopaque circular markers and undergoes serial belly radiographs to determine the distribution of the markers. The presence of markers more proximally in the gastrointestinal tract suggests enteric nervous system or neuromuscular pathology. A rectal motility evaluation could additionally be useful in the prognosis and management of chronic constipation. Anorectal manometry can be utilized to evaluate the integrity of the muscles and the innervation of the defecatory mechanism. Hirschsprung disease is unlikely if reflexive relaxation of the internal anal sphincter occurs within the presence of rectal distention. Manometry and electromyography document the presence of paradoxical contraction of the exterior anal sphincter on tried defecation. Anorectal manometry can also be used as a therapeutic modality in biofeedback therapy in sufferers with constipation and encopresis and in sufferers with paradoxical external anal sphincter contraction. Total colonic motility is carried out by putting a catheter in the colon to monitor pressures from the rectum to the cecum.

Purchase avodart 0.5 mg on line
Hemoglobinopathies often happen on account of a single amino acid substitution in - or -globin chains medicine 666 colds avodart 0.5 mg discount amex. The sickle hemoglobinopathy syndromes are a bunch of genetically inherited problems encountered most incessantly in people of African descent medicine the 1975 order avodart 0.5 mg with visa. Thus, a type of sickle cell disease must be thought-about within the differential diagnosis of anemia in any African-American youngster. These problems happen less incessantly in people of Mediterranean or Arabic background. Sickle hemoglobin is characterised by a single amino acid substitution of the -globin chain, specifically valine for glutamic acid in the number 6 position. Approximately 8% of African-Americans are carriers of the hemoglobin S gene, which can be termed sickle cell trait. Spontaneous hematuria might sometimes occur in sickle trait as a result of the induction of sickling within the extremely hypertonic environment of the renal medulla. Patients with sickle cell trait are distinctly not anemic and have a normal peripheral blood smear. The definitive prognosis have to be established by hemoglobin identification methods (Table 37. Diagnosis in newborns is routinely and precisely performed in most areas throughout the United States as a part of state-mandated universal neonatal screening applications. The medical manifestations are extraordinarily broad however generally include (1) persistent hemolytic anemia, (2) vasoocclusion leading to ischemic harm to tissue, and (3) susceptibility to infection (Table 37. Infants younger than 4-6 months normally show no scientific manifestations because of naturally excessive ranges of fetal hemoglobin. By 1-2 years of age, most affected patients have had a specific sickle cell�related manifestation. Patients could appear variably pale and icteric relying on the degree of hemolysis. Gallstones occur frequently and should lead to signs of cholelithiasis, acute cholecystitis, biliary tract obstruction, and/or pancreatitis. Many sufferers have delayed development and pubertal development, but finally obtain normal adult height. Hemoglobin E is seen with appreciable frequency amongst people of Asian descent. When hemoglobin E happens within the double heterozygous state with -thalassemia, sufferers usually have a moderately severe thalassemic syndrome; therefore, genetic counseling is advisable. Hemolysis is normally brisk; thus, most patients are symptomatic and current with pallor, jaundice, fatigue and tachycardia. Cold antibodies (usually IgM) can also be seen in response to viral infections, Mycoplasma pneumoniae and syphilis infections, or in the context of autoimmune issues. Aggressive therapy is really helpful because life-threatening anemia is understood to happen. Corticosteroids (prednisone) must be administered if the patient is discovered to have heat autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Intravenous immunoglobulin and high-dose steroids (methylprednisolone) should be thought-about in severe cases. Frequent hemoglobin monitoring and reticulocyte counts ought to be done to comply with the speed of hemolysis. Recombinant antibodies directed to B lymphocytes corresponding to rituximab have been efficient in refractory cases. Familial genetic issues might manifest in the neonatal period or any time throughout infancy (Table 37. This discovering represents a practical adaptation to the comparatively hypoxic in utero surroundings. This physiologic anemia of infancy is exaggerated in preterm infants whose hemoglobin levels might fall to roughly 7 g/dL at about 1-1. This fall in hemoglobin worth represents a physiologic response to the oxygen-rich extrauterine surroundings. Ocular Gallbladderdisease Renal Cardiomyopathy Legulceration Infections Growthfailure, delayedpuberty Psychologicproblems Neonatal Anemia Caused by Blood Loss Anemia attributable to blood loss is usually obvious. Other etiologies of hemorrhage may be occult and embody intracranial and intrahepatic hematomas. Internal hemorrhage is much more likely to happen in tough, traumatic deliveries. Twin-twin transfusion could happen resulting in anemia in 1 infant and polycythemia in the different. Fetal� maternal hemorrhage is sufficiently extreme to cause anemia in only a small percentage of neonates. Fetal�maternal hemorrhage should all the time be suspected when otherwise unexplained anemia occurs in a newborn. If blood loss is delicate or chronic, infants may appear normal or have mild pallor and tachycardia. In the event of extreme acute blood loss, the newborn could current with indicators of acute illness *Clinical manifestations with sickle cell trait are uncommon however include renal papillary necrosis (hematuria), sudden death on exertion, intraocular hyphema extension, and sickling in unpressurized airplanes. The diploma of anemia is very variable, and the reticulocyte rely is elevated in most sufferers; nonetheless, a minority of sufferers current with a low reticulocyte count due to immune destruction of reticulocytes. Congenital leukemia is a uncommon disorder characterised by infiltration of the bone marrow resulting in anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukocytosis in affiliation with hepatosplenomegaly and infrequently cutaneous leukemic infiltrates manifesting as blue papular lesions ("blueberry muffin" spots). Infants with Down syndrome could present with a medical and hematologic picture identical to that of congenital leukemia, which is a transient myeloproliferative course of that spontaneously remits over a number of months. Infants with hereditary spherocytosis, pyropoikilocytosis, or elliptocytosis might develop anemia and extreme hyperbilirubinemia that necessitates phototherapy and, hardly ever, exchange transfusion. Isoimmune hemolytic anemia is the most typical reason for hemolytic anemia in the newborn. It is attributable to incompatibility including lethargy, tachycardia, hypotension, and respiratory misery. The hemoglobin value is a poor index of the severity of acute blood loss as a result of equilibration of fluid compartments may take 24-36 hours. Blood loss as a reason for anemia should at all times be suspected in instances of obstetric issues, a quantity of births, or tough and traumatic deliveries. In Rh incompatibility, the mother is Rh negative and the infant is Rh optimistic (inherited from the father). If the mother has been exposed to Rh-positive blood cells via prior being pregnant, miscarriage, therapeutic abortion, or mismatched blood transfusion, IgG antibodies may develop that traverse the placenta and trigger immune destruction of fetal Rh-positive cells. In severe circumstances the fetus may be extremely anemic, which ends up in heart failure, hydrops fetalis, and death. In much less critical instances infants may be born fairly anemic and develop brisk hyperbilirubinemia, which can result in kernicterus.