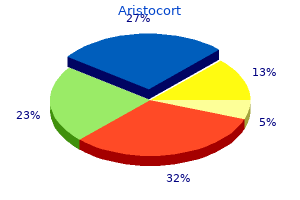
Aristocort
Aristocort dosages: 40 mg, 15 mg, 10 mg, 4 mg
Aristocort packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Aristocort 10 mg discount overnight delivery
Detection of such abnormalities allergy shots side effects aristocort 4 mg with amex, when slight allergy medicine heart patients aristocort 40 mg discount line, requires careful observation and consideration of quite lots of elements. To guarantee consistency and avoid confusion, I use only three phrases to characterize the extent of alertness: normal, stupor, and coma (Table 9. These characterizations are based principally on three readily determined criteria: (1) the response to arousal maneuvers. In slight stupor, the infant is awake but "sleepy" or "torpid," whereas in reasonable stupor the toddler seems to be asleep; in both states an arousal response, though diminished, is current. The distinction between deep stupor and coma is predicated totally on the standard of the motor responses. Most problems that affect the neonatal central nervous system disturb the extent of alertness at some time, and longitudinal characterization of this level is the ks fre fre. Whenever attainable, these anatomical loci within the neuraxis that, when deranged, may cause the neurological deficits are identified. In common, such clinicoanatomical correlations in the newborn should be made cautiously. The organization of this dialogue is similar to that used to describe the traditional neonatal neurological examination. Consistent failure to reveal visible following (or opticokinetic nystagmus with a rotating drum) in a full-term newborn is a disturbing sign. However, if pendular "searching" nystagmus, digital manipulation of the globe, and repetitive hand actions earlier than the eyes seem in the first weeks or months of life, congenital blindness is likely, and the locus of the disturbance of optic pathways have to be sought within the usual means. Distinction of optic ks ks oo oo eb o eb eb okay sf nerve hypoplasia-dysplasia and optic atrophy is beneficial. A number of abnormalities of the optic disc and retina may be detected in the neonatal interval (Table 9. Vision co Abnormalities of olfaction, detected by the simple bedside method whereby a cotton pledget soaked with peppermint extract is used, have been demonstrated in infants with absent olfactory bulbs and tracts. This lesion accounts for about 25% of instances of congenital blindness248 and pertains to a dysfunction throughout midline prosencephalic improvement. Approximately 50% of affected patients subsequently exhibit different signs of cerebral abnormality. In one series of septo-optic dysplasia (absence of the septum pellucidum with optic hypoplasia-dysplasia), schizencephaly (porencephaly) or agenesis of the corpus callosum was associated with 81% of circumstances with severe bilateral optic illness (see Chapter 2). The endocrine abnormalities are related to impairment in trophic hormone secretions (indicative of hypothalamic maldevelopment), the commonest of which entails growth hormone. The etiology is often attributed to damage attributable to abnormalities of pregnancy, labor, or delivery, but conclusive information are lacking. Abnormal pupillary findings are of nice worth in medical neurology within the localization of pathological occasions that occur in older infants and children. The occurrence and significance of such pupillary findings within the newborn interval, nonetheless, are nonetheless not properly outlined. A unilateral lower in dimension of a pupil that continues to be reactive to mild is seen most often with Horner syndrome (see Table 9. In the new child, this syndrome is nearly always associated with a brachial plexus injury, which includes involvement of the eighth cervical root and first thoracic root, destined for the cervical sympathetic ganglion (see Chapter 36). This finding probably relates to systemic epinephrine release in affiliation with asphyxia. A unilateral enhance in the size of a pupil which may be sluggishly reactive or unreactive to light is very unusual within the new child (unlike older youngsters and adults); this displays the rarity of the uncal type of transtentorial herniation, which leads to compression of the third cranial nerve and its related parasympathetic fibers. In roughly 10% of circumstances, retinoblastoma is inherited in an autosomal dominant trend. Thus a household history of an affected sibling should provoke a particularly thorough examination. A bilateral lower in the size of pupils that are reactive to light (although the response could additionally be difficult to detect) is seen most frequently once the first 12 to 24 hours after perinatal asphyxia have passed (see Table 9. With hypoxic-ischemic insults which have been properly established for hours intrapartum, nevertheless, this miosis could also be apparent earlier. The pupillary change is often accompanied by other indicators suggestive of parasympathetic discharge. Whether this apparent parasympathetic predominance pertains to a central autonomic disturbance or a lower in systemic catecholamine launch is unclear. The earliest vascular modifications of retinopathy of prematurity are tough to detect with certainty by direct ophthalmoscopy. These phases embody dilation and tortuosity of vessels, neovascularization, hemorrhages, intravitreous proliferation, and, lastly, retinal detachment, starting on the periphery. In native anesthetic intoxication, pupils may be giant and unreactive to gentle because of peripheral parasympatholytic effects (see Chapter 12). In infantile botulism, pupils are usually midposition in size (although they may be dilated) and unreactive to mild, also secondary to peripheral synaptic results (see Chapter 32). Chorioretinitis is kind of a continuing feature of symptomatic congenital toxoplasmosis, has a predilection for the macular region, and consists of outstanding necrotic lesions with putting black pigment as nicely as yellow scarring. In symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus an infection, retinal lesions happen in about 20% of affected newborns, and though the lesions bear similarities to these in toxoplasmosis, they have a tendency to be less pigmented and extra peripheral in location. The chorioretinitis of rubella is readily distinguished from that of toxoplasmosis or cytomegalovirus an infection in that it consists of small areas of depigmentation and pigmentation, giving a "salt and pepper" appearance to the retinal floor. Large preretinal hemorrhages are noticed most commonly with major intracranial hemorrhage. Consequently elevated intracranial stress is prone to be or to have been current. However, in small preterm infants (<1500 g), these abnormalities are extra frequent and will persist (Table 9. At least four abnormalities of eye place or eye motion could additionally be observed in otherwise healthy time period infants examined on the first 3 postnatal days. In my experience, convexity subdural hematoma is the commonest cause of this syndrome in the newborn infant (see Table 9. However, I even have noticed unilateral pupillary dilation secondary to transtentorial uncal herniation in neonatal bacterial meningitis. The defects of extraocular movement relate to disturbed innervation of the superior, inferior, and medial rectus and inferior indirect muscles, and the ptosis relates to disturbed innervation of the levator palpebrae. An uncommon acquired explanation for unilateral third nerve palsy is neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury, documented neuropathologically as causing unilateral as well as bilateral nuclear damage in the mind stem, particularly including the third nerve nucleus (see Chapter 18). I really have seen this finding in association with the mind stem neuronal injury caused by severe, abrupt, late intrapartum asphyxia (see Chapter 19). Thus, on follow-up, the incidence varied from approximately 5% in infants with no intraventricular hemorrhage to 16% in those with hemorrhage and to 50% in these with cystic periventricular leukomalacia. Interestingly, though most of these cases resolve by 1 month of age, 23% later evolve to esotropia.
Aristocort 40 mg buy low price
Minocycline prevents glutamateinduced apoptosis of cerebellar granule neurons by differential regulation of p38 and Akt pathways allergy forecast for chicago discount aristocort 10 mg without prescription. Cerebral lactate and N-acetyl-aspartate/choline ratios in asphyxiated full-term neonates demonstrated in vivo using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy can allergy medicine kill you purchase aristocort 40 mg without prescription. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain in normal preterm and time period infants, and early changes after perinatal hypoxia-ischemia. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: an rising know-how in pediatric neurology research. Glutamate in cerebral tissue of asphyxiated neonates during the first week of life demonstrated in vivo using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proton spectroscopy and diffusion imaging on the primary day of life after perinatal asphyxia: preliminary report. Prediction of adverse consequence with cerebral lactate level and obvious diffusion coefficient in infants with perinatal asphyxia. Diffusion-weighted imaging and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in perinatal hypoxic�ischemic encephalopathy: affiliation with neuromotor outcome at 18 months of age. Comparative prognostic utilities of early quantitative magnetic resonance imaging spin-spin relaxometry and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in neonatal encephalopathy. Cerebral magnetic resonance biomarkers in neonatal encephalopathy: a metaanalysis. The prognostic worth of multivoxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy decided metabolite ranges in white and gray matter mind tissue for adverse end result in time period newborns following perinatal asphyxia. Clinical, neurophysiologic, and neuropathological features of an infant with brain damage of whole asphyxia kind (Myers). Changes in cell proliferation kinetics in the mouse cerebellum after total asphyxia. Dendritic development of cortical neurons of mice subjected to total asphyxia: a Golgi-Cox research. The aetiology of delayed visible maturation: brief evaluate and personal findings in relation to magnetic resonance imaging. Visual function at college age in children with neonatal encephalopathy and low Apgar scores. Rolandic kind cerebral palsy in children as a sample of hypoxic�ischemic damage in the full-term neonate. Prenatal and perinatal striatal damage: a hypothetical cause of attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder Clinical profiles of children with cerebral palsy having lesions of the thalamus, putamen and/or peri-Rolandic space. Dyskinetic cerebral palsy: a population-based study of kids born between 1991 and 1998. The evolution of infantile postural reflexes in the presence of chronic mind syndromes. Symmetrical bithalamic hyperdensities in asphyxiated full-term newborns: an early indicator of standing marmoratus. Prognostic value of early somatosensory evoked potentials for opposed end result in full-term infants with delivery asphyxia. The spectrum of irregular neurologic outcomes subsequent to term intrapartum asphyxia. Focal cerebral hypoperfusion in kids with dysphasia and/or consideration deficit disorder. School performance of survivors of neonatal encephalopathy related to birth asphyxia at term. Neuropsychological and educational problems at school age related to neonatal encephalopathy. The affiliation of Apgar rating with subsequent dying and cerebral palsy: a population-based study in term infants. Apgar rating, meconium and acidaemia at birth in small-for-gestational age infants born at time period, and their relation to neonatal neurological morbidity. The effect of profound umbilical artery acidemia in term neonates admitted to a newborn nursery. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation of apparently stillborn infants: survival and long-term end result. Apgar scores at 10 min and outcomes at 6-7 years following hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Comparison of the 4 proposed Apgar scoring methods in the evaluation of start asphyxia and antagonistic early neurologic outcomes. Intrapartum hypoxic�ischemic cerebral injury and subsequent cerebral palsy: medicolegal issues. Postasphyxial hypoxic�ischemic encephalopathy in neonates: consequence prediction rule inside 4 hours of birth. The prognostic value of computed tomography as an adjunct to evaluation of the term infant with postasphyxial encephalopathy. Acute neonatal morbidity and long-term central nervous system sequelae of perinatal asphyxia in term infants. Renal damage within the asphyxiated new child toddler: relationship to neurologic consequence. Early predictors of neurodevelopmental consequence at 12-36 months in very lowbirthweight infants. Educational readiness of survivors of neonatal encephalopathy associated with birth asphyxia at time period. The prognostic worth of computed tomography of the brain in asphyxiated untimely infants. Clinical indicators predict 30-month neurodevelopmental end result after neonatal encephalopathy. Early brain injury in premature newborns detected with magnetic resonance imaging is associated with adverse early neurodevelopmental end result. Corpus callosum size in relation to motor efficiency in 9- to 10-year-old children with neonatal encephalopathy. Behavioral end result in kids with a historical past of neonatal encephalopathy following perinatal asphyxia. Antecedents and end result of very early neonatal seizures in infants born at or after term. The current etiologic profile and neurodevelopmental end result of seizures in term newborn infants. Assessment of neonatal encephalopathy by amplitude-integrated electroencephalography.
40 mg aristocort buy free shipping
In affected families allergy forecast minnesota aristocort 10 mg purchase fast delivery, ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency was complete in the male sufferers and partial in the female sufferers allergy testing equipment order aristocort 4 mg amex. In several giant collection, argininosuccinic acid synthetase deficiency accounted for about 15% to 20% of instances of urea cycle issues with neonatal onset, and approximately 80% of instances of argininosuccinic acid synthetase deficiency have been of neonatal onset. Onset on the primary postnatal day, earlier than the institution of feeding, has been reported. Poor feeding, vomiting, tachypnea, alteration of muscle tone, and seizures are the commonest options. Most male infants affected with the malignant neonatal type of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency have less than 2% of normal hepatic enzymatic activity. Hyperammonemia with citrullinemia ks ks oo oo eb o eb eb ok sf is usually not as marked as in carbamyl phosphate synthetase re. In the preliminary sequence of reported cases, practically all infants died within the neonatal period. In two comparatively large later collection, only 1 of 23 infants died, but sixteen of the 18 survivors had been mentally retarded on follow-up. Affected newborns have exhibited hepatic activities of argininosuccinic acid synthetase that are lower than 20% of normal values. The enzymatic defect could be demonstrated readily in cultured pores and skin fibroblasts and in lymphocytes. Indeed, in a single report, marked elevations of intracranial stress were documented and shown to correlate with the severity of the neurological options. Note the numerous linear relationship between the serum ammonia ranges and the interburst durations in three newborns with citrullinemia. A 10-minute steady epoch was chosen for quantitative evaluation of the burst. The acute neuropathology is more doubtless to be much like that described earlier for the opposite defects of the urea cycle but, to my data, has not been reported. The chance that this observation mirrored a disturbance in myelin formation somewhat than myelin destruction is indicated by the absence of myelin breakdown merchandise or of gliosis within the affected areas. The earlier discussion of potential glutamate-induced oligodendroglial damage may be related in this context. The mechanism of the hyperammonemia is unknown, though a deficiency of ornithine and maybe arginine and thereby dysfunction of the urea cycle is feasible. The mechanism of the hyperammonemia within the natural acid disorders is unknown, however obtainable knowledge indicate that the coenzyme A derivatives of the accrued organic acids are potent inhibitors of human liver carbamyl phosphate synthetase (see Chapter 28 for details). Hyperammonemia and elevated levels co argininosuccinase (argininosuccinic acid lyase) deficiency is a extreme neonatal sort. Poor feeding, stupor, and tachypnea, progressing to vomiting, seizures, and coma, constitute the medical syndrome. The neonatal type of argininosuccinase deficiency is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. One of the several clinical forms of oo ks to elevated intracranial stress have been documented in neonatal citrullinemia. Although metabolic features other than hyperammonemia (particularly acidosis, ketosis, or both) normally predominate, the hyperammonemia might dominate the medical syndrome and strongly raise the risk of a primary defect within the urea cycle. The findings strongly help the role of glutamine because the toxic issue on this and other urea cycle problems. The typical later-onset syndrome is commonly mistakenly characterised as cerebral palsy. Possible mechanisms embody deficiency within the development of urea cycle perform, both because of inadequate ranges of urea cycle intermediates or enzymatic actions, insufficient hepatic blood circulate, platelet aggregation with impairment of the hepatic microcirculation, and hypoxia-ischemia. With regard to the potential for limiting substrate quantities, investigators have proven that roughly 50% of (asymptomatic) preterm infants have an approximately twofold enhance in blood ammonia level, accompanied by a lower in blood arginine and ornithine ranges, and that the hyperammonemia may be lowered by the oral administration of arginine. Whether this defect in regular preterm infants is exacerbated greatly by sickness, corresponding to respiratory disease, and then results in the massive hyperammonemia of the symptomatic syndrome just eb Most acknowledged circumstances of severe neonatal hyperammonemia have exhibited inherited issues of the urea cycle or natural acid metabolism. However, different inherited metabolic defects (as just discussed), as properly as quite a lot of acquired issues, could lead to extreme neonatal hyperammonemia (see Table 27. Hepatic failure and whole parenteral diet are uncommon examples of the noninherited issues. Possibly a related syndrome is hyperammonemia observed after perinatal asphyxia, as mentioned in Chapter 20. The fundamental defect includes transport of ornithine into the mitochondrion via the ornithine transporter protein,297,299-301 with ammonia metabolism affected secondarily because of functional impairment on the ornithine transcarbamylase step. Elevations of plasma glutamine stage and orotic acid excretion have been observed. Analysis of the urea cycle enzymes in liver of a number of infants revealed normal values. Indeed, the mixture of coma with absent pupillary responses and eye movements instructed advanced hypoxic-ischemic harm or severe intracranial hemorrhage earlier than the diagnosis of transient symptomatic hyperammonemia was sought and found. A dramatic response to change transfusion, hemodialysis, or peritoneal dialysis has been noticed repeatedly. In newer years, for unknown causes, this disorder has been a lot much less frequent. In reported circumstances, mortality rates of roughly 20% to 30% and rates of neurological sequelae in survivors of approximately 35% to 45% had been documented. The fulminating course of great neonatal hyperammonemia is noticed in all of the issues discussed beforehand, together with transient hyperammonemia of the preterm toddler. Early detection and immediate institution of therapy may make the difference between the onset of irreversible central nervous system harm and recovery. A striking demonstration of the significance of prompt intervention is derived from a study of two large sequence consisting of 116 infants with neonatal hyperammonemic coma secondary to congenital defects of the urea cycle. The most distinct correlate of consequence was length of neonatal coma; four of five infants with coma for less than three days had a re ks fre fre ks f ok s co. Similarly, (sodium) phenylacetate acetylates glutamine, the latter formed from ammonia by the transamination of glutamate, which itself is formed by transamination of alphaketoglutarate. Each of the four defects of the urea cycle discussed earlier could be recognized antenatally. Antenatal Diagnosis and Prevention co the basic elements within the management of the infant with hyperammonemia are shown in Table 27. Not all elements of management are applicable to every patient, and these variations are discussed subsequently. Ammonia Removal the main therapeutic approaches for the rapid elimination of ammonia (and glutamine) are hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and hemofiltration methods (see Table 27. Survival rates were 20% in those newborns treated with exchange transfusion, 50% in those treated with peritoneal dialysis after trade transfusion, and one hundred pc in those handled solely with peritoneal dialysis. Later work demonstrated the prevalence of hemodialysis relative to peritoneal dialysis, and this strategy is now the beneficial process.
15 mg aristocort best
Catch-up development of head circumference of very low birth weight allergy shots side effects weight gain cheap 40 mg aristocort mastercard, small for gestational age preterm infants and psychological development to maturity allergy itchy eyes generic aristocort 10 mg without a prescription. Postnatal head progress deficit among premature infants parallels retinopathy of prematurity and insulin-like progress factor-1 deficit. Growth, head development, and neurocognitive end result in youngsters born very preterm: methodological features and selected outcomes. Intrauterine, early neonatal, and postdischarge progress and neurodevelopmental outcome at 5. Alterations in head shape of newborn infants after caesarean section or vaginal delivery. Slower postnatal development is related to delayed cerebral cortical maturation in preterm newborns. Developmental psychobiology: prenatal, perinatal, and early postnatal aspects of behavioral growth. State profile in low-risk pre-term infants: a longitudinal research of seven infants from 32�36 weeks of postmenstrual age. Development of the sleep and wakefulness rhythm in preterm infants discharged from a neonatal care unit. Sleep state adjustments associated with cerebral blood quantity modifications in wholesome term newborn infants. Clinical usefulness of maternal odor in newborns: soothing and feeding preparatory responses. Neurological and neurobehavioural differences between preterm infants at time period and full-term newborn infants. Maturation of visual operate in infants with neonatal mind lesions: correlation with neuroimaging. Delayed visual maturation: pupillary responses implicate subcortical and cortical visual systems. Visual acuity of low-risk and high-risk neonates and acuity growth during the first year. Visual subject and grating acuity development in low-risk preterm infants through the 1st 2 1 2 years after time period. Acuity card procedures and the linearity of grating resolution development in the course of the first yr of human infants. Visual acuity in the newborn human: a study based mostly on induced optokinetic nystagmus recorded by electroculography. Visual skills and pattern preferences of premature infants and full-term neonates. Visual activation in infants and younger youngsters studied by useful magnetic resonance imaging. Index finger motion imitation by human neonates: motivation, learning and left-hand desire. Maturation of the vestibulo-ocular reflex in regular infants through the first 2 months of life. Space notion in early infancy: perception within a typical auditory-visual space. Reflex modification audiometry: assessment of acoustic sensory processing in the time period neonate. Sound frequency change detection in fetuses and newborns, a magnetoencephalographic research. Development of co-ordination of sucking, swallowing and respiration: ultrasound research of time period and preterm infants. The relationship between rhythmic swallowing and breathing throughout suckle feeding in term neonates. Integration of suck and swallow rhythms during feeding in preterm infants with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Disorders of sucking and swallowing within the new child toddler: clinicopathological correlations. Neonatal nutritive sucking: effects of style stimulation upon sucking rhythm and coronary heart price. Posture during head turning in pre-term infants: a longitudinal research of 15 low-risk infants of 32�36 weeks of conceptional age. Asymmetrical head-turning of preterm infants: some results on later postural and useful lateralities. General movement assessment as a technique of developmental neurology: new paradigms and their consequences. Neurologic examination of preterm infants at time period age: comparability with time period infants. Spontaneous motility in untimely infants: options of behavioral activity and rhythmic organization. Keeping the arm in the limelight: superior visual management of arm actions in neonates. Comparison between observation of spontaneous actions and neurologic examination in preterm infants. Which higher predicts later end result in fullterm infants: high quality of basic movement or neurological examination Quality of basic movements in preterm infants with transient periventricular echodensities. General movements detect early indicators of hemiplegia in time period infants with neonatal cerebral infarction. General movements in early infancy predict neuromotor improvement at 9 to 12 years of age. Predictive value of neurodevelopmental assessment versus evaluation of common movements for motor outcome in preterm infants with birth weights <1500 g. Primitive reflex profiles in infants: variations primarily based on categories of neurological abnormality. Ease of habituation to repeated auditory and somesthetic stimulation in the human newborn. Neonatal pain cries: impact of circumcision on acoustic features and perceived urgency. The neuroanatomy, neurophysiology, and neurochemistry of ache, stress, and analgesia in newborns and youngsters. Familial congenital saccade initiation failure and isolated cerebellar vermis hypoplasia. Blindness as a result of optic-nerve atrophy and hypoplasia in kids: an epidemiological study (1944�1974). Optic nerve hypoplasia related to absent septum pellucidum and hypopituitarism. Confluent diode laser coagulation: the gold normal of therapy for retinopathy of prematurity. Plasma adrenalin and noradrenalin within the neonatal period, and infants with respiratory distress syndrome and placental insufficiency.
Order 10 mg aristocort fast delivery
The border zone idea has obtained ample further experimental help in a number of creating animal models allergy control products aristocort 40 mg purchase with visa. Parasagittal cerebral cortical-subcortical damage has been documented in the perinatal monkey allergy free dogs aristocort 15 mg generic without prescription, sheep, rabbit, and mouse subjected to a wide selection of insults complicated by hypotension and presumed or documented cerebral ischemia. Moreover, the cellular sample of laminar necrosis of cortical pyramidal neurons was similar to the sample observed within the asphyxiated human toddler. The latter scenario is paying homage to findings with severely asphyxiated human infants who die. Moreover, certain border zones provided by bigger proximal branches of cerebral vessels. Note the symmetrical, parasagittal distribution of necrosis and observe the similarity to the topography of the damage in asphyxiated infants (see Chapter 18). Takashima and co-workers61 have shown that as sulci type and deepen near time period within the human mind, the penetrating vessels from the meningeal arteries are pressured to bend acutely on the cortical�white matter junction. This relatively avascular region presumably is even more weak to a fall in perfusion pressure throughout the border zone regions between the major cerebral vessels. Postmortem microarteriography demonstrates the comparatively avascular, triangular area (T) on the depth of the sulcus. Approximately 15% of infants exhibit this pattern of harm because the dominant abnormality on neuroimaging (see Chapter 18). Periventricular and central cerebral white matter are concerned, and the looks is just like "noncystic periventricular leukomalacia," as described for premature infants in Chapter 14. Indeed, this oligodendroglial sub-type is probably the most plentiful stage of the oligodendroglial lineage even at time period within the human mind. Selective symmetrical necrosis of tegmental neuronal aggregates following cardiac arrest. Expression of cell death-associated proteins in neuronal apoptosis associated with pontosubicular neuron necrosis. Caspase-3 activation and caspase-like proteolytic exercise in human perinatal hypoxicischemic brain damage. Density and distribution of excitatory amino acid receptors in the creating human fetal brain-a quantitative autoradiographic examine. Differential expression of glutamate receptor subtypes in human brainstem sites involved in perinatal hypoxia-ischemia. Ontogeny of excitotoxic damage to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase reactive neurons within the neonatal rat striatum. Frequent episodes of temporary ischemia sensitize the fetal sheep mind to neuronal loss and induce striatal injury. Repeated asphyxia causes lack of striatal projection neurons within the fetal sheep brain. Repeated episodes of umbilical twine occlusion in fetal sheep lead to preferential damage to the striatum and sensitize the heart to additional insults. Four patterns of perinatal mind injury and their situations of incidence in primates. Uterine rupture after earlier cesarean supply: maternal and fetal penalties. Interleukin-6 within the cerebrospinal fluid after perinatal asphyxia is related to early and late neurological manifestations. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor- ranges in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of time period new child infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. The Maternal-fetal medicine items cesarean registry: chorioamnionitis at term and its duration-relationship to outcomes. Placental pathology is related to severity of neonatal encephalopathy and opposed developmental outcomes following hypothermia. Chorioamnionitis and neonatal encephalopathy in term infants with fetal acidemia: histopathologic correlations. Die pathogenese von massenblutung und erweichung unter besonderer berucksichtigung klinischer gesichtspunkte. Positron emission tomography within the asphyxiated time period newborn: parasagittal impairment of cerebral blood flow. Outcome after ischemia within the creating sheep mind: an electroencephalographic and histological examine. Cerebral histologic and electrocorticographic modifications after asphyxia in fetal sheep. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition attenuates delayed vasodilation and increases damage after cerebral ischemia in fetal sheep. Idiopathic cerebral arterial infarction with paucity of signs within the full-term neonate. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in term perinatal brain harm: a comparability with website of lesion and time from birth. Encephalopathy of congenital coronary heart disease-destructive and developmental effects intertwined. To provoke such remedy requires a recognition of the toddler who could have suffered hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury-predominantly in the peripartum period. The peripartum interval is outlined as the interval shortly before, throughout, and immediately after birth. Hypoxemia results in brain harm principally by causing myocardial disturbance and loss of cerebrovascular autoregulation, with ischemia the major consequence. The temporal characteristics and the severity of the hypoxemia and ischemia, as nicely as the gestational age of the toddler, are the principal determinants of the type of resulting neuropathology (see Chapters 18 and 19). The main causes of significant hypoxemia in the peripartum interval are: (1) hypoxia-ischemia with intrauterine disturbance of fuel exchange throughout the placenta. Moreover, selection of applicable diagnostic modalities, formulation of rational prognostic statements, and development of appropriate plans of administration are based, in many ways, on awareness of the probable neuropathologies. We prefer the term "peripartum" hypoxic-ischemic damage because it acknowledges the potential presence of (1) fetal or maternal prepartum circumstances which will accentuate propensity to intrapartum hypoxic-ischemic injury; (2) intrapartum hypoxic�ischemic damage per se; and (3) the often related protracted postpartum resuscitative efforts for such infants, with no or low coronary heart fee for several minutes. In one giant population-based observational study, the prevalence of average to extreme encephalopathy was 1. These findings are in keeping with a more recent giant cohort research of 4165 singleton time period infants with any one of the following: seizures, stupor, coma, Apgar rating at 5 minutes less than three and/or receiving hypothermia therapy. Almost one half of the infants displayed umbilical wire blood gas acidemia and/or fetal bradycardia. Of observe, indicators of inflammation had been also not uncommon with 27% of mothers displaying elevated maternal temperature in labor and 11% medical chorioamnionitis. On the premise of earlier work,11-27 roughly 20% of hypoxic-ischemic damage acknowledged in the newborn interval was said to be associated primarily to antepartum insults. These data should be interpreted with the awareness that evaluation of timing of insults to the fetus in these reviews usually was based on imprecise strategies, and the variability of findings is appreciable. Hypothyroidism Obesity Diabetes (particularly pregestational) Fetal development restriction <5% Hypertension Clinical chorioamnionitis 0. However, antepartum components seem to be of some importance in the risk for neonatal encephalopathy related to peripartum occasions.
40 mg aristocort purchase visa
Relating effortful management allergy medicine drowsy aristocort 40 mg buy cheap on-line, executive operate allergy to chlorine aristocort 4 mg buy discount online, and false perception understanding to rising math and literacy ability in kindergarten. Examining an govt operate battery to be used with preschool youngsters with disabilities. Test-retest reliability of a new government function battery to be used in early childhood. Measuring executive perform in early childhood: a focus on maximal reliability and the derivation of brief varieties. Executive perform in early childhood: longitudinal measurement invariance and developmental change. High rates of school readiness difficulties at 5 years of age in very preterm infants compared with time period controls. Meta-analysis of neurobehavioral outcomes in very preterm and/or very low birth weight youngsters. Neonatal cerebral morphometry and later danger of persistent inattention/ hyperactivity in kids born very preterm. Attention and Regional Gray Matter Development in Very Preterm Children at Age 12 Years. Preschool self regulation predicts later psychological health and educational achievement in very preterm and sometimes developing kids. Prognostic Factors for Behavioral Problems and Psychiatric Disorders in Children Born Very Preterm or Very Low Birth Weight: A Systematic Review. Development of comorbid crying, sleeping, feeding issues across infancy: neurodevelopmental vulnerability and parenting. The prolonged model of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire as a information to baby psychiatric caseness and consequent burden. Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist and Revised Children Behavior Profile; 1983. The Development and Well-Being Assessment: description and preliminary validation of an integrated evaluation of child and adolescent psychopathology. Development of a structured psychiatric interview for kids: settlement between child and father or mother on particular person signs. Screening for autism in older and younger toddlers with the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers. However, recognition of seizures in the newborn period could be very tough due to subtle or absent scientific manifestations. To help in both the correct identification of seizures in the newborn and the successful treatment with antiepileptic drug therapy, electrophysiological monitoring-either typical or restricted channel monitoring-now performs a crucial role throughout the neonatal intensive care unit. Treatment of neonatal seizures is usually thought-about essential as a outcome of experimental and human proof suggests seizures might result in secondary mind damage and are related to much less favorable outcomes. However, antiseizure medicines could have related dangers, and there are few data to information evidence-based administration. This article reviews the pathophysiology and medical elements of neonatal seizures with explicit emphasis on the affect of the developmental characteristics of the immature mind. Second, an excess of excitatory neurotransmitters can lead to extreme depolarization. This imbalance of extra excitatory neurotransmitters, significantly in relation to the principal excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate, could result from increased synaptic launch and/or diminished reuptake in presynaptic nerve endings and glia. Cellular harm, from hypoxic-ischemic neuronal injury, can end result in the release of excessive extracellular glutamate. Developmentally, this enhanced excitation is essential for activity-dependent synaptogenesis. Thus, hypocalcemia or hypomagnesemia improve the Na+ influx, resulting in depolarization. The relevant events embody the attainment of proper cellular orientation, alignment, and layering. The exact causes for these variations relate to the status of neuroanatomical and neurophysiological improvement in the perinatal period. The relation of excitatory to inhibitory synapses is necessary in determining the capacity of a focal discharge to each form after which to unfold to contiguous and distant brain areas. Strong evidence signifies that the charges of improvement of the excitatory and inhibitory synaptic actions differ within the newborn cerebral cortex (see Table 12. The latter two occasions (neurite outgrowth and synaptogenesis) required to present the cortical connectivity to propagate and sustain a generalized seizure is rudimentary within the time period new child toddler. In distinction, in the new child monkey, the unfold of seizure discharges is relatively fast, and well-organized, synchronous, generalized seizures are readily obvious clinically and electroencephalographically. Functional inhibition, however, is steadily reached overdevelopment in rats and humans. Kainate receptor binding is initially low and progressively rises to grownup levels by the fourth postnatal week. With seizure exercise, nevertheless, a considerable proportion of pyruvate is transformed within the cytoplasm to lactate within the presence of elevated levels of the reduced form of nicotinamide re ks fre fre. Electroencephalographic recordings with representations of ictal discharges (A) during hypoxia, zero to 2 days, three to 10 days, 14 to 21 days, 22 to 27 days, and 28 to 47 days following hypoxia. Abnormal activity was categorized as seizures when exercise was paroxysmal, rhythmic, rising in amplitude, and higher than 3 seconds in period. Electrographic seizures associated with irregular behavioral automatisms have been noticed within the first forty eight hours following hypoxia-induced seizures at P10. There was a lower within the frequency (B) and length (C) of the electrographic seizure exercise between the ages of P13 and P20. The frequency (B and C) of electrographic seizures associated with irregular conduct elevated once more in the animals at P24 to P31 and continued to improve into adulthood. The excess of lactate, specifically the associated hydrogen ion,87 has the useful impact of inflicting local vasodilation and a consequent enhance in native blood supply and substrate inflow. Concomitant with the autumn in mind glucose is a rise in brain lactate, which is used readily as a metabolic gas within the neonatal mind. Seizures may be accompanied by hypoventilation and apnea, which end in hypoxemia and hypercapnia. Hypoxemia might yield cardiovascular dysfunction and ischemic injury to mind, notably in a newborn whose mind already has been compromised by an insult. While minimal information are available in human newborns (see later discussion), experimental research are plentiful, primarily in growing rodent models. Importantly, although the edge for seizure era is decrease in the creating mind than within the mature mind, developing neurons are less vulnerable to injury from single prolonged seizures than are mature neurons. This may be as a result of a lower density of active synapses, lower power consumption, and immaturity of related biochemical cascades to cell death. Ratio of mind glucose to blood glucose ranges in convulsing neonatal rats as a function of duration of seizure exercise. For example, depending on such factors as the gestational age of the newborn or the neuropathological substrate for the seizures, some newborns might have extremely vulnerable capillary beds, such as the germinal matrix in untimely infants or the margins of ischemic lesions in premature infants or asphyxiated term newborns. The electroencephalogram demonstrated seizure activity emanating from the left temporal region. The magnetic resonance spectrum from the nonictal hemisphere (dotted line) is normal.
Buy aristocort 10 mg on-line
Induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha within the mouse hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia allergy shots every 2 weeks 15 mg aristocort discount with amex. Microglia as a singular cellular goal in the therapy of stroke: potential neurotoxic mediators produced by activated microglia allergy xyzal aristocort 15 mg free shipping. Identification of two distinct macrophage subsets with divergent results inflicting either neurotoxicity or regeneration in the injured mouse spinal twine. Macrophages/microglial cells in human central nervous system throughout growth: an immunohistochemical research. Expression of adhesion molecules on human fetal cerebral vessels: relationship to microglial colonisation during growth. Periventricular leukomalacia, inflammation and white matter lesions within the growing nervous system. Development of microglia in the cerebral white matter of the human fetus and infant. Distribution and differentiation of microglia within the human encephalon in the course of the first two trimesters of gestation. Entry and distribution of microglial cells in human embryonic and fetal cerebral cortex. Early microglial colonization of the human forebrain and possible involvement in periventricular white-matter damage of preterm infants. Microglial reaction in axonal crossroads is a trademark of noncystic periventricular white matter damage in very preterm infants. Prolonged reductions in placental blood flow and cerebral oxygen delivery in preterm fetal sheep exposed to endotoxin: possible components in white matter damage after acute an infection. Variability in cerebral oxygen supply is reduced in premature neonates uncovered to chorioamnionitis. Low blood strain among very-low-birth-weight infants with fetal vessel inflammation. Interleukin-10 reverses acute detrimental effects of endotoxin-induced inflammation on perinatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. Fetal stress and programming of hypoxic/ischemic-sensitive phenotype in the neonatal brain: mechanisms and attainable interventions. The results of hypoxic preconditioning on white matter harm following hypoxic-ischaemic damage within the neonatal rat mind. Neuroprotection by the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A in a model of lipopolysaccharide-sensitised neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic brain damage. The Akt-endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway in lipopolysaccharide preconditioning-induced hypoxic-ischemic tolerance within the neonatal rat mind. Development of cerebral gray and white matter injury and cerebral inflammation over time after inflammatory perinatal asphyxia. Lipid peroxidation in creating fetal guinea pig brain during normoxia and hypoxia. Malondialdehyde and thiobarbituric acid-reactivity as diagnostic indices of lipid peroxidation and peroxidative tissue harm. Developmental lag in superoxide dismutases relative to different antioxidant enzymes in premyelinated human telencephalic white matter. Glutathione peroxidase-catalase cooperativity is required for resistance to hydrogen peroxide by mature rat oligodendrocytes. Relationship between periventricular hemorrhage, leukomalacia and brainstem lesions in prematurely born infants. Iron release in erythrocytes and plasma non protein-bound iron in hypoxic and non hypoxic newborns. Vulnerability of oligodendroglia to glutamate: pharmacology, mechanisms and prevention. Hypoxia-Ischemia preferentially triggers glutamate depletion from oligodendroglia and axons in perinatal cerebral white matter. Mature myelin basic protein expressing oligodendrocytes are insensitive to kainate toxicity. Glutamate receptor-mediated oligodendrocyte toxicity in periventricular leukomalacia: a protective function for topiramate. The mechanisms of acute ischemic injury in the cell processes of growing white matter astrocytes. Involvement of the subplate zone in preterm infants with periventricular white matter injury. Neonatal lack of gammaaminobutyric acid pathway expression after human perinatal mind damage. Differential susceptibility to axonopathy in necrotic and non-necrotic perinatal white matter harm. Long-term cognitive impairment and myelination deficiency in a rat mannequin of perinatal hypoxic-ischemia brain damage. Age-related modifications within the oligodendrocyte progenitor pool affect brain reworking after injury. New oligodendrocytes are generated after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic mind harm in rodents. Neural stem/progenitor cells take part within the regenerative response to perinatal hypoxia/ ischemia. Hypoxia/ischemia expands the regenerative capability of progenitors in the perinatal subventricular zone. Multiple extracellular alerts are required for long-term oligodendrocyte survival. Toward improved animal models of neonatal white matter injury associate with cerebral palsy. Overcoming remyelination failure in multiple sclerosis and other myelin problems. Sirtuin 2, a mammalian homolog of yeast silent info regulator-2 longevity regulator, is an oligodendroglial protein that decelerates cell differentiation via deacetylating alpha-tubulin. Histone modifications have an result on timing of oligodendrocyte progenitor differentiation in the growing rat brain. Dicer1 and miR-219 Are required for normal oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination. Extracellular matrix of central nervous system white matter: demonstration of an hyaluronan-protein advanced. Hyaluronan accumulates in demyelinated lesions and inhibits oligodendrocyte progenitor maturation. Astrocytes from the contused spinal cord inhibit oligodendrocyte differentiation of grownup oligodendrocyte precursor cells by increasing the expression of bone morphogenetic proteins. Multiple sclerosis: re-expression of a developmental pathway that restricts oligodendrocyte maturation.
15 mg aristocort cheap amex
It is essential to notice that the infratentorial posterior fossa subdural hemorrhages could relate also to tears of cerebellar bridging veins allergy medicine starts with l order aristocort 15 mg otc, with or with out accompanying overt tears of the tentorium allergy medicine for toddlers under 2 aristocort 10 mg low cost. In addition to infratentorial or supratentorial extension, the hemorrhage of a tentorial tear could remain confined. A distinguished traumatic lesion in some infants who die after breech supply is occipital diastasis with posterior fossa subdural hemorrhage and laceration of the cerebellum (see Table 22. The superior sagittal sinus runs within the superior border of the falx; the inferior sagittal and straight sinuses run in the inferior border; and the transverse sinus runs in the outer border of the tentorium. The occipital sinus (shown however not labeled) runs within the midline of the posterior fossa and empties into the torcular. Engorgement and venous rupture result in hemorrhage into the encompassing subdural space. In asymptomatic infants, subdural hemorrhages are related to vaginal delivery and never cesarean part, supporting that vaginal supply may be related to larger threat for trauma. However, in asymptomatic time period infants with subdural hemorrhages, neither assisted vaginal supply nor medical proof of neonatal birth trauma could be used to predict the presence of hemorrhage. Most (13 of 17, or 76%) of the circumstances were in the setting of nonassisted vaginal birth. The authors concluded that a subdural hematoma was not essentially related to apparent start trauma. With regard to symptomatic subdural hemorrhages, because the incidence of grossly traumatic deliveries has decreased, the relative proportion of untimely infants with subdural hemorrhage has elevated as nicely. Indeed, in some surveys, the proportion of circumstances in untimely and full-term infants has been roughly similar. Thus massive symptomatic subdural hemorrhage is more than likely to occur underneath the circumstances the place the pinnacle of the infant is subjected to unusual or speedy deforming stresses corresponding to compression, molding, or stresses on extraction. These results can lead to stretching of both the falx and one or both leaves of the tentorium, with an inclination for tearing of the tentorium, particularly near its junction with the falx, or, less generally, tearing of the falx itself. Extreme vertical molding appears to underlie many tears of superficial cerebral veins and the formation of a convexity subdural hematoma. In the particular case of occipital osteodiastasis with breech delivery, the harm results from suboccipital stress, which most commonly happens if the fetus is forcibly hyperextended with the top trapped beneath the symphysis. The hematoma is often extra in depth over the lateral aspect of the convexity than near the superior sagittal sinus. With such infratentorial hemorrhage, nuchal rigidity with retrocollis or opisthotonos may also be a helpful early signal. Over minutes to hours, because the clot turns into bigger, stupor progresses to coma, pupils might turn out to be fixed and dilated, and indicators of lower brain-stem compression appear. Ocular bobbing and ataxic respirations could occur; lastly, respiratory arrest ensues. The severe medical syndrome associated with occipital osteodiastasis resembles that described for main tentorial laceration. A depressed Apgar rating at 1 minute is frequent, and the course is certainly one of speedy deterioration. In the six infants described by Wigglesworth and Husemeyer,59 the age on the time of demise ranged from 7 to forty five hours. First, no neurological indicators are obvious for a period that varies from several hours after delivery (usually a difficult vacuum, forceps, or breech extraction or all three) to as a lot as three or 4 days of age. First and doubtless most commonly, minor degrees of hemorrhage happen, and minimal or no medical indicators are apparent. Irritability, a hyperalert look, unexplained apneic episodes, or no indicators have been noted. With this syndrome, seizures, typically focal, are common and are frequently accompanied by other focal cerebral indicators. However, some essential conclusions could be drawn from our personal observations and from those recorded by different investigators. Third, indicators referable to disturbance of brain stem develop, together with respiratory abnormalities, apnea, bradycardia, oculomotor abnormalities, skew deviation of eyes, and facial paresis. These deficits relate to direct compressive results of the posterior fossa hematoma. In addition to brain-stem indicators, seizures occur within the majority of infants, maybe due to accompanying subarachnoid blood. In infants who clearly worsen over hours or a day or more, as do approximately half, deadly brain-stem compression could develop. There is excessive signal in the posterior fossa, in maintaining with subdural hemorrhage (arrow). Clinical Syndromes co the diagnosis of main neonatal subdural hemorrhage relies upon principally on recognition of the scientific syndrome, with subsequent definitive demonstration by a mind imaging research. The most distinctive neurological sign with major convexity subdural hemorrhage is dysfunction of the third cranial nerve on the facet of the hematoma; this dysfunction is often manifested by a nonreactive or poorly reactive, dilated pupil. An excellent example of such a neurological syndrome related to subdural hematoma was a new child with hemophilia that we studied. Neurological signs primarily referable to the brain stem should suggest infratentorial hematoma. Neurological indicators primarily referable to the cerebrum should counsel convexity subdural hematoma. These indicators should provoke extra definitive and immediate diagnostic studies as a outcome of the medical course may deteriorate very rapidly. Computed Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Ultrasound Scans fre oo ks oo oo oo ks f ks fre. T the overwhelming majority of subdural hematomas are infratentorial, where ultrasound has even larger challenges in accurate diagnosis. The major difficulty of ultrasound scanning pertains to acoustical interference by bone and to near-field transducer artifacts. Coronal T1-weighted image reveals the central tentorial hematoma and layered blood along each leaves of the tentorium and the posterior falx. The blood in the proper parietal area is due to a cephalhematoma (better seen on axial images). Cranial ultrasound scan on admission to the neonatal intensive care unit displayed a really giant subdural hemorrhage. Note the world of increased attenuation on the right, representing the hematoma, and the shift of ventricles to the left. Note additionally deviation of midline structures to the proper and probable tentorial tear, with associated hemorrhage. Schematic diagram of the cranium illustrating (A) the normal state (arrow) and (B) occipital osteodiastasis with posterior fossa encroachment (arrow). Approximately 15% of surgically handled sufferers developed communicating hydrocephalus that required shunt placement. Of 40 nonsurgically handled infants, nearly 90% had a favorable end result (see Table 22. The small posterior fossa subdural hemorrhages described in hospital-based series are related to no main sequelae or dying.