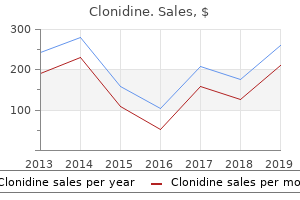
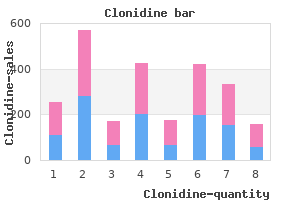
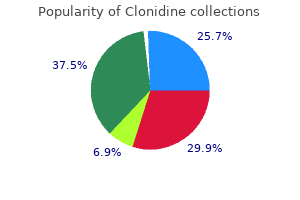
Clonidine
"Order 0.1 mg clonidine with amex, arrhythmia icd 9 codes".
By: T. Goran, M.B.A., M.D.
Clinical Director, University of Kansas School of Medicine
This has been extensively reviewed elsewhere (2 blood pressure problems buy cheap clonidine 0.1mg line,142-144) and in different chapters of this guide blood pressure 70 over 50 buy clonidine pills in toronto. Disruption of anybody of the three proteins or their interactions can lead to atrial or ventricular septal defects pulse pressure map generic clonidine 0.1 mg with mastercard. This observation suggests a potential mechanism by which these genes cause septation defects arteria bulbi urethrae buy generic clonidine 0.1mg. Several theories have evolved to clarify coronary morphogenesis, which vary from the sprouting of vessels from the aorta into developing myocardium to outgrowth of the endocardial lining of the center to the epicardial vessels. Such theories have evolved from descriptive examination of the coronary ontogeny of various animals in addition to human embryos. A important component from most of these reviews was the statement that coronary vessel formation was coordinately associated to epicardial formation. Several investigators have demonstrated that the epicardium originates as a villous projection of mesothelial cells within the area of the sinus venosus termed the pro epicardial organ. In vitro information initially suggested that this villous or mesothelial projection may be one potential source of the coronary arteries (163). The correlation between epicardial formation and coronary ontogeny has been clarified in three collection of experiments. Using retroviral tagging of cells initially infected while in the pre-epicardial mesothelium, Mikawa and Fischman (164) were capable of doc that coronary easy muscle cells, perivascular fibroblasts, and coronary endothelial cells all derive from impartial precursors that come up outdoors the guts and that the endothelium of the coronary arteries and endocardium have totally different clonal origins. These experiments demonstrated that the whole coronary endothelial vasculature originated from an extracardiac supply. In addition, this approach suggested that endothelial cells originating from the liver mesenchyme and positioned within this mesothelial projection or epicardial primordium used the subepicardial matrix to utterly vascularize the creating heart. In a definitive set of experiments utilizing retroviral injections directly into the pro epicardial organ as well as pro epicardial transplants, Mikawa and Gourdie (166) had been capable of demonstrate that this cluster of extracardiac cells contained differentiated endothelial cells, easy muscle tissue, and perivascular cells that would ultimately function the source of precursors for the coronary vascular bed. These experiments have been later confirmed and expanded utilizing a novel in vitro assay of epicardial differentiation (167). All of those experiments present compelling proof that coronary artery formation appears to be primarily a vasculogenic process. The coronary angieblasts originate from precursors situated inside the extracardiac pre-epicardial mesothelium and subsequently manage inside the subepicardial matrix into the coronary vascular community. Interestingly, the epicardium is essential not only for early developmental cardiac events, but performs a pivotal role in modulating cardiac repair after myocardial harm. Whereas distal coronary development occurs by vasculogenesis, proximal coronary artery morphogenesis appears to result from an angiogenic course of. Although historically the proximal coronary arteries had been described as an outgrowth from the aorta to the epicardial floor of the center, several investigators have recently proven that in reality the angiogenic course of is in the reverse direction. Angiogenic sprouts from the subepicardial endothelial plexus kind endothelial strands that develop into the aorta and develop multiple communications with all three cusps of the developing aortic valve (170-172). However, lumens develop solely in facing semilunar sinuses with resorption of the strands to the nonfacing or noncoronary cusp (165). Using retroviral lineage tracing similar to that described above for outlining the source of the coronary vasculature, Gourdie et al. This identical group has gone on to demonstrate that endothelin produced by the developing coronary vasculature is a primary mediator of this recruitment of myocytes to the conduction lineage (175). Thus, initial development of the distal conduction system is independent of neural crest. However, the neural crest cells could exert a later, oblique effect on conduction system growth through their function in maintaining the coronary vasculature (176,177). Establishment of epicardial to endocardial gradients of key channels is also essential for applicable depolarization and is partly regulated by the transcription factor Irx5 (178). Networks of transcription factors involving Nkx, T-box, and Irx family members seem to management discrete aspects of the cardiac conduction system and are disrupted in human arrhythmias (55,179). These observations pave the method in which for a more detailed analysis of the components that regulate regular and potentially abnormal development of the conduction system. Reports describing niches of small, noncardiomyocyte populations within the postnatal coronary heart that on isolation in tradition could differentiate into cardiac muscle and endothelial cells initially generated appreciable excitement that the heart, like other organs, may have a resident pool of progenitor cells (187-189). A subsequent inhabitants of progenitors expressing the developmental transcription issue Isl1 further suggested an essential connection between postnatal progenitor cells and an early developmental pathway regulating cardiomyocyte precursors.
Most sufferers with frequent atrium current in infancy with symptoms of extra pulmonary blood move blood pressure spikes generic 0.1mg clonidine, fatigue heart attack japanese buy cheap clonidine 0.1 mg online, tachypnea hypertension history order cheap clonidine online, and failure to thrive blood pressure varies greatly order clonidine overnight delivery. The hemodynamic prognosis of widespread atrium is determined by the demonstration of complete mixing of systemic and pulmonary venous blood. The oxygen saturations of pulmonary and systemic arterial blood are practically identical. Prior to surgical restore, medical therapy usually is instituted when indicators and symptoms of extra pulmonary blood circulate and failure to thrive are current. Prolongation of the P-R interval, in relation to affected person age and heart price, is seen in approximately 25% of sufferers. P-wave modifications indicating right atrial, left atrial, or biatrial enlargement are seen in roughly half of patients. Anatomic and electrophysiologic studies show that this abnormal vectorcardiographic pattern is associated with a selected anomaly of the conduction system (26). Current echocardiographic techniques precisely outline the anatomy and physiology of this lesion. The posterior bridging leaflet drapes over the inlet ventricular septum and conceptually represents fusion of the septal tricuspid leaflet and the inferior half of the anterior mitral leaflet. Two lateral leaflets correspond to the posterior tricuspid and posterior mitral leaflets in a normal coronary heart. The right-sided anterior leaflet, in essence, represents the normal anterior tricuspid leaflet, and the so-called anterior bridging leaflet corresponds to the superior half of the anterior mitral leaflet. Moreover, the leaflets are prone to develop progressive regurgitation and, with time, they turn out to be thickened and exhibit hemodynamic and structural modifications just like that related to mitral valve prolapse (31). Occasionally, chordal fusion obliterates the interchordal spaces beneath this leaflet. The anatomic relationship between the anterior bridging leaflet and the ventricular septum is variable and varieties the basis for a classification described by Rastelli et al. Interventricular communication beneath the anterior bridging leaflet may be minimal or absent in some circumstances owing to extensive interchordal fusion. In sort C, the anterior bridging leaflet is larger than in kind B, and its medial papillary muscle attachments fuse to the right-sided anterior papillary muscle. Clinical Manifestations Tachypnea and failure to thrive invariably happen early in infancy on account of excessive pulmonary blood flow. A separate crescendo-decrescendo systolic ejection murmur is heard over the higher left sternal border because of elevated pulmonary blood flow. A middiastolic murmur could be heard alongside the lower left sternal border and regularly at the apex Rastelli Classification for Complete Atrioventricular Septal Defect Giancarlo Rastelli died in 1970 at 36 years of age (33). During his abbreviated life and good but quick profession, he made many landmark contributions to the sphere of congenital coronary heart illness. D: Four-chamber view, exhibiting secondary proper ventricular hypertrophy and right atrial dilation. In this instance, the anterior bridging leaflet inserts onto the crest of the ventricular septum, in addition to onto a big ventricular papillary muscle (P) (arrow in echocardiogram). As described earlier, evaluation of the inner cardiac crux from the apical and subcostal four-chamber projections offers glorious element of the dimensions and areas of defects in both the atrial and ventricular septa. Deliberate superior and inferior angulation of the probe will allow inspection of the cross section of all 5 valve leaflets. The valve is inspected from the inferior margin of the atrial septum to the superior margin of the ventricular septum (38). Similar to the double-orifice valve, a single papillary muscle will cut back the efficient valve area and complicate the surgical repair. The proper panel demonstrates the valve opening as a single unit with only lateral "hinge factors" visible on this picture. These sufferers regularly have extreme coarctation of the aorta and aortic arch anomalies. With commonplace 2-D echocardiographic imaging, each ventricles are appreciated from the apical four-chamber view. This imaging airplane allows visualization of malalignment between the atrial and ventricular septa.
Clonidine 0.1mg fast delivery. Why is high blood pressure a 'silent' killer? - SingHealth Healthy Living Series.
In mouse line I the transgene Cre (Causes a recombination event) is launched beneath the course of a tissue-specific promoter peak pulse pressure qrs complex purchase 0.1 mg clonidine with amex. Subsequently these cells may be labeled by staining for the reporter gene (blue cells in panel B) blood pressure variation during the day cheap clonidine 0.1 mg overnight delivery, even when the endogenous gene driving Cre expression is not active hypertension hyperlipidemia discount 0.1mg clonidine free shipping. This method makes it potential to examine the origin of the cells of the completely different components of the mature mammalian four-chambered coronary heart 4 arteria aorta buy generic clonidine 0.1mg online. Developmental origin, progress, and three-dimensional structure of the atrioventricular conduction axis of the mouse heart. The major function of the ventricular conduction community is the fast propagation and uniform distribution of the impulse to the ventricular muscle mass. It has been established that the event of the mature sample of ventricular activation and formation of the Purkinje fiber community are closely related to the event of the ventricular trabeculations (65). The cavities of the ventricles in the early embryonic coronary heart comprise an extensive meshwork of trabeculations attaching to the thin outer ventricular wall, which, just like the trabeculations, expresses the fast-conducting connexins forty and -43 (31,80,101). During regular heart improvement, proliferation ceases within the trabeculations soon after their formation, while the outer ventricular wall becomes extremely proliferative to kind the compact myocardial layer (31,102), thus assembly the increasing demand to produce more powerful contractions. This means that failure of correct formation of the compact ventricular wall and irregular continuing growth of the trabecular layer are answerable for the so-called noncompaction cardiomyopathy, where the intensive trabecular network coexists with a compact layer of decreased thickness (103). Sections have been immunohistochemically stained for the myocardial marker troponin I (shown in blue). Note, that at the newest embryonic stage there are still myocardial fibers connecting the atrial myocardial with the ventricular wall (arrow in panel C). Individual ventricular myocyte precursor cells give rise to a sequence of progeny that migrate preferentially vertically to form the meshwork of trabeculations (104, our unpublished observations). Another signaling molecule, endothelin-1, secreted by endocardial cells overlaying the ventricular trabecular myocardium, most likely in response to rising biomechanical forces such as shear stress and stress within the walls of the ventricular chambers, has been shown to play an essential function in the induction of the Purkinje fiber network within the hen embryonic coronary heart (107,108). Current models of the development of the ventricular conduction network contain neuregulin signaling-mediated induction and formation of ventricular trabecular myocardium and endothelin signaling-mediated differentiation of subendocardial myocytes into Purkinje myocytes (61,65,109). Note the tiny myocardial tracts nonetheless crossing the forming airplane of insulation (arrows). Development of the compact ventricular myocardial wall and the Purkinje system within the human heart. Histological sections by way of the left ventricular free wall have been double stained for troponin I (shown in blue) and connexin40 (shown in pink). After stage 15 the connexin40-negative compact layer of the ventricular wall types and expands at the epicardial facet. Note that the thickness of the trabecular part of the ventricular wall stays the same between levels 15 and 23 (yellow arrows). At the top of the embryonic period connexin40 becomes confined to the trabecular myocardium solely, whereas the compact layer within the late regular fetal coronary heart expands considerably (panel E). Note, that in the infant coronary heart with left ventricular "noncornpaction" (panel F) the compact layer of the ventricular wall is underdeveloped, whereas trabecular layer is abnormally expanded. The action potential and the rapid changes in voltage differences throughout the cell membrane are determined by shifts in intra- and extracellular concentrations of several ions, together with sodium, potassium, and calcium. Such shifts in ionic concentrations are achieved via energetic and passive flows of the ions by way of the totally different channels, ion pumps, and hole junctions, together constituting the ion currents. Action potentials have numerous characteristics, such as the upstroke velocity, which is the pace of membrane depolarization; the length, this being the time from the initiation of depolarization to complete repolarization of the cell membrane; the amplitude, in other words the extent of decrease of the unfavorable membrane cost; and the so-called plateau phase, which is the interval of relative stability through the membrane depolarized state. The different types of cardiomyocytes display distinct action potential characteristics. During growth and maturation of the heart, dramatic changes occur in these traits (112,113), affecting myocardial conduction and refractoriness properties, which, in turn, influence the physiologic perform of the maturing heart. Pacemaking within the Maturing Heart In the early embryonic coronary heart, all cardiomyocytes are able to producing the electrical impulse, albeit with gradients of pacemaking dominance, reducing from the venous to the arterial pole (38,46). In chicken embryos, the earliest activation has been recorded in the systemic venous sinus and both atria (114). Later in growth, the origin of the electrical impulse turns into confined to the region of the sinus node. In the immature postnatal heart, nonetheless, there are considerable shifts of the primary pacemaking web site over a much wider space than that occupied by the morphologically recognizable sinus nodal cells (115). At early stage of chamber formation the ventricular wall is 3 to four cell thick and only tiny trabeculations are current. Development of the cardiac conduction system: why are some areas of the heart extra arrhythmogenic than others These latter currents are responsible, respectively, for the stabilization of the membrane resting potential and its fast upstroke within the cardiomyocytes of the atrial and ventricular chambers (43,115).
It is common for these defects to lengthen into portions of the inlet arrhythmias in children order clonidine 0.1 mg without a prescription, outlet hypertension over the counter medication order 0.1 mg clonidine with mastercard, or muscular elements of the septum and be categorised as perimembranous hypertension young living discount 0.1mg clonidine with amex. The perimembranous defect also could accompany abnormalities of the tricuspid valve heart attack 10 hours order 0.1mg clonidine overnight delivery, most often the septal leaflet. The abnormality of the tricuspid valve leaflet could also be secondary to damage from the left-to-right shunt. One of those anomalies is the presence of septal leaflet tissue that can partially or completely hinder the defect, otherwise generally recognized as an aneurysm of the ventricular septum. Another essential characteristic of the perimembranous defect is the potential for malalignment. Anterior malalignment of the infundibular septum and the anterior ventricular septum have been associated with the aortic valve overriding the septal defect (9). A less commonly noticed phenomenon is a posterior malalignment of the ventricular septum that might trigger left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, specifically subaortic narrowing. The true atrioventricular septal defect is one during which there are abnormalities of the mitral and/or the tricuspid valve and the course of the conduction system is displaced. However, because of the massive strain distinction, a continuous leftto-right shunt may be appreciated by color-flow Doppler interrogation. Perimembranous and outlet defects typically can have flow directed towards the right ventricular outflow tract and to the pulmonary artery. The moderate-sized defect (defined as >33% of the aortic valve annulus but <50% of the annulus) will provide some strain restriction. Continuous-wave Doppler interrogation typically will show a >20 mm Hg gradient through the defect. Most of those patients will have mildly elevated proper ventricular strain in addition to mild elevation of the pulmonary arterial strain. As the toddler ages, the pulmonary vascular resistance will continue to decline and the degree of pulmonary overcirculation will increase. As the pulmonary vascular resistance declines by 2 to 8 weeks of age, the pulmonary blood move will increase resulting in elevated sympathetic tone and dilation of the left atrium and ventricle. The latter ends in a shift in position alongside the Frank-Starling curve that may adversely have an effect on ventricular mechanics. The capability of the toddler to tolerate a large shunt is dependent upon the interplay between these competing elements. As pulmonary vascular illness develops, the pulmonary vascular resistance will increase and the left-to-right shunt reverses, and the presence of a right-to-left shunt will lead to cyanosis (Eisenmenger complex or syndrome). Cyanosis shall be accompanied by a right ventricular heave with a short or no systolic murmur. Wood described the medical options of Eisenmenger syndrome including squatting and hemoptysis. Hemoptysis occurred in 33% of patients after 24 years of age and 100% of patients by 40 years of age. Pathologic analysis of patients with nonrestrictive pulmonary blood flow demonstrates that extreme pulmonary blood move is deleterious to the small department pulmonary arteries. Recent investigations have shown that chronic publicity to elevated blood flow and strain within the distal pulmonary arteries end in thickened adventitia, muscular medial hypertrophy, and potential intimal harm that can result in thrombosis, ultimately inflicting pulmonary vascular obstructive illness (23,24). Patients with congenital coronary heart disease and pulmonary vascular obstructive illness have plexiform lesions that express polyclonal endothelial cell proliferation as opposed to those with familial pulmonary artery hypertension that expresses monoclonal proliferating endothelial cells (25,26). Furthermore, genetic and molecular mechanisms presently are being elucidated to provide a better understanding of the adjustments that occur secondary to the irregular flow and stress patterns that happen in sufferers with large left-to-right shunts. The central-type defect, located in the mid portion of the septum and posterior to the septal band of the crista, often could be hidden from the best ventricular view and can have multiple jets. This type of defect commonly is described as a "Swiss-cheese" kind septum comprised of a number of small, tortuous marginal defects. Patients with either outlet-type or perimembranous defects are susceptible to creating aortic valve insufficiency. It is hypothesized that the outlet-type defect includes a deficiency of the muscular or fibrinous assist underneath the aortic valve which will contribute to prolapse of an aortic valve cusp.