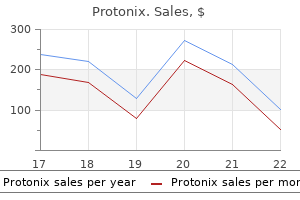
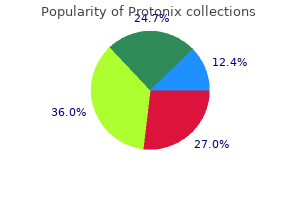
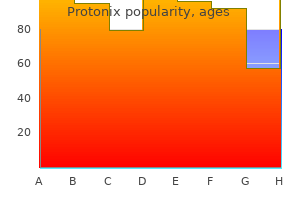
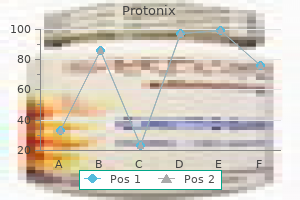
Protonix
Protonix dosages: 40 mg, 20 mg
Protonix packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Purchase 20 mg protonix mastercard
Precautions: (1) To be certain that the needle is in the amniotic cavity evidenced by clear liquor popping out gastritis diet 7-up cheap protonix 20 mg mastercard. A fast infusion of 1 gastritis diet ���� order 40 mg protonix otc,000 mL dextrose in water together with intravenous diuretics is indicated in such cases. Mode of action: There is liberation of prostaglandins following necrosis of the amniotic epithelium and the decidua. This in flip excites uterine contraction and ends in the expulsion of the fetus. Success rate: the strategy is effective in 90�95% cases with induction-abortion interval of about 32 hours. The technique failure (end point) is considered when abortion fails to happen within forty eight hours. Complications: the complications include-(a) Minor complaints like fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, belly ache. Intra-amniotic instillation of hyperosmotic urea: Intra-amniotic instillation of 40% urea solution (80 g of urea in 200 mL distilled water) along with syntocinon drip is efficient with less complications. The problems are both related to the methods employed or to the abortion process. Obstetrical issues include-(a) recurrent midtrimester abortion because of cervical incompetence, (b) ectopic being pregnant (threefold increase), (c) preterm labor, (d) dysmaturity, (e) increased perinatal loss, (f) rupture uterus, (g) Rh-isoimmunization in Rh-negative girls, if not prophylactically protected with immunoglobulin and (h) failed abortion and continued pregnancy. Midtrimester: the mortality price will increase five to six instances to that of first trimester. Contrary to the outcomes of the advanced international locations, the mortality from saline method has been discovered much larger in India compared to termination by abdominal hysterotomy with tubectomy. While there has been about fourfold enhance in incidence over the couple of a long time, but the mortality has been slashed down by 80%. Secondly early diagnosis helps to detect some circumstances, that within the past, might have resolved spontaneously. Early diagnosis and therapy have helped to scale back maternal deaths due to ectopic pregnancy. Contraception failure: Women using any type of contraception have significantly reduced probability of having a ectopic pregnancy. CuT 380A and levonorgestrel devices have got the lowest fee of ectopic whereas Progestasert has obtained the highest one. The danger is highest History of tubal ligation following laparoscopic bipolar coagulation. Contraception failure (c) Use of progestin solely pill or postcoital estrogen Previous ectopic pregnancy preparations will increase the chance of tubal Tubal reconstructive surgery pregnancy probably by impaired tubal motility. The risk of ectopic is 5�7% and that of heterotypic being pregnant is 1% in contrast to 1 in 5,000 in spontaneous being pregnant. Others: Previous ectopic being pregnant: There is 10�15% chances of repeat ectopic being pregnant. Transperitoneal migration of the ovum-contralateral presence of corpus luteum is noticed in tubal pregnancy in about 10% cases. Factors facilitating nidation in the tube: (i) Early resumption of the trophoblastic activity is probably because of untimely degeneration of the zona pellucida. Finally, tubal rupture occurs when the muscles and the serosa are maximally stretched and endure necrosis. The decidua develops all of the characteristics of intrauterine being pregnant besides that it contains no evidence of chorionic villi. Earliest interruption occurs within the isthmial implantation whereas being pregnant may continue as a lot as 3�4 months in interstitial implantation. However, real circumstances are on record of gestation continuing to term in the Fallopian tube. Repeated small hemorrhages occur in the choriocapsular house, separating the villi from their attachments. The fate of the mole is either-(a) full absorption or (b) expulsion by way of the abdominal ostium as tubal abortion with a variable amount of inside hemorrhage. The encysted blood so collected within the pouch of Douglas is known as pelvic hematocele. Muscular contraction enhances separation and facilitates its expulsion via the stomach ostium. Tubal rupture: Tubal rupture is predominantly widespread in isthmic and interstitial implantation. As the isthmic portion is slim and the wall is less distensible, the wall may be easily eroded by the chorionic villi. Isthmic rupture usually occurs at 6�8 weeks, the ampullary one at 8�12 weeks and the interstitial one at about 4 months. Depending upon the site of rupture, it is named: (1) Intraperitoneal rupture: this kind of rupture is widespread. Secondary abdominal being pregnant: the conditions for the continuation of fetal progress exterior the tube are: (1) Perforation of the tubal wall should be a slow process. The fibrin is deposited over the exposed amnion to represent a secondary amniotic sac. Secondary broad ligament being pregnant: Rarely pregnancy could proceed in the identical process as in belly pregnancy between the 2 layers of the peritoneum. Arias-Stella response: this is characterised by a typical adenomatous change of the endometrial glands. Intraluminal budding along with typical cell modifications (loss of polarity of cells, pleomorphism, hyperchromatic nuclei, vacuolated cytoplasm and occasional mitosis) are collectively referred to as Arias-Stella reaction. Fate of Secondary Abdominal Pregnancy Death of the blastocyst Massive intraperitoneal hemorrhage Infection separation fistulous communication with intestine, bladder, umbilicus Fetal death mummification, suppuration, adipocere formation, calcification (lithopedion) Continue to time period being pregnant (rare-1. On rare occasion, the bleeding may be as a result of tubal abortion through the uterine ostium in interstitial being pregnant. The clinical varieties are correlated with the morbid pathological changes in the tube subsequent to implantation and the amount of intraperitoneal bleeding. Patient profile: (1) the incidence is maximum between the age of 20 years and 30 years, being the utmost period of fertility. The sufferers, however, have got persistent unilateral uneasiness in about one-third of circumstances before the acute symptoms appear. Symptoms: the classic triad of signs of disturbed tubal being pregnant are: stomach. Hugely dilated ampulla is seen (arrow) ache (100%), preceded by amenorrhea (75%) and lastly, appearance of vaginal bleeding (70%). Amenorrhea: Short interval of 6�8 weeks (usually); there could additionally be delayed interval or history of vaginal recognizing. Shoulder tip ache (25%) (referred pain as a result of diaphragmatic irritation from hemoperitoneum) may be current. Syncopal attack (10%) is due to reflex vasomotor disturbances following peritoneal irritation from hemoperitoneum.
Protonix 40 mg buy generic
Narcotic antagonists are used to reverse the respiratory depression induced by opioid narcotics chronic gastritis yahoo answers protonix 40 mg sale. Naloxone is given to a new child born of a narcotic addicted mother gastritis symptoms toddler protonix 40 mg generic on-line, with correct ventilation arrangement solely otherwise withdrawal signs are precipitated. Major disadvantages are: Loss of beat to beat variability in labor, neonatal hypotonia and hypothermia. Combination of narcotics and antiemetics: Narcotics could additionally be used in combination with promethazine, metoclopramide or ondansetron. The advantages claimed that the mixture potentiates the action of narcotic, produces much less respiratory melancholy and prevents vomiting. But there are also disadvantages like hypotension and delay of second stage of labor. This agent is used in the second part (from eight cm dilatation of cervix to delivery). The woman is to take gradual and deep breaths before the contractions and to cease when the contractions are over. It offers sensory as nicely as varied levels of motor blockade over a region of the body. But anesthetists/obstetricians should be trained correctly to make use of this very priceless technique in regular and abnormal labor. Continuous lumbar epidural block: A lumbar puncture is benefits of Regional anesthesia made between L2 and L3 with the epidural needle (Tuohy needle). The patient is awake and may enjoy the With the patient on her left side, the again of the affected person is cleansed birth time with antiseptics earlier than injection. Epidural analgesia, as a basic rule should be given when labor is properly established. Epidural analgesia is particularly helpful in instances like pregnancy-induced hypertension, breech presentation, twin being pregnant and preterm labor. This may result in frequent need of instrumental delivery like forceps or ventouse. Back pain Postspinal headache as a outcome of leakage of cerebrospinal uid via the needle hole in the dura Total spinal due to inadvertent administration of the drug in the subarachnoid area Injury to nerves, convulsions, pyrexia Ine ective analgesia Supine hypotension Hypovolemia Neurological illnesses Spinal deformity or chronic low again pain Skin infection on the injection website Paracervical nerve block: Is helpful for pain aid in the course of the first stage of labor. This dose is sort of adequate to relieve pain for about an hour or two, and injections may be given greater than once if necessary. Paracervical block can only relieve the pain of uterine contraction and the perineal discomfort is eliminated by pudendal nerve block. This is as a end result of of decreased placental perfusion resulting from uterine artery vasoconstriction or its direct depressant impact on the fetus following transplacental switch. Simultaneous perineal and vulval infiltration is required to block the perineal department of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh and the labial branches of the ilioinguinal and genitofemoral nerves (vide supra). This technique of analgesia is related to less hazard, each for mother and baby than general anesthesia. Technique: the pudendal nerve could also be blocked by both the transvaginal or the transperineal route. A 20 mL syringe, one 15 cm (6") 22 gauge spinal needle and about 20 mL of 1% lignocaine hydrochloride are required. The index and center fingers of one hand are launched into the vagina, the finger ideas are positioned on the tip of the ischial spine of 1 facet. The needle is passed along the groove of the fingers and guided to pierce the vaginal wall on the apex of ischial backbone and thereafter to push slightly to pierce the sacrospinous ligament just above the ischial spine tip. The comparable procedure is adopted to block the nerve of the opposite aspect by changing the hands. Note the relation of the pudendal nerve to the ischial spine in the inset chapter 34 Pharmacotherapeutics in Obstetrics 595 Complications: Hematoma formation, infection and barely intravascular injection or allergic response. Spinal anesthesia: Spinal anesthesia is obtained by injection of local anesthetic agent into the subarachnoid space. Spinal anesthesia may be employed to alleviate the ache of delivery and in the course of the third stage of labor. For normal supply or for outlet forceps with episiotomy, ventouse supply, block should extend from T10 (umbilicus) to S1. Addition of fentanyl (to enhance the onset of block) or morphine (to improve ache control) may be accomplished. The blood stress and respiratory rate should be recorded each 3 minutes for the primary 10 minutes and every 5 minutes thereafter. Sometimes vasopressor drugs could also be required if a marked fall in blood pressure happens. A small gauge spinal needle is launched via the epidural needle into the subarachnoid area (needle through needle technique). The methodology gives rapid and effective analgesia during labor and cesarean supply. A 10 mL syringe, with a fantastic needle and about 8�10 mL 1% lignocaine hydrochloride (Xylocaine) are required. For outlet forceps or ventouse-(Perineal and labial infiltration): the mixed perineal and labial infiltration is efficient in outlet forceps operation or ventouse traction. A 20 mL syringe, a protracted nice needle and about 20 mL of 1% lignocaine hydrochloride are required. About 10 mL of the solution is infiltrated in a fanwise manner on either side of the midline (as for episiotomy). The needle is then directed anteriorly along each side of the vulva so far as the anterior-third to block the genital branch of the genitofemoral and ilioinguinal nerve. Technique: the pores and skin is infiltrated along the line of incision with diluted resolution of lignocaine (2%) with regular saline. The subcutaneous fatty layer, muscle, rectus sheath layers are infiltrated as the layers are seen during operation. Patient is taught about the physiology of being pregnant and labor in antenatal (mothercraft) classes. Preoperative preparations: these security measures ought to be taken to forestall issues of general anesthesia. H2-blocker (Ranitidine a hundred and fifty mg orally) ought to be given evening earlier than (elective procedure). While on the theater table, left lateral tilt of the lady is maintained with a wedge on the again. Uterine incision - Delivery (U-D) interval is extra predictive of neonatal standing (Apgar score). Prolonged U-D interval of greater than 3 minutes leads to lower Apgar scores and neonatal acidosis. Preoxygenation with 100% oxygen is administered by tight mask fit for more than 3 minutes. Induction of anesthesia is finished with the injection of thiopentone sodium 200�250 mg (4 mg/kg) as a 2.
Protonix 40 mg purchase without a prescription
Assessment of the pelvis particularly in primigravidae is to be accomplished gastritis diet 50 buy 20 mg protonix free shipping, and elasticity of the pelvic floor and presence of vulval varicosity gastritis que comer 40 mg protonix best, if any, are to be noted. Pelvic assessment specially in primigravidae ought to be accomplished during the preliminary examination. Chapter thirteen Normal Labor 157 - the progress of labor may be judged on periodic examinations noting the dilatation of the cervix and descent of the head in relation to the spines (station). Enquiry is to be made concerning the onset of labor pains or leakage of liquor, if any. Thorough general and obstetrical examinations including vaginal examination are to be carried out and recorded. Records of antenatal visits, investigation reports and any specific remedy given, if available, are to be reviewed. Bowel-An enema with cleaning soap and water or glycerin suppository is traditionally given in early stage. Rest and ambulation-If the membranes are intact, the affected person is allowed to walk about. Ambulation can cut back the period of labor, need of analgesia and improve maternal consolation. If, however, labor is monitored electronically or analgesic drug (epidural analgesia) is given, she ought to be in mattress. Low pH of the gastric contents is an actual danger if aspirated following common anesthesia when needed unexpectedly (see p. Fluids in the type of plain water, ice chips or fruit juice could additionally be given in early labor. Intravenous fluid with ringer resolution is began where any intervention is anticipated or the patient is under regional anesthesia. Bladder care-Patient is inspired to cross urine by herself as full bladder usually inhibits uterine contraction and may result in an infection. If the patient fails to pass urine particularly in late first stage, catheterization is to be carried out with strict aseptic precautions. For sensible functions, the widespread analgesic drug used is pethidine 50�100 mg intramuscularly when the pain is properly established within the energetic part of labor. Abdominal palpation-(a) Uterine contractions as regard the frequency, intensity and period are assessed. The variety of contractions in 10 minutes and period of every contraction in seconds are recorded within the partograph (see p. To be of worth, the remark ought to be made instantly following uterine contraction. Doppler ultrasonic cardiography (Dopplex), however, is useful in the case of weight problems and polyhydramnios. To avoid confusion of maternal and fetal heart charges, maternal pulse ought to be counted. Vaginal examination-(a) Dilatation of the cervix in centimeters in relation to hours of labor is a reliable index to note the progress of labor. The position and the station of the top are once extra to be reviewed and the progressive descent of the top is ensured. Dorsal place with 15� left lateral tilt is often favored because it avoids aortocaval compression and facilitates pushing effort. One sterile sheet is positioned beneath the buttocks of the patient and one over the stomach. Essential aseptic procedures are remembered as three Cs: (a) Clean palms, (b) Clean surface and (c) Clean chopping and ligaturing of the cord. The affected person is encouraged for the bearing-down efforts during uterine contractions. When the scalp is visible for about 5 cm in diameter, flexion of the head is maintained during contractions. This is achieved by pushing the occiput downward and backward by using thumb and index fingers of the left hand while urgent the perineum by the best palm with a sterile vulval pad. If the patient passes stool, it ought to be cleaned and the region is washed with antiseptic lotion. The course of is repeated throughout subsequent contractions until the subocciput is placed beneath the symphysis pubis. At this stage, the maximum diameter of the pinnacle (biparietal diameter) stretches the vulval. The purpose of accelerating the flexion of the top is to make certain that the small suboccipitofrontal diameter 10 cm (4") distends the vulval outlet as an alternative of bigger occipitofrontal diameter 11. Bulging thinned out perineum is a better criterion than the visibility of 4�5 cm of scalp to resolve the time of performing episiotomy (details in Chapter 37). Care following delivery of the head: - Immediately following supply of the top, the mucus and blood in mouth and pharynx are to be wiped with sterile gauze piece on a little finger. This easy procedure prevents the intense consequence of mucus blocking the air passage during vigorous inspiratory efforts. Flexion of the subocciput comes beneath the symphysis pubis in order that lesser suboccipitofrontal 10 cm (4") diameter emerges out of the introitus. Spontaneous forcible delivery of the pinnacle is to be prevented by assuring the affected person not to bear down throughout contractions. To take care during delivery of the shoulders as the wider bisacromial diameter (12 cm) emerges out of the introitus. This not directly signifies that the bisacromial diameter is positioned within the anteroposterior diameter of the pelvis. By drawing the top in upward path, the posterior shoulder is delivered out of the perineum. Traction on the head should be gentle to avoid extreme stretching of the neck causing injury to the brachial plexus, hematoma of the neck or fracture of the clavicle. Delivery of the trunk: After the delivery of the shoulders, the fore finger of each hand are inserted beneath the axillae and the trunk is delivered gently by lateral flexion. It facilitates drainage of the mucus accumulated in the tracheobronchial tree by gravity. The tray is placed between the legs of the mother and should be at a lower stage than the uterus to facilitate gravitation of blood from the placenta to the infant. Two separate cord ligatures are utilized with sterile cotton threads 1 cm apart using reef-knot, the proximal one being placed 2. Squeezing the wire with fingers previous to making use of ligatures or plastic twine clamps. Leaving behind a length of the wire connected to the navel not solely prevents inclusion of the embryonic construction, if present, but additionally facilitates management of main hemorrhage because of a slipped ligature. The twine is split with scissors about 1 cm past the ligatures taking aseptic precautions so as to stop twine sepsis. Presence of any abnormality in twine vessels (single umbilical artery) is to be noted. The function of clamping the twine on the maternal finish is to forestall soiling of the bed with blood and to prevent fetal blood lack of the second baby in undiagnosed monozygotic twin.
20 mg protonix order with mastercard
Diagnosis is principally based mostly on: (a) Aspiration of meconium from the trachea at birth; (b) Signs of respiratory misery; (c) Radiologically hyperinflated lung fields gastritis diet �?��� purchase protonix 40 mg amex, flattened diaphragm with coarse and patchy infiltration and (d) Cyanosis chronic gastritis natural remedies protonix 20 mg purchase on-line. Management: Proper intrapartum monitoring and care; Amnio infusion in oligohydramnios-may reduce wire compression, grasping and intrapartum aspiration; Maintenance of (a) Thermoneutral setting; (b) Minimum dealing with; (c) To correct metabolic abnormalities; (d) Circulatory assist (N. Saline or entire blood) and (e) Airway and oral suctioning may be wanted; Liberal oxygen supply; Antibiotic coverage, as meconium invitations infection; In a extreme case arterial blood gasoline analysis should be accomplished; Inhaled nitric oxide or surfactant therapy could additionally be beneficial; General management contains correction of hypoxia, acidosis, hypoglycemia and hypocalcemia. Bilirubin sure to serum albumin is transported to the liver cells carried to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum by cytoplasmic ligandin (Y protein). In a untimely toddler the peak stage of 12�15 mg/dL in the 1st week could additionally be with none abnormality. In premature infants, cautious statement is required and evidences of rising bilirubin close to critical level need trade transfusion. Excessive purple cell hemolysis Absolute Features of Nonphysiologic Jaundice (i) Hemolytic illness of the new child: Jaundice appearing inside 24 hours of birth. Fetomaternal blood group incomBilirubin level rising on the fee of > 5 mg/dL/ pati bilities: Rh (most common), day or >0. Clinical jaundice persisting > 1 week in a time period infant Increased purple cell fragility-Congeor > 2 weeks in a preterm infant. Defective conjugation of bilirubin (i) Congenital deficiency of glucuronyl transferase Crigler-Najjar syndrome (autosomal recessive), Gilbert syndrome (autosomal dominant), Preterm infants with impaired liver perform. Breast milk jaundice: the activity of the enzyme-glucuronyl transferase is inhibited by a specific steroid three, 20b�pregnanediol and elevated fatty acids of breast milk. The bilirubin stage rises from the 7th day after delivery to a maximum of 20�30 mg/dL by 14th day. If the bilirubin stage is extra, temporary withdrawal of breastfeeding cures jaundice. Breastfeeding jaundice is as a end result of of decreased consumption of milk that leads to elevated enterohepatic circulation. Metabolic and endocrine issues: Galactosemia, hypothyroidism (unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia). Galactosemia-There is hereditary deficiency of an enzyme-galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase which converts galactose derived from the milk into glucose-1-phosphate. The biliary canaliculi are blocked by inspissated bile and obstructive jaundice outcomes. Increased enterohepatic circulation of unconjugated bilirubin: Duodenal atresia, pyloric stenosis, much less frequent feeding. Substances and disorders that affect binding of bilirubin to albumin: Aspirin, sulfonamides, fatty acids and asphyxia, acidosis, sepsis, or hypothermia increases free unconjugated bilirubin level. Miscellaneous: Congenital obstruction (atresia or stricture of biliary canaliculi), asphyxia, polycythemia and thalassemia. Clinical: Evaluation of jaundice is finished by blanching the skin with digital pressure. Dermal icterus zone and serum bilirubin (indirect) degree in a time period toddler (Kramer-1969). Abnormal neurologic signs are: lethargy, poor feeding, vomiting, hypotonia and seizures. Laboratory studies: Serum bilirubin degree > 12 mg/dL, requires further investigations. Complete hemogram together with reticulocyte depend: Hemolytic anemia: Hb%, Reticulocyte depend, presence of nucleated red cells. Serum albumin to detect total bilirubin binding websites and to assess the necessity of albumin infusion. Other laboratory tests: Urine for reducing substance (galactosemia), tradition for an infection. Radiology and Ultrasonography to detect intestinal obstruction, intraventricular hemorrhage and tumor. Basal ganglia, cranial nerve nuclei, hippocampus, brainstem nuclei and anterior horn cells of the spinal wire are generally affected. The important level of bilirubin inflicting kernicterus in a term toddler is greater than 20 mg/dL (340 �mol/L). Risk of bilirubin encephalopathy is unlikely, if the total bilirubin degree is < 20 mg/dL. Hypoxia, acidosis, hypoglycemia, hypothermia, sepsis or prematurity enhances the pathogenesis so that affection could occur even at a low degree of bilirubin. It is clinically characterized by lethargy, hypotonia, poor feeding and lack of neonatal reflexes. Gradually hypertonia, severe sickness is manifested by prostration, respiratory distress and at last opisthotonos, hyperpyrexia, convulsions, enlarged liver, spleen and continual bilirubin encephalopathy. Prevention and management: Regular and periodic estimation of serum bilirubin degree in vulnerable infants and the tendency to rise must be successfully tackled by double floor phototherapy and trade transfusion. Those who survive typically undergo from mental retardation and choreoathetoid cerebral palsy. It is finest when utilized in moderate cases where the bilirubin level rises above 12 mg%. Phototherapy is discontinued when serum bilirubin degree is <13mg/dL in time period and <11 mg/dL in preterm neonates. Special blue lamps with an output of 420�480 nm wavelengths are the simplest. Double Phototherapy (over head light�plus mild from under or fiberoptic blanket) is twice as efficient as single phototherapy. Bilirubin (indirect) absorbs light maximally at that vary and undergoes photoisomerization and is converted to much less poisonous polar isomer (4Z, 15E) which is excreted into the bile. Phototherapy also converts bilirubin to lumibilirubin by structural isomerization. Phototherapy must be began early, exposing the maximum floor space and shielding the eyes. Complications of phototherapy are: Watery diarrhea, pores and skin rashes, dehydration, bronze child syndrome (dark brown discoloration of the skin), low calcium levels and retinal harm. Phototherapy is contraindicated in infants with direct hyperbilirubinemia attributable to liver illness or obstructive jaundice. A loading dose of 10 mg/kg on day 1 and maintenance dose of 5�8 mg/kg/day for next four days is given. However, as a prophylaxis, it might be used within the mom for 2 weeks prior to supply within the dose of 90 mg/day. By competitive inhibition, metalloporphyrins lower the production of bilirubin.
Diseases
- Chronic fatigue immune dysfunction syndrome
- Central type neurofibromatosis
- Epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma Vorner type
- Klippel Feil syndrome
- Pulmonary hypertension, secondary
- Dennis Fairhurst Moore syndrome
- Dermatoosteolysis Kirghizian type
- Osteopetrosis lethal
- Oral facial digital syndrome type 4
Protonix 20 mg quality
In the region anterior to the precentral gyrus gastritis diet pregnancy protonix 20 mg order online, there are two sulci that run in an anteroposterior direction gastritis symptoms relief protonix 20 mg sale. The anterior and ascending rami of the lateral sulcus prolong into the inferior frontal gyrus dividing it into three elements: a. The temporal lobe has two sulci that run parallel to the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus. They divide the superolateral surface of this lobe into superior, middle and inferior temporal gyri. The postcentral sulcus runs downwards and forwards parallel to and slightly behind the central sulcus. The rest of the parietal lobe is split into a superior parietal lobule and an inferior parietal lobule by the intraparietal sulcus. The upturned posterior end of the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus extends into the inferior parietal lobule. The posterior ends of the superior and inferior temporal sulci additionally turn upwards to enter this lobule. The upturned ends of these three sulci divide the inferior parietal lobule into three parts: a. The half that arches over the upturned posterior end of the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus known as the supramarginal gyrus. The part that arches over the superior temporal sulcus is called the angular gyrus. The half that arches over the posterior finish of the inferior temporal sulcus known as the arcus temporooccipitalis. One of these, the lateral occipital sulcus lies horizontally and divides the lobe into superior and inferior occipital gyri. The lunate sulcus runs downwards and barely forwards simply in entrance of the occipital pole. The transverse occipital sulcus is situated within the uppermost a half of the occipital lobe. The upper end of the parieto-occipital sulcus (which just reaches the superolateral surface from the medial surface) is surrounded by the arcus parieto-occipitalis. As its name suggests, it belongs partly to the parietal lobe and partly to the occipital lobe. In the depth of the stem and posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus, there is half of the cerebral hemisphere called the insula (insula = insulated or hidden). During improvement of the cerebral hemisphere, this space grows less than surrounding areas that, therefore, come to overlap it and occlude it from floor view. The frontal operculum lies between the anterior and ascending rami of the lateral sulcus. The frontoparietal operculum lies above the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus. The temporal operculum has a superior floor hidden in the depth of the lateral sulcus (49. On this surface, we see two gyri referred to as the anterior and posterior transverse temporal gyri. When the 2 cerebral hemispheres are separated from each other by a cut in the middle line the appearances seen are shown in forty nine. The corpus callosum is a prominent arched construction consisting of commissural fibres passing from one hemisphere to the opposite (49. The interventricular foramen through which the third ventricle communicates with the lateral ventricle may be seen in the upper and anterior part. The lateral wall of the ventricle is shaped in larger part by a large mass of grey matter called the thalamus. The right and left thalami are often interconnected (across the middle line) by a strip of gray matter referred to as the interthalamic connexus. The anteroinferior a half of the lateral wall of the third ventricle is fashioned by a collection of grey matter that constitutes the hypothalamus. But anteriorly, it disappears from view just in entrance of the interventricular foramen. Removal of the septum pellucidum brings the interior of the lateral ventricle into view. In the anterior wall of the third ventricle, there are the anterior commissure and the lamina terminalis. The anterior commissure is hooked up to the genu of the corpus callosum via a skinny lamina of fibres that constitutes the rostrum of the corpus callosum. Below, the anterior commissure is steady with the lamina terminalis that could be a thin lamina of nervous tissue. Posteriorly, the third ventricle is related to the pineal gland and inferiorly to the hypophysis cerebri. Above the corpus callosum (and also in front of and behind it), we see the sulci and gyri of the medial floor of the hemisphere (49. The most outstanding of the sulci is the cingulate sulcus that follows a curved course parallel to the upper convex margin of the corpus callosum. Posteriorly, it turns upwards to reach the superomedial border slightly behind the upper end of the central sulcus. The area between the cingulate sulcus and the corpus callosum is called the gyrus cinguli. The a part of the medial surface of the hemisphere between the cingulate sulcus and the superomedial border consists of two elements. These two components are separated by a short sulcus steady with the cingulate sulcus. The part of the medial floor behind the paracentral lobule and the gyrus cinguli exhibits two main sulci that cut off a triangular area called the cuneus. The calcarine sulcus extends forwards beyond its junction with the parieto-occipital sulcus and ends somewhat under the splenium of the corpus callosum. The small area separating the splenium from the calcarine sulcus known as the isthmus. Anteroinferiorly, the precuneus is separated from the posterior part of the gyrus cinguli by the suprasplenial (or subparietal) sulcus. When the cerebrum is separated from the hindbrain by chopping throughout the midbrain, and is considered from below, the appearances seen are shown in 49. Posterior to the midbrain, we see the undersurface of the splenium of the corpus callosum. The fossa is bounded in front by the optic chiasma and on the sides by the proper and left optic tracts. The optic tracts wind round the sides of the midbrain to terminate on its posterolateral aspect.
Protonix 20 mg buy cheap
Abdominovaginal technique (Muller-Munro Kerr): this bimanual method is superior to the abdominal method because the pelvic evaluation could be done concurrently gastritis diet ������ protonix 40 mg mastercard. Muller introduced the strategy by placing the vaginal finger tips on the level of ischial spines to note the descent of the pinnacle gastritis diet shopping list protonix 40 mg generic without prescription. Munro Kerr added placement of the thumb over the symphysis pubis to observe the diploma of overlapping. The patient is positioned in lithotomy place and the inner examination is finished taking all aseptic precautions. Two fingers of the proper hand are introduced into the vagina with the finger suggestions positioned on the stage of ischial spines and thumb is placed over the symphysis pubis. The head is grasped by the left hand and is pushed in a downward and backward path into the pelvis. X-ray pelvimetry: Lateral X-ray view with the affected person in standing place is useful in assessing cephalopelvic proportion in all planes of the pelvis - inlet, midpelvic and outlet. Cephalometry: While a tough estimation of the size of the top may be assessed clinically, correct measurement of the biparietal diameter would have been best to elicit its relation with the diameters of the planes of a given pelvis through which it has to cross. It is equally informative to assess the fetal measurement, fetal head volume and pelvic soft tissues that are additionally important for successful vaginal delivery (p. When both the anteroposterior diameter (< 10 cm) and the transverse diameter (< 12 cm) of the inlet are reduced, the risk of dystocia is high than when just one diameter is contracted. However, the next may occur: (1) There is extra probability of incarceration of the retroverted gravid uterus in flat pelvis; (2) Abdomen turns into pendulous especially in multigravida with lax stomach wall; (3) Malpresentations are elevated three to four times and so also increased frequency of unstable lie. Labor: the course of events in labor is significantly modified depending upon the degree of pelvic contraction and presentation of the fetus: (1) There is increased incidence of early rupture of the membranes; (2) Incidence of twine prolapse is elevated; (3) Cervical dilatation is slowed; (4) There is increased tendency of extended labor and in uncared for instances, obstructed labor with options of exhaustion, dehydration, ketoacidosis and sepsis (see p. Maternal accidents: the accidents of the genital tract might occur spontaneously or following operative delivery (see p. However, in a selected multigravida with earlier history of inauspicious vaginal supply, this method could also be considered 2�3 weeks before the date. Elective cesarean part at time period is indicated in-(1) major diploma of inlet contraction and likewise in (2) average degree of inlet contraction associated with outlet contraction or complicating elements like elderly primigravida, malpresentation, post-cesarean pregnancy, etc. Every arrangement ought to be made obtainable for operative delivery, both vaginal or abdominal, if the condition so arises. Aims: A trial labor goals at avoiding an pointless cesarean section and at delivering a wholesome baby. The phrase "trial" was used originally to test for pelvic adequacy but subsequently its use has been prolonged to take a look at numerous elements apart from the pelvic capability. For instance, the trial is carried out to test the integrity of the scar in a lady with prior cesarean delivery when she goes into labor. Contraindications: (1) Associated midpelvic and outlet contraction; (2) Presence of complicating elements like aged primigravida, malpresentation, postmaturity, post-cesarean being pregnant, pre-eclampsia, medical disorders like heart disease, diabetes, tuberculosis, etc. Conduction of trial labor: the administration of a trial labor requires cautious supervision and consideration. But in cases where the labor fails to begin even on due date, induction of labor could also be accomplished. On no account should the process be employed before the cervix is no less than 3 cm (2 fingers) dilated. After the membranes rupture, pelvic examination is to be done: (a) To exclude cord prolapse; (b) To notice the color of liquor; (c) To assess the pelvis once extra and (d) To notice the situation of the cervix together with pressure of the presenting half on the cervix. Successful consequence is decided by: (1) Degree of pelvic contraction; (2) Shape of the pelvis-flat pelvis is best than android or typically contracted pelvis; (3) Favorable vertex presentation-anterior parietal presentation with less parietal obliquity is favorable; (4) Intact membranes until full dilatation of cervix; (5) Effective uterine contractions and (6) Emotional stability of the woman. Unfavorable features: (1) Appearance of abnormal uterine contraction; (2) Cervical dilatation lower than 1 cm per hour in the energetic section (protracted lively phase); (3) Descent of fetal head lower than 1 cm per hour (protracted energetic phase) inspite of regular uterine contractions; (4) Arrest of cervical dilatation and nondescent of fetal head regardless of oxytocin remedy; (5) Early rupture of the membranes; (6) Formation of caput and evidence of excessive molding; (7) Fetal distress. It is indeed difficult to set an arbitrary time limit which is relevant to all cases. So lengthy because the progress is satisfactory (evidenced by descent of the top and progressive cervical dilatation) and the maternal and fetal situation stay good, trial could also be continued safely. Termination of trial labor: the strategies of termination are any one of the following: Spontaneous supply with or without episiotomy (30%). Cesarean section (40%)-Judicious and timely determination for cesarean supply is to be taken. However, in vital cases, the section is completed even earlier than full dilatation of the cervix, the indication being uterine inertia or fetal distress. Delivery by cesarean part or delivery of a dead child, spontaneously or by craniotomy, is called failure of trial labor. Advantages of trial labor: (1) It eliminates pointless cesarean part electively determined upon; (2) It eliminates injudicious use of untimely induction of labor with its antecedent hazards; (3) A successful trial ensures the girl a great future obstetrics. Disadvantages of trial labor: (1) Test of disproportion remains unproven when cesarean delivery is done as a end result of fetal distress or uterine dysfunction; (2) Increased perinatal morbidity or mortality due to asphyxia or intracranial hemorrhage when the trial is extended and/or ends in troublesome supply; (3) Increased maternal morbidity because of the effects of extended labor and/or operative delivery; (4) Increased psychological morbidity when trial ends with a traumatic vaginal supply or in cesarean delivery. As such, in apply the 2 issues are jointly thought of as outlet contraction. Cephalopelvic disproportion at the outlet is defined as one where the biparietal-suboccipitobregmatic plane fails to pass by way of the bispinous and anteroposterior planes of the outlet. Management: Unlike inlet disproportion, medical analysis of midpelvic and outlet disproportion can only be made after the top sufficiently comes down into the pelvis. Molding and adaptation of the pinnacle and "give" of the pelvis could allow the head to move through the contracted zone. Delivery is accomplished by forceps or ventouse with deep episiotomy to prevent perineal injuries, especially with slender pubic arch. Labor progress must be mapped with a partograph to make an early prognosis of dysfunctional labor because of disproportion. The principles of administration rest on: (i) Cesarean section to avoid troublesome forceps; (ii) Forceps with deep episiotomy; (iii) Symphysiotomy (see p. Chapter 25 Abnormal Uterine Action Normal labor is characterised by coordinated uterine contractions. Normal labor is associated with cervical dilatation greater than or equal to 1 cm/hr in a nulliparous woman and 1. Overall labor abnormalities happen in about 25% of the nulliparous ladies and 10% of multiparous ladies. The commonest cause of protraction disorder is inadequate or abnormal uterine contractions. Any deviation of the traditional sample of uterine contractions (as talked about in page 138) affecting the course of labor is designated as disordered or irregular uterine motion. Normal uterine contractions: Polarity of the uterus means when the higher section contracts, the decrease segment relaxes. The properties of a standard uterine contraction wave are: (i) the intensity of contraction diminishes from high to backside of the uterus; (ii) the contraction wave starts from the pacemaker and propagates towards the decrease uterine section; (iii) the length of contraction diminishes progressively as the wave strikes away from the pacemaker. The uterine pacemaker is situated on the cornua of the uterus and this generates uterine contractions. Effective uterine contraction, begins on the cornua and steadily sweeps downwards over the uterus.
Discount 20 mg protonix visa
Changes in the usage of C region gene segments with out changes in V regions are the basis of isotype switching gastritis rice protonix 40 mg buy cheap, which results in gastritis treatment probiotics protonix 40 mg buy low cost modifications in effector operate without a change in specificity. Point mutations within the V regions of an antibody specific for an antigen result in increased affinity for that antigen (affinity maturation). The activation and capabilities of T cells have several features that replicate the special properties of this cell sort. Antigens are captured from their site of entry and concentrated in peripheral (secondary) lymphoid organs by way of which naive T cells circulate constantly. Microbes and different antigens most frequently enter the physique by way of epithelium-lined surfaces, which interface with the exterior surroundings. Microbes may also colonize any tissue, and antigens may be produced in these tissues. Because the immune system generates numerous lymphocyte clones each with a unique specificity, there are only a few naive T and B cells specific for any one antigen, in the vary of 1 per one hundred and five or 106 lymphocytes. It is impossible for the few T cells particular for any antigen to continually patrol all the possible tissues where antigens may enter or be produced. The mechanism that solves this drawback is a specialized system for capturing an antigen from its website of entry or production and bringing it to lymphoid organs via which naive T cells circulate. T lymphocytes recognize and respond to cell-associated antigens and to not soluble, cell-free antigens. A principal perform of T lymphocytes is to eliminate microbes that survive inside cells. In addition, T cells interact with and activate different cells, such as B lymphocytes and macrophages. To make positive that T cells acknowledge cell-associated and never free antigens, and work together with other cells, T cell antigen receptors have evolved to see antigens derived from antigens which may be inside cells and are displayed by cell floor molecules. This is in hanging distinction to B lymphocytes, whose antigen receptors and secreted merchandise, antibodies, can acknowledge antigens on microbial and host cell surfaces, and soluble cell-free antigens. Elucidation of the cell biology and molecular basis of antigen presentation has been a powerful accomplishment, based on functional experiments, biochemical analyses, and structural biology. T cells recognize linear peptides and not conformational determinants of protein antigens. Most T lymphocytes recognize only short peptides, whereas B cells can acknowledge peptides, intact folded proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids, and small chemicals. As a outcome, T cell�mediated immune responses are normally induced by international protein antigens (the pure supply of international peptides), whereas humoral immune responses are induced by protein and nonprotein antigens. Some T cells are particular for small chemical substances similar to urushiol of poison ivy, -lactams of penicillin antibiotics, and even metallic ions corresponding to nickel and beryllium. The underlying mechanisms and useful significance of this separation are mentioned later. The end result was that the injected antigens had been associated mainly with nonlymphoid cells, which was a shock since it was recognized that lymphocytes were the cells that particularly acknowledged and responded to overseas antigens. This sort of experiment was quickly adopted by research exhibiting that protein antigens that had been bodily associated with macrophages were rather more immunogenic, on a molar basis, than the same antigens injected into mice in soluble form. General Properties of Antigen-Presenting Cells Different cell sorts perform as antigen-presenting cells to activate naive T cells or previously differentiated effector T cells. Note that effector T cells activate macrophages and B lymphocytes by manufacturing of cytokines and by expressing floor molecules; these will be described in later chapters. Contraction of this sphincter produces a ridge (of Passavant) on the posterior pharyngeal wall with which the soft palate comes in contact. The communication between the oral cavity and the pharynx is called the oropharyngeal isthmus (45. The oropharyngeal isthmus could be closed by contraction of the palatoglossus muscular tissues. The laryngopharynx lies just behind the inlet of the larynx, and behind the posterior wall of the larynx. Above and behind the opening of the auditory tube the wall of the nasopharynx shows a bulging called the tubal elevation. This elevation is produced by the projecting end of a cartilage which types part of the wall of the auditory tube. A fold of mucous membrane starting at the tubal elevation passes down the pharyngeal wall. This is the salpingopharyngeal fold and is produced by a muscle called the salpingopharyngeus. Behind the tubal elevation the wall of the nasopharynx reveals a depression called the pharyngeal recess. The nasopharynx has a roof steady with the posterior end of the roof of the nasal cavity. The roof and posterior wall of the nasopharynx kind a steady curve that rests on the posterior part of the physique of the sphenoid, the basilar a half of the occipital bone, and the anterior arch of the atlas. The mucosa of the median part of the roof reveals a bulging produced by a mass of lymphoid tissue. The limits of the subdivisions of the pharynx are indicated in dotted lines Chapter forty five Oral Cavity, Nasal Cavity, Pharynx, Larynx, Trachea and Oesophagus the Oral Part of the Pharynx 993 1. The oropharynx lies in front of the second cervical vertebra and the higher a part of the third. The only features to be famous on its lateral partitions are the palatopharyngeal folds (or arches). These stretch from the uvula to the lateral wall of the pharynx and enclose the palatopharyngeus muscle. The laryngeal a part of the pharynx lies in entrance of the third to sixth cervical vertebrae. In terms of laryngeal cartilages the higher finish of the laryngeal a part of the pharynx corresponds to the upper finish of the epiglottis; and its decrease finish lies at the caudal border of the cricoid cartilage. The higher a half of the anterior wall is formed by the inlet of the larynx; and beneath by the posterior surfaces of the arytenoid and cricoid cartilages. Lateral to the inlet of the larynx the mucosa reveals a depression called the piriform recess or fossa. The layer of muscle is roofed on the skin by a layer of fascia known as the buccopharyngeal fascia. The origins of the constrictors are located anteriorly in relation to the posterior openings of the nose, mouth and larynx (from above downwards). The three constrictors are so arranged that the inferior overlaps the center, which in turn, overlaps the superior. The lower edge of the inferior constrictor turns into continuous with the round muscle of the oesophagus. It passes through the hole between the superior and center constrictors to run downwards on the inner surface of the middle and inferior constrictors. The salpingopharyngeus descends from the auditory tube to merge with the palatopharyngeus. All the constrictors of the pharynx are inserted into a median raphe on the posterior wall of the pharynx. There is a gap between the higher edge of the superior constrictor and the base of the skull.
20 mg protonix order overnight delivery
The parietal department begins on the upper end of the principle stem of the middle meningeal artery (see above) gastritis diet ����� cheap protonix 20 mg on-line. It runs backwards to a degree about 6 cm above the exterior occipital protuberance gastritis diet ��� generic protonix 20 mg amex. VeinS inner Jugular Vein the interior jugular vein has been described on web page 854. The vein runs downwards throughout the sternocleidomastoid and ends deep to the clavicle instantly behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Its anterior finish reaches the raised space between the best and left eyebrows (glabella). The line joining the 2 points is brief because of foreshortening of the projection. The nerves considered are those than may be approached surgically from the floor (It is at all times useful to learn the course of the nerve earlier than attempting to perceive surface marking). The main stem of the mandibular nerve can be marked on the surface as a short vertical line just in front of the head of the mandible. It can be marked by a line that runs backwards from the principle stem of the mandibular nerve, across the neck of the mandible. The nerve then turns upwards passing instantly in entrance of the tragus (preauricular point). To mark it draw a line steady with the main stem of the mandibular nerve (see above). It is represented by a line that runs downwards and forwards to reach reverse the decrease third molar tooth. It is beneficial solely to mark the extracranial part of the nerve, before it divides into several branches. This foramen lies deep to the middle of the anterior border of the mastoid course of (In the adult, the nerve lies at a depth of two cm, however the depth is far much less in children). From right here draw a horizontal line that runs forwards to end just behind the neck of the mandible. This nerve is marked by a line that runs downwards and forwards with a downward convexity. It could be represented by a straight line operating down the entire size of the neck. From here draw a line downwards and backwards to attain a point halfway between the mastoid course of and the angle of the mandible. From this point carry the line further downwards and backwards to attain the middle of the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The nerve then runs across the posterior triangle to reach the anterior border of the trapezius about two inches above the clavicle. From here draw a line downwards and medially to attain the medial finish of the clavicle. To mark this chain keep in mind that it runs vertically instantly behind the carotid sheath. In distinction, the peripheral nervous system consists of the cranial nerves and the spinal nerves. The nervous system is made up, predominantly, of tissue that has the particular property of having the ability to conduct impulses rapidly from one a part of the physique to one other. The specialised cells that constitute the useful items of the nervous system are known as neurons. Within the brain and spinal twine, neurons are supported by a particular type of connective tissue that known as neuroglia. Most neurons give off a number of short branching processes called dendrites and one longer process called an axon. In a dendrite, the nerve impulse travels towards the cell body whereas in an axon the impulse travels away from the cell physique. Peripheral nerves are made up of aggregations of axons (and in some instances of dendrites). During its formation, every axon (and some dendrites) involves be associated with sure cells that provide a sheath for it. The cells offering this sheath for axons lying outside the central nervous system are known as Schwann cells. Axons lying inside the central nervous system are supplied a similar covering by a sort of neuroglial cell known as an oligodendrocyte. Within the central nervous system, it all the time terminates by coming in intimate relationship with another neuron, the junction between the two neurons being known as a synapse. Outside the central nervous system, the axon may end in relation to an effector organ. Neurons vary significantly in the size and shape of their cell bodies (somata) and within the length and manner of branching of their processes. The form of the cell physique depends on the variety of processes arising from it. The commonest kind of neuron gives off several processes and the cell physique is, subsequently, multipolar. Another sort of neuron has a single course of and is therefore described as unipolar. One of the divisions represents the axon; the opposite is functionally a dendrite, but its structure is indistinguishable from that of an axon. Depending on the shapes of their cell bodies some neurons are referred to as stellate (star shaped) or pyramidal. These descriptions might be essential in understanding some elements of the structure of the brain. Sections by way of the spinal twine or by way of any part of the brain show sure areas that seem whitish, and others which have a darker greyish color. The arrangement of the gray and white matter differs at different conditions in the brain and spinal wire. In the spinal cord and brainstem the white matter is on the surface whereas the grey matter types a quantity of plenty embedded throughout the white matter. Such isolated lots of grey matter, current anywhere within the central nervous system, are referred to as nuclei. Aggregations of the cell our bodies of neurons may also be discovered outdoors the central nervous system. Examples of sensory ganglia are the dorsal nerve root ganglia of spinal nerves, and the trigeminal ganglion. Chapter 48 Introduction to Central Nervous System and Internal Structure of Spinal Cord 1035 10. Autonomic ganglia embrace sympathetic ganglia positioned on the sympathetic chain, and parasympathetic ganglia. Some autonomic neurons are situated in nerve plexuses (often known as ganglia) current in close relationship to some viscera. The axons arising in one mass of grey matter terminate very incessantly by synapsing with neurons in different masses of gray matter. The axons connecting two (or more) lots of gray matter are incessantly quite a few enough to kind recognisable bundles.