Celexa
Celexa dosages: 40 mg, 20 mg, 10 mg
Celexa packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Celexa 20 mg buy generic on-line
Polymorphisms of the noncoding promoter space affect bilirubin conjugation by diminishing expression of a normally structured enzyme; whereas mutations of the gene coding space could have an effect on enzyme function by altering the structure of the enzyme molecule medications high blood pressure 10 mg celexa mastercard. Further info is equipped in the part on Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia treatment yellow fever buy celexa 10 mg with visa, later. In humans, this provider might play an essential function within the metabolism of bilirubin and within the prevention of hyperbilirubinemia by facilitating the entry of bilirubin into hepatocytes. Next, we offer a short overview to allow the reader to comprehend mutations of this gene and interactions of these mutations with genetic or environmental factors within the mechanism of jaundice. Bilirubin and the genome: the hereditary foundation of unconjugated neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Coexpression of genes one with the other, with mutations or polymorphisms, or with environmental factors could potentiate their role and contribute to the pathophysiology of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia to a higher extent than every gene individually. A more acceptable time period that might add to our understanding of the phenomenon and distinguish the traditional or physiologic state with the pathologic entity implied in the time period hyperbilirubinemia could additionally be physiologic bilirubinemia. Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia within the human, no matter age, is outlined as an indirect-reacting bilirubin concentration of 2. Nearly all adults and older children normally have indirect-reacting bilirubin concentrations in circulation of lower than zero. Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia is defined as an elevation of the direct-reacting fraction within the van den Bergh diazo reaction of higher than 1. The latter portion of the definition is added to guard in opposition to over-interpretation of direct reactions in newborns with markedly elevated indirect-reacting bilirubin concentrations, because up to 10% of the unconjugated pigment behaves as directreacting pigment within the van den Bergh-type methods. In the neonate with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, the hyperbilirubinemia is usually "blended," the elevated direct-reacting fraction accounting for 20% to 70% of the entire pigment. Thus a neonate with mixed hyperbilirubinemia must be considered primarily to have conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Except in circumstances of utmost hemolysis, corresponding to in hemolytic disease of the newborn, pathology resulting from interference with hepatic cell excretion and bile transport, somewhat than from abnormalities of increased bilirubin production or poor hepatic bilirubin uptake or conjugation, ought to be sought. Predictive capacity of a predischarge hourspecific serum bilirubin for subsequent vital hyperbilirubinemia in wholesome time period and near-term newborns. However, notable species differences exist in the sample of improvement of hepatic bilirubin conjugation. Significant hyperbilirubinemia is uncommon within the human fetus because the placenta transports unconjugated bilirubin from the fetus to the mom. Administration of radioactive unconjugated bilirubin into the fetal circulation of a dog, guinea pig, or monkey exhibits a fast disappearance from the fetal side and restoration within the maternal bile. Even in states of extreme intrauterine hemolysis from circumstances corresponding to Rh or different isoimmunizations, the degree of anemia by far exceeds the extent of hyperbilirubinemia, and medical jaundice is often mild at start. Thus in the absence of evidence of hemolytic disease, if medical jaundice is present at delivery, a conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, caused by intrauterine hepatic pathology, must be suspected. A great amount of bilirubin is found in meconium, indicating appreciable exercise of fetal hepatic bilirubin conjugation. A significant level of -glucuronidase activity is present in meconium, suggesting that conjugated bilirubin in the fetal gut may be hydrolyzed back to unconjugated bilirubin after which absorbed from the bowel into the portal circulation. This absorbed bilirubin could re-enter the hepatocyte for subsequent reconjugation and re-excretion, or may be transferred via the placenta into the maternal circulation. The effectivity of this course of is protecting to the fetus in opposition to severe hyperbilirubinemia, even when hemolysis is extreme. Severe hemolytic disease within the fetus results in small, but vital, will increase in amniotic fluid bilirubin concentrations. Although to an excellent extent replaced by noninvasive measurement of anterior cerebral artery circulate as an index of fetal anemia, in latest a long time measurement of amniotic fluid bilirubin concentrations by spectrophotometry, combined with percutaneous umbilical blood sampling allowing for serial hematocrit determinations and fetal intravascular transfusions, resulted in markedly improved end result for the now uncommon fetus and toddler with Rh erythroblastosis (see Chapter 24). This early interval of physiologic jaundice has been designated as part 1 physiologic jaundice. This late neonatal period of minimal, slowly declining hyperbilirubinemia has been designated as phase 2 physiologic jaundice. The presence of either of these components alone would result in retention of unconjugated bilirubin to a lesser extent than when in combination. Hepatic uptake and excretion of bilirubin are also decreased throughout this era, although their operate as rate-limiting steps in the transport of bilirubin from plasma into bile is dwarfed by the combination of elevated bilirubin load to the liver and diminished conjugative capability. The very massive increase in bilirubin load seems to end result from both increased de novo bilirubin synthesis and enteric reabsorption of unconjugated bilirubin. In the newborn monkey, the markedly elevated load persists for 3 to 6 weeks, primarily due to enhanced intestinal bilirubin absorption. Phase 2 physiologic jaundice appears to outcome from an imbalance in which hepatic uptake of bilirubin remains diminished while the elevated bilirubin load presented to the liver persists. Developmental deficiency of B-ligandin may contribute to poor uptake of bilirubin. Despite the development of physiologic jaundice of a point in almost each newborn, solely half of all white and African-American term newborns turn into visibly jaundiced in the course of the first three days of life. A higher proportion of solely breastfed infants could be anticipated to show some extent of jaundice. Variations in period of hyperbilirubinemia, in skin shade, and in perfusion might account for these differences. As the intensity of jaundice will increase, medical icterus progresses in a caudal direction. Visual assessment of jaundice, however, is basically subjective, inaccurate, and dependent on observer experience. Development of transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) monitoring gadgets meant to measure the pores and skin color objectively and noninvasively and convert this color reading to a bilirubin estimation may enhance on the reliability of visible estimation. Daily noninvasive transcutaneous determinations could improve the predictive value of the approach by allowing the precise trajectory to be plotted in opposition to these of the bilirubin nomogram (see Transcutaneous Bilirubinometry, later). This is particularly essential in predischarge evaluation of newborns, particularly those discharged before seventy two hours of age. The natural peak bilirubin in small untimely infants is subsequently mainly unknown. Genetic, Ethnic, and Cultural Effects the severity of physiologic jaundice varies significantly among completely different ethnic populations. The incidence of bilirubin toxicity as defined by autopsy-proven kernicterus can be elevated significantly in Asian newborns. Late Preterm Neonate Late preterm gestation (newborns born between 34 zero 7 and 366 7 completed weeks) is a crucial risk issue for the event of severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and kernicterus. These infants are physiologically immature and have limited compensatory responses in contrast with time period infants. At this point of gestation, hepatic conjugative capability is still immature and should contribute to the larger prevalence, severity, and period of neonatal jaundice in these infants. These infants are at increased threat for readmission, primarily for hyperbilirubinemia. The most dramatic of those are from sure Greek islands, especially the islands of Lesbos and Rhodes. Unless aggressively handled with phenobarbital prophylaxis, phototherapy, and change transfusion, the incidence of kernicterus was additionally a lot greater within the newborns from these Greek islands than in those of the mainland inhabitants.
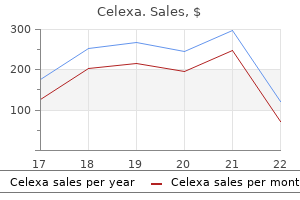
Cheap celexa 40 mg with amex
If pharmacologic suppression of gastric acid secretion fails to prevent recurrent strictures symptoms you may be pregnant celexa 10 mg order mastercard, an antireflux process may be required medications via g-tube 20 mg celexa cheap overnight delivery. Finally, a stricture refractory to aggressive management may require segmental resection. Recurrent fistulas occur in 5% to 10% of instances and often present with respiratory misery throughout feeding or with recurrent aspiration pneumonia. Most recurrent fistulas result from small, contained anastomotic leaks that cause chronic inflammatory modifications and gradually erode again by way of the tracheal restore. Surgical choices range from major closure to segmental esophageal resection, and they should embody interposition of wholesome, well-vascularized delicate tissue such as a pleural or strap muscle rotation flap. Some repairs may be approached from a cervical incision, which limits the issues related to secondary leaks. Occasionally, dysphagia is related to extreme esophageal dysmotility in the absence of a stricture. Solid-phase esophagography demonstrates that stable meals have great problem traversing the anastomosis and decrease esophagus because of an absence of peristaltic pressure. In these conditions, dietary modification and adjustment of feeding conduct could also be all that may be supplied. Lower esophageal sphincter incompetence is exacerbated by esophageal dysmotility, reducing clearance of gastric acid from the esophagus. Most patients exhibit the everyday raspy cough attributable to vibration of the weak and flattened tracheal wall, and so they outgrow these minor signs with age. Over the previous 20 years, nonetheless, the proportion of sufferers with pure atresia who ultimately endure successful esophageal repair has increased dramatically, obviating esophageal substitution in a lot of kids. Elongating the upper and decrease pouches over a 1- to 3-week interval, adopted by major anastomosis, has been very successful at preserving the native esophagus and avoiding esophageal replacement. Reflux requiring fundoplication is common in these sufferers, as are dilations to relieve strictures. Many stratification schemes subsequently evolved, and Spitz and associates refined this prognostic model to embody only delivery weight and the presence of great congenital coronary heart disease (Table 93-1). Esophageal Duplications Esophageal duplication cysts are uncommon causes of esophageal obstruction throughout infancy. These constructions end result either from abnormalities within the vacuolization process that re-establishes the esophageal lumen after obliterative epithelial proliferation throughout early embryonic improvement, or from the "budding" and separation of a portion of the creating foregut. These constructions are usually cystic, but they could be tubular and could also be positioned inside the muscular wall of the esophagus or exist individually within the posterior mediastinum. They comprise an epithelial lining derived from any foregut structure: squamous, columnar, or pseudostratified ciliated respiratory epithelium. Infants with esophageal duplication cysts are often asymptomatic, and the prognosis is made when chest radiography unexpectedly demonstrates a mediastinal mass. Some infants, however, experience feeding difficulties or respiratory compromise if the cystic structure compresses the adjacent esophagus or trachea. Cysts containing gastric mucosa could current with problems of acidinduced damage: higher gastrointestinal hemorrhage, ulceration, perforation, or erosion into the bronchial tree. Magnetic resonance imaging offers additional details about the status of the spinal wire, which may be abnormal; this data ought to be obtained in all patients with a vertebral abnormality or a cystic construction in shut proximity to the backbone. Surgical therapy includes resection of the cyst and repair of any esophageal defect. This might require a thoracotomy, but many lesions lend themselves to thoracoscopic resection. Cysts complicated by an infection with abscess formation or by inside hemorrhage might increase rapidly and should require urgent drainage earlier than resection. Abdominal Wall Defects the commonest stomach wall defects seen in neonates are omphalocele and gastroschisis, occurring in approximately 4 per 10,000 reside births. These conditions outcome from totally different developmental miscues and manifest as distinct medical entities. In the case of omphalocele, a central abdominal wall defect of variable measurement is covered by a domelike mesenchymal membrane composed of amnion. In gastroschisis, the defect is usually smaller and located to the best of the umbilical attachment. The lateral physique folds and craniocaudal folds converge on the umbilical ring, which contracts, closing the ventral belly wall. In sufferers with omphalocele, this ring fails to contract and leaves a spherical defect of variable dimension and a corresponding sac composed of amnion. The liver and small gut normally occupy a portion of the sac, together with a variable quantity of different abdominal contents. The underlying failure of umbilical ring closure could also be related to aberrant growth and migration of stomach wall muscular components, or to failure of the creating midgut to return to the belly cavity after a period of herniation into the umbilical stalk. The reason for gastroschisis is equally unclear, but it could contain a rupture of the umbilical stalk through the period of midgut herniation. Gastroschisis is often described as an stomach wall defect, to the best of a normally inserted umbilical cord, with out membranous masking of the extruded organs. Etiologically it has been advised that gastroschisis represents a failure in the regular attachment between umbilical cord and umbilical ring. Because the belly contents are protected all through gestation, little morbidity accrues from harm to the intestinal tract. The discrepancy between the quantity of eviscerated abdominal organs and the dimensions of the belly cavity-the "lack of domain"-accounts for the opposite major source of morbidity in these sufferers. Additionally, infants with giant omphaloceles could have a high incidence of pulmonary hypoplasia, resulting in respiratory compromise and pulmonary hypertension. Chromosomal abnormalities, including trisomies 13, 18, and 21, happen in 25% to 50% of affected patients. The presence of a small sac, the absence of liver in the sac, and the presence of different malformations strongly predict an abnormal karyotype. Risk elements for gastroschisis embody younger maternal age, decrease socioeconomic standing, and publicity to exterior agents similar to vasoconstricting decongestants, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory brokers, cocaine, and probably pesticides/herbicides. Morbidity in infants with gastroschisis, as opposed to those with omphalocele, is kind of entirely related to intestinal dysfunction caused by in utero injury to the eviscerated bowel. The spectrum of damage displayed by the eviscerated bowel in gastroschisis ranges from delicate to catastrophic. Histologically, the intestine is characterized by villous atrophy and blunting, submucosal fibrosis, muscular hypertrophy and hyperplasia, and serosal irritation. Exposure to amniotic fluid appears to be a major contributing factor, as amniotic fluid exchange can prevent peel formation. This causes progressive constriction across the intestinal mesentery, ensuing within the obstruction of luminal, lymphatic, and venous outflow. Intra-abdominal bowel distension is related to increased postnatal problems, including delay to full feeds and increased duration of hospital keep in infants with prenatally diagnosed gastroschisis; nonetheless, this association seems to be limited to these with multiple loops of dilated intra-abdominal bowel. This dietary failure and the complications arising from extended enteral and parenteral nutritional therapy represent a significant proportion of the opposed scientific outcomes in these patients.
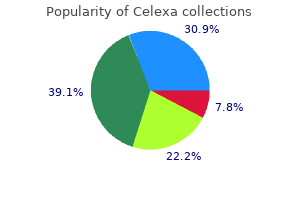
20 mg celexa best
Second medications used to treat ptsd purchase 10 mg celexa visa, prognosis could be supplied by mutational analysis symptoms vomiting diarrhea celexa 10 mg order visa, however not by standard biochemical studies. A considerate but direct discussion should be arranged before death with the dad and mom, during which the reasons for a postmortem examination are introduced. It ought to be explained that an autopsy carried out for the purpose of investigating a suspected metabolic disorder may be different from autopsies carried out for different functions in that the autopsy examination have to be carried out within hours of demise, ideally inside lower than four hours. This urgency is dictated by the want to obtain tissue before postmortem adjustments compromise the integrity of enzyme systems. Similar specimens of heart tissue should be obtained from patients with cardiomyopathy. If permission for a limited postmortem examination is refused, permission for premortem percutaneous liver and open skeletal muscle biopsies must be sought; these procedures could be carried out on the bedside. Similar arrangements also needs to be made for neonates who die abruptly in the hospital or at residence, as a result of inborn errors have become a well-recognized reason for sudden dying. Approximately 2% of sudden, unexpected deaths in the neonatal interval are the consequence of a metabolic disorder. The diagnostic entities that need to be considered primarily include defects in power metabolism: glycogen storage illnesses, defects in fatty acid oxidation, and electron transport chain defects. The most common pathogenetic mechanism that results in sudden dying in these disorders is cardiomyopathy or cardiac arrhythmia, which is the consequence of myocardial power deficiency or disruption of the electrical conduction system by toxic metabolites that accumulate in these issues. Practically, recommendations are that a full autopsy be carried out inside seventy two hours of dying. The post-mortem ought to include explicit attention to examination of the guts, liver, and skeletal muscle for evidence of glycogen or lipid storage. The following specimens must be obtained and stored frozen: liver, urine from the bladder (no matter how small the pattern size), and bile from the gallbladder. The outcomes of the metabolite research are dictated partly by the results of the usual pathologic analysis. For instance, findings according to a possible fatty acid oxidation defect should include measurement of glucose, free fatty acids, and whole and free acylcarnitines in the liver specimen; organic acids and an acylcarnitine profile in urine; and an acylcarnitine profile in bile. The risk of an inborn error of metabolism may additionally be investigated by genetic testing of cultured pores and skin fibroblasts or from frozen tissue specimens. An approach to differential diagnosis of inborn errors with every of these findings is now introduced. As with all makes an attempt to develop a helpful method to differential prognosis, it is essential to do not overlook that the algorithm never fairly fits all patients. Such probably would be the case for these algorithms as nicely due to the vary of diagnostic potentialities and the appreciable genetic heterogeneity that characterizes all inborn errors of metabolism. Nevertheless, the approaches presented should function helpful first approximations. The neurotransmitter defects and associated issues are mentioned earlier on this chapter (see the Abnormal Newborn Infant: Clinical Phenotypes). Maple syrup urine disease was not mentioned in detail beforehand, and is introduced within the following. Maple syrup urine illness is an inborn error of branched-chain amino acid metabolism caused by branched-chain -ketoacid dehydrogenase deficiency, which impairs isoleucine, leucine, and valine metabolism. If the patient recovers from this initial episode, the dysfunction can be characterized by growth failure, psychological retardation, and recurrent episodes of metabolic decompensation. Bedside detection of the attribute odor of maple syrup by an alert parent or nurse may be the primary clue to the diagnosis of this dysfunction. The diagnosis should then be established by plasma amino acid analysis and urine natural acid analysis. The rationale for this remedy is to suppress protein catabolism (which will improve production of leucine and the other poisonous branched-chain amino acids) and induce an anabolic state (which will stimulate de novo protein synthesis and thereby lower the focus of the free branched-chain amino acids). The concentrations of isoleucine and/or valine might turn into too low on this regimen and restrict the rate of latest protein synthesis. The progress of therapy should due to this fact be monitored frequently to determine when the branched-chain amino acids (isoleucine, valine, and in the end leucine) must be added back to the diet. The offending amino acids should be rigorously reintroduced, both parenterally or orally. The commonest remedy of acidosis is to "correct" the acidosis with bicarbonate; nonetheless, the simplest treatment of acidosis is to appropriate the trigger of the acidosis. It is usually attainable to correct the acidosis attributable to an inborn error of metabolism by decreasing endogenous overproduction of specific acids. The evaluation of metabolic acidosis should start with an investigation for systemic shock, renal failure, and generalized liver disease. In the case of shock, the patient ought to be re-evaluated for recurrent acidosis after restoration of normal cardiopulmonary function. Similarly, sufferers with severe liver disease ought to be evaluated for an underlying inborn error of metabolism as the reason for their liver illness (see Table 99-5). The presence of a standard kidney response to the systemic acidosis (urine pH <5) and an increased anion gap means that the surplus acid load is systemic in origin somewhat than renal (see Chapter 44). Additional studies that must be performed embody determinations of blood lactate and pyruvate, serum glucose, plasma amino acids, plasma and urinary ketones, blood ammonia, plasma and urinary carnitine, and urinary organic acids. This algorithm uses the blood lactate focus because the discriminant at its first department point, thereby dividing the causes of metabolic acidosis into the lactic acidemias and different acidemias. The advantage to this method is that a discrete algorithm can then be used to consider sufferers with lactic acidemia. Therefore, the presence of lactic acidemia can serve as a useful discriminant so lengthy as one is conscious of its limitations. The issues related to lactic acidemia are discussed later under Lactic Acidemia. Several teams of problems are associated with a normal or increased serum glucose focus at onset, whereas different groups of Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic acidosis is a common laboratory finding in sick neonates. It is most frequently a consequence of shock or extreme organ failure of the kidney or liver. In other circumstances, acidosis is a discrete finding suggesting that the patient has an inborn error affecting acid manufacturing or renal acid excretion. The possibility of ketosis must be looked for fastidiously in blood and urine within the sick new child toddler. If current, ketosis must be taken as strong evidence that the neonate has a metabolic dysfunction. Other information from the initial screening research also needs to be thought-about at this point. The blood ammonia concentration should be assessed because it has diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Plasma amino acid analysis and plasma and urine carnitine analyses must be reviewed because in addition they may need diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Approximately a dozen natural acidemias can have their onset in the neonatal period (see Box 99-1). Many of the organic acid issues have a typical set of options, including ketoacidosis, vomiting, convulsions, coma, and in some problems, an unusual scent (see Table 99-7).
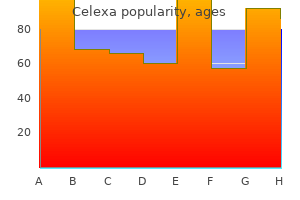
Safe celexa 10 mg
The second feature that distinguishes the organic acidemias from the urea cycle defects is the presence of ketosis within the natural acidemias treatment ringworm celexa 10 mg effective. Ketosis could be detected rapidly by the screening studies outlined previously (see Tables 99-10 to 99-12) red carpet treatment order celexa 40 mg amex. Definitive diagnosis of an natural acidemia requires quantitative urinary organic acid evaluation. The distinguishing options of a fatty acid oxidation dysfunction are nonketotic or hypoketotic hypoglycemia. In the absence of severe acidosis, ketosis, or hypoglycemia, a provisional prognosis of a urea cycle defect must be made. The urea is excreted within the urine, and the ornithine is on the market to restart the cycle. Urea cycle problems may be differentiated from each other by performing amino acid analysis and urine orotic acid evaluation (see Specialized Biochemical Testing). Except within the case of arginase deficiency, the entire urea cycle issues are characterized typically by an increased plasma concentration of glutamine and a decreased plasma arginine concentration. Argininosuccinate lyase deficiency leads to increased excretion of argininosuccinate (and its anhydrides) and average elevation of plasma citrulline. The protocols for detoxifying ammonia make use of drugs that type excretable compounds with amino acids that accumulate throughout hyperammonemic disaster. The first drug to be developed was sodium benzoate, which conjugates with glycine to form benzoylglycine (hippurate); formation and excretion of 1 molecule of hippurate eliminates one molecule of ammonia. The second drug to be developed was sodium phenylacetate, which conjugates with glutamine to form phenylacetylglutamine; formation and excretion of 1 molecule of phenylacetylglutamine eliminates two molecules of ammonia. Sodium phenylacetate continues to be available for intravenous use, however it has been replaced by sodium phenylbutyrate for oral use as a outcome of sodium phenylbutyrate has a much less offensive odor than sodium phenylacetate. Ncarbamylglutamate (Carbaglu) is an analogue of Nacetylglutamate that can be taken orally and appears to be an effective remedy for N-acetylglutamate synthetase deficiency. Long-term management of those disorders after the acute illness entails modification of this fundamental plan. With therapy, the mortality is reduced, however survivors are sometimes left with significant neurologic impairments and a lifelong illness that predisposes them to recurrent life-threatening metabolic crises. Four teams of issues are associated with secondary hyperammonemia in neonates (see Box 99-2). The mechanism of the hyperammonemia in these disorders is impaired intracellular transport of one or more of the amino acids that make up the urea cycle. The issues are detected by plasma amino acid analysis, urinary amino acid evaluation, and urinary orotic acid evaluation. Treatments for a few of these inborn errors of metabolism have been discussed within the related sections of this chapter. General principles which might be relevant to many of these diseases are discussed in the following section. With few exceptions, the inborn errors of metabolism expressed in the newborn interval are inherited as recessive traits. In easy terms, sufferers with these metabolic diseases are missing a particular enzyme that converts substance B to substance C. Deficient enzyme exercise could additionally be brought on by an error in apoenzyme perform or cofactor availability. It is assumed that tyrosinemia sort I, for instance, produces its hepatotoxic and neurotoxic effects by way of overproduction of toxic secondary metabolites. Third, the disease state may be caused by deficiency of substance C or D, which is distal to the enzyme block. Defects of gluconeogenesis, similar to pyruvate carboxylase deficiency, presumably work via this mechanism. It is assumed that many of the natural acidemias produce their toxic effects through a mixture of mechanisms. In many of these issues, acyl-CoA molecules accumulate proximal to the enzyme block and interfere with a number of other metabolic pathways. Traditional approaches to treating inborn errors of metabolism have centered on this mannequin of pathogenesis. The general approaches in use or under growth embody: (1) manipulation on the metabolite degree; (2) manipulation on the protein (or enzyme) degree; (3) organ transplantation; and (4) genetic manipulation (Table 99-18). Other types of diversion remedy embody carnitine and glycine supplementation for the organic acidurias. Carnitine and glycine are transesterified with acyl-CoAs to form acylcarnitines and acylglycines, respectively. These transesterifications launch free CoA, making it available for essential intracellular processes, whereas the potentially toxic acyl teams are excreted within the urine as acylcarnitines and acylglycines. Historically, the first instance of this strategy was to stimulate residual enzyme exercise by providing pharmacologic quantities of cofactor required by the deficient enzyme. Unfortunately, only a fraction of patients with any of these disorders respond to vitamin supplementation for causes that are still not fully understood. The converse of the primary approach is to inhibit enzyme exercise and block production of toxic metabolites. Tyrosinemia kind I is a defect within the distal portion of the catabolic pathway for tyrosine. The enzyme deficiency that causes tyrosinemia type I leads to overproduction of toxic metabolites that produce the hepatic and neurologic issues of the illness. A more direct method to treating an enzyme deficiency is to exchange the dysfunctional enzyme. In the case of 1+-antitrypsin deficiency, enzyme alternative therapy is efficient for the adult-onset pulmonary manifestations of the illness but not for the hepatic issues expressed within the neonatal interval. Dietary restriction is usually combined with other treatment approaches, such as metabolite diversion. The remedy for the urea cycle defects is perhaps the most effective studied of the metabolite diversion methods. Two medicine, sodium phenylacetate and sodium benzoate, are provided to these sufferers to serve as ammonia traps (see Hyperammonemia). Phenylacetate conjugates with glutamine to kind phenylacetylglutamine, eliminating two ammonia molecules because the nitrogen component of glutamine; benzoate conjugates with glycine to form benzoylglycine (hippurate), eliminating one ammonia molecule because the nitrogen component of glycine. Enzyme alternative remedy is now out there for Fabry illness, Hurler syndrome, Hunter syndrome, Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome, and Pompe illness. Perhaps one of the best studied approach is liver transplantation, which has been carried out efficiently for about two dozen different inborn errors of metabolism, including glycogen storage disorders, organic acidemias, and urea cycle disorders. This seems to be the case for a lot of patients with a respiratory chain disorder, but not all. The advantage of bone marrow transplantation or stem cell transplantation for the lysosomal storage ailments appears promising and is an space of intense interest. Successful somatic cell gene therapy has not been demonstrated conclusively for any inborn error of metabolism.
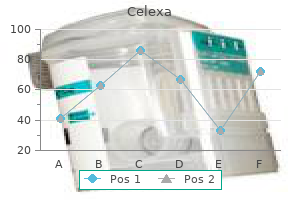
Generic celexa 40 mg free shipping
For gentle or localized cases treatment 2 stroke discount 20 mg celexa, transfusion could be continued once signs have subsided; nevertheless medicine head celexa 10 mg order, extreme allergic reactions (anaphylactoid or anaphylactic reactions) may require therapy with corticosteroids and/or epinephrine. The identical blood unit ought to never be restarted in severe cases, even after symptoms have abated. In these situations, IgA-deficientlasma products could additionally be obtained, but require using uncommon donor registries. Prolonged latency of medical manifestations and death is believed to end result from thymic and/or extrathymic semi-tolerance for allogeneic cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Fortunately, this complication can be prevented by pretransfusion gamma irradiation of cellular blood components at a dose of 2. Many transfusion providers irradiate all mobile blood merchandise given to preterm infants born weighing 1. The known and presumed indications for irradiation of blood components for neonates are listed in Box 89-1. Treatment is especially supportive, together with fluid and/or vasopressor help within the face of hypotension. These antibodies activate and sequester recipient neutrophils inside the endothelium of the lungs, in the end resulting in the production of vasoactive mediators and capillary leak. Transfusion of adult blood products containing plasma with naturally occurring anti-T antibodies into neonates with T-activation can present with intravascular hemolysis following transfusion, or unexplained failure to obtain the expected post-transfusion hemoglobin increment. Alternatively, T-activation could also be detected within the laboratory without any proof of medical hemolysis, making broad-based screening impractical. T-activation has been reported mainly in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis, especially in these with extreme disease requiring surgical intervention but additionally in septic infants with different surgical problems. Those infants with T-activation had Clostridia cultured from blood, peritoneal fluid, or stool in 14 of sixteen (88%) of circumstances and had been more prone to have intestinal perforation at laparoscopy. Infants with discrepancies in ahead and reverse blood typing and proof of hemolysis on smear must be suspected of T-activation. The diagnosis is confirmed by specific agglutination checks utilizing peanut lectin Arachis hypogea and Glycine soja. Severity and therapy can vary from full recovery with conservative medical management to intestinal perforation and bowel necrosis requiring surgical intervention. Some hypothesize that even delicate reductions in blood flow and subsequent reperfusion occurring in response to hypoxia could contribute to bowel injury. Infection results in neuroinvasive disease (meningo-encephalitis, spastic paralysis) in roughly 20% of individuals, with more severe sequelae in the elderly and immunocompromised. Despite intensive donor screening and laboratory testing, infections can still be transmitted through blood products. Pathogen inactivation presents the benefit of eliminating the danger of an infection with any nucleic acidcontaining agent, which incorporates viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and fungi (prions excluded). However, present pathogen-inactivation methods utilizing nucleic acidinactivating brokers are nonetheless under investigation as a end result of no single approach has proved to be efficient for all blood elements. Approximately one third of those with untreated chronic hepatitis will develop hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis within 2 decades; these with cirrhosis have a 1% to 5% risk of hepatocellular carcinoma 20 years after cirrhosis is recognized. This is due to shorter window durations from time of acute infection to laboratory markers of an infection (16-32 days) throughout the donor population. This is done by holding the placental finish of the umbilical cord, and gently moving blood throughout the umbilical vessels towards the neonate. This "stripping" is carried out one to four occasions previous to clamping and cutting the wire. In these circumstances transfused paternal cells specific the antigens to which the mother has been sensitized, and are passively transferred via the placenta to the neonate. Antileukocyte and antiplatelet antibodies have been found in 16% and 12% of moms, respectively. Additionally, it was found that the height bilirubin concentration was higher for infants who had obtained delayed cord clamping compared to infants with quick clamping. Current tips for alternative transfusion remedy in neonates are given in Box 89-2. Although very completely different in design and outcome, neither research clearly established an applicable hemoglobin target. The disparate outcomes may be a result of a greater hemoglobin difference in the restrictive/liberal transfusion teams (Bell study: 2. Long-term neurodevelopmental assessments within the Bell examine cohort demonstrated that these individuals in the liberal transfusion group carried out poorer than these in the restrictive group on visual reminiscence, reading, and associative verbal fluency measures in school age, in accord with structural findings in a subgroup of the original new child cohort. Iatrogenic losses from phlebotomy can be considerable, however can be minimized by considered testing strategies, sampling from indwelling catheters, utilizing microtainers for laboratory assays, and implementing point-of-care testing. The use of wire blood specimens for toddler blood kind determination is discouraged because of potential contamination with Wharton jelly and because of concerns about correct identification of the specimen. In circumstances when reconstituted entire blood is required for big volume transfusion procedures. An different used by some transfusion facilities entails the usage of low isohemagglutinin titer, group-O entire blood, if out there. The clinician should distinguish this case from Rh hemolytic illness of the newborn. In infants older than four months of age, repeat testing for blood group, Rh-type and antibody screening is performed inside seventy two hours of every purple blood cell transfusion if the affected person has obtained a transfusion over the last three months or if the historical past is unsure or unavailable. Red Blood Cell Dose and Administration the very best relative blood volumes (mL/kg) are present in neonates. Adult blood volumes on a per-kilogram basis are achieved by three months of age (Table 89-3). Because pink blood cell items are stored at 4�to 6�C, hypothermia can develop after huge transfusion except the blood merchandise are first warmed to physique temperature. When phototherapy is in progress, the blood part and tubing should be positioned in order to decrease publicity to phototherapy gentle, which may additionally cause hemolysis. Neonates have completely different dangers of bleeding given the same diploma of thrombocytopenia. Differences in platelet function or concurrent coagulopathy are doubtless causes for these discrepancies. Routine volume-reduction methods for all neonates ought to be avoided as a result of roughly 20% of platelets are misplaced within the final product, which is resuspended in both saline or appropriate plasma. Component Definition and Dosing A commonplace unit of platelets, prepared from a single donation of entire blood contains at least 5. There are two methods to calculate platelet doses in neonates, based on mL/kg or based on equivalent units/kg. Platelet parts could also be volume decreased to 15 to 20 mL for sufferers requiring significant quantity restrictions, but this is related to important platelet loss of 15% to 35% and may affect platelet perform adversely. Platelets are saved at 20�to 24�C underneath constant agitation, and have a shelf lifetime of 5 days after assortment. It is necessary to account for device-related useless area (10-30 mL) when issuing the product, as this may be appreciable in relation to the general platelet dose. Immune-mediated causes of platelet refractoriness, similar to alloantibodies to platelet-specific antigens. Administration of amphotericin B should be not carried out within 6 hours of granulocytes because of suspected elevated risk of extreme pulmonary reactions.
Celexa 20 mg discount otc
Active flexibility is assessed by gently stroking the lateral border of the concerned foot 911 treatment for hair 20 mg celexa discount fast delivery. This approach induces reflex activity within the peroneal muscles along the lateral aspect of the calf medicine quinine generic celexa 20 mg amex. In reasonably versatile metatarsus adductus, the forefoot could be corrected to the impartial place. Approximately 85% of neonatal metatarsus adductus deformities resolve spontaneously by 3 years of age47,50 and 95% resolve by 16 years of age. Metatarsus Adductus Metatarsus adductus, or forefoot adduction, might be the commonest neonatal foot downside. It outcomes from in utero positioning, occurring equally in girls and boys, and is bilateral in roughly 50% of neonates. The dysfunction has hereditary tendencies and is more widespread in the first-born than subsequent children because of an increased molding effect from the primigravid uterus and abdominal wall. Three conditions should be distinguished from the benign calcaneovalgus foot: congenital vertical talus; posteromedial bowing of the tibia; and neuromuscular problems which would possibly be related to paralysis of the gastrocnemius muscle tissue. However, in severe deformities or in these with restricted mobility, anteroposterior and lateral simulated weight-bearing radiographs of the foot and probably the decrease leg are essential. These radiographs permit the popularity of a congenital vertical talus or posteromedial bowing of the tibia. However, exterior tibial torsion follows the identical pure historical past as that of internal tibial torsion. Most neonates presenting with a benign calcaneovalgus foot and exterior tibial torsion have a normally aligned foot and decrease extremity by 2 years of age. Talipes Equinovarus (Clubfoot) A congenital clubfoot is one of the most typical pathologic entities affecting the neonatal foot. The congenital clubfoot is usually an isolated abnormality, whereas the teratologic kind is related to an underlying neuromuscular dysfunction, similar to myelodysplasia or arthrogryposis multiplex congenita. Positional clubfoot refers to a normal foot that has been held in an equinovarus place in utero. The probability of the deformity occurring randomly is 1 in 1000 live births, but within affected households the chance is approximately 3% for subsequent siblings and 20% to 30% for the offspring of affected mother and father. Muscle biopsies of the extrinsic muscular tissues, electromyographic studies of these muscles, and histologic analysis of the associated connective tissue have indicated a possible neuromuscular etiology. These findings distinction with previous etiologic theories in which the deformity of the talus was thought to be the primary abnormality. These findings also suggest a cause as to why clubfoot is ubiquitous in syndromes and neuromuscular issues; any child with a clubfoot deformity requires a careful musculoskeletal and neurologic evaluation to search for different abnormalities. This condition is manifested by a hyper-dorsiflexed foot, with an abducted forefoot and valgus hindfoot. When these two conditions are mixed with the conventional, increased exterior rotation of the hip. The neonate typically presents with external rotation of the concerned extremity and a calcaneovalgus foot. The foot may be hyperdorsiflexed to convey its dorsal surface involved with the anterior aspect of the decrease leg. Anteroposterior and lateral standing or simulated weight-bearing radiographs are used in the evaluation of clubfoot. Line measurements are required to determine the place of the unossified navicular bone and the overall alignment of the foot. Both nonoperative and operative methods are used within the therapy of clubfoot deformities. Taping and malleable splints are significantly useful in premature infants till they attain an acceptable measurement for casting. For each forged change, the foot is gently manipulated towards the corrected place. Complete clinical and radiographic correction ought to be achieved by three months of age. The failure to obtain clinical and radiographic correction by three months of age is a sign for surgical therapy as a end result of additional makes an attempt at casting may result in articular damage or a midfoot break. Previously, main operative treatment of congenital clubfoot typically required an entire soft tissue launch, usually carried out between 6 and 12 months of age, and passable long-term results were anticipated in 80% to 90% of cases. However, over the last decade, the aforementioned Ponseti method of serial casting47 (augmented with percutaneous tendo Achilles tenotomy when necessary) has turn into extensively accepted. The Ponseti casting method and tendo Achilles tenotomy are followed by a protracted interval of bracing, which lasts from 2 to 4 years. Congenital Vertical Talus Congenital vertical talus is an unusual neonatal foot deformity however its etiology is much like that of clubfoot. Most of these deformities are related to an underlying disorder corresponding to teratologic malformation, myelodysplasia, arthrogryposis multiplex congenita, or a syndrome such as trisomy 18. There is an equinus hindfoot, a valgus hindfoot, a convex plantar surface, forefoot abduction and dorsiflexion, and rigidity. A cautious musculoskeletal and neurologic examination must be performed on all neonates to seek for related issues or syndromes. The radiographic evaluation of congenital vertical talus is much like that of clubfoot. Many of those issues are recognizable at delivery, whereas others are manifested throughout development and growth. The defects can happen in the epiphysis or physis (growth plate) or as abnormalities of bone reworking that will have an result on the metaphysis or diaphysis. It is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, but roughly 80% of instances are new mutations. Achondroplasia produces a rhizomelic sample of shortening, with the proximal segments. The analysis is usually made at delivery due to the characteristic options of the head, face, and quick extremities. The head is typically enlarged; there are disproportionately short limbs and a normal trunk. Facial features embody frontal bossing, flattening of the nasal bridge, midfacial hypoplasia, and prominence of the mandible. The palms characteristically have a space between the long and ring fingers, producing a "trident" hand. The thoracolumbar spine could show an acute kyphotic deformity (gibbus) before the onset of walking. It is important to make an early prognosis in order that genetic counseling may be performed.
Celexa 40 mg discount otc
When the pulmonary arterial strain is low treatment 3 nail fungus celexa 10 mg buy line, valve insufficiency is recognized by a really low- to medium-pitched early diastolic murmur that begins with P2 symptoms quit smoking cheap celexa 20 mg without a prescription. This is heard best within the pulmonary space and extends for a brief distance down the left sternal edge. The extra frequent forms of pulmonary regurgitation are acquired, commonly after surgery for extreme pulmonary valve stenosis, as happens with tetralogy of Fallot, when the pulmonary outflow patch is positioned and the valve leaflets are poor or absent. Because these patients often have surgically acquired right bundle department block, the pulmonary valve closure could be well separated from aortic valve closure if the sound might be heard. Pulmonary hypertension, significantly when related to a high pulmonary vascular resistance, is a typical reason for secondary pulmonary insufficiency. Often, a pulmonary ejection click may be present because of the dilated pulmonary root. The S2 is narrowly cut up or single because the excessive pulmonary artery diastolic stress closes the valve early. A diastolic decrescendo murmur then begins with pulmonary valve closure and is high in frequency as a outcome of the pulmonary artery stress is high. The S2 split is regular, though the A2 could additionally be loud and will have a "tambour" high quality. They occur in synchrony with cardiac movement and may be heard during the early interval after myocardial infarction and most frequently after cardiac surgical procedure (see Chapter 7). Many illnesses have profound results on the pulmonary circulation and may elevate pressures within the pulmonary arteries. These embody illnesses of lung, pulmonary vasculature, heart, or liver; collagen vascular ailments; and obstruction of the upper airways. One consistent physical discovering detected in pulmonary hypertension is an energetic right ventricular parasternal faucet with a distinctive, sharp palpable P2. There could additionally be no audible murmur; a high-pitched murmur of pulmonary valve insufficiency or a high-pitched systolic murmur of tricuspid valve insufficiency could additionally be current. Recognition of pulmonary hypertension warrants a diligent search for the underlying trigger. If the rationale for the elevated pulmonary artery pressure remains unclear, the dysfunction is referred to as main pulmonary hypertension. If an etiology can be discovered, the disorder is termed secondary pulmonary hypertension. In contrast to the low-pressure murmur of pulmonary valve insufficiency (in the absence of pulmonary hypertension), the murmur of aortic valve insufficiency is high pitched and audible from the aortic space extending to the apex. The peripheral pulses and the intensity and size of the murmur provide medical quantification of the magnitude of regurgitant move. Malformations related to profound and fixed cyanosis with out heart failure are often associated with right-sided obstructive lesions and a right-to-left shunt. Transposition of the nice arteries with intact ventricular septum also manifests with profound and glued hypoxia, with mild tachypnea, and with no coronary heart failure. In addition, obstructed whole anomalous pulmonary veins might produce extreme cyanosis, pulmonary venous engorgement, and pulmonary hypertension. Lesions associated with left-sided obstruction (critical aortic stenosis, interrupted aortic arch, hypoplastic left heart syndrome) produce significant cardiogenic shock, poor perfusion, and profound lactic acidosis. The chest radiograph might present helpful clues to the cause for the lesion, relying on the paucity (pulmonary atresia) or plethora (obstructed complete anomalous pulmonary venous return) of the pulmonary vascular markings; the left- or right-sided (tetralogy of Fallot, truncus arteriosus) place of the aorta; the configuration of the heart (boot-shaped, as in tetralogy of Fallot; egg-shaped, as in transposition of the great arteries; or huge enlargement, as in Ebstein anomaly); or the aspect of the chest (risk of coronary heart disease is greater with dextrocardia, particularly if the abdomen bubble is on the left side of the stomach or if the liver is midline). The chest radiograph is of some assist in distinguishing coronary heart disease from congenital pneumonia, respiratory distress syndrome, pneumothorax, and congenital diaphragmatic hernia. After closure of the aortic valve (A2), regurgitation of leakage at this site creates the high-pitched, early diastolic decrescendo murmur of aortic insufficiency. This murmur is heard greatest on the third left or right intercostal space whereas the affected person is sitting. The most common form of aortic insufficiency is acquired, most frequently as a consequence of extreme rheumatic carditis, and may be present in each acute rheumatic fever and continual rheumatic heart illness. The left ventricular impulse is abnormal and hyperdynamic, and a wide pulse stress is present. A lengthy, low-frequency musical diastolic rumble beginning onethird of the time into diastole may happen, particularly within the left lateral decubitus position in sufferers with vital valve insufficiency. It is believed to be related to regurgitant aortic move passing across the anterior mitral valve and fluttering of the leaflet in conjunction with mitral valve influx. Two-dimensional real-time shade Doppler echocardiography is most helpful in identifying the anatomy of congenital coronary heart lesions. The echocardiogram enables evaluation of the four chambers, the interconnecting valves, the great arteries, the pulmonary venous return, and the anatomic relationships between these constructions. Furthermore, shade Doppler move research can determine the presence, path, and magnitude of right-to-left or left-to-right shunts. Echocardiography has changed cardiac catheterization for all however probably the most complex congenital heart lesions. Valvulitis, as manifested by particular and new heart murmurs, is often part of the preliminary scientific picture. The specific coronary heart murmurs are three: mitral regurgitation, aortic regurgitation, and the uncommon Carey-Coombs murmur, a mid-diastolic rumble on the apex. After the acute rheumatic fever has run its course, any remaining murmurs turn out to be part of continual rheumatic heart illness. If the affected person has continued permanent reliable penicillin prophylaxis, the severity of the mitral regurgitation often disappears; this occurs much less generally with aortic regurgitation. The development of mitral valve stenosis is part of the pure historical past of severe repeated episodes of acute rheumatic fever. The diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever is recommended (although not definitively confirmed) by application of the revised Jones standards, final edited in 2015 (Table eight. In addition, proof of a group A streptococcal pharyngitis have to be current, which can include a constructive throat tradition, constructive streptococcal antigen or antistreptococcal antibody, or a history of prior episodes of rheumatic fever. In circumstances the place carditis could also be subclinical (no audible murmur), the analysis is supported by echocardiographic proof of subclinical carditis (no audible murmur) by demonstrating important mitral regurgitation with a regurgitant jet seen in 2 planes with chaotic flow and being holosystolic and extending 1 cm into the left atrium. Criteria for subclinical vital echocardiographic aortic regurgitation embrace its being seen in 2 imaging planes, being holodiastolic, and lengthening 1 cm into the ventricle (Table 8. The differential analysis is proscribed within the presence of carditis and arthritis (see Chapter 33) but consists of systemic lupus erythematosus. Carditis is now defined as clinical and/or subclinical (echocardiographic valvulitis). Arthritis (major) refers only to polyarthritis in Low-Risk populations, but additionally to monoarthritis or polyarthralgia in Moderate/High-Risk populations. Minor standards for Moderate/High-Risk populations only embrace monoarthralgia (polyarthralgia for Low-Risk populations), fever of >38� C (>38. Pan-diastolic jet in at least 1 envelope Pathologic Mitral Regurgitation (All 4 Met) 1.