Celebrex
Celebrex dosages: 200 mg, 100 mg
Celebrex packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Effective 100 mg celebrex
It is located at decrease portion of esophagus just above the esophagogastric junction arthritis swelling celebrex 100 mg on-line. It opens in response to primary peristalsis and vomiting and permits air to escape from the stomach exercises for arthritis in your neck generic 100 mg celebrex visa. Bolus of food is taken in to the stomach with the peristaltic waves after which gastroesophageal sphincter closes. Oral phase: the meals is chewed, lubricated and converted in to a bolus, which is then propelled in to the pharynx. There occurs short-term cessation of respiration and rising of larynx beneath the base of tongue. Esophageal section: Once the meals enters in to the esophagus, cricopharyngeal sphincter closes and primary peristalsis of w Section 1 Pharyngeal arches. Muscles: Intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of tongue develop Section 1 w Clinical highlights 1. Philtrum: Vertical midline sulcus of higher lip extending from nasal columella to vermilion border. Structures passing between superior and center constrictors: Glossopharyngeal nerve and stylopharyngeus muscle. Types: Hyaline: Thyroid, cricoid and most of the arytenoid cartilage (except its tip) are hyaline cartilages, which bear sixty two fig. Cricoid: this ring formed cartilage has slender anterior arch and expanded posterior lamina, over which articulate arytenoids. Epiglottis: this leaf-like, yellow, elastic cartilage types anterior wall of laryngeal inlet. Parts: the anterior surface of epiglottis is connected to body of hyoid bone by hyoepiglottic ligament that divides epiglottis in to two elements suprahyoid and infrahyoid. Arytenoid cartilages: the pyramidal form arytenoid cartilage has the following elements: Base: It articulates with cricoid cartilage. Section 1 w fundamental Sciences JointS Cricoarytenoid joint: this synovial joint is formed between the bottom of arytenoid and a aspect on the upper border of cricoid lamina. Thyrohyoid membrane: this membrane, which is pierced by neurovascular bundle of superior laryngeal vessels and inner laryngeal nerve, connects thyroid cartilage to hyoid bone. Hyoepiglottic ligament: It connects the epiglottic cartilage to the body of hyoid bone. Subglottic foreign bodies typically get impacted in the area of conus elasticus. Cricothyroid membrane: the anterior a half of conus elasticus is thick and types cricothyroid membrane, which connects thyroid cartilage to cricoid cartilage. Its free decrease border varieties the vestibular ligament, which lies in the vestibular fold (false cord). Mucous glands are abundant on the epiglottis, posterior part of the aryepiglottic folds and within the saccule. Saccule: this diverticulum of mucous membrane starts from the anterior a half of ventricle and extends superiorly between vestibular folds and thyroid lamina. Infraglottic: Lymphatics drain in to prelaryngeal (Delphian node) and pretracheal nodes (through cricothyroid membrane) and then to lower deep cervical and mediastinal nodes. Some lymphatics pierce cricotracheal membrane and drain in to decrease deep cervical nodes. The vocal twine consists of a vocal ligament (upper fringe of cricovocal membrane), which is roofed with mucous membrane that has scanty subepithelial connective tissue. Paraglottic space: It communicates with pre-epiglottic area and is bounded by Anterolateral: Thyroid cartilage and cricothyroid membrane. Anterior two-third of glottis is shaped by membranous vocal cords while posterior one-third by vocal Growths invading paraglottic house destroy cricothyroid membrane and present within the neck. Vocal wire tumors involving thyroarytenoid muscle invade paraglottic space and then subglottic and extralaryngeal area. There happen two kinds of phase differences during the phonation (vibrations of the closed vocal folds) vertical and horizontal: Vertical phase distinction: Inferior vocal fold edges separate before superior edges and return again in similar order. Horizontal phase distinction: the anterior part separates earlier than posterior half and shut in same order. Larynx under the vocal cords is provided by the internal department of recurrent laryngeal nerve. Further divisions of lung buds kind the lung lobes and bronchial tree together with bronchopulmonary segments down to alveolar sacs. It loops round aortic arch and ascends in to the neck within the tracheoesophageal gutter. Right recurrent laryngeal nerve: It arises from the vagus at the level of subclavian artery and loops around subclavian artery and then ascends in the tracheoesophageal gutter. External laryngeal nerve: It travels in relation with the superior thyroid artery and provides cricothyroid muscle. Arytenoids: They are relatively massive and canopy significant posterior a part of glottis. DeveLopment the hypobranchial eminence appears within the ground of primitive pharynx between the 2nd, 3rd and 4th branchial arches (Table 2). The subglottis is the narrowest portion of larynx in kids and has the whole cartilaginous ring (cricoid). Vocal cords: They descend to C5 level and increase in size especially in males and lead to voice adjustments (Table 3). Vocal folds are adducted and stress of moving air causes vibrations of the elastic vocal folds. The modulator motion of lips, tongue, palate, pharynx and teeth converts the sound in to speech. Cough reflex: Coughing dislodges and expels any foreign particle that is out there in contact with respiratory mucosa. It expands and contracts longitudinally in response to the demands of respiration, swallowing and gravity. Trachea is about 10�12 cm long and extends from decrease border of cricoid cartilage of larynx to the carina (level of V thoracic vertebra), the place trachea divides in to right and left primary bronchi. Right main bronchus is wider shorter, and extra vertical than left bronchus and therefore extra common web site of international our bodies. Speech: There are three phases in the manufacturing of speech: pulmonary, laryngeal and supraglottis/oral. Pulmonary part: It creates vitality circulate with inflation of lungs and expulsion of air. As the bronchi divide, the cartilages turn into progressively smaller and fewer complete, until the alveoli are formed. The bronchoscopist needs an prolonged internal anatomic nomenclature that correlates carefully with the endobronchial system and the areas description could be reliably described to another bronchoscopist.
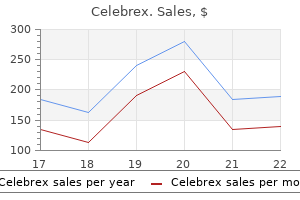
Celebrex 100 mg order amex
The variant bifurcation is extra generally discovered excessive than low and may be as excessive as the level of the hyoid bone and more rarely as little as the cricoid cartilage arthritis in back diet discount 200 mg celebrex visa. Subdavlon Artery the best subclavian artery is anomalous in approximately 1% of people arthritis in feet pain relief celebrex 200 mg with mastercard. It could originate in any place from the first to the fourth relative to the other arch vessels, could rise larger or lower in the neck, and may vary in position relative to the scalene muscular tissues. In its course, the best subclavian artery may rise as excessive as 4 em above the clavicle, depending on the extent of brachiocephalic bifurcation. The subclavian artery might hardly ever be discovered anterior to the anterior scalene muscle together with the subclavian vein (occasionally the vein is discovered between the anterior and center scalene muscle tissue with the artery), may penetrate the center scalene, or might cross between the middle and posterior scalene muscles. In rare instances, the subclavian artery may divide on the medial border of the scalene muscle in to radial and ulnar arteries instead of constant in to the axillary artery. In addition, the vertebral artery might come up from the thyrocervical or costocervical trunk, from the left common carotid, or immediately from the aorta in uncommon instances. The vertebral artery enters the sixth vertebral transverse foramen 88% of the time, the fifth and seventh with equal frequency (7%), and barely whilst excessive as the second foramen. The internal thoracic artery, like the vertebral artery, follows the similar old pattern in a relatively excessive proportion of circumstances (79%). The origins and branching patterns of the thyrocervical and costocervical trunks are so highly variable amongst people and between sides that the commonest sample for every is found in lower than half ofthe inhabitants. The branches of the axillary artery, conversely, are so variable that the commonest sample occurred in solely 20 of 47 bodies studied by Hitzrot. Two-thirds of those are unilateml, and many of the remaining bilateral anomalies had been totally different from aspect to side. The frequent interosseous artery and its volar and dorsal branches are variable of their origins, dimension, and terminations. When this happens, the vessels in the forearm often lie in a more superficial airplane than normal, usually just beneath the deep antebrachial Art. The inferior phrenic arteries could come up independently or from a common stem, could have supernumerary branches, and should come up from the aorta or from the celiac artery or its branches. These embody variations within the level ofbifurcation, tortuosity, and direct origin of usually secondary visceral branches. The secondary branches ofthe belly the typical three-branched celiac trunk has been found in 60% to 89% of our bodies. In uncommon cases, the superior mesenteric artery is combined with the celiac trunk. It may come up from the superior mesenteric artery, and it might give rise to the left gastric, center colic, or left hepatic artery. There could additionally be two splenic arteries, with one or both arising immediately from the aorta. The superior mesenteric artery can also present accessory branches to the abdomen, pancreas, or spleen. The biggest variability within the superior mesenteric artery is present in its colic branches. Rare anomalies embrace duplication, absence, origin from the left frequent iliac, and con1ribution of accessozy branches to the liver or kidneys. Two hilar vessels have been present in 11% ofcases, there was a hilar artery with an upper pole department arising from the aorta in 6%, and 3% had a hilar and an aortic decrease polar branch. The renal artery may divide in to anterior and posterior trunks anyplace along its c~e and has between two and five branches at the renal hilus. The inferior suprarenal artery might arise from the renal (46%) or aorta (30%) or each (23%), may be absent (12%), and is multiple 11% of the time (average of three). Gtmltlt4Vemls the gonadal vessels could additionally be multiple and may come from the inferior phrenic arteries (recall the variable origins of the inferior phrenics), and there could also be three to 30 branches. The most clinically important variation is the inferior epigastric origin in one of 5 individuals, which poses a hazard during herniorrhaphy. It artery within the adductor canal and leaves the canal to accompany the nice saphenous vein on the knee. The other department, the deep circumflex iliac, may be absent, multiple, or arise in widespread with the inferior epigastric artery and will give rise to the external pudendal, medial, or lateral femoral circumflex artery. In 50% to 60% of circumstances, the medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries arise from the proximal profunda. The profunda has between two and six perforating branches excluding the termination ofthe artery. When the anterior tibial artery arises abnormally high, it could move deep to the popliteus muscle and be compressed. The artery may pass medial to a traditional or irregular origin of the medial head of the gastrocnemius. Variations embrace the absence of the posterior tibial artery with plantar vessels coDtinuing from the peroneal artery (B), absence of 1he anterior tibial artery wi1h 1he dorsalis pedis artery continuing from the perforating branch of the peroneal artery (C). The dorsalis pedis artezy in such cases is a continuation of the perforating department of the peroneal artery. Occasionally, the posterior tibial penetrates the interosseous membrane and joins the anterior tibial artery. Major variations in the large veins of the trunk occur and are normally traceable to embryonic events. The two venae cavae may also be joined by an iliac communication at their caudal end. Ptlttlll Vein the portal vein is sort of constant, with uncommon situations of the vein being situated anterior to the duodenum, widespread bile duct, and hepatic artery. In additi~ the left gastric vein, whose disconnection is necessary in selective shunts, drains in to the portal vein (54%), splenic vein 29%), or their junction (16%). Anatomic variants of the celiac, superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric arteries and their medical relevance. Relations: It articulates with 5 cranial bones: parietal, sphenoid, occipital, zygomatic and mandible. The composite grafts of the pores and skin and cartilage can be utilized for restore of defects of ala of nostril. Lesser occipital nerve (C2): this nerve of cervical plexus supplies higher part of medial floor of auricle and postauricular region. In the anterosuperior region, squamous part articulates with tympanic bone (tympanosquamous suture). Inferiorly and medially squamous half joins with the lateral superior portion of the petrous bone (petrosquamous suture). Its outer one-third (8 mm) is cartilaginous and its inner two-third (16 mm) is bony. Parts: Tympanic membrane consists of two elements: (1) pars tensa and (2) pars flaccida.
100 mg celebrex purchase amex
Nonoperative administration of elbow arthritis is the preliminary treatment and consists of exercise modification rheumatoid arthritis cream generic 200 mg celebrex fast delivery, range-of-motion workouts arthritis in neck and face buy generic celebrex 200 mg, use of braces and different support gadgets, intra-articular cortisone injections, and administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or disease-modifying antirheumatic medicine. Arthroscopic shaver Loose body Arthroscopic picture of free body inside the anterior elbow joint Articular surface of distal humerus, capitellum Initial surgical treatments for elbow arthritis include open or arthroscopic debridement procedures (see Plate 2-33). These surgical procedures are done to improve ache and range of motion, and should embody elimination of unfastened bodies, osteophyte resection, capsular release or excision, and synovectomy. In osteoarthritis, osteophytes generally type at the tip of the olecranon and the olecranon fossa and on the tip of the coronoid and the coronoid fossa. These bone spurs can cause impingement-type pain at the finish ranges of motion, and their elimination can help relieve such symptoms. Synovitis is a common supply of pain and limited movement in a affected person with rheumatoid arthritis; due to this fact, surgical synovectomy can be useful and can also prevent additional destruction of cartilage and bone. Finally, ulnar nerve symptoms might develop in an arthritic elbow with important lack of vary of movement, and thus ulnar nerve decompression or transposition is beneficial in combination with the debridement procedure in such situations. Although debridement procedures can provide vital symptom aid, they may not be as useful in sufferers with more superior arthritis and their effect may put on off over time because the arthritis progresses. In these cases, surgery is geared toward reconstruction of the diseased elbow joint. Most generally, this is within the type of a total elbow alternative, but other methods have occasionally been employed, including interpositional arthroplasty, resection arthroplasty, and elbow arthrodesis. Interpositional arthroplasty may be an choice in younger sufferers with severe arthritis, who could additionally be too lively for consideration of a complete elbow replacement. The procedure entails masking the diseased joint surfaces with a biologic material. Linked implants have a hinged mechanism that can be classified as constrained or semiconstrained on the idea of the absence or presence of sideto-side laxity within the implant. Linked, constrained designs had an unacceptably excessive failure fee and were abandoned for semiconstrained prostheses. Modern linked, semiconstrained implants enable some sideto-side laxity, so as to lower stress throughout the implant and lower the speed of element loosening. Elbow arthrodesis is also hardly ever used presently, as a end result of fusion in a single position could be tough for reasonable upper extremity perform. It can be thought of a salvage procedure in circumstances of infection and should hardly ever be thought-about an option in a younger heavy laborer who might place too high a requirement on an elbow alternative. Total joint replacement restores joint movement and relieves ache by replacing the diseased articular surfaces with a plastic and steel prosthesis. A hinge mechanism is current to link the humeral and ulnar components and supply implant stability. Linked implants directly join the humeral and ulnar components by way of the bearing floor and are indicated in sufferers with excessive bone destruction and/ or ligamentous destruction or instability. The hinge mechanism can be classified as constrained or semiconstrained on the idea of the absence or presence of side-to-side laxity within the implant. Modern linked designs have a semiconstrained articulation that permits some side-to-side laxity, so as to decrease stress across the implant and lower the rate of part loosening (see Plate 2-35). The most typical complication of total elbow arthroplasty and the one that causes essentially the most concern over time is implant loosening and resultant instability. Implant survival charges range depending on the etiology of the underlying arthritis, with survival charges as high as 94% at 15 years in rheumatoid arthritis patients but as little as 70% at 15 years within the post-traumatic population. This discrepancy is due partially to differences in age and exercise level, with patients present process complete elbow substitute for post-traumatic arthritis usually of a much youthful age and/or greater activity degree than rheumatoid arthritis sufferers. Unlinked whole elbow arthroplasty, with no direct connection between the humeral and ulnar elements. Adequate bone stock and ligament integrity is required for implant stability with this design. Arthritic adjustments at the radiocapitellar joint can also have to be treated with joint replacement, either in isolation or in combination with complete elbow arthroplasty. This is mostly addressed with radial head resection or substitute (see Plate 2-25). Whereas resection of the radial head alone can provide pain reduction, over time it could result in proximal displacement of the radial shaft if the interosseous membrane and distal radioulnar joint are or become deficient. Proximal radial migration could cause ache and dysfunction, notably with pronation-supination actions. Traditional implants were made from silicone, but this materials has been changed by metallic prostheses because of the high complication fee noted with silicone, significantly the technology of a major inflammatory response from particulate particles. The cubital tunnel is a fascial sheath that the ulnar nerve runs via simply posterior to the medial epicondyle. Nerve compression can happen by way of the tunnel or at websites just proximal or distal to it, such because the medial intermuscular septum, the arcade of Struthers, the flexor carpi ulnaris fascia, and the deep flexor-pronator aponeurosis. A subluxating ulnar nerve may also produce signs similar to those of nerve compression. Other causes of ulnar nerve symptoms around the elbow can embody adhesions from prior surgical procedure; presence of an anomalous muscle (anconeus epitrochlearis); tumors; snapping of the medial triceps; bony modifications from arthritis, prior fractures, or heterotopic bone; and anatomic deformities, such as cubitus valgus and cubitus varus. The arcade of Struthers is an aponeurotic band positioned approximately 8 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle that runs from the medial head of the triceps to the medial intermuscular septum. As the ulnar nerve crosses from the anterior to the posterior compartment in the distal a half of the higher arm, it might possibly pass underneath this band, if current. A constructive Tinel signal will re-create these paresthesias by tapping alongside the course of the ulnar nerve on the medial facet of the elbow. The location of the Tinel sign could assist to localize the exact website of nerve compression. Direct pressure can exacerbate signs by increasing compression of the nerve in the cubital tunnel, whereas elbow flexion may cause traction-related deformation of the nerve that increases symptoms. Elbow flexion can even reveal evidence of nerve instability, as a outcome of the ulnar nerve will sometimes dislocate or subluxate anterior to the medial epicondyle with elbow flexion and cause a snapping or clicking sensation. With more persistent or extreme circumstances of entrapment, motor findings can be current, including weak spot and wasting of the intrinsic muscular tissues of the hand. When symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome are current, an electromyographic research of the extremity can be carried out both to affirm that the abnormality is localized to the elbow and to decide the severity of the neuropathy. Ulnar nerve compression can happen proximally on the cervical spine or brachial plexus, as well as distally within the forearm, wrist, or hand, though a lot much less generally. Nonoperative management is the initial treatment in milder circumstances of cubital tunnel syndrome and consists of activity modification and splinting to take strain off the nerve, corresponding to avoidance of repetitive or extended elbow flexion and use of splints that keep the elbow in a comparatively prolonged position, particularly at night time. Surgery is indicated when nonoperative measures fail and includes in-situ decompression of the ulnar nerve or ulnar nerve transposition. In-situ decompression is often used in milder cases, whereas transposition is carried out in extreme instances and in conditions during which nerve instability is present. When performing an ulnar nerve transposition, all possible sites of nerve entrapment proximal Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle Anterior transposition of ulnar nerve Divided tendon of origin and distal to the cubital tunnel should be decompressed, along with releasing the cubital tunnel. This consists of launch of the arcade of Struthers if current, excision of the medial intermuscular septum, and release of the flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum superficialis fascia. Ulnar nerve transposition may be subcutaneous or submuscular and acts to decompress the nerve by placing it able anterior to the medial epicondyle. Subcutaneous transposition is extra commonly performed, and in this approach the nerve is stabilized anteriorly by a free fasciodermal sling.
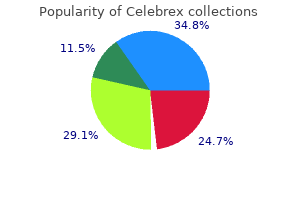
Generic celebrex 200 mg on-line
A gradual transition from plump cells to the spindle cell component is frequently observed arthritis diet chinese medicine purchase 100 mg celebrex. These tumours are nearly invariably p63-positive 707 arthritis in dogs generic celebrex 200 mg,1168B,1171A; keratins are invariably expressed in these lesions, occasionally focally and never uncommonly restricted to the plump spindle and epithelioid cells. Squamous cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinomas often current as a cystic lesion, the place the cavity is lined by squamous cells with various degrees of nuclear atypia and pleomorphism. The neoplastic cells infiltrate the adjoining stroma within the type of sheets, cords and nests, which elicit a conspicuous stromal reaction. The infiltrating squamous components might range in levels of squamous differentiation, with spindle cells commonly noticed on the invasive fronts of the tumour 659A,1551D. The acantholytic variant of squamous cell carcinoma, characterised by the formation of irregular areas lined by atypical squamous cells resulting in a pseudoglandular or pseudoangiosarcomatous appearance, should be thought of as a potential differential prognosis with angiosarcoma 398A. It must be famous that squamous differentiation can be found in carcinomas with medullary-like options (see Medullary carcinoma). For a prognosis of main squamous cell carcinoma of the breast to be rendered, a main squamous cell carcinoma from different sites, especially pores and skin, have to be dominated out 1551D. Cords of spindle cells immersed in free myxoid stroma can be noticed (C), which are highlighted by immunohistochemistry with antibodies to highmolecular-weight keratins (D). Spindle cell carcinoma Spindle cell carcinomas are characterized by atypical spindle cells, arranged in a large number of architectural patterns ranging from lengthy fascicles in herringbone or interwoven patterns to short fascicles in a storiform ("cartwheel") patterns 233,485A, 1551A. C Higher magnification exhibiting a variety of squamous-cell differentiation with most differentiated on the right. D Immunostaining for keratins 5/6 is positive as anticipated for squamous epithelium. In such tumours, true chondroid differentiation or chondroid matrix is usually discovered. It should be noted that though within the vast majority of cases areas of epithelial differentiation could be readily discovered, in some cases, in depth sampling is required for the carcinomatous areas to be documented. Importantly, immunohistochemical analysis also reveals the expression of epithelial markers, often high-molecular-weight keratins. Areas the place the neoplastic cells kind small clusters, with more epithelioid morphology or squamous differentiation may be discovered. It ought to be famous that this group of tumours includes lesions that are more doubtless to represent the end of the spectrum of spindle squamous cell carcinomas on one hand, and malignant myoepithelioma/myoepithelial carcinoma on the opposite 613. Metaplastic spindle cell carcinoma ought to all the time be thought-about as a primary differential diagnosis of atypical spindle cell proliferations of the breast. A prognosis of metaplastic spindle cell carcinoma could be rendered based on the presence of any evidence of epithelial differentiation by histopathological and/or immunohistochemical evaluation (see below). Metaplastic carcinoma with mesenchymal differentiation Metaplastic breast carcinomas with mesenchymal parts are often composed of an admixture of mesenchymal parts, together with chondroid, osseous, rhabdomyoid and even neuroglial differentiation, with carcinomatous areas, which could be in the type of glandular tubules, strong clusters and/ or foci of squamous differentiation 233,353B,1019A,1551B, 1551C. The mesenchymal components can either seem differentiated with minimal atypia to exhibiting frankly malignant options that to some extent recapitulate the patterns present in true sarcomas of the delicate tissues. Historically, the time period "matrixproducing carcinomas" was applied to a subgroup of metaplastic carcinomas with mesenchymal components the place an abrupt Mixed metaplastic carcinomas It should be noted that upon intensive sampling, a large proportion of metaplastic breast cancers show a mix of various parts. These circumstances ought to be reported as metaplastic carcinomas and the distinct elements recorded in the final report. Different forms of metaplastic carcinomas have been described arising in association with complicated sclerosing lesions and papillomas 331,499A. The identification of epithelial differentiation in metaplastic breast carcinomas requires the utilization of more than one. Although the tumour is completely composed of neoplastic spindle cells, the presence of ductal carcinoma in situ at the periphery and admixed with the lesion should immediate a prognosis of spindle cell carcinoma. It must be noted that the expression of keratins is usually variable, and not uncommonly focal. P63, which is expressed in > 90% of metaplastic breast carcinomas, has proven to be a helpful marker for the identification of these tumours and for their differentiation with other spindle and mesenchymal malignancies 233,707, 1169A,1171A. In a pure spindle cell lesion, unequivocal expression of high-molecular-weight keratins and/ or p63 in any proportion of cells should prompt a diagnosis of metaplastic carcinoma. Genetics Microarray-based gene-expression profiling has demonstrated that metaplastic breast tumours are preferentially categorized as of basal-like subtype 1569, 1569B. Independent research, nevertheless, have advised that a subgroup of these cancers, in particular these with spindle cell metaplasia, show transcriptomic features according to those of cells undergoing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. B Immunostaining reveals absence of reactivity with a pan-keratin antibody cocktail within the mesenchymal part, whereas the epithelial cells are constructive. Claudin-low tumours are reported to be enriched in cells with epithelial-to-mesenchymal options and within the so-called cancer stem cells 1122. Genetic analysis of metaplastic breast cancers has been performed in a limited variety of samples and solely in part substratified based on histological kind. These tumours, as a bunch, have complex genomes, characterized by complex patterns of gene copy-number positive aspects and losses, just like these found in different forms of triple-negative and basal-like breast cancers 485B,485C,568B, 1170A. Genomic characterization of the completely different components from metaplastic breast cancers performed to date has revealed that the histologically distinct components are clonally related within the vast majority of instances 485C,1436A; however, specific genetic aberrations could additionally be restricted to particular parts within a most cancers. In a means akin to other triple-negative breast cancers, distant metastases could be discovered in the absence of lymph-node metastases, and preferentially have an result on mind and lungs. C the adenocarcinoma is admixed, partly, with chondroid matrix containing lacunar spaces and rare chondrocytes. The prognostic value of histological grading of metaplastic breast carcinomas is unsure. Lakhani Definition Any invasive carcinoma during which the cells present the cytological options of apocrine cells. However, extensive apocrine differentiation is seen in approximately 4% of invasive breast carcinomas 398,1214. Clinical features Carcinomas with apocrine differentiation are indistinguishable clinically and radiologically from these without apocrine options. Macroscopy these tumours can present as a mass of any measurement and at any site in the breast. Apocrine differentiation is also seen in lobular carcinoma in situ and ductal carcinoma in situ 258,292,390,768. Intracytoplasmic lipid has also been demonstrated in tumours with apocrine differentiation 398, 947. Differential analysis Tumours composed completely of sort A cells could additionally be confused with a granular cell tumour and those during which kind B cells predominate could resemble an inflammatory reaction or a histiocytic proliferation 395; antibodies to keratin can assist prognosis in such cases 1416. Approximately half of carcinomas with apocrine differentiation present this molecular signature, together with most pleomorphic lobular carcinomas with apocrine features 396. It is most likely going that this immunophenotype identifies tumours which have the distinct "apocrine molecular signature," as mentioned below. A Note the abundant, granular, intensely eosinophilic cytoplasm and the enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli (type A cells).
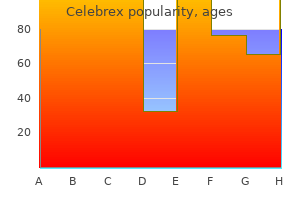
Celebrex 200 mg discount fast delivery
Neurovascular buildings in danger with this method embrace the axillary nerve and anterior humeral circumflex vessels proximally; the radial nerve as it runs within the spiral groove on the posterior floor of the midshaft of the humerus and extra distally because it emerges between the brachioradialis and brachialis muscles laterally; and the musculocutaneous nerve arthritis in the knee bone on bone 200 mg celebrex discount overnight delivery, in its location on the surface of the brachialis muscle and deep to the biceps muscle degenerative joint disease arthritis in dogs celebrex 200 mg order on-line. More distal fractures of the humeral shaft may be difficult to expose with the anterolateral method, owing to the proximity of the elbow joint. The humeral shaft can be uncovered posteriorly both by splitting the triceps muscle down the midline, by taking care to establish the radial nerve, or by elevating the triceps muscle along its lateral border and reflecting all three heads of the muscle medially. The radial nerve is recognized within the latter approach because it passes via the lateral intermuscular septum from posterior to anterior. The lateral or Kocher strategy to the elbow is often used for many procedures on the lateral facet of the elbow, such as fracture fixation (radial head, capitellum), radial head replacement, and lateral collateral ligament repair or reconstruction. The strategy makes use of the internervous airplane between the extensor carpi ulnaris (posterior interosseous nerve) anteriorly and the anconeus (radial nerve) posteriorly. The posterior interosseous nerve can be protected by maintaining the forearm pronated, and the radial nerve is avoided by not straying too far proximally or anteriorly. Posterior approaches to the elbow can involve mobilization of the triceps tendon or go away the triceps intact. This approach reflects the olecranon and triceps insertion proximally to expose the distal humerus and elbow joint. Outstanding exposure of the joint is achieved, and the strategy is especially useful in fixation of complicated, intra-articular distal humerus fractures and whole elbow arthroplasty. The Bryan-Morrey posterior method is a substitute for olecranon osteotomy and includes reflection of the extensor mechanism laterally, together with the triceps and anconeus. The anteromedial portal is made roughly 2 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle and anterior to the intermuscular septum. The ulnar nerve and medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve are at risk with this portal. The anterolateral portal is similarly made on the lateral side of the elbow, taking care to keep anterior to the humerus. The posterocentral and posterolateral portals are mostly employed to visualize the posterior compartment of the elbow. Finally, the direct lateral "soft spot" portal is made at the "soft spot" on the lateral side of the elbow to assist with visualization and instrumentation within the lateral gutter, such as when working on a capitellar osteochondritis dissecans. The medial surface of the distal extremity of the radius is also concave and articular. Dorsally, the distal a part of the radius reveals its tubercle and is otherwise somewhat ridged and grooved for the passage of the tendons of the forearm extensor muscular tissues. The distal radius and ulna have a wealthy vascular supply coming from the radial, ulnar, anterior interosseous, and posterior interosseous arteries. The vessels that offer the dorsum of the distal radius can be described for the corresponding extensor tendon compartments as both intercompartmental or compartmental. Nutrient vessels department off the main vessels and penetrate the retinaculum and underlying bone. A department off the radial artery, it provides nutrient branches to the bone between the first and second extensor tendon compartments. Clinically, the vessel and its corresponding branches and underlying bone could be harvested and utilized for vascularized bone grafting procedures within the carpus (for example, for a scaphoid nonunion with avascular proximal pole). Ossification begins in the distal extremity of the radius at the end of the first 12 months, and fusion takes place at age 19 to 20. An ossification heart for the distal finish of the ulna seems at age 5 or 6 and fuses with the shaft at age 18 to 20. Carpal articular surface the skeleton of the wrist consists of eight small bones arranged in two rows, proximal and distal. The bones of the proximal row, from the radial to the ulnar side, are the scaphoid, the lunate, the triquetrum, and the pisiform. Those of the distal row, in the identical order, are the trapezium, the trapezoid, the capitate, and the hamate. Their dorsal and palmar surfaces are nonarticular and supply for the attachment of the dorsal and palmar ligaments that hold them intently together. The other surfaces are articular, aside from the subcutaneous surfaces of the bones that type the borders of the wrist. The proximal articular surfaces are generally convex; the distal surfaces are usually concave. Foramina for the doorway of blood vessels are discovered on nonarticular areas of each bone. The smooth distal floor is triangular but concave and receives each the trapezium and the trapezoid. The lunate is crescentic; its proximal convexity is for the more medial of the articular surfaces of the distal end of the radius. The distal surface is deeply concave for the capitate and for a small contact with the hamate. On its radial surface, this bone contacts the scaphoid; medially, it has a surface for the bottom of the triquetrum. The triquetrum is pyramidal, with the base of the pyramid toward the lunate and the apex downward and ulnarward on the ulnar border of the wrist. The inferior floor is sinuously curved for articulation with the hamate, and the palmar surface has an oval facet for the pisiform. The pisiform could additionally be thought to be a sesamoid fashioned in the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. Its proximomedial floor is concave for articulation with the scaphoid, and its distal floor has Trapezoid Trapezium Radial styloid course of Scaphoid Dorsal tubercle of radius (Lister) Radius Triquetrum Lunate Ulnar styloid process Ulna a saddle-shaped side for the base of the primary metacarpal. On the palmar surface of the bone is a tubercle and a deep groove, through which passes the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle. The tubercle gives attachment to the superficial lamina of the flexor retinaculum and to several thumb muscular tissues. The medial surface of the trapezium has a big concave aspect proximally for articulation with the trapezoid and has a small, flat oval floor on the distal angle of the bone for the second metacarpal. The trapezoid is somewhat wedge formed, with the broader base of the wedge dorsally. The lateral surface is convex for the trapezium, whereas the medial surface has a clean side for the capitate. The capitate is the biggest of the carpal bones and occupies the center of the wrist. The distal, considerably cuboidal extremity articulates mainly with the bottom of the third metacarpal, however via small lateral and medial facets it also makes contact with the bases of the second and third metacarpals. The lateral surface has, distally, a small, smooth side for the distal extremity of the trapezoid, and the medial surface has an rectangular articular surface for the hamate. The hamate is wedge formed and has a characteristic hooklike course of, the hamulus, or hook.
Syndromes
- High-dose test: no change
- Inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis), such as Henoch-Schonlein purpura, which causes a raised type of purpura
- Unusual odor
- Confirm findings of another test or x-rays
- Enlarged (dilated) pupil of the affected eye
- Learn to relax. Try methods such as yoga, tai chi, or massage.
- Shingles (herpes zoster)
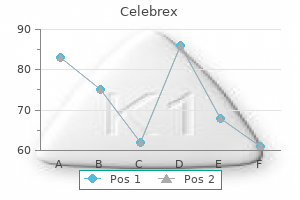
Order celebrex 200 mg
Pyriform sinus (Fossa): Each pyriform fossa arthritis during pregnancy cheap celebrex 200 mg online, which lies on both facet of the larynx arthritis in neck icd 9 code 200 mg celebrex discount with visa, forms the lateral channel for food. Communications Superior: It is continuous with oropharynx on the degree of hyoid bone. Anterior: It communicates with larynx by way of the laryngeal inlet, which is bounded by the epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds and arytenoids. Postcricoid area: Parapharyngeal nodes and nodes of supraclavicular and paratracheal chain. Upper and middle jugular nodes are commonly affected but retropharyngeal, paratracheal, paraesophageal, and parapharyngeal house nodes may additionally be concerned esophagus inclines to the left from its origin to thoracic inlet. Thoracic esophagus additionally inclines to the left from T7 to the esophageal opening in the diaphragm. Constrictions Esophagus exhibits four normal constrictions, which can be seen in esophagogram as properly as during esophagoscopy. These constrictions, the place foreign our bodies can be held up, are at the following ranges: Pharyngoesophageal junction (C6)-15 cm from the upper incisors. The muscle fibers are striated in upper third, smooth within the lower third and both striated and clean in the center third of esophagus. Main stem bronchi (first generation): Left and right (right lung accounts for 55�60% of total lung parenchyma). Lobar bronchi (second generation): Right higher, center and decrease lobes and left upper and its lingular part and lower lobes. The direct laryngoscopy examination is required to rule out malignancies of those areas. Laryngeal areas: the pre-epiglottic and paraglottic areas could additionally be invaded by carcinoma arising within the laryngeal mucosa. It is proscribed above and below by the arcuate lines, anteriorly by anterior commissure and posteriorly by vocal process of arytenoids. Adductors of vocal twine: They are lateral cricoarytenoid, thyroarytenoid, and interarytenoid muscle tissue. The flooring of mouth forms the higher restrict of neck anteriorly while posteriorly upper border is base of cranium. Surface anatoMy the next landmarks of surface anatomy are important for neck examination in addition to for planning the surgical incision. Anterior and posterior neck triangles separated by sternocleidomastoid muscle Mastoid: It offers insertion to sternocleidomastoid muscle. Mandible: the submandibular gland can be palpated just below the ramus of mandible. The marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve crosses the decrease border of mandible superficial to facial vessels just anterior to masseter muscle. The cricothyroid membrane located between thyroid and cricoid cartilages is the positioning of emergency tracheostomy. Trachea: the cervical trachea may be shifted to either aspect as a end result of thyroid and superior mediastinal tumors. The accessory nerve courses across the roof of posterior triangle and enters the anterior border of trapezius at the junction of its middle and decrease third. Blood supply: Branches of occipital and superior thyroid arteries (branches of exterior carotid artery). Trapezius muscle: this massive muscle makes the posterior boundary of posterior triangle and elevates the shoulder. The digastric and omohyoid muscular tissues divide these triangles in to further sub-triangles. The anterior and posterior bellies of digastric and superior stomach of omohyoid divide the anterior triangle in to 4 triangles: 74 supply because the vessels penetrate the superficial fascia. The space between superficial fascia and investing layer of deep cervical fascia incorporates following buildings: 1. The inside lamina covers medial floor of pterygoid muscle as a lot as the cranium base tympanic bone, styloid process and forms stylomandibular ligament. Submandibular: It is bounded by the decrease border of mandible and anterior and posterior bellies of digastric. Contents embrace submandibular salivary gland, lymph nodes, facial vessels and marginal branch of facial nerve. The contents include infrahyoid strap muscles and constructions which lie deep to them in central compartment like thyroid and parathyroids, larynx and trachea, laryngopharynx and cervical esophagus and carotid sheath. Its contents embrace accessory nerve, lymph nodes, fibrofatty tissue and nerves of cervical plexus. At the transverse processes of cervical vertebra it divides in to two divisions: anterior (alar) and posterior (prevertebral). Prevertebral division: It extends from cranium base down the length of vertebral column up to coccyx. It forms the floor of posterior triangle and facilitates gliding movement of pharynx in the course of the swallowing. Submental nodes, two to eight in number, lie on the mylohyoid muscle in the submental triangle, which is located between right and left anterior bellies of digastric muscles and the hyoid bone. Submandibular nodes, that are in relation to submandibular gland and facial artery, lie in submandibular (digastric) triangle, which is located between anterior and posterior bellies of digastric muscle and bounded superiorly by the lower border of mandible and an imaginary line drawn between the angle of mandible and mastoid. Occipital nodes, on the apex of the posterior triangle, are located each superficial and deep in to splenius capitus muscle. Internal jugular chain, which is further divided in to upper (jugulodigastric node), middle and lower teams, lie anterior, lateral and posterior to internal jugular vein and extends from the digastric muscle to the subclavian vein. The posterior cervical triangle lies between posterior border of sternocleidomastoid, anterior border of trapezius and the clavicle under. Anterior cervical nodes, which lie between the two carotids and under the extent of hyoid bone, encompass two chains: anterior jugular chain and juxtavisceral chain. Middle deep cervical group: Afferents from oral cavity, oropharynx, hypopharynx, larynx, and thyroid. Afferents from scalp, skin of the neck, nasopharynx, occipital and postauricular nodes; Efferents to transverse cervical chain. Medial supraclavicular (scalene nodes): Afferents from breast, lung, abdomen, colon, ovary and testis. Paratracheal nodes (recurrent laryngeal nerve chain): Afferents from thyroid lobes, subglottic larynx, trachea and cervical esophagus. Section 1 w � lymph Nodes Not Clinically Palpable � retropharyngeal nodes: lateral (rouviere) and medial teams: Afferent from nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, onerous and soft palate, nasopharynx, and posterior wall of pharynx; Efferents to upper internal jugular group. Afferents from anterior part of the floor of mouth and ventral floor of tongue; Efferents to submandibular or upper jugular nodes. The deep cervical jugular groups receive in addition to their direct areas of drainage all of the efferents from the pericraniocervical ring, efferents from the superficial cervical nodes and efferents from different paravisceral deep nodes (such as retropharyngeal, infrahyoid, prelaryngeal, pretracheal, paratracheal and subclavian).
100 mg celebrex visa
Numerous small branches drain from the tail and body of the pancreas in to the apposed floor ofthe vein rheumatoid arthritis urine buy 100 mg celebrex fast delivery. The inferior mesenteric vein lies deep to the left posterior parietal peritoneum and ascends in shut proximity to the underlying infrarenal aorta can arthritis in your back get worse order celebrex 100 mg without prescription. The right gastric vein lies along the lesser curvature of the abdomen beneath the gastric root of the gastrohepatic omentum. The left gastric vein spans the gap between the esophagogastric junction and the posterior wall of the omental bursa lying alongside the left gastric artecy. It descends diagonally over the celiac trunk beneath the posterior peritoneum of the omental bursa to reach the portal vein. Small pyloric and duodenal veins additionally enter the portal vein near the gastric veins. The gastroepiploic arch connects the terminal splenic vein with the superior mesenteric vein and runs in the gastrocolic omentum where it receives dnrinage from the omentum and higher curvature of the stomach. It is related to a number of hepatic and extmhepatic disorders which were nicely described e1Bewhere. Peripheral dilation is most dangerous within the submucosal esophageal plexus connecting the portal circulation to the azygous system. Resultant esophageal varicosities are in danger of erosion and massive hemorrhage. Beyond portal decompression sw:gery, there are two modem indications for publicity of the portal venous system: restore of traumatic injuries7�8 and resection and reconstruction of the portal and superior mesenteric veins in patients with invasive pancreatic tumors 1�10 the following dialogue concerns exposure of the portal vein and its tributaries in consideration of performing decompression procedures, repair of traumatic accidents, or reconstruction in sufferers with invasive pancreatic most cancers. Alternatively, a midline incision could additionally be more appropriate in sufferers undergoing exploratory laparotomy for trauma or pancreaticoduodenectomy for most cancers. The hepatic flexw-e of the colon could sometimes require mobilization to improve publicity, however unnecessary dissection ought to be avoided to minimize blood loss. The portal vein is usually distended and easily palpable as probably the most posterior structure within the hepatoduodenal ligament. It is important to place the incision posteriorly and never too near the free margin of the hepatoduodenalligament. U the incision is fastidiously prolonged superiorly so far as the liver hilum and inferiorly so far as the pinnacle of the pancreas. Gentle traction positioned on the portal vein exposes main branches, together with the pyloric, duodenal, proper gastric, and coronary veins, that drain in to its medial surfaces. After meticulous ligation and division of all portal vein tributaries are ensured, the portal vein may be uncovered and utterly mobilized from the extent of the pancreas to its bifurcation on the liver hilum. A midline stomach incision made from some extent halfway between the umbilicus and xiphoid course of to the top of the pubis supplies glorious publicity and can be prolonged superiorly as needed. The incision must be carried to the left ofthe umbilicus to stop entry in to the engmged umbilical vein. A transverse midabdoo:rinal incision is a helpful alternative but may be associated with increased blood loss from venous collateral. The superior mesenteric artery can be palpated at the base of the transverse mesocolon; the vein lies to the best of the artery near the midline. A 7-cm transverse incision is made in the peritoneum at the root of the transverse mesocolon, and the superior mesenteric vein is rigorously uncovered. If necessary, a superior T extension can be made on to the transverse mesocolon for additional exposure. Multiple well-vascularized lymphatics overlying the vein require careful dissection and meticulous control to keep away from hemorrhage. Still, sufficient of the superior mesenteric vein can often be isolated over the uncinate process to permit creation of a large anastomosis. Alternatively, a brief H-graft configuration could be brought more directly from the vena cava to the posterior surface of the superior mesenteric vein. Grafts dropped at the mesenteric vein from the vena cava in this fashion are routed across the third portion of the duodenum and again anastomosed to the anterior floor of the superior mesenteric vein over the uncinate process. The affected person is placed in the supine place with the decrease chest and stomach prepped and draped. Warren and Millikan12 advocate a "hockey stick" incision 1 to 2 em below the left costal margin, extending across the midline to the lateral border of the proper rectus muscle. On entering the belly cavity, the falciform ligament and the umbilical vein are ligated and divided. After dividing adhesions between the posterior wall of the abdomen and the pancreas, the greater curvature of the abdomen is elevated, allowing cephalad retraction of the posterior stomach. The posterior parietal peritoneum between the pancreas and the duodenum is comparatively avascular and must be incised from the extent of the superior mesenteric vessels to the tail of the pancreas. The left adrenal and gonadal branches ought to be divided close to the renal vein to allow extensive mobilization. In preparation for anastomosis, the splenic vein ought to be divided as close to the splenic-portal- mesenteric junction as potential and introduced on to the left renal vein. An upper midline incision offers glorious exposure, although a supraumbilical transverse incision could additionally be used as a substitute. The retroperitoneal space is entered via a vertical incision within the posterior peritoneum over the infrarenal aorta. The incision is carried superiorly to embody division of the ligament of Treitz, permitting rightward reflection of the third and fourth portions of the duodenum. The left renal vein is identified as it crosses the aorta within the superior incision. The vein is encircled, and its gonadal and adrenal branches are divided to permit broad mobilization. The inferior mesenteric vein ought to be identified because it courses alongside beneath the posterior parietal peritoneum to the left of the aorta and tJaced superiorly to find the splenic vein. Anterior and cephalad retraction of the inferior border ofthe pancreas exposes the splenic vein coursing along the posterior pancreatic surface. A 20-year experience with portal and superior mesenteric venous injuries: has anything modified Techniques and results of portal vein/superior mesenteric vein reconstruction using femoral and saphenous vein during pancreaticoduodenectomy. After crossing the pectineal line of the pubis, the vessels cross the pectineus musc:le en path to the subsartorial femoral canal. The boundary marking the transition between the external iliac and common femoral arteries is the inguinal ligament. The sheath fits snugly across the vessels except on the medial facet, the place a slim channel (femoral canal) Psoas main m. The hernia dissects and breaches the medial femoral sheath below the inguinal ligament to prolrude. The lateral margin of the triangle is fashioned by the sartorius muscle, the medial margin by the adductor longus muscle, and the cephalad base of the Deep circumflex iliac a. Between these boundaries, the triangle appears as a depressed plane when the thigh is flexed in exterior rotation. Itis breached by an oval opening fossa ovalis) through which lymphatics and the great saphenous.

Generic celebrex 200 mg overnight delivery
High decision computerized tomography: It is the take a look at of choice in instances of skull base trauma/temporal bone fracture embro arthritis medication celebrex 200 mg cheap mastercard. Drooling during chewing and ingesting and impairment of speech may result in social problems arthritis diet mayo clinic order celebrex 100 mg visa. The findings of corneal irritation are redness, itching, overseas physique sensation and visible blurring. Contractures: the fastened contraction or fibrosis of atrophied muscle tissue affects actions of face. It causes increased capillary permeability that leads to exudation of fluid, edema and compression of microcirculation of the nerve (secondary ischemia). Protect the attention from wind, overseas bodies and drying with glasses and moisture chambers. Steroids have been reported to prevent incidence of synkinesis and crocodile tears and shorten the recovery time. Patient requires cautious history and examination to exclude other recognized causes of facial paralysis. Surgical Facial Nerve Decompression It relieves strain on the nerve fibers and improves their microcirculation. The possibilities of complete restoration are better when clinical restoration begins inside three weeks of onset. Penetrating wounds of cheek, face and parotid gland can lacerate facial nerve trunk and its branches. Fall and previous pointing are in the direction of the affected ear (toward the gradual part of nystagmus). Stimuli for viral reactivation: Immunosuppression, bodily and psychological stressors. Profuse bleeding not managed by packing is managed by carotid ligation or angiography for balloon occlusion. Immediate facial paralysis normally requires surgery (decompression, reanastomosis of minimize ends or cable nerve graft), which is performed 3 weeks after damage. Other antibiotics are amoxicillin, erythromycin, cefuroxime, ceftriaxone and imipenem. This congenital facial palsy, which can be unilateral or bilateral, full or incomplete, is associated with bilateral abducens palsy. The paralysis may be instant (needs earliest surgical decompression and repair) or delayed (treated conservatively). Suppurative otitis media: In addition to the aggressive antibiotic remedy following surgical measures are taken in circumstances of otitis media: Myringotomy: It is indicated in instances of acute otitis media, otitis media with effusion and coalescent mastoiditis. End to finish anastomosis: It is an appropriate procedure for extratemporal a half of facial nerve, when the hole between the severed ends of nerves is few millimeters, so that ends could possibly be approximated with none tension. Nerve graft is usually taken from larger auricular nerve, lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh or the sural nerve. However, affected person Prophylaxis Thorough anatomical information and temporal bones dissection underneath good high quality operative microscope trains the surgeon and avoids facial nerve injuries in the course of the ear surgeries. Constant irrigation in the course of the drilling avoids thermal injury to the facial nerve. Injection of botulinum blocks the neuromuscular junction by stopping launch of acetylcholine within the affected muscle 2. Vascular loop on the cerebellopontine angle: Treated by microvascular decompression via posterior fossa craniotomy blepharospasm Twitching and spasms of the orbicularis oculi muscle tissue on each side leads to closure of each the eyes causing functional blindness. Posterior tympanotomy through facial recess exhibits incus and stapes adjusts to the difficulty in chewing and articulation within few weeks. Parotid relations: During superficial parotidectomy, probably the most reliable landmark to determine primary trunk of facial nerve is tympanomastoid suture. Tympanic segment of facial nerve lies above the oval window and below the horizontal semicircular canal. Mastoid segment of facial nerve all the time lies behind the tympanomastoid suture and can be located 6�8 mm deeper to tympanomastoid fissure. Patient can shut both eyes with equal energy and might wrinkle his brow scalp bilaterally. Vesicular eruptions are seen in concha, posteromedial surface of pinna and soft palate. Pre-eclampsia: Facial paralysis during being pregnant can happen in instances of preeclampsia. Ear polyps, which are usually not true neoplasms, are (Chapter Otologic Symptoms) commonly related to persistent suppurative otitis media. Hemangiomas Hemangiomas are congenital tumors seen in youngsters and will contain different elements of face and neck. Sebaceous adenoma: It arises from sebaceous glands of the meatus and presents as a smooth, skin-covered swelling within the outer meatus. Dermoid cyst: It is normally current as a rounded mass over the upper a part of mastoid behind the pinna. Keratoacanthoma Keratoacanthoma, though a benign tumor, clinically resembles malignant one and presents as a raised nodule with a central crater. Recurrence could be avoided by local injection of triamcinolone in to the surgical site and pre and postoperative radiation with a complete dose of 600�800 rads, which are delivered in four divided doses. Surgical elimination is completed by fracturing by way of its pedicle or removing with a drill. Occupations: It is frequent in divers and swimmers, as their ear canals are incessantly exposed to chilly water. Clinical options: this benign tumor presents as a smooth, agency, skin-covered polypoid swelling. If malignancy is suspected on histology, postoperative radiotherapy must be given. Lesion: A painless nodule or an ulcer with raised everted edges and indurated base. Histology reveals of lots or sheets of epithelial cells which have giant nuclei and a granular cytoplasm. The thin walled blood sinusoids without any contractile muscle coat are in abundance and account for profuse bleeding. Glomus Jugulare: this tumor arises from the dome of jugular bulb and invades the hypotympanum and jugular foramen. Treatment Early lesion: Wedge resection and primary closure in cases of superficial melanoma which is lower than 1 cm in diameter and situated over the helix. It might afterward invade following structures: labyrinth, petrous pyramid and the mastoid. Otorrhea: It is due to secondary an infection and simulates persistent suppurative otitis media polyp. Catecholamine features: Headache, sweating, palpitation, hypertension and anxiety. Break-down products of catecholamines in urine: Vanillylmandelic acid, metanephrine, and so on.
100 mg celebrex order amex
The incision is made at the deltopectoral interval proximally after which runs along the lateral border of the biceps muscle distally arthritis in neck cause sore throat generic 100 mg celebrex overnight delivery. An internervous plane is utilized between the deltoid (axillary nerve) and pectoralis main (medial and lateral pectoral nerves) proximally arthritis back bone spurs cheap 200 mg celebrex otc. More distally, after retracting the biceps medially, the brachialis muscle is cut up longitudinally alongside the outer third of the muscle, using an internervous airplane between its medial (musculocutaneous nerve) and lateral fibers (radial nerve). The apical proximal a half of the wedge articulates with the lunate; the broad distal floor has two concave facets for the bases of the fourth and fifth metacarpals. Articular surfaces laterally and medially are for the capitate and triquetrum, respectively. It begins first within the capitate and then in the hamate early in the 1st year; in the triquetrum, in the course of the 3rd yr; in the lunate, within the 4th yr; within the trapezium, trapezoid, and scaphoid, in quite shut sequence, in the 4th to 6th years; and within the pisiform, within the eleventh or twelfth year. Ossification begins earlier in the female and is accomplished between ages 14 and sixteen. An os centrale, usually a half of the scaphoid, could additionally be current between the scaphoid, capitate, and trapezoid. Confusion relating to these structures typically centers on the numerous totally different names utilized to identify these buildings. The volar radiocarpal ligaments are the most crucial of these structures and supply the majority of ligamentous stability to the carpus. The volar ligaments encompass the radioscaphocapitate ligament, the long/short radiolunate ligaments, the radioscapholunate ligaments (more of a vascular conduit), and the ulnotriquetral and ulnolunate ligaments. The radioscaphocapitate ligament is a crucial restraint to ulnar translocation of the carpus and have to be preserved during proximal row carpectomy and/or throughout radial styloidectomy. The area of Poirier is a weak point between the radioscaphocapitate and lengthy radiolunate ligaments, the place the lunate can dislocate during a lunate dislocation. During a volar approach to lunate/perilunate dislocations this space may be sutured to present elevated stability to the injured carpus. The dorsal intercapsular ligaments encompass the dorsal radiocarpal and dorsal intercarpal ligaments. These present further structural assist to the carpus, and numerous "ligament-sparing approaches" to the wrist have been described to protect these buildings. These dorsal ligaments can additionally be utilized to right carpal instability by being transferred to function as a capsulodesis. There are quite a few intercarpal ligaments, essentially the most important being the scapholunate and lunotriquetral ligaments. Repair of these ligaments may be performed within the acute setting, whereas quite a few reconstructive procedures have been described for use in the continual setting when symptomatic. The individual components embrace dorsal and palmar radioulnar ligaments, meniscus homologue, ulnotriquetral and ulnolunate ligaments, articular disc, and the extensor carpi ulnaris subsheath. Advances in digital camera technology, small instrument design, secure portal identification, and, most importantly, surgeon expertise and luxury have all played a task in the growth of this therapy modality. Currently, wrist arthroscopy is considered the gold commonplace for evaluating and infrequently treating persistent wrist ache. Wrist arthroscopy permits correct identification of these accidents, determination of central versus peripheral harm, and remedy. Radiocarpal and midcarpal synovectomy, ganglion excision, scapholunate and lunotriquetral tear debridement versus restore, and unfastened physique elimination also can all be efficiently handled arthroscopically. Arthroscopic visualization of each distal radius and scaphoid fracture fixation has also been reported as an adjunct to commonplace therapy, allowing direct visualization of intra-articular reduction and fixation. Wrist arthroscopy requires an intensive understanding of wrist anatomy to allow safe passage of instrumentation and recognition of the anatomy and pathologic processes encountered. Arthroscopic portals are recognized by their relationship to the numbered extensor tendon compartments alongside the dorsum of the wrist. The standard viewing portal is the 3-4 portal, with supplemental portals for instrumentation typically occurring at the 4-5 interval or on both side of the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon (6R and 6U). Midcarpal arthroscopy is a important part to any diagnostic wrist arthroscopy. The midcarpal viewing and working portals permit accurate evaluation and grading of each scapholunate and lunotriquetral instability. The muscles are organized as a flexor mass anteriorly and an extensor mass posteriorly. These designations are merely group traits, because certain muscle tissue are primarily rotators of the forearm bones. Eighteen of the muscular tissues could be grouped in to six useful teams of 3 muscles every. The muscle excluded from these groups is the brachioradialis, which is actually an elbow flexor with no motion within the digits or at the wrist. All the teams, except for the primary, are composed of muscle tissue that move the hand and digits. Rotate the radius on the ulna: � Pronator teres � Pronator quadratus � Supinator 2. Flex the hand on the wrist: � Flexor carpi radialis � Flexor carpi ulnaris � Palmaris longus three. Flex the digits: � Flexor digitorum superficialis � Flexor digitorum profundus � Flexor pollicis longus 4. Extend the hand at the wrist: � Extensor carpi radialis longus � Extensor carpi radialis brevis � Extensor carpi ulnaris 5. Extend the digits, besides the thumb: � Extensor digitorum � Extensor indicis � Extensor digiti minimi 6. Extend the thumb: � Abductor pollicis longus � Extensor pollicis brevis � Extensor pollicis longus the muscular tissues of the primary three teams lie in the anterior compartment of the forearm; these of the last three teams are located within the posterior compartment. The intermuscular septa and the antebrachial fascia additionally provide partial origins, and certain muscular tissues have additional bony origins. The large humeral head arises in the medial epicondyle via the common tendon and from the adjacent fascia and intermuscular septa. The small, deep ulnar head takes origin from the medial facet of the coronoid strategy of the ulna. It joins the deep aspect of the humeral head, the median nerve descending between them. This obliquely descending muscle ends on the shaft of the radius at the middle of its lateral surface. The palmaris longus muscle additionally uses the widespread tendon of origin, when current (it is absent in 13% of cases). It terminates in a slender, flattened tendon, crossing the wrist superficial to the flexor retinaculum. The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle has a humeral and an ulnar head, the humeral head coming from the frequent flexor tendon. The ulnar head springs from the medial border of the olecranon and the higher two thirds of the posterior border of the ulna. The tendon of the muscle inserts on the pisiform of the wrist and, through it by two ligaments, in to the hamulus of the hamate and the base of the fifth metacarpal. The flexor digitorum superficialis muscle arises by a humeroulnar and a radial head of origin; these are related by a fibrous band that crosses the median nerve and the ulnar blood vessels.
100 mg celebrex cheap fast delivery
The palmar ligament is a dense arthritis in back after injury generic celebrex 100 mg line, fibrocartilaginous plate seronegative arthritis definition celebrex 100 mg order, which, via its agency attachment to the proximal palmar fringe of the phalanx, extends and deepens the phalangeal articular floor. It is loosely connected to the neck of the metacarpal; in flexion, it passes beneath the top of the metacarpal and serves as a half of the articular contact of the bones. At its sides, the palmar ligament is steady with the deep transverse metacarpal ligaments and the collateral ligaments. The collateral ligaments are strong, cordlike bands connected proximally to the tubercle and adjacent pit of the head of the metacarpals and distally to the palmar surface of the aspect of the phalanx. Movements of flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, and circumduction are permitted at these joints. With extension is related abduction, as in fanning the fingers; with flexion is associated adduction, as in making a fist. The metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb is limited in abduction and adduction; its particular freedom of motion derives from its carpometacarpal joint. Structurally similar to the metacarpophalangeal series, the interphalangeal joints have the identical unfastened capsule, palmar and collateral ligaments, and dorsal reinforcement from the extensor expansion. Flexion is freer than extension and will attain 115 levels at the proximal interphalangeal joint. Arteries and nerves serving these joints are twigs of adjoining correct digital branches. By conference, motion towards the palm is described as palmar or volar or anterior and movement toward the again of the hand is described as dorsal or posterior. Movement of the hand towards the thumb side of the arm is described as radial or lateral and towards the small finger as ulnar or medial. These prominently interconnect the tendons for the third, fourth, and fifth digits and severely restrict the independent action of these digits, particularly the fourth digit. The convergence of the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle toward the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis muscle tissue defines a hollow known as the anatomic snuffbox (see Plate 4-14). In the floor of this hollow, the radial artery passes towards the dorsum of the hand and offers off its dorsal carpal department. Except for about 5 mm of their proximal ends, these synovial sheaths (and the tendons) are contained within the fibrous sheaths of the digits of the hand. The fibrous sheaths of the digits are robust coverings of the flexor tendons, which lengthen from the heads of the metacarpals to the bottom of the distal phalanges and serve to stop "bowstringing" of the tendon away from the bones during flexion. They connect along the borders of the proximal and middle phalanges, the capsules of the interphalangeal joints, and the palmar floor of the distal phalanx. They kind robust semicylindrical sheaths that, with the bones, produce fibro-osseous tunnels through which the flexor tendons move to their insertions. Over the shafts of the proximal and middle phalanges, the sheaths exhibit thick accumulations of transversely working fibers (sometimes known as annular ligaments, or pulleys), whereas reverse the joints, an obliquely crisscrossing association is attribute (cruciate ligaments). Proximally, the digital slips of the palmar aponeurosis connect to the fibrous digital sheaths. The tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle insert on the bases of the distal phalanges of digits 2 to 5, while the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle end on the shafts of the middle phalanges of those digits. It is thus necessary for the tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle to pass these of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle, and this is achieved by a splitting of the tendon of the superficialis to allow that of the profundus to cross distalward. The division of the flexor digitorum Insertion of lumbrical muscle to extensor tendon Palmar ligament (plate) Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon (cut) Collateral ligaments Flexor digitorum profundus tendon (cut) Palmar ligament (plate) Interosseous muscle tissue Lumbrical muscle Finger in flexion: lateral (radial) view Note: Black arrows point out pull of long extensor tendon; purple arrows indicate pull of interosseous and lumbrical muscle tissue; dots point out axis of rotation of joints. Lateral band relaxed in this position; right for splinting of "mallet finger" superficialis tendon takes place over the proximal phalanx, and the two halves separate and roll in underneath the flexor digitorum profundus tendon to reach the bone of the middle phalanx, their fibers crisscrossing as they connect to that phalanx. The vincula tendinum spring from the internal surface of the digital sheaths of those muscular tissues. They are folds of synovial membrane strengthened by some fibrous tissue, which conduct blood vessels to the tendons. The smaller vinculum breve is at the distal finish of the sheath; the vincula longa are narrow strands that reach the tendons more proximally. The lumbrical muscle tissue are 4 small, cylindrical muscles related to the tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle. The two lateral muscles arise distal to the flexor retinaculum from the radial sides and palmar surfaces of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle destined for the second and third digits. The two medial muscles come up from the contiguous sides of the tendons for the third and fourth and the fourth and fifth digits. Each lumbrical tendon passes distalward on the palmar aspect of the deep transverse metacarpal ligament and then shifts towards the dorsum. It inserts, on the degree of the proximal phalanx, in to the radial border of the growth of the extensor digitorum muscle. At the metacarpophalangeal joint and over the proximal two phalanges, an extensor expansion is shaped for every tendon by the participation of the tendons of the lumbrical and interosseous muscular tissues of the hand. Opposite the metacarpophalangeal joints, a band of fibers passes from each side of the digital extensor tendon anteriorly on both sides of the joint and attaches to the palmar ligament of the joint. This proximal spreading of the extensor enlargement seems like a hood of fibers over the metacarpophalangeal joint. Over the dorsum of the proximal phalanx, the digital extensor tendon divides in to three slips. Of these, the central, broader slip passes directly ahead and inserts on the dorsum of the middle phalanx. The diverging bundles on both side, the lateral bands, obtain and mix with the broadening tendon of a lumbrical muscle on the radial aspect of the digit, and with interosseous tendons on both sides of the digit. These tendons unite in to a typical band that proceeds distalward, the bands of the 2 sides forming a triangular aponeurosis over the distal finish of the middle phalanx. Muscle Actions in Digital Movement Certain forearm muscle tissue take part in actions of the digits. The tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus muscular tissues emerge from the wrist at the distal border of the flexor retinaculum and enter the central compartment of the palm (see Plate 4-9). Here, they fan out towards their respective digits, organized in pairs, superficial and deep. They are invested by the ulnar bursa through the upper a part of the palm, besides that the extension of the bursa alongside the tendons for the fifth digit continues to the base of its distal phalanx. The flexor digitorum superficialis muscle is a flexor of the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints of the medial 4 fingers and is the principal flexor of the wrist. Tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus muscle tissue (Synovial) tendon sheath act, also flexes the middle and proximal phalanges. This muscle flexes the digits in sluggish action, the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle being recruited for pace and against resistance. The extensor digitorum muscle, assisted by the extensors of the index and fifth fingers, is the extensor of the fingers.